SEO
The Smart Investor’s Guide to Buying a Website

Buying a website can help you reach a new audience, get a foothold in a new market, expand your business online, or earn “passive” income.
It’s a similar, yet simpler, process compared to merging or acquiring an existing business. But, just like with a business acquisition, not all website purchases come equal.
In this post, we share tips on everything you need to know to buy your first website with confidence, including:
- Where you can find available websites to buy
- The process for buying a website
- Essential due diligence tips to determine if a website is a good investment
- Common concerns and how to overcome them
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to buying a website or determining what a good investment will be. Following these steps will help you identify if a site is right for you or not.
Knowing what your goals are with your website acquisition influences the entire process. Different types of websites are better suited to achieving different goals.
If you’re seeking to reach a new audience, look for digital businesses with established audiences. For example, in 2021 Hubspot acquired media startup The Hustle and exposed its brand to new audiences in the startup and investing communities.
If you want to expand your reach online, consider competing websites or those in adjacent spaces. For example, in 2016, a blog about car advice sold for over $35 million to an Australian news publication seeking to expand its online reach in the automotive industry, even though it already had an automotive media publication under its wing.
If you’d like to earn more passive income, look for websites already earning a stable monthly income. Marketplaces and brokerages show earning reports of websites available for sale and in some cases, you can also continue to work with the existing team so there’s less work on your shoulders with managing the asset.
Overall, the best investments are the ones you have the skills to grow and manage. For instance, don’t buy a media publication if you have little experience growing a blog. Likewise, if you’ve never worked in eCommerce, don’t go all in on an online store, dropshipping or any kind of website that deals with physical products.
The most common places to buy websites are website marketplaces and brokerages, though you can also do your own outreach and set up a private deal.
Website marketplaces
Marketplaces, like Flippa, allow individual sellers to list their websites for sale and to manage the negotiations and asset handover on their own.
You can typically find very low-cost websites for sale on marketplaces, making them a great place to start for micro-acquisitions. You can buy anything from low-risk starter sites for three figures to seasoned websites earning thousands per month in passive income.
However, it is entirely on your shoulders to do thorough due diligence and make sure you’re not buying a lemon since most marketplaces do very little verification on each listing.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Low-risk starter sites available | No verification from the marketplace |
| Many options to choose from | Little support available |
| Deal directly with the seller | Not all sellers are trustworthy |
Brokerages
Brokerages offer a more boutique experience when buying a website and are a great place for beginners with some extra cash saved up due to the extra support you can receive.
Instead of listing every website available to buy, brokerages typically have curated lists of websites their internal teams have verified. For example, Empire Flippers and FE International are two brokerages selling different kinds of online businesses.
Typically brokerages deal with larger transactions and you will be hard-pressed to find available websites for sale in the three or four-figure ranges so it’s only advisable to search here if these deals are well within your financial means.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Receive direct support from your broker | Websites tend to be more costly |
| Tailored experience | You may need to pay a brokerage fee |
| Choose from verified websites |
Private deals
If you have some experience with negotiating business deals, you can put those skills to work and secure private website buying deals.
Arguably, the best sites to acquire are the ones people don’t want to sell. Plus, you don’t have to worry about outbidding others to acquire the site.
To find such websites, enter a well-known site in your niche into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer and navigate to the Organic Competitors report. Here you’ll see up to 20 websites performing well in the niche:
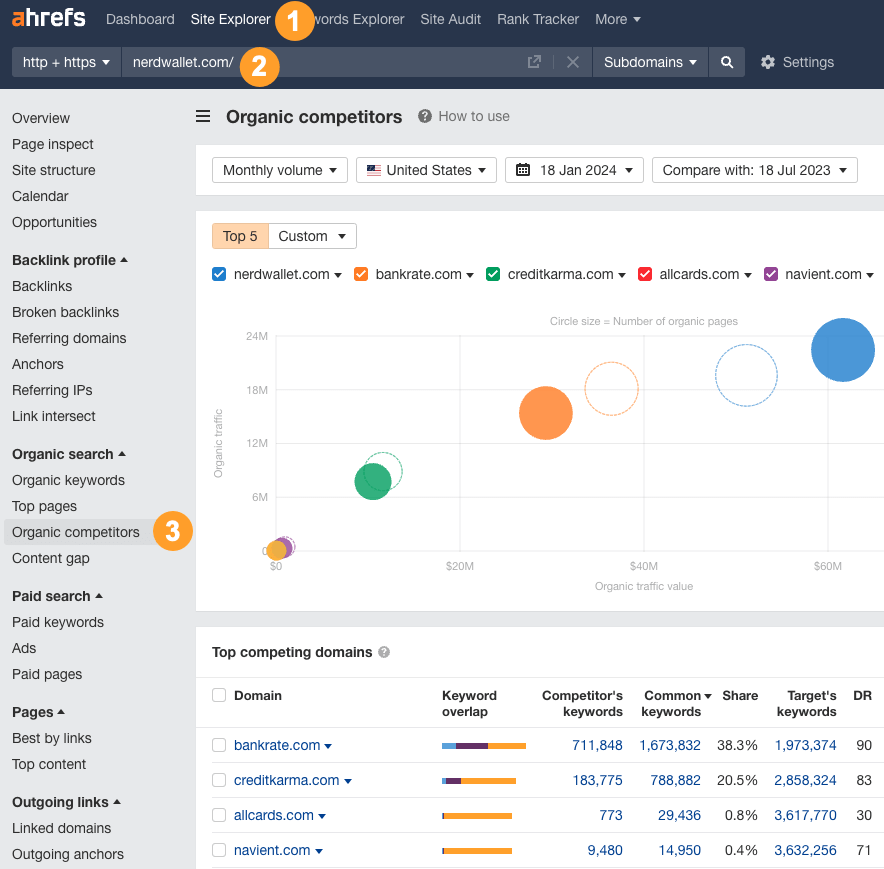

