SEO
The Future of AI Chatbots and Search

Here it is, Google finally announced their own AI chatbot— Google Bard. Like its presumed rivals, ChatGPT and Bing Bot, Bard can understand queries and generate human-like answers in response.
But is this the start of a new way of how we search the web in the future?
This unveiling is just the next stage in the AI arms race between Google and OpenAI and Microsoft. And, with a recent update–and many more features to come–Google is already promising to transform the online search landscape as we know it.
Now that it’s widely available, here’s all you need to know about Google Bard.
What is Google Bard?
Google Bard is an experimental conversational AI chat service from Google that serves like a ChatGPT. It is Google’s own AI chatbot that can generate human-like responses to any prompt you wish to tell the AI.
But unlike ChatGPT, Google Bard was initially based on LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications)–a family of conversational large language models (LLM). LaMDA is trained on massive data sets and parameters, which has allowed the AI to “learn” useful information, as well as our language.
Recently at Google’s I/O 2023, it was revealed that Bard was now powered by their other, most advanced LLM: PaLM 2. This, as they stated, will allow Bard to be a highly efficient bot, and even fix previous issues (likely linked to their misinformation blunder when they first announced Bard a few months ago).
Powered by their LLMs, the result is that Bard can perform tasks such as answering questions and following instructions, and can carry a conversation with users in a surprisingly natural way.
Aside from that, it can do what most AI chatbots nowadays can do: write and debug code, and answer math problems. A more popular use is helping with one’s writer’s block by creating outlines, collaborating on essays, or even providing more details for articles. The sky’s the limit, it seems, with a powerful AI chatbot like Bard.
What is Google Bard used for?
This experimental, conversational AI is trained to communicate with users and provide the answers or results they’re looking for. As I said, the sky’s the limit for this kind of tech, but here are a few examples of how you can use Google Bard:
- Get information–Bard generally can provide easy-to-understand and factual answers to the questions you have. As long as your prompt does not violate any content guidelines from Google, Bard will respond with the information you would like to know. You can even ask strange questions such as “What is the meaning of life?” and it will give you an answer.
- Generate different kinds of writing–from poems to emails to blog articles, Google Bard can help you with your writing. Bard’s answers can range from formal, creative, and even casual, depending on your prompt. The pieces or ideas you can get from Bard’s content responses can help you build ideas for your craft or job.
- Translate–It can function pretty similarly to Google Translate. It even knows informal words or phrases in foreign languages, such as slang, which can be pretty useful. But, Google can only answer in English, with support for Japanese and Korean languages. The expansion of language support beyond English is planned and part of a 40-year expansion plan for Bard.
- Code–A more recent feature, Bard is now able to help users with simple programming and software development tasks. This includes code generation, code debugging, and explanation.
- Summarize data–Bard can quickly digest and summarize the most important points from articles, blog posts, and web pages for you. You can also ask it to help you compare data or research.
This, of course, is not an exhaustive list of what this AI chatbot can do. You can ask it to find a recipe, write your CV, and even help you prepare for a presentation.
It would be impossible for me to list all of Bard’s use cases here, and what you’ll use it for will depend on what you’re looking for.
Is Google’s Bard available?
Yes, Google Bard is now available. Google announced Bard and its functions and features back in February 2023 and they announced that it is now available for everyone to use in May 2023 at Google I/O. It is currently accessible in 180 countries and territories.
How can I access Google Bard?
Bard can be accessed by searching bard.google.com, using the Google Bard Chrome Extension, or just by searching it up in any browser you use.
When accessed, you will see this page and you can now start using and providing whatever prompts you want.
How to use Google Bard
The user interface (UI) of Bard is pretty easy to navigate. Simply type in your prompt in the text box, press enter, and a conversation with the AI chatbot starts.
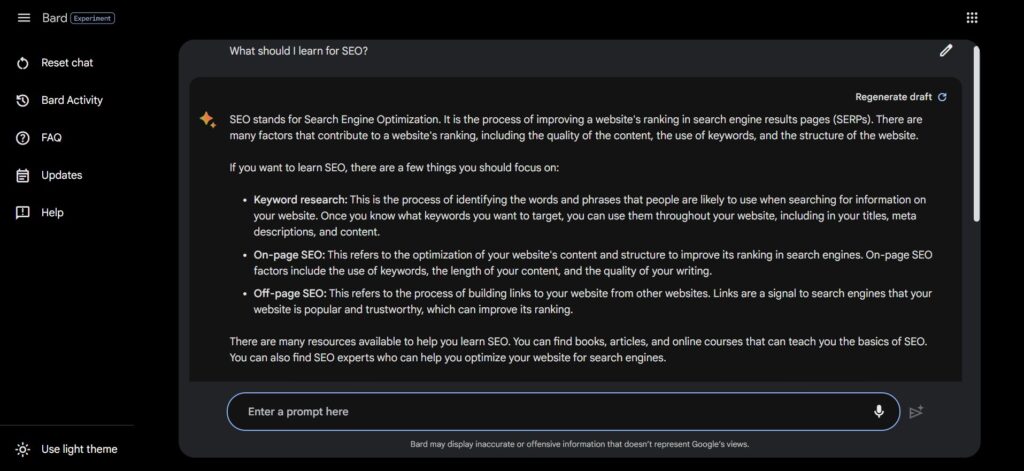
Longer answers are broken down and can also use rich text formatting, often in bullet points or lists, which makes it easy to scan.
