SEO
Why Content Is Important for SEO

At their best, they form a bond that can catapult any website to the top of search engine rankings.
But that’s only when they’re at their best. Because, when they’re at their worst, they can cause Google penalties that are near impossible to recover from.
The purpose of this chapter is simple; to provide you with an understanding of why content is important for SEO and show you what you can do to make sure they work together in harmony.
As we dive in, we’ll gain a better understanding of what content means, what its SEO value is, and how to go about creating optimized content that lands you on the search engine radar.
Let’s get started.
What ‘Content’ Means
Providing an exact definition for content, and one that is agreed upon by all marketers would be near impossible.
But, while it is a challenge, TopRank Marketing CEO Lee Odden gathered some definitions of content from marketers around the world that give us a solid starting point.
Actionable marketer Heidi Cohen describes content as:
“High quality, useful information that conveys a story presented in a contextually relevant manner with the goal of soliciting an emotion or engagement. Delivered live or asynchronously, content can be expressed using a variety of formats including text, images, video, audio, and/or presentations.”
While Cohen’s description is right on point, it’s important to understand that content found online isn’t always high quality and useful.
There’s a lot of bad content out there that doesn’t come close to providing any type of relevancy or usefulness to the reader.
In a more simplified but similar definition, Social Triggers founder Derek Halpern says:
“Content comes in any form (audio, text, video), and it informs, entertains, enlightens, or teaches the people who consume it.”
Once again, Halpern is describing content that is, at the very least, relevant and useful to its intended audience.
If we avoid a description of “quality” content, we can take a more direct approach by looking at the dozens of different types of digital content.
At this point, you should have a pretty good idea of what content is while also understanding some of the different formats where it can be presented.
But what exactly is its value to SEO, and why is it so important that the two work together?
What Is the SEO Value of Content?
Google, the king of search engines, processes over 6.7 billion searches per day.
And since we’re talking about search engine optimization, that means they’re pretty well suited to answer this question.
Larry Page and Sergey Brin co-founded Google in 1998 with a mission:

That mission remains the same today. The way in which they organize that information, however, has changed quite a bit over the years.
Google’s algorithms are constantly evolving in an effort to deliver, as they say, “…useful and relevant results in a fraction of a second.”
The “useful and relevant results” that Google is attempting to deliver are the pieces of content that are available throughout the web.
These pieces of content are ranked by their order of usefulness and relevancy to the user performing the search.
And that means, in order for your content to have any SEO value at all, it needs to be beneficial to searchers.
How do you make sure it’s beneficial? Google helps us with that answer too.
Their recommendation is that, as you begin creating content, make sure it’s:
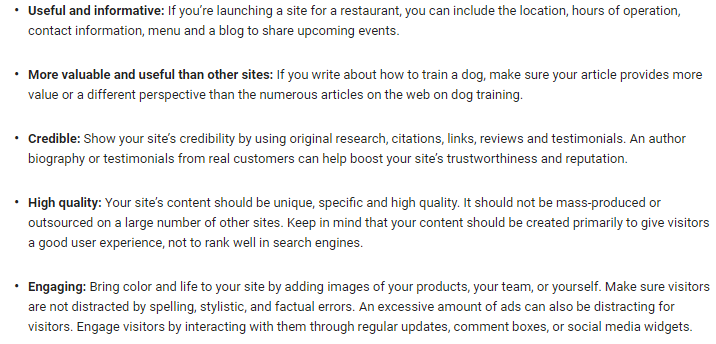
When these elements are in place, you maximize the potential of the SEO value of your content. Without them, however, your content will have very little value.
But, creating great content isn’t the only piece of the puzzle. There’s a technical side that you need to be aware of as well.
While we’ll talk about that later in this chapter, Maddy Osman put together a comprehensive resource on How to Evaluate the SEO Value of a Piece of Content that further elaborates on the topic.
For now, we can conclude that the SEO value of content depends on how useful, informative, valuable, credible, and engaging it is.
The Importance of Optimizing Content
The reason optimized content is important is simple… you won’t rank in search engines without it.
But, as we’ve already touched on briefly, it’s important to understand that there are multiple factors at play here.
On one side, you have content creation.
Optimizing content during creation is done by ensuring that your content is audience-centric and follows the recommendations laid out in the previous section.
But what does audience-centric mean, and how does it differ from other types of content?
Audience-centric simply means that you’re focusing on what audiences want to hear rather than what you want to talk about.