Alternatively, if you don’t know any sites in your niche, try this method instead:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter a handful of keywords that represent your niche
- Go to the Traffic share by domain report
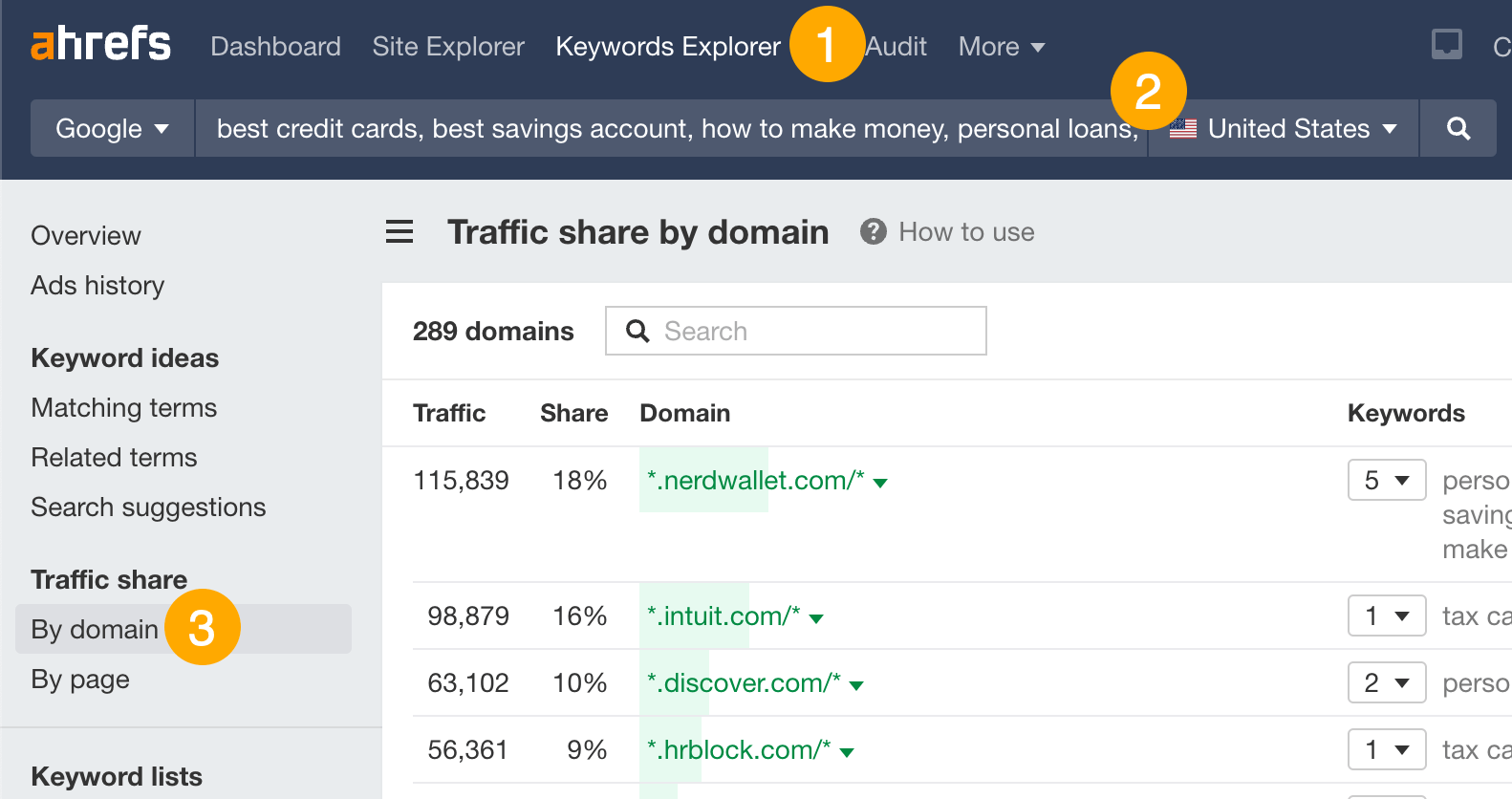

This will show you the websites getting the most estimated organic search traffic from those keywords.
Either way, you can then choose sites to investigate further based on metrics like how much traffic they’re getting or how much they’ve grown over a specific time period.
If you like any of them, reach out to them privately to negotiate a sale.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| No competition to outbid you | Requires existing negotiating skills |
| Find higher quality websites | Needs extra legwork to find great deals |
| Negotiate your terms more comfortably |
No matter how you’re looking for available websites to buy, you’ll need to audit each and every one to weed out the lemons from the goldmines.
Two essential checks to perform are for a website’s traffic and its backlink profile. Here’s the process in a nutshell:
- Enter the site in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Check out the Performance graph in the “Overview” report
- Filter for referring domains and organic traffic for a TL;DR view
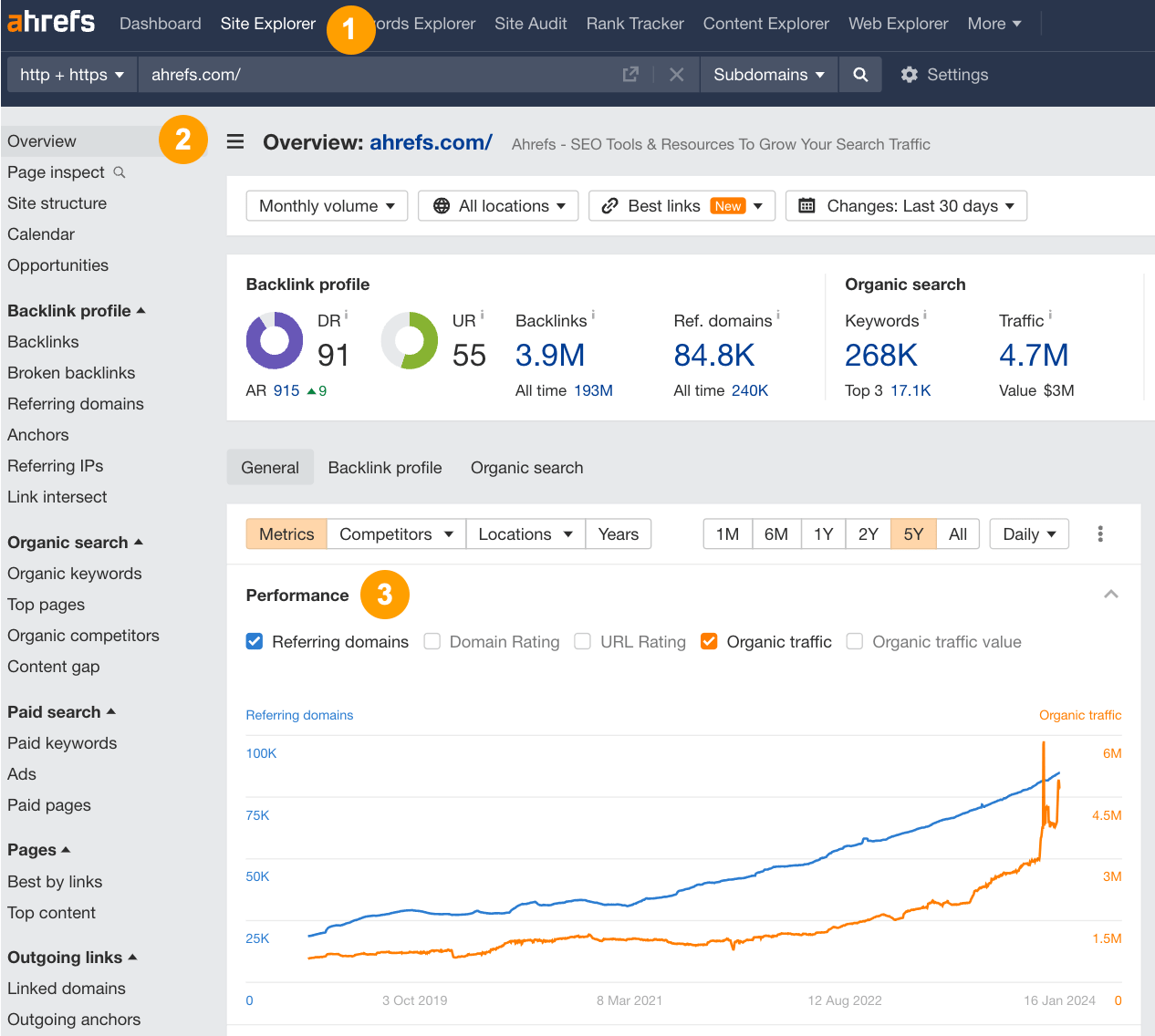