If you want more information, If you’re not happy with Bard’s first response, or if you want more information, it provides the option of viewing its other drafted answers. This can provide a more detailed response or more context. You can also like or dislike the draft to let Bard know if you preferred its other answers or not.
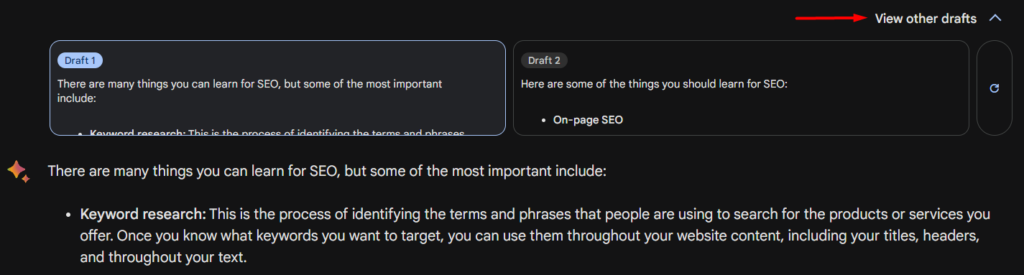
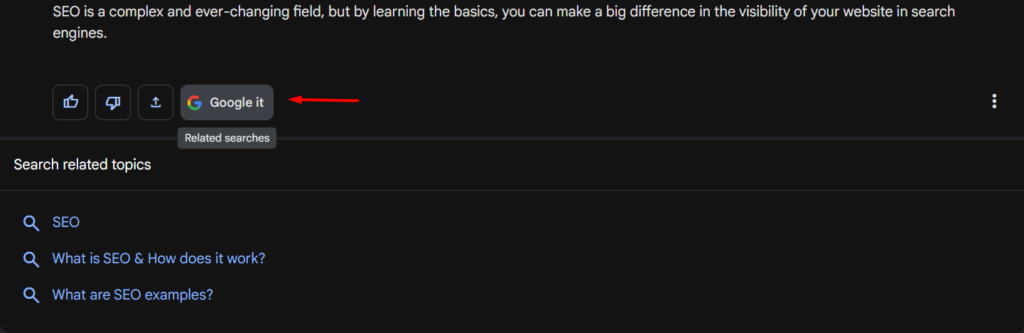
If you want to see other topics or look at more information online, you have the option to Google it. This shows related search topics that, when clicked, lead to organic search results.
Is Google Bard Safe to Use?
Google Bard, while pretty powerful, isn’t infallible.
When generating answers, Bard typically follows prompts from the user and can remember past instructions and questions (similar to Bing Bot). However, it doesn’t follow every prompt, as it has built-in safety controls and strictly adheres to Google’s content policies and AI principles.
This reduces the chances of it producing “bad” results, such as offensive dialogue.
That said, there’s still a chance that it can provide misleading information or potentially malicious answers.
It’s important to understand that Google Bard is a still-developing AI tool that may at times produce bad results. Understanding this will lessen the risks for us users.
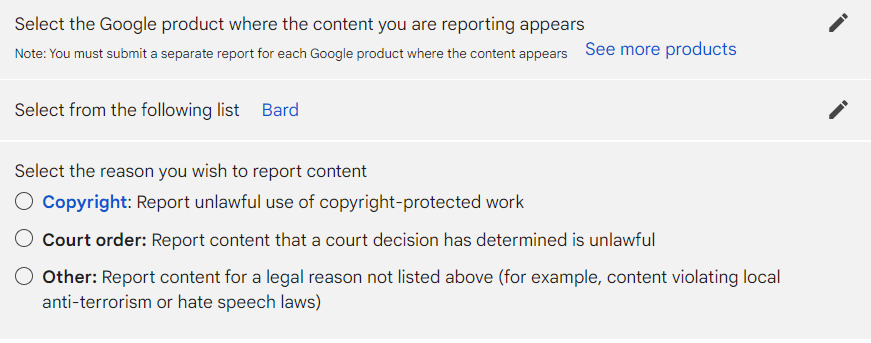
Bard is also trained to learn from its users, as it provides a way to rate its responses. On the UI, there is also the option to report legal issues with its response, which includes the following:
Are Google Bard’s Answers Accurate?
No. Bard is still considered an experimental AI, meaning that its accuracy is still flawed—Google Bard itself disclosed that it might produce false or misleading information from time to time, and encourages users to fact-check.