And, as we’ve identified, producing useful and relevant content is the name of the game if you’re looking to rank in search engines.
On the other side of the optimization equation is the technical stuff.
This involves factors like keywords, meta titles, meta descriptions, and URLs.
And that’s what we’re going to talk about next as we dive into how to actually create optimized content.
How to Create Optimized Content
When attempting to create optimized content, there are a few steps that we need to follow.
They include:
1. Perform Keyword Research & Determine Your Topic
While we’ve already identified that your main goal should be to create audience-centric content, keyword research is necessary to ensure that the resulting content can be found through search engines.
A few things to keep in mind when choosing your keywords and topic:
- Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
- Avoid Highly Competitive Keywords With Massive Search Numbers
- Use a Proven Keyword Research Tool
- Match Your Topic to Your Keyword
2. Develop Your Outline & Format for Optimal Readability
As you’re creating your outline, be sure that you’re formatting your core content so that it’s broken down into small chunks.
Online readers have incredibly short attention spans. And they’re not going to stick around if your article is just one ginormous paragraph.
It’s best to stick with paragraphs that are 1-2 sentences in length, although it’s all right if they stretch to 3-4 shorter sentences.
You’ll also want to be sure that you’re inserting sub-headers and/or visuals every 150-300 words to break up the content even further.
As you can see from the graph below, website engagement impacts organic rankings.
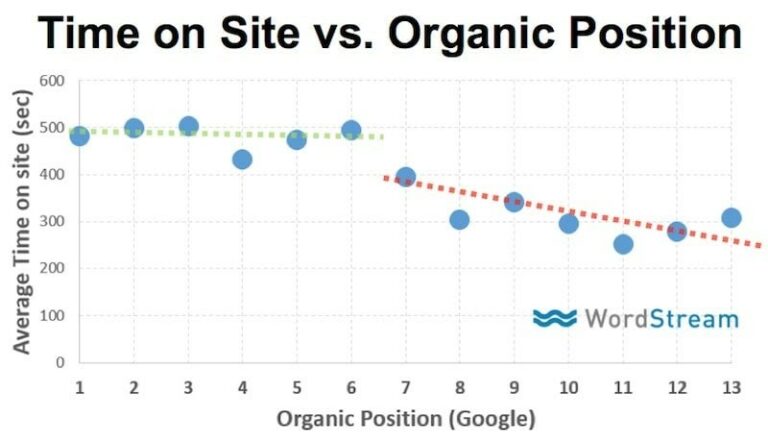
And, if you want to increase engagement, readability is crucial.
Example of Properly Formatted Content
Here’s an example of a page that is formatted for optimal readability:
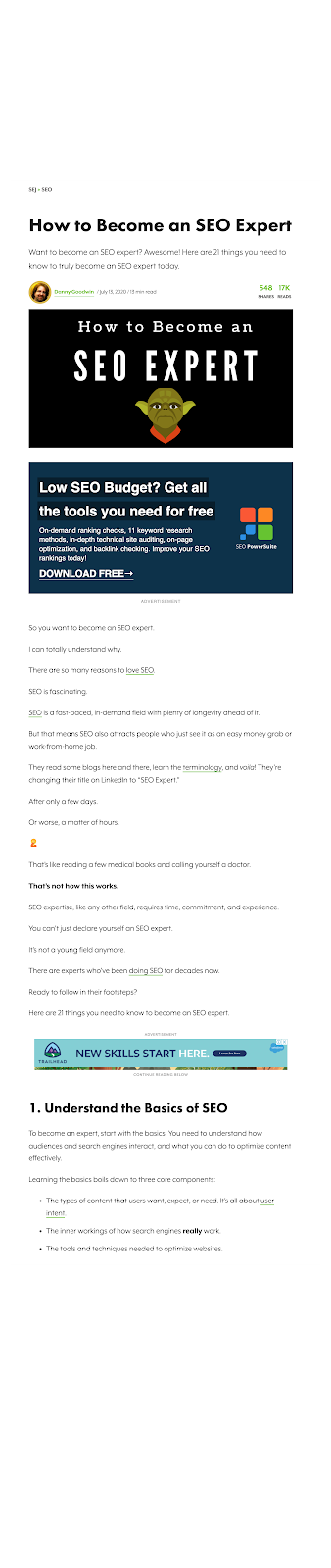
As you can see, most of the paragraphs are only a sentence or two long.
The text is also broken up using subheadings every 100-200 words.