Look for any big drops in traffic or any unnatural-looking spikes in referring domains. Both of these can signal either declining performance overall or some shady things going on in the background.
For example, if you notice a lot of links added in a short period of time, the seller may have purchased links in bulk and there is a risk of the website receiving penalties from Google in future.
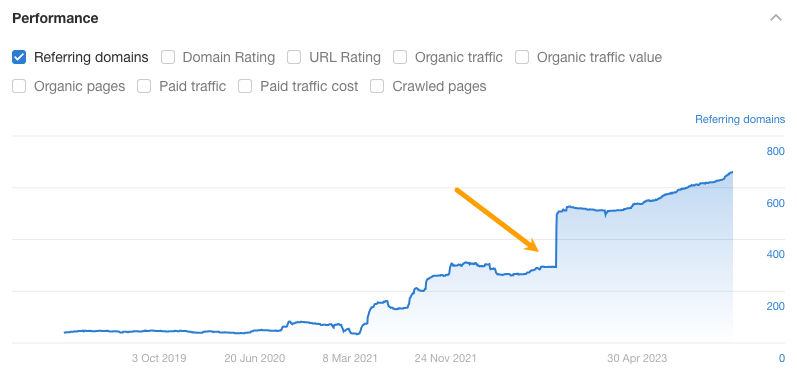

You can then take a closer look at a site’s link profile in the Backlinks report. Exclude “Best links” to hone in on potentially problematic links.
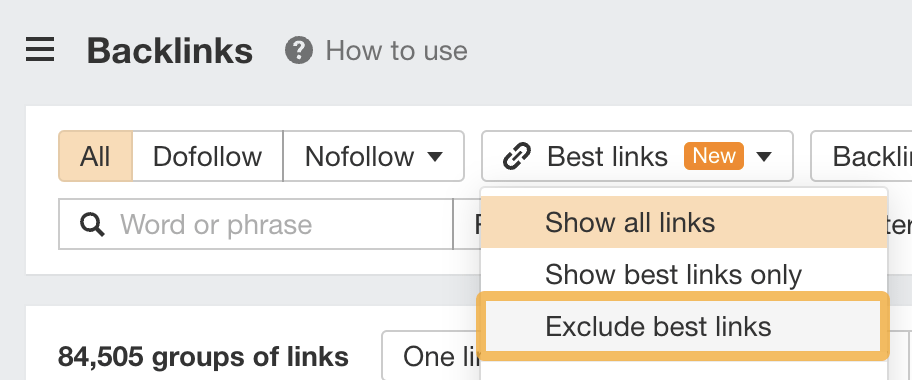

Paid links usually use the target keyword as the anchor text (the clickable part of the link) and come from poor content on low-quality sites, so look out for sites with lots of those.
For example, look at this link to a page about sleep apnea:


Based on this data, we can see that it:
- Comes from a low authority site that nobody’s ever heard of
- Comes from a page with zero estimated traffic
- Has exact-match anchor text (“sleep apnea”)
If we look at the referring page itself, we can also see that the content is extremely low quality. The site is plastered in ads and although it’s not visible in the screenshot below (because of all the ads!), it has lots of suspicious outlinks too.
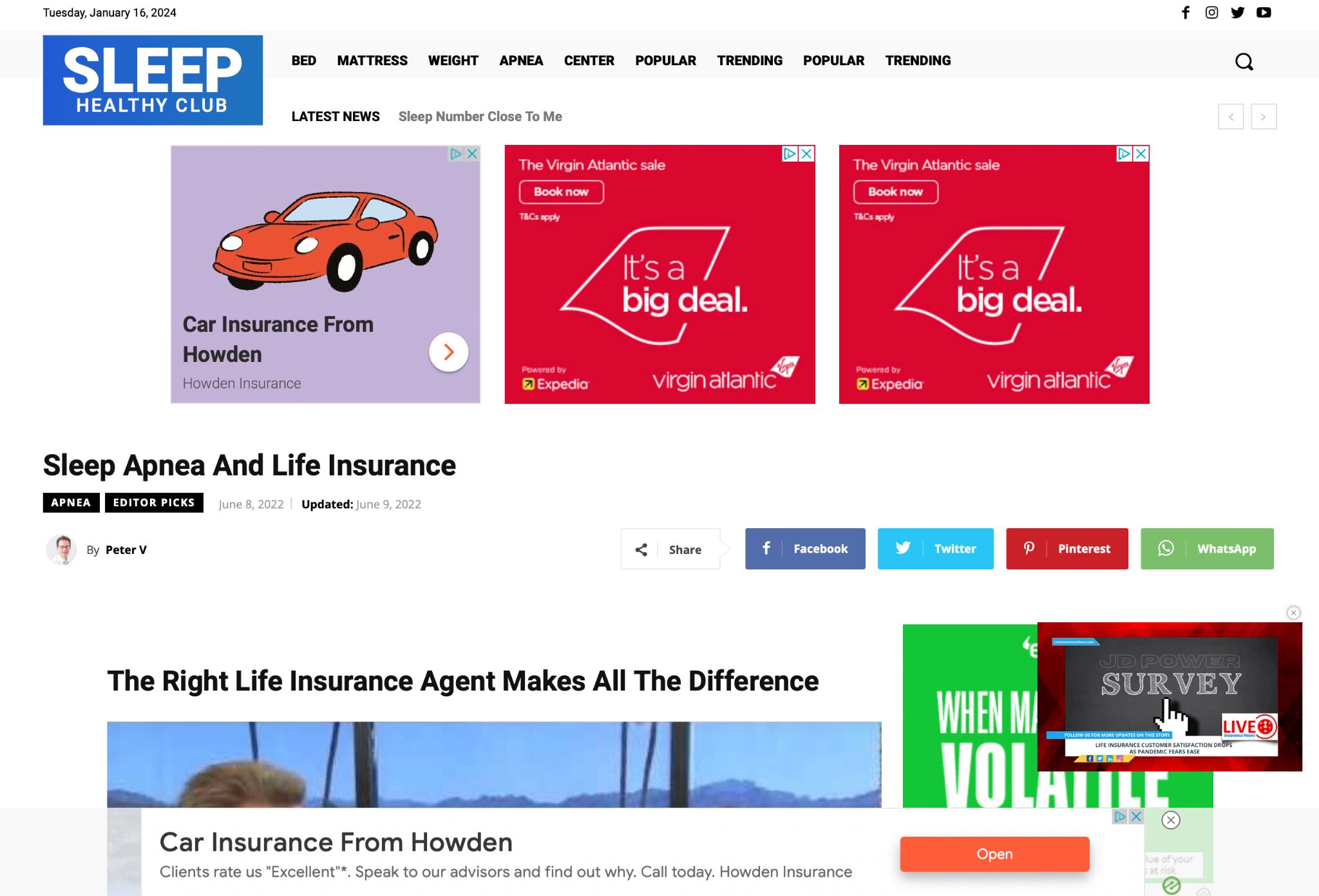

