SEO
What Is A Sitemap? Do I Need One?

Sitemap. While this is a term you may be familiar with, what does it mean?
Do you need one? Where do you find one? How do you make one?
These are valid questions; for some, there might be more than one answer.
Today, we will take a deep dive into the sitemap world, so that you can walk away with the necessary answers and confidence around the topic!
What Is A Sitemap?
Let’s start here.
Defining a sitemap is essential for several reasons, and we are going to go through the two main types that apply to technical SEO: XML and HTML sitemaps.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a file that provides a website’s essential pages, videos, and other important files for Google to discover when crawling the site.
Not only are these listed in the file, but the sitemap can also provide details for Google to know – for instance, when the page was last updated, and if the content is available in other languages.
As I mentioned, you can also provide details about content types like videos, photos, and news-related content, specifically in your XML sitemap.
According to the Google Developers Sitemaps section, the following can be included for specific types of content in your sitemap:
- A sitemap video entry can specify the video running time, rating, and age-appropriateness rating.
- A sitemap image entry can include the location of the images included on a page.
- A sitemap news entry can include the article title and publication date.
Next, we will talk about what an HTML sitemap is and the differences between the two.
HTML Sitemap
An HTML sitemap is more targeted for users on your site than for Google.
This is a page that exists on your site and has links to the pages on your website – and in some cases, includes a little context into what those pages are.
Google mentions that you should try to establish a consistent and clear hierarchy on the HTML sitemap as, although not its purpose, it can help with indexation.
You can think of an HTML sitemap as a directory that users can leverage to navigate your site and find what they need.
An HTML sitemap should not be an attempt to replace the important pages in your site’s navigation.
XML Sitemaps Vs. HTML Sitemaps
So, what are the key differences between these two types of sitemaps? Let’s review.
XML
- The intent is for Google and other bots.
- There is no hierarchy.
- Used primarily for indexing.
- You can submit via Google Webmaster Tools.
HTML
- The intent is for users.
- A hierarchy should be used.
- No place to submit in Google Webmaster Tools.
Do You Need A Sitemap?
If you are wondering if you need a sitemap, that depends!
First, let’s discuss the XML sitemap. There are a few questions you can ask to determine if you need an XML sitemap:
- How big is your site? Is it large enough that Google may miss newly updated content when it is crawling?
- Is your site relatively new? If so, it may not have a ton of external links on the Internet that point to it to help Google discover it. Even if your site isn’t new, and you don’t have external links, your answer to this question should be yes.
- Is your site content heavy? Do you have many photos, videos, news content, etc.?
- Does your site need a better architecture that results in pages not being well linked to each other? This can also be the case with archived and orphan pages you want to be indexed.
If you answered yes to any of the questions above, then yes, it is best practice to have an XML sitemap.
Even if you answered no to all of the above, I would recommend an XML sitemap for a few reasons; If your site grows, expands its scope, and other situations may arise, having a sitemap will be beneficial!
Next, let’s review whether it makes sense for you to have an HTML sitemap. Depending on where you look, you will find that answer to be yes or no.
HTML sitemaps are known to be an older concept, but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t have one.
The XML sitemap has the information needed for Google to crawl, index, and learn other important information about these pages. However, an XML sitemap does not show hierarchy like an HTML sitemap.
Google will crawl the links on your site, and including an HTML sitemap could allow Google to understand your site’s architecture and relationships better.
This is even more useful for sites that have an incredibly large number of pages.
So, is having an HTML sitemap critical? No, it is not.
It is also not a cure-all for a poorly architected and nested website. While it isn’t a critical element of success, it has shown benefits that make having one a best practice.
To close this topic out, I recommend you have an XML and HTML sitemap because let’s be honest, why not, when the pros outweigh the cons very clearly?
Now you may be wondering how to create these two assets and what to do with them – so, let’s jump into some ways you can create these files and where to put them on the site.
How To Create An XML Sitemap
First, we will go over how you can generate sitemaps from scratch, and then we will get into some great tools that can do it for you.
XML sitemaps have specific criteria in order to be rendered valid.
Below are a few specific requirements for XML sitemaps:
- Begin with a <urlset> tag and end with that tag closing </urlset>.
- Include the protocol you are using within the <urlset> tag.
- Each URL entry must have a <url> tag as a parent XML tag.
- Include a <loc> child entry for each <url> parent tag.
- Each sitemap can only contain up to 50,000 URLs and 50MB.
- Must be UTF-encoded.
XML Sitemap Best Practices
Now, let’s look at some key best practices when it comes to creating XML sitemaps:
- Only URLs you want to be indexed should appear in your sitemap. This means no redirected URLs, non-canonical URLs, or pages marked as no-index.