Example of Poorly Formatted Content
On the other end of the spectrum, here’s an example of a post that’s likely to send readers away directly:
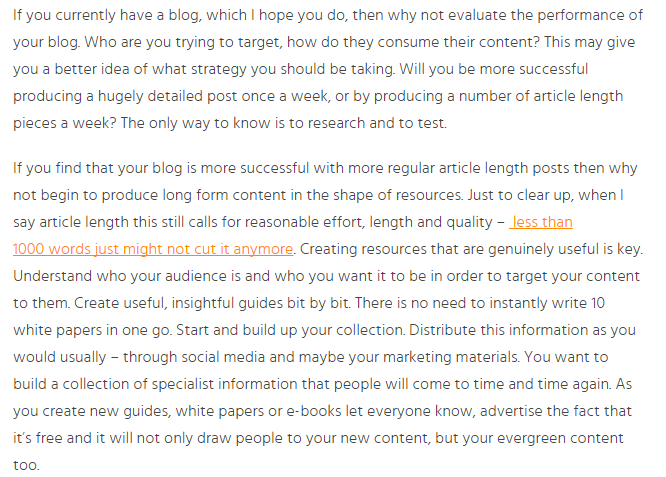
In this post, the content itself is fine. The problem is the extremely long sentences and paragraphs.
With better formatting, the author could easily increase visitors’ average time on site.
3. Stick to Your Topic & Target Keyword
As you begin writing your content, keep in mind the importance of sticking to the topic, and target keyword that you’ve chosen.
Don’t try to write about everything and anything within a single piece of content. And don’t try to target dozens of keywords.
Doing so is not only a huge waste of time, but it also prevents you from creating the most “useful and relevant” content on your topic.
Focus on what you’ve chosen as your topic and stay hyper-relevant to that topic and the keyword that supports it.
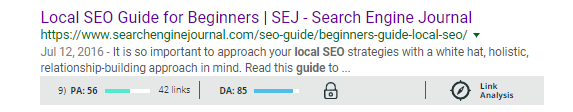
Brian Harnish’s Local SEO Guide for Beginners is a great example of an author staying hyper-relevant to a specific topic and keyword.
Just by looking at his title, the topic and target keyword are immediately clear.
And, due to this focus, Harnish’s guide ranks on the first page of Google for the phrase ‘local SEO guide.’
4. Include Backlinks Throughout Your Content
If you read the local SEO guide, you’ll notice that Harnish includes several links to external sites.
Since Google has made it clear that credibility is an important SEO factor, linking to relevant, trustworthy, and authoritative sites can help ensure that search engines see your content as credible.
Be sure, however, that the words you’re using for the link are actually relevant to the site the user will be sent to.
For example, take a look at this sentence:
“You need to understand how to create a compelling headline for your content.”
If you were to link to a resource showing the reader how to create compelling headlines, you’d want to link the bolded portion shown below:
“You need to understand how to create a compelling headline for your content.”
In most cases, it’s recommended that you keep your links to six words or fewer.
How to Optimize Your Content Once It’s Created
Now onto the “technical” part of content optimization.
The most important steps include optimizing the following:
- Title Tag
- Meta Description
- URL
Let’s take a look at how to complete each step.
1. How to Optimize Your Title Tag
When a user performs a search, the title tag is the clickable headline that they see at the top of each result.
For reference, it’s the highlighted portion in the image below:
Title tags are important for a few reasons. First and foremost, they help search engines understand what your page is about.
In addition, they can be a determining factor for which search result a user chooses.
To optimize your title tag, you’ll want to be sure of the following:
- Keep it under 60 characters.
- Don’t stuff multiple keywords into the title.
- Be specific about what the content is about.
- Place target keywords at the beginning.
The example above is a good one.
Here’s an example of a tag that fails to follow these guidelines:

The difference between the two is clear, and it shows the importance of optimizing your title tags.
2. How to Optimize Your Meta Description
Your meta description is the small snippet of text that appears under the title tag and URL.
When performing a search, it’s the section that’s circled below:
While Google has said that meta descriptions don’t have a direct impact on rankings, they do affect whether a user clicks on your page.
And click-through rate can have an indirect impact on rankings as well.
As far as meta description best practices, you should:
- Keep it under 160 characters.
- Provide a short, specific overview of what the content is about.
- Include relevant keywords (they will be highlighted when a user sees search results).