Conclusion? This is almost certainly a paid link. If a large percentage of the links to the site you’re considering look like this, that’s a major red flag.
Another of my favorite checks to do at this stage is to look at the Site Structure report to get a feel for the information architecture of the website and the traffic distribution across the content.
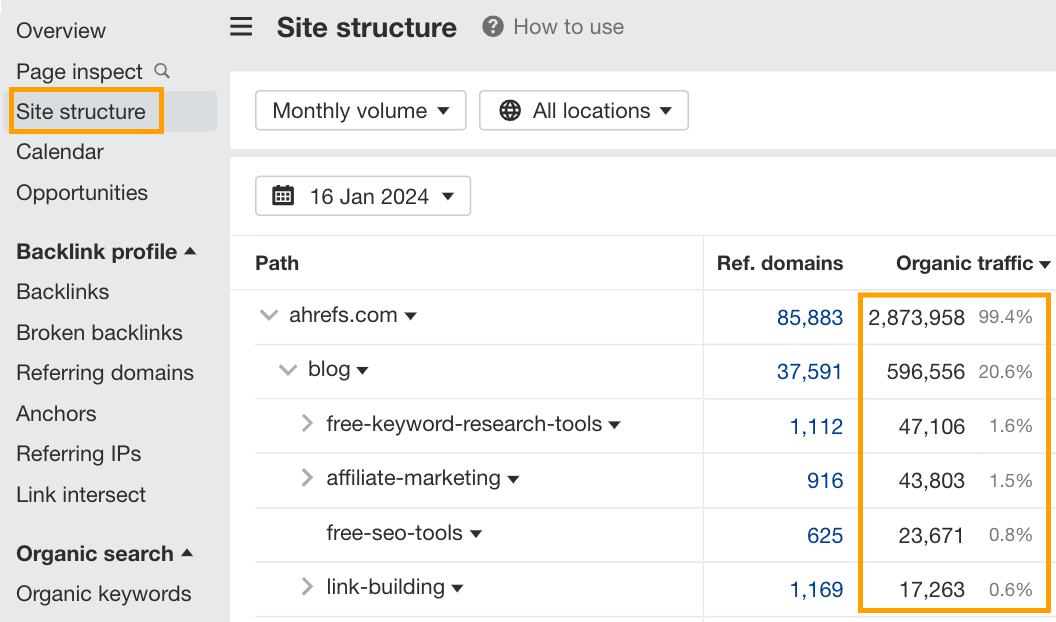

Poorly structured websites with decent performance are my favorite kind to work on. Generally, they’re run by people who aren’t the most SEO savvy, but they have built a genuine audience who like what they’re putting out there. Implementing some quick and easy SEO best practices can often see major gains on sites like this in a relatively small timeframe.
To assess the state of the market, check out Keywords Explorer for the top categories or broad terms and assess the search potential over time. Here are some common patterns you may see:
- Steady markets are great for consistent, recurring revenue and tend to form the bread and butter foundation of a website’s performance.
- Seasonal markets are great for growing your audience and short injections of new revenue but offer inconsistent income.
- New and growing markets typically have lower competition levels and offer a great opportunity to become the market leader.
- Declining markets offer a great opportunity to revolutionize an outdated way of doing things and to absorb an existing, knowledgeable audience.
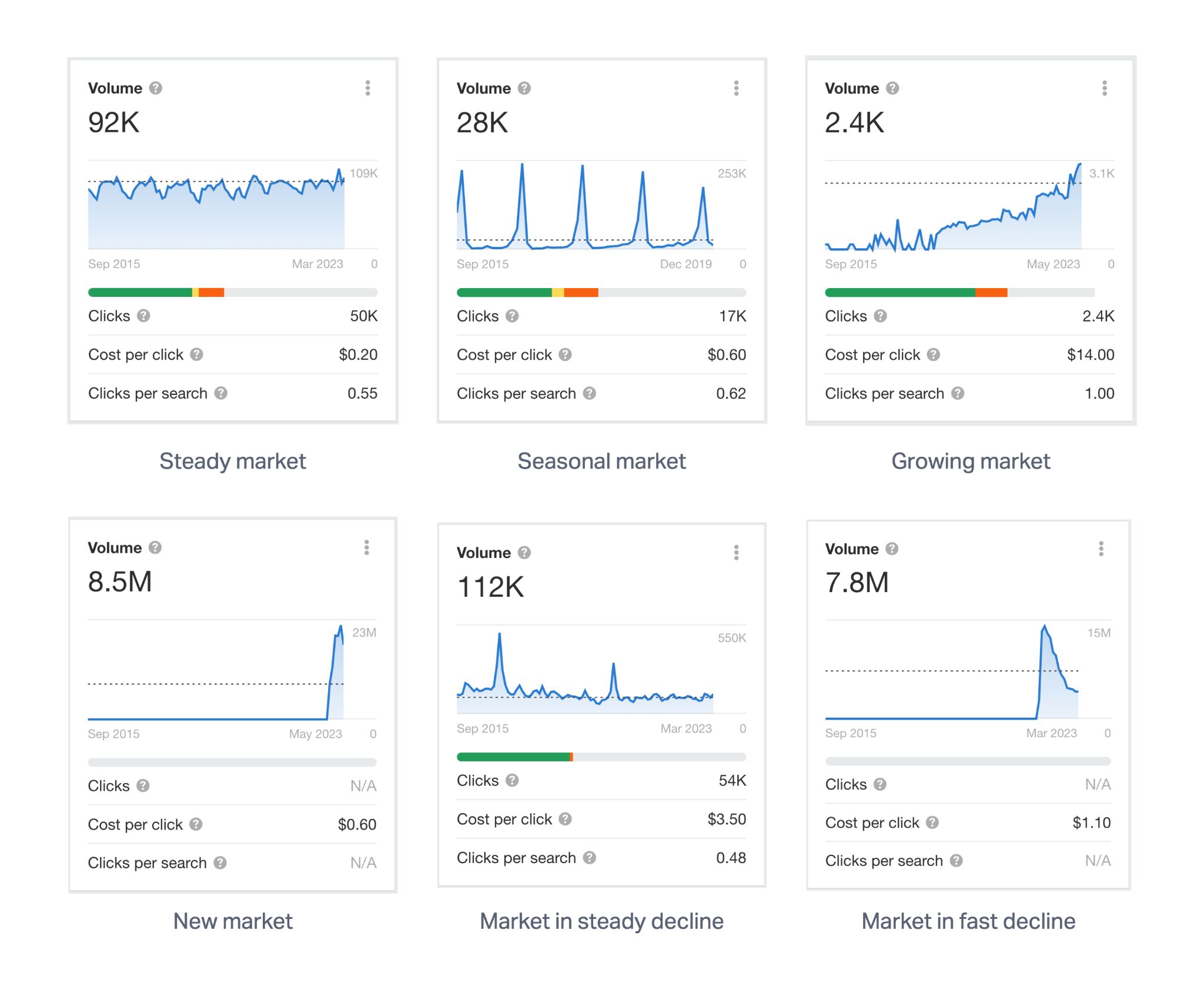