- Do not use session Ids.
- Only include the primary if you have two versions (mobile and desktop) of your site.
- Include media assets like videos, photos, and news items.
- Use hreflang to show Google that there are alternative language versions of your website.
- Google documentation notes it leverages <lastmod>, but only if it’s consistent and verifiable. If you can’t keep this accurate, don’t use it.
- Google ignores the <priority> and <changefreq> tags at this time, according to John Mueller on this Search Off the Record podcast.
- Google will not crawl your URLs in the order they are listed, nor does it guarantee indexation.
- Your sitemap should be updated regularly – automatically, or manually – or Google may not trust it.
Now, if you felt lost reading those beginning requirements, that is okay, because there are tools to help you achieve your desired outcomes! We will go over some later in this article.
Check out the refined version below:
 Screenshot from lowes.com, January 2023
Screenshot from lowes.com, January 2023How To Create An HTML Sitemap
When putting together an HTML sitemap, remember its purpose is to serve a user on the site and help Google understand the hierarchy of your website.
You do not want to no index this page from Google; keep it crawlable!
You will want to ensure you don’t just throw thousands of links on an HTML sitemap page with no sense of organization, as this won’t help anyone – bots included.
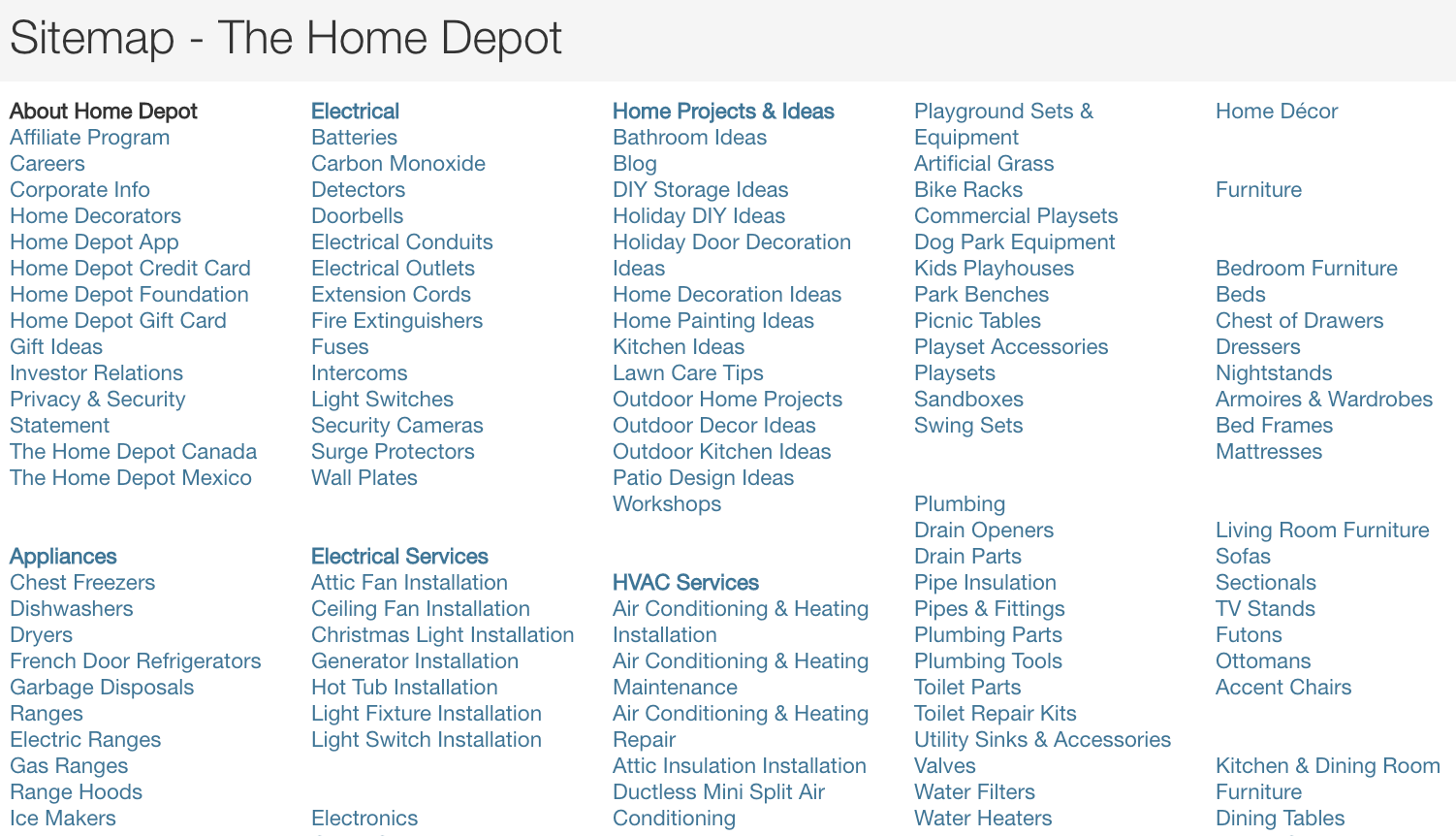 Screenshot from Home Depot, January 2023
Screenshot from Home Depot, January 2023HTML Sitemap Best Practices
Let’s go over a few quick best practices when it comes to HTML sitemaps:
- Arrange the page’s structure to align with your website’s structure. You will want to make sure that the hierarchy is easily understood.