The example above shows a well put together description. Here’s an example of one that could use some work:

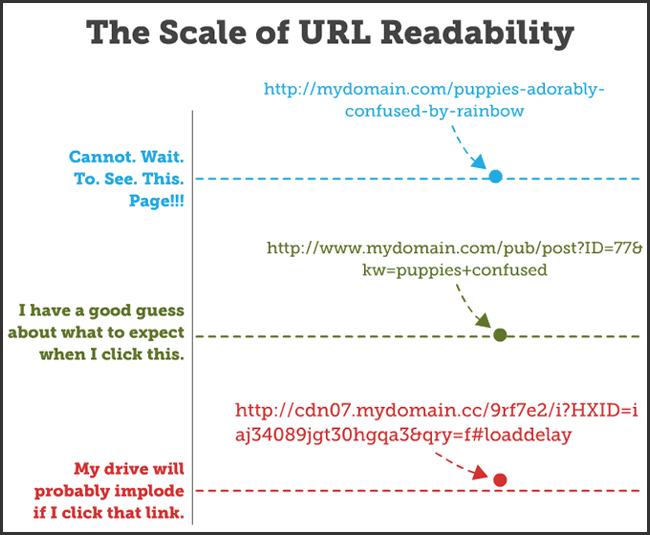
3. How to Optimize Your URL
Your URL structure is another component of SEO that has an indirect impact on rankings, as it can be a factor that determines whether a user clicks on your content.
Readability is most important here, as it ensures that search users aren’t scared off by long and mysterious URLs.
The image below provides a great example of how URL readability can affect the way a user sees results.
So, Why is Content Important for SEO?
The answer?
Because when content is optimized, it drastically improves your visibility.
And without visibility and exposure, your content is just another one of the millions of articles that are posted every day on the web.
Nobody sees it.
Nobody shares it.
Nobody does anything with it.
But it’s actually easy to get visible when you know what to do.
Sometimes, it can be the difference of something as small as writing optimized, unique meta descriptions for all your pages to send a huge visibility boost to Google.
If you want visibility and exposure, you have to commit yourself to the grind of consistently creating optimized content.
Featured Image Credit: Paulo Bobita
SEO
Google Declares It The “Gemini Era” As Revenue Grows 15%

Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, announced its first quarter 2024 financial results today.
While Google reported double-digit growth in key revenue areas, the focus was on its AI developments, dubbed the “Gemini era” by CEO Sundar Pichai.
The Numbers: 15% Revenue Growth, Operating Margins Expand
Alphabet reported Q1 revenues of $80.5 billion, a 15% increase year-over-year, exceeding Wall Street’s projections.
Net income was $23.7 billion, with diluted earnings per share of $1.89. Operating margins expanded to 32%, up from 25% in the prior year.
Ruth Porat, Alphabet’s President and CFO, stated:
“Our strong financial results reflect revenue strength across the company and ongoing efforts to durably reengineer our cost base.”
Google’s core advertising units, such as Search and YouTube, drove growth. Google advertising revenues hit $61.7 billion for the quarter.
The Cloud division also maintained momentum, with revenues of $9.6 billion, up 28% year-over-year.
Pichai highlighted that YouTube and Cloud are expected to exit 2024 at a combined $100 billion annual revenue run rate.
Generative AI Integration in Search
Google experimented with AI-powered features in Search Labs before recently introducing AI overviews into the main search results page.
Regarding the gradual rollout, Pichai states:
“We are being measured in how we do this, focusing on areas where gen AI can improve the Search experience, while also prioritizing traffic to websites and merchants.”
Pichai reports that Google’s generative AI features have answered over a billion queries already:
“We’ve already served billions of queries with our generative AI features. It’s enabling people to access new information, to ask questions in new ways, and to ask more complex questions.”
Google reports increased Search usage and user satisfaction among those interacting with the new AI overview results.
The company also highlighted its “Circle to Search” feature on Android, which allows users to circle objects on their screen or in videos to get instant AI-powered answers via Google Lens.
Reorganizing For The “Gemini Era”
As part of the AI roadmap, Alphabet is consolidating all teams building AI models under the Google DeepMind umbrella.
Pichai revealed that, through hardware and software improvements, the company has reduced machine costs associated with its generative AI search results by 80% over the past year.
He states:
“Our data centers are some of the most high-performing, secure, reliable and efficient in the world. We’ve developed new AI models and algorithms that are more than one hundred times more efficient than they were 18 months ago.
How Will Google Make Money With AI?