In short, there are opportunities in every kind of market, though the best ones for you depend on your goals.
In addition to understanding the market, you’ll need to also scope out existing competitors in the space and how the website you’re looking at is positioned against them.
The Organic Competitors report in Site Explorer will show you the top websites competing for similar keywords and how much bigger or smaller they are compared to the website available for sale.
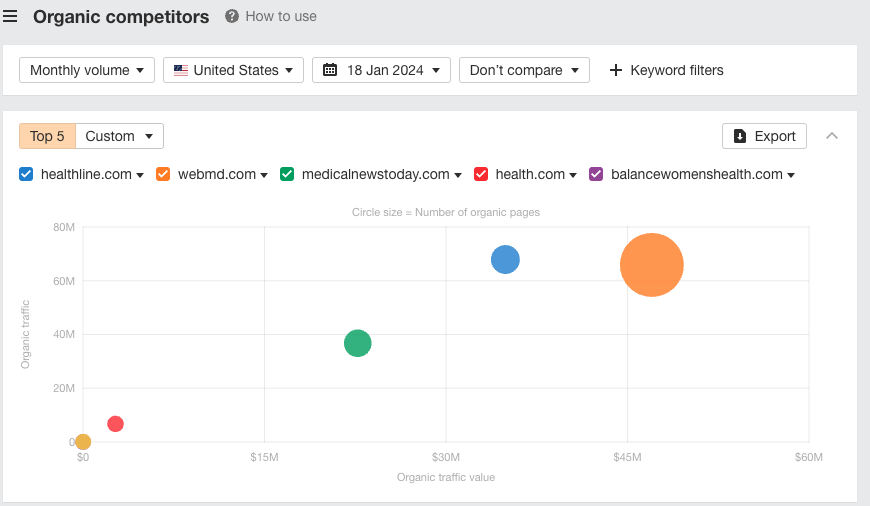

Having bigger competitors is not a bad thing. In fact, it could be a sign that the market is lucrative and worth investing in.
However, if the website you’re looking at is currently not very competitive, it will also require more skills and technical knowledge to improve it.
Website due diligence is the process of dotting your i’s and crossing your t’s when evaluating whether a website is a worthwhile investment.
No matter if you’re reaching out to a seller through a marketplace or brokerage or if you’re securing a private deal, this is an essential step of the process.
You can ask the seller to share access with analytics tools and some financial accounts and you can often schedule a video chat to ask more detailed questions about the website.
Here are some questions to consider.
Have you optimized the website for SEO?
If a seller has optimized the site for SEO, it helps to know exactly what they’ve done. You can also learn a great deal about what they tried that worked wonders and what didn’t work as well.
If the seller has not done any SEO, that may be ok depending on your goals. Many people don’t know where to start with optimizing a website and this presents a great opportunity for buyers with SEO know-how to take the website to the next level.
You can also verify the actual SEO performance of the website using Google Search Console if the seller has set it up. If they haven’t, Ahrefs’ Site Explorer is a great alternative for estimating overall organic performance.
Where does the majority of the traffic come from?
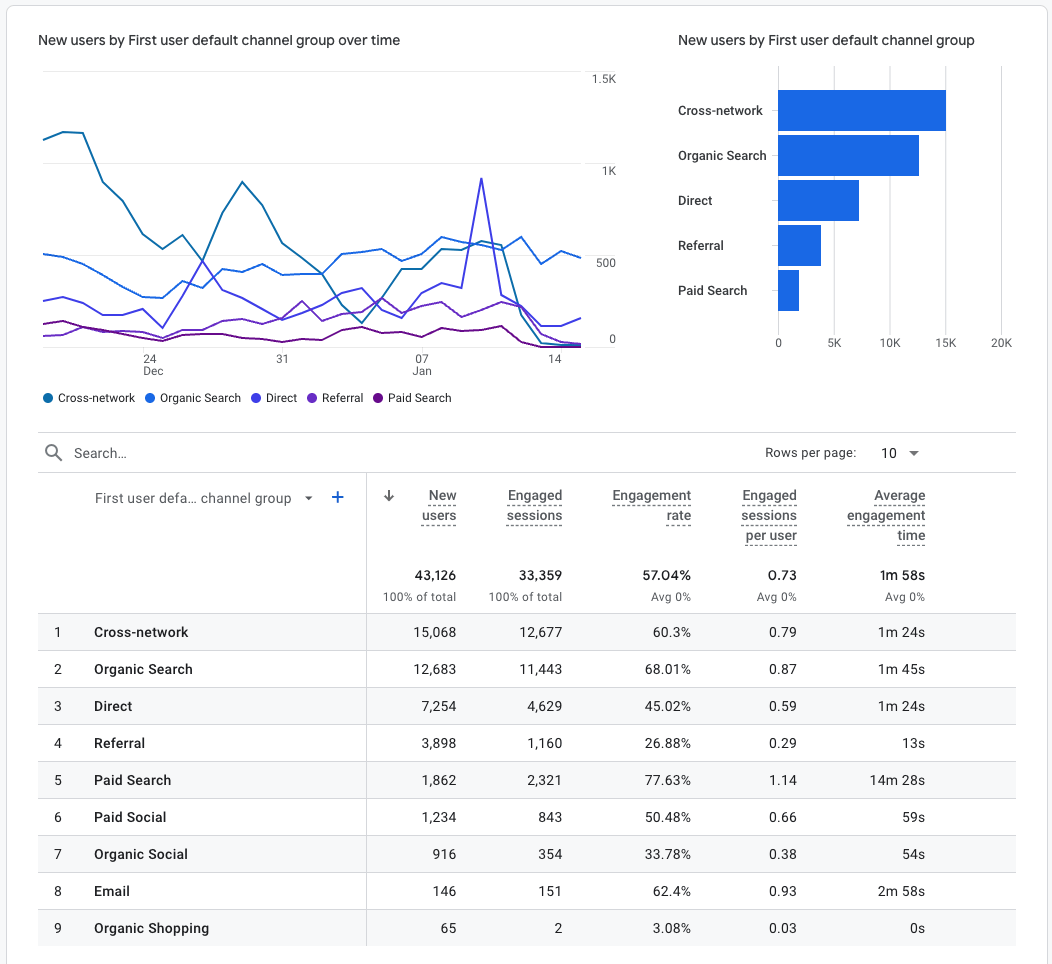
Make sure you check out the different countries and channels the website receives traffic from. Both of these can be assessed in Google Analytics (or similar tools) so make sure to request access from the seller.
In particular, check out the “Acquisition” reports to assess what channels users are coming from and how well SEO, ads and social campaigns may be working.
You should see something like this:

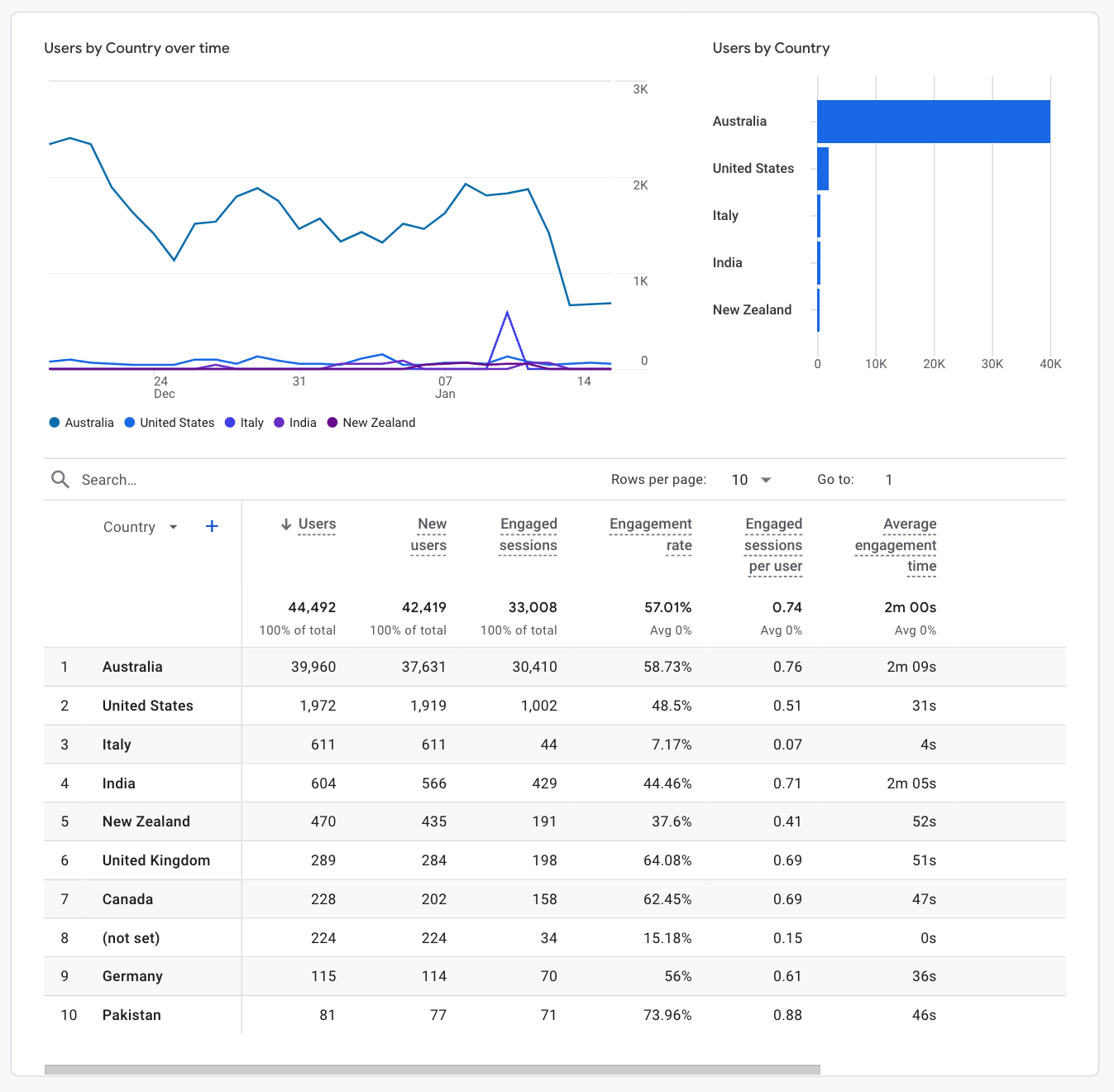
You should also check out the User Attributes > Demographic Details report to see what countries people are visiting the website from. It will look a little like this:

Have you done any link building?
Some sellers are honest about purchasing links or using private blog networks (PBNs), which opens up the opportunity for you to ask more follow-up questions about what they did.
Other sellers are not so forthcoming which is why scopipng out the backlink profile in Ahrefs is critical. Poor quality paid links can have very nasty consequences for websites.
How was your content created and how often do you upload new content?
With the latest move towards helpful content and combatingcombatting the rise of AI content, it can be a big boon to know exactly how the seller went about content creation.
- Did they create everything themselves?
- Do they work with subject matter experts?
- Did they use AI?
Content creation is the number one activity you can do from day one after you buy a website to help it reach new heights or to improve its performance if it’sits a bit of a fixer-upper.
If you’re comfortable creating all the content, great! If not, it really helps to know what relationships the seller had with writers, editors and subject matter experts that you can leverage.
It also helps to know how frequently they were publishing content so you can maintain a similar cadence. You can increase the cadence, but be wary of going too fast too quicklyquick. Big jumps in content production can be a sign the seller started using AI content.
You can use Ahrefs to spot mass AI-generated content in the Top Pages report and verify the information the seller has shared with you about their process:
Publishing 14k pages in a matter of a few weeks.
How long before the “Wrath of Google” kicks in?
Make your bets, ladies & gentlemen. pic.twitter.com/Nf4lQZcj9K
— Tim Soulo 🇺🇦 (@timsoulo) December 14, 2023
What do you see as the low-hanging fruit for a buyer?
Many sellers and website brokers will be happy to share the low-hanging fruit opportunities for continuing to grow the website. Asking questions along this line of thought will help you uncover opportunities you may not have become aware of during your research.
About 90% of the time, the best opportunities will come from things like:
- Targeting additional keywords
- Updating content
- Closing content gaps
- Building more or better links
- Exploring additional channels like paid or social platforms
How are traffic and profits diversified?
In our book, this is the most important question to consider if the reason you’re buying a website is to establish a passive income stream.
Ask the seller about the history of profit distribution across their top pages or products. You can also assess this yourself in the website’s analytics.
Look at the top three pages or products and see if any are pulling in more than 20% of the traffic or profits. It could be a sign that the website is not very well diversified.
Sometimes this is ok and could be used as an opportunity, but other times it may be a major risk that is a deal breaker for you.
If everything is looking and feeling good, it’s time to negotiate the sale and then migrate the assets into your possession.
You’ll likely need to put forward an offer you think is fair for the asset. If a broker is involved in the sale, you can negotiate with them or directly with the seller until an agreement is reached.
Keep in mind that many website and business sales fall down at the negotiating phase.
Before you start negotiating, decide what the asset is worth to you and make an offer at around 70% of that amount. Then, negotiate with the seller to reach a deal, but don’t get too excited and exceed your personal maximum.
Once you’ve secured the deal, it’s just a matter of transferring ownership of all the assets attached to the website, including:
- Domain name
- Hosting
- Website files
- Email accounts
- Google Business Profile (if any)
- Social media accounts (if any)
- Financial accounts (if possible)
In some cases, you may need to migrate the website to a new hosting account and if this isn’t managed properly, it could affect the website’s performance. Check out our full website migration process to ensure this step goes smoothly for you.
If you’re like most first-time website buyers, you’ve probably got a few questions brewing. Here are answers to the most common ones we see.
Can a website lose performance after a sale?
Yes, website performance can be affected by a few things immediately after a sale:
- A poor migration (especially if consolidating the new website into an existing one)
- Inflated figures in the seller’s reports
- Dishonest sellers removing any fake links they used to inflate the SEO performance
You can avoid this issue by paying close attention during the due diligence process and listening to your gut as you ask the seller various questions.
It may also be worth paying for a reputable SEO professional to oversee the migration of the website and its assets after the sale so you risk minimal losses in performance.
How do I know if a seller is legitimate?
If you’re buying a website through a marketplace like Flippa, you’ll need to pay more attention to traffic and profit validation to make sure you’re not buying a lemon the seller has painted as a chunk of gold.
Brokerages have a much more rigorous process for verifying both sellers and analytics.
Overall, you’ll have to rely on the information you’re able to gather from the seller along with your intuition on whether they are being transparent and can be trusted.
How do you know the website will be transferred after you pay for it?
You have the option of paying through escrow for almost all website transactions that occur through a marketplace or brokerage. Escrow is a payment method designed to minimize risk for both sellers and buyers in high-value transactions.
Instead of paying the seller everything upfront, you’ll pay a deposit to the escrow provider. Consider it like a legal holding account. Your funds will be kept in this account until certain conditions are met, namely all website files are transferred to you successfully.
Once you’ve received the files, account access and the website is officially yours, the escrow service releases your payment to the seller. It’s the most secure way to buy a digital asset minimizing your risk substantially.
Key Takeaways
Overall, buying a website can be a very rewarding experience! Whether a specific website is a good investment for you depends on your goals, skills, and resources.
But if you dot your i’s and cross your t’s with due diligence, you can’t go wrong. If this is your first time buying a website and you have some decent resources to put towards this purchase, we recommend going through a brokerage like Empire Flippers if you’d like the security of carefully vetted websites.
If you already have some experience up your sleeve, perhaps exploring some private deals may lead to more rewarding investments to grow your portfolio.
Got any questions? Reach out on LinkedIn.
SEO
Big Update To Google’s Ranking Drop Documentation