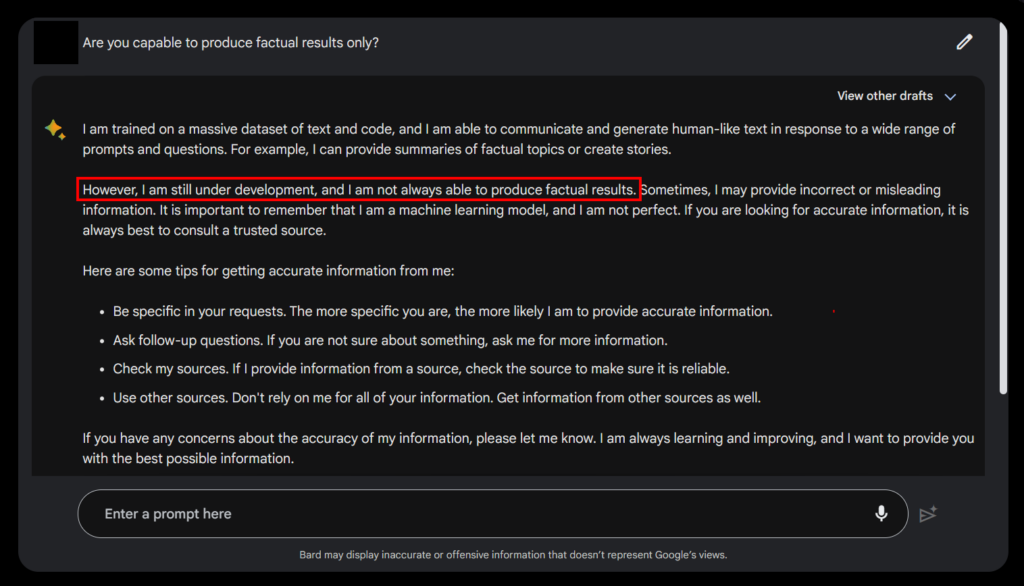
This statement above is important because, unlike ChatGPT, Google Bard has access to all of the internet. That means it can see information about current events and modern context, and therefore reference them in its answers. However, this doesn’t mean that the AI is fully updated with real-time information.
So while it can provide relevant answers to topical questions, it doesn’t mean that the answers it provides are 100% correct–hence the need for a disclaimer.
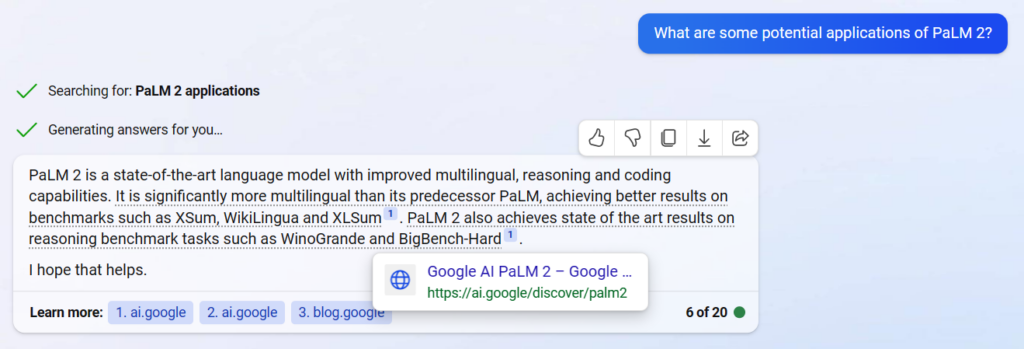
Does Google Bard Cite its Sources?
As of May 2023, Bard now cites its sources. Announced by Google’s representative, Jack Krawczyk, he says this update is part of their goal to make Bard more useful, while also increasing the reach of the original publishers it gets its information from.
This is a very welcome update for web publishers and SEOs like me and me. If Bard decides to cite your article, users can easily navigate to it, if they’re interested in learning more. But we have yet to see if this update does lead to more traffic, or if users will ignore these citations.
That said, Bard’s citations don’t seem to be successfully implemented, as of the time of writing. Bing Bot, in comparison, has been providing citations for a while now, and does so more reliably. But still, it’s a step in the right direction.
What Does Google Bard Mean for SEO?
As I hinted earlier, the release of Google Bard effectively ushers in the new age of search, which many are calling the new Search Generative Experience or SGE.
An experimental version of search as we know, it deprioritized the 10 blue links that have defined Google’s first page for years.
How? Well, Bard does the heavy lifting for you. Instead of sifting through several articles or pages to get the answer you want, Bard can potentially present it to you in a more concise manner. It even allows you to ask follow-up questions.
It might be incredibly useful and time-saving for many, but it now means that users have the option to not visit multiple sites to get their answers or make their decision. These clicks are what our websites rely on–and are very important for SEO.
What does this entail? We might see less traffic for the next few months, especially if more and more users adopt and prefer Bard over organic search.
But, ultimately, Google will be pushed to find ways for traffic (and revenue) to continue reaching creators and their sites, so there’s still an incentive for us to create content.
Key Takeaway
The race towards AI and the new age of search shows no signs of stopping with the official release of Google Bard.
While appealing to many, and offering several use cases, Bard is still in its early stages and has a few limitations that we need to be aware of.
I will continue to test Bard’s features as they are rolled out, but for now, all we know about this AI is covered in this article–and with several implications to SEO that we have to consider as the chatbot may become more mainstream in the coming months.








![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)