Alphabet sees opportunities to monetize AI through its advertising products, Cloud offerings, and subscription services.
Google is integrating Gemini into ad products like Performance Max. The company’s Cloud division is bringing “the best of Google AI” to enterprise customers worldwide.
Google One, the company’s subscription service, surpassed 100 million paid subscribers in Q1 and introduced a new premium plan featuring advanced generative AI capabilities powered by Gemini models.
Future Outlook
Pichai outlined six key advantages positioning Alphabet to lead the “next wave of AI innovation”:
- Research leadership in AI breakthroughs like the multimodal Gemini model
- Robust AI infrastructure and custom TPU chips
- Integrating generative AI into Search to enhance the user experience
- A global product footprint reaching billions
- Streamlined teams and improved execution velocity
- Multiple revenue streams to monetize AI through advertising and cloud
With upcoming events like Google I/O and Google Marketing Live, the company is expected to share further updates on its AI initiatives and product roadmap.
Featured Image: Sergei Elagin/Shutterstock
SEO
brightonSEO Live Blog

Hello everyone. It’s April again, so I’m back in Brighton for another two days of Being the introvert I am, my idea of fun isn’t hanging around our booth all day explaining we’ve run out of t-shirts (seriously, you need to be fast if you want swag!). So I decided to do something useful and live-blog the event instead.
Follow below for talk takeaways and (very) mildly humorous commentary. sun, sea, and SEO!
SEO
Google Further Postpones Third-Party Cookie Deprecation In Chrome

Google has again delayed its plan to phase out third-party cookies in the Chrome web browser. The latest postponement comes after ongoing challenges in reconciling feedback from industry stakeholders and regulators.
The announcement was made in Google and the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) joint quarterly report on the Privacy Sandbox initiative, scheduled for release on April 26.
Chrome’s Third-Party Cookie Phaseout Pushed To 2025
Google states it “will not complete third-party cookie deprecation during the second half of Q4” this year as planned.
Instead, the tech giant aims to begin deprecating third-party cookies in Chrome “starting early next year,” assuming an agreement can be reached with the CMA and the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO).
The statement reads:
“We recognize that there are ongoing challenges related to reconciling divergent feedback from the industry, regulators and developers, and will continue to engage closely with the entire ecosystem. It’s also critical that the CMA has sufficient time to review all evidence, including results from industry tests, which the CMA has asked market participants to provide by the end of June.”
Continued Engagement With Regulators
Google reiterated its commitment to “engaging closely with the CMA and ICO” throughout the process and hopes to conclude discussions this year.
This marks the third delay to Google’s plan to deprecate third-party cookies, initially aiming for a Q3 2023 phaseout before pushing it back to late 2024.
The postponements reflect the challenges in transitioning away from cross-site user tracking while balancing privacy and advertiser interests.
Transition Period & Impact
In January, Chrome began restricting third-party cookie access for 1% of users globally. This percentage was expected to gradually increase until 100% of users were covered by Q3 2024.
However, the latest delay gives websites and services more time to migrate away from third-party cookie dependencies through Google’s limited “deprecation trials” program.
The trials offer temporary cookie access extensions until December 27, 2024, for non-advertising use cases that can demonstrate direct user impact and functional breakage.
While easing the transition, the trials have strict eligibility rules. Advertising-related services are ineligible, and origins matching known ad-related domains are rejected.
Google states the program aims to address functional issues rather than relieve general data collection inconveniences.
Publisher & Advertiser Implications
The repeated delays highlight the potential disruption for digital publishers and advertisers relying on third-party cookie tracking.
Industry groups have raised concerns that restricting cross-site tracking could push websites toward more opaque privacy-invasive practices.
However, privacy advocates view the phaseout as crucial in preventing covert user profiling across the web.
With the latest postponement, all parties have more time to prepare for the eventual loss of third-party cookies and adopt Google’s proposed Privacy Sandbox APIs as replacements.
Featured Image: Novikov Aleksey/Shutterstock
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago13 Best HubSpot Alternatives for 2024 (Free + Paid)
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoBattling for Attention in the 2024 Election Year Media Frenzy
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago7 Best WooCommerce Points and Rewards Plugins (Free & Paid)
-

 AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days ago
AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days agoAI Will Transform the Workplace. Here’s How HR Can Prepare for It.
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Answers Whether Having Two Sites Affects Rankings
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoAdvertising in local markets: A playbook for success