Google updated their guidance with five changes on how to debug ranking drops. The new version contains over 400 more words that address small and large ranking drops. There’s room to quibble about some of the changes but overall the revised version is a step up from what it replaced.
Change# 1: Downplays Fixing Traffic Drops
The opening sentence was changed so that it offers less hope for bouncing back from an algorithmic traffic drop. Google also joined two sentences into one sentence in the revised version of the documentation.
The documentation previously said that most traffic drops can be reversed and that identifying the reasons for a drop aren’t straightforward. The part about most of them can be reversed was completely removed.
Here is the original two sentences:
“A drop in organic Search traffic can happen for several reasons, and most of them can be reversed. It may not be straightforward to understand what exactly happened to your site”
Now there’s no hope offered for “most of them can be reversed” and more emphasis on understanding what happened is not straightforward.
This is the new guidance
“A drop in organic Search traffic can happen for several reasons, and it may not be straightforward to understand what exactly happened to your site.”
Change #2 Security Or Spam Issues
Google updated the traffic graph illustrations so that they precisely align with the causes for each kind of traffic decline.
The previous version of the graph was labeled:
“Site-level technical issue (Manual Action, strong algorithmic changes)”
The problem with the previous label is that manual actions and strong algorithmic changes are not technical issues and the new version fixes that issue.
The updated version now reads:
“Large drop from an algorithmic update, site-wide security or spam issue”
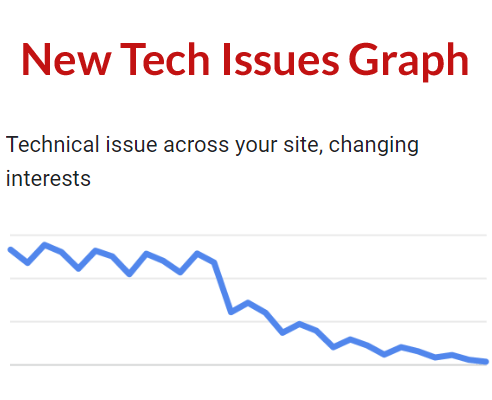
Change #3 Technical Issues
There’s one more change to a graph label, also to make it more accurate.
This is how the previous graph was labeled:
“Page-level technical issue (algorithmic changes, market disruption)”
The updated graph is now labeled:
“Technical issue across your site, changing interests”
Now the graph and label are more specific as a sitewide change and “changing interests” is more general and covers a wider range of changes than market disruption. Changing interests includes market disruption (where a new product makes a previous one obsolete or less desirable) but it also includes products that go out of style or loses their trendiness.
Change #4 Google Adds New Guidance For Algorithmic Changes
The biggest change by far is their brand new section for algorithmic changes which replaces two smaller sections, one about policy violations and manual actions and a second one about algorithm changes.
The old version of this one section had 108 words. The updated version contains 443 words.
A section that’s particularly helpful is where the guidance splits algorithmic update damage into two categories.
Two New Categories:
- Small drop in position? For example, dropping from position 2 to 4.
- Large drop in position? For example, dropping from position 4 to 29.
The two new categories are perfect and align with what I’ve seen in the search results for sites that have lost rankings. The reasons for dropping up and down within the top ten are different from the reasons why a site drops completely out of the top ten.
I don’t agree with the guidance for large drops. They recommend reviewing your site for large drops, which is good advice for some sites that have lost rankings. But in other cases there’s nothing wrong with the site and this is where less experienced SEOs tend to be unable to fix the problems because there’s nothing wrong with the site. Recommendations for improving EEAT, adding author bios or filing link disavows do not solve what’s going on because there’s nothing wrong with the site. The problem is something else in some of the cases.
Here is the new guidance for debugging search position drops:
“Algorithmic update
Google is always improving how it assesses content and updating its search ranking and serving algorithms accordingly; core updates and other smaller updates may change how some pages perform in Google Search results. We post about notable improvements to our systems on our list of ranking updates page; check it to see if there’s anything that’s applicable to your site.If you suspect a drop in traffic is due to an algorithmic update, it’s important to understand that there might not be anything fundamentally wrong with your content. To determine whether you need to make a change, review your top pages in Search Console and assess how they were ranking:
Small drop in position? For example, dropping from position 2 to 4.
Large drop in position? For example, dropping from position 4 to 29.Keep in mind that positions aren’t static or fixed in place. Google’s search results are dynamic in nature because the open web itself is constantly changing with new and updated content. This constant change can cause both gains and drops in organic Search traffic.
Small drop in position
A small drop in position is when there’s a small shift in position in the top results (for example, dropping from position 2 to 4 for a search query). In Search Console, you might see a noticeable drop in traffic without a big change in impressions.Small fluctuations in position can happen at any time (including moving back up in position, without you needing to do anything). In fact, we recommend avoiding making radical changes if your page is already performing well.
Large drop in position
A large drop in position is when you see a notable drop out of the top results for a wide range of terms (for example, dropping from the top 10 results to position 29).In cases like this, self-assess your whole website overall (not just individual pages) to make sure it’s helpful, reliable and people-first. If you’ve made changes to your site, it may take time to see an effect: some changes can take effect in a few days, while others could take several months. For example, it may take months before our systems determine that a site is now producing helpful content in the long term. In general, you’ll likely want to wait a few weeks to analyze your site in Search Console again to see if your efforts had a beneficial effect on ranking position.
Keep in mind that there’s no guarantee that changes you make to your website will result in noticeable impact in search results. If there’s more deserving content, it will continue to rank well with our systems.”
Change #5 Trivial Changes
The rest of the changes are relatively trivial but nonetheless makes the documentation more precise.
For example, one of the headings was changed from this:
You recently moved your site
To this new heading:
Site moves and migrations
Google’s Updated Ranking Drops Documentation
Google’s updated documentation is a well thought out but I think that the recommendations for large algorithmic drops are helpful for some cases and not helpful for other cases. I have 25 years of SEO experience and have experienced every single Google algorithm update. There are certain updates where the problem is not solved by trying to fix things and Google’s guidance used to be that sometimes there’s nothing to fix. The documentation is better but in my opinion it can be improved even further.
Read the new documentation here:
Debugging drops in Google Search traffic
Review the previous documentation:
Internet Archive Wayback Machine: Debugging drops in Google Search traffic
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Tomacco
SEO
Google March 2024 Core Update Officially Completed A Week Ago

Google has officially completed its March 2024 Core Update, ending over a month of ranking volatility across the web.
However, Google didn’t confirm the rollout’s conclusion on its data anomaly page until April 26—a whole week after the update was completed on April 19.
Many in the SEO community had been speculating for days about whether the turbulent update had wrapped up.
The delayed transparency exemplifies Google’s communication issues with publishers and the need for clarity during core updates
Google March 2024 Core Update Timeline & Status
First announced on March 5, the core algorithm update is complete as of April 19. It took 45 days to complete.
Unlike more routine core refreshes, Google warned this one was more complex.
Google’s documentation reads:
“As this is a complex update, the rollout may take up to a month. It’s likely there will be more fluctuations in rankings than with a regular core update, as different systems get fully updated and reinforce each other.”
The aftershocks were tangible, with some websites reporting losses of over 60% of their organic search traffic, according to data from industry observers.
The ripple effects also led to the deindexing of hundreds of sites that were allegedly violating Google’s guidelines.
Addressing Manipulation Attempts
In its official guidance, Google highlighted the criteria it looks for when targeting link spam and manipulation attempts:
- Creating “low-value content” purely to garner manipulative links and inflate rankings.
- Links intended to boost sites’ rankings artificially, including manipulative outgoing links.
- The “repurposing” of expired domains with radically different content to game search visibility.
The updated guidelines warn:
“Any links that are intended to manipulate rankings in Google Search results may be considered link spam. This includes any behavior that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site.”
John Mueller, a Search Advocate at Google, responded to the turbulence by advising publishers not to make rash changes while the core update was ongoing.
However, he suggested sites could proactively fix issues like unnatural paid links.
“If you have noticed things that are worth improving on your site, I’d go ahead and get things done. The idea is not to make changes just for search engines, right? Your users will be happy if you can make things better even if search engines haven’t updated their view of your site yet.”
Emphasizing Quality Over Links
The core update made notable changes to how Google ranks websites.
Most significantly, Google reduced the importance of links in determining a website’s ranking.
In contrast to the description of links as “an important factor in determining relevancy,” Google’s updated spam policies stripped away the “important” designation, simply calling links “a factor.”
This change aligns with Google’s Gary Illyes’ statements that links aren’t among the top three most influential ranking signals.
Instead, Google is giving more weight to quality, credibility, and substantive content.
Consequently, long-running campaigns favoring low-quality link acquisition and keyword optimizations have been demoted.
With the update complete, SEOs and publishers are left to audit their strategies and websites to ensure alignment with Google’s new perspective on ranking.
Core Update Feedback
Google has opened a ranking feedback form related to this core update.
You can use this form until May 31 to provide feedback to Google’s Search team about any issues noticed after the core update.
While the feedback provided won’t be used to make changes for specific queries or websites, Google says it may help inform general improvements to its search ranking systems for future updates.
Google also updated its help documentation on “Debugging drops in Google Search traffic” to help people understand ranking changes after a core update.
Featured Image: Rohit-Tripathi/Shutterstock
FAQ
After the update, what steps should websites take to align with Google’s new ranking criteria?
After Google’s March 2024 Core Update, websites should:
- Improve the quality, trustworthiness, and depth of their website content.
- Stop heavily focusing on getting as many links as possible and prioritize relevant, high-quality links instead.
- Fix any shady or spam-like SEO tactics on their sites.
- Carefully review their SEO strategies to ensure they follow Google’s new guidelines.
SEO
Google Declares It The “Gemini Era” As Revenue Grows 15%

Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, announced its first quarter 2024 financial results today.
While Google reported double-digit growth in key revenue areas, the focus was on its AI developments, dubbed the “Gemini era” by CEO Sundar Pichai.
The Numbers: 15% Revenue Growth, Operating Margins Expand
Alphabet reported Q1 revenues of $80.5 billion, a 15% increase year-over-year, exceeding Wall Street’s projections.
Net income was $23.7 billion, with diluted earnings per share of $1.89. Operating margins expanded to 32%, up from 25% in the prior year.
Ruth Porat, Alphabet’s President and CFO, stated:
“Our strong financial results reflect revenue strength across the company and ongoing efforts to durably reengineer our cost base.”
Google’s core advertising units, such as Search and YouTube, drove growth. Google advertising revenues hit $61.7 billion for the quarter.
The Cloud division also maintained momentum, with revenues of $9.6 billion, up 28% year-over-year.
Pichai highlighted that YouTube and Cloud are expected to exit 2024 at a combined $100 billion annual revenue run rate.
Generative AI Integration in Search
Google experimented with AI-powered features in Search Labs before recently introducing AI overviews into the main search results page.
Regarding the gradual rollout, Pichai states:
“We are being measured in how we do this, focusing on areas where gen AI can improve the Search experience, while also prioritizing traffic to websites and merchants.”
Pichai reports that Google’s generative AI features have answered over a billion queries already:
“We’ve already served billions of queries with our generative AI features. It’s enabling people to access new information, to ask questions in new ways, and to ask more complex questions.”
Google reports increased Search usage and user satisfaction among those interacting with the new AI overview results.
The company also highlighted its “Circle to Search” feature on Android, which allows users to circle objects on their screen or in videos to get instant AI-powered answers via Google Lens.
Reorganizing For The “Gemini Era”
As part of the AI roadmap, Alphabet is consolidating all teams building AI models under the Google DeepMind umbrella.
Pichai revealed that, through hardware and software improvements, the company has reduced machine costs associated with its generative AI search results by 80% over the past year.
He states:
“Our data centers are some of the most high-performing, secure, reliable and efficient in the world. We’ve developed new AI models and algorithms that are more than one hundred times more efficient than they were 18 months ago.
How Will Google Make Money With AI?
Alphabet sees opportunities to monetize AI through its advertising products, Cloud offerings, and subscription services.
Google is integrating Gemini into ad products like Performance Max. The company’s Cloud division is bringing “the best of Google AI” to enterprise customers worldwide.
Google One, the company’s subscription service, surpassed 100 million paid subscribers in Q1 and introduced a new premium plan featuring advanced generative AI capabilities powered by Gemini models.
Future Outlook
Pichai outlined six key advantages positioning Alphabet to lead the “next wave of AI innovation”:
- Research leadership in AI breakthroughs like the multimodal Gemini model
- Robust AI infrastructure and custom TPU chips
- Integrating generative AI into Search to enhance the user experience
- A global product footprint reaching billions
- Streamlined teams and improved execution velocity
- Multiple revenue streams to monetize AI through advertising and cloud
With upcoming events like Google I/O and Google Marketing Live, the company is expected to share further updates on its AI initiatives and product roadmap.
Featured Image: Sergei Elagin/Shutterstock
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days ago13 Best HubSpot Alternatives for 2024 (Free + Paid)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoAdvertising in local markets: A playbook for success
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Core Update Flux, AdSense Ad Intent, California Link Tax & More
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Needs Very Few Links To Rank Pages; Links Are Less Important
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days agoHow to Become an SEO Lead (10 Tips That Advanced My Career)
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoHow to Use AI For a More Effective Social Media Strategy, According to Ross Simmonds
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days ago10 Most Effective Franchise Marketing Strategies
-

 SEARCHENGINES3 days ago
SEARCHENGINES3 days agoGoogle Won’t Change The 301 Signals For Ranking & SEO








![The Current State of Google’s Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] person typing on laptop with](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It.webp-400x240.webp)
![The Current State of Google’s Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] person typing on laptop with](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It.webp-80x80.webp)