- The HTML sitemap should be located somewhere the user can easily find it. You will often see it in the footer links of a website.
- Use anchor text that is valuable to the user.
Need a little help getting started? No worries – there are plenty of tools to help you.
Sitemap Generator Tools
There are a number of tools to help you generate different types of sitemaps. Let’s go over a few now.
XML Sitemap Generator Tools
- Screaming Frog – This tool is a great option for generating a sitemap, especially if you want to generate one after crawling your URLs. Screaming Frog is free if you have under 1,000 URLs, but you would have to buy a license if you have more.
- XML-Sitemaps.com – This web-based application allows you to enter your website URL and it generates an XML file for you. This is a free tool for up to 500 URLs.
Depending on which CMS you are leveraging, there are also thousands of XML sitemap generator plug-ins, but be cautious as even the best generator tools have their limitations, so make sure to double-check the output.
Here are a few popular XML sitemap plugins for WordPress:
HTML Sitemap Generator Tools
- com: this is a free online tool where you can scan your website URL or upload a document to generate an HTML sitemap. As we discussed earlier, there may be better approaches than a generator if your site is poorly architected.
- Crawler: Like Eli mentions, if you have a large site and are already using a crawler like OnCrawl, DeepCrawl, Screaming Frog, or SiteBulb, you can leverage the output from a crawl to help generate your HTML sitemap.
Like XML sitemaps, there are also a variety of CMS plugins for creating HTML sitemaps. Here are a few for WordPress:
In Conclusion
Sitemaps have existed in the SEO world for some time as a method for helping search engines discover and crawl websites.
And, while having a sitemap isn’t always necessary for every site, it certainly doesn’t hurt – and can be especially useful for both new and large sites.
When you are determining your next steps for creating a sitemap for your website – whether XML or HTML – I hope you can leverage this guide to decide which path makes the most sense for your site’s needs.
More resources:
Featured Image: Sammby/Shutterstock
SEO
Google March 2024 Core Update Officially Completed A Week Ago

Google has officially completed its March 2024 Core Update, ending over a month of ranking volatility across the web.
However, Google didn’t confirm the rollout’s conclusion on its data anomaly page until April 26—a whole week after the update was completed on April 19.
Many in the SEO community had been speculating for days about whether the turbulent update had wrapped up.
The delayed transparency exemplifies Google’s communication issues with publishers and the need for clarity during core updates
Google March 2024 Core Update Timeline & Status
First announced on March 5, the core algorithm update is complete as of April 19. It took 45 days to complete.
Unlike more routine core refreshes, Google warned this one was more complex.
Google’s documentation reads:
“As this is a complex update, the rollout may take up to a month. It’s likely there will be more fluctuations in rankings than with a regular core update, as different systems get fully updated and reinforce each other.”
The aftershocks were tangible, with some websites reporting losses of over 60% of their organic search traffic, according to data from industry observers.
The ripple effects also led to the deindexing of hundreds of sites that were allegedly violating Google’s guidelines.
Addressing Manipulation Attempts
In its official guidance, Google highlighted the criteria it looks for when targeting link spam and manipulation attempts:
- Creating “low-value content” purely to garner manipulative links and inflate rankings.
- Links intended to boost sites’ rankings artificially, including manipulative outgoing links.
- The “repurposing” of expired domains with radically different content to game search visibility.
The updated guidelines warn:
“Any links that are intended to manipulate rankings in Google Search results may be considered link spam. This includes any behavior that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site.”
John Mueller, a Search Advocate at Google, responded to the turbulence by advising publishers not to make rash changes while the core update was ongoing.
However, he suggested sites could proactively fix issues like unnatural paid links.
“If you have noticed things that are worth improving on your site, I’d go ahead and get things done. The idea is not to make changes just for search engines, right? Your users will be happy if you can make things better even if search engines haven’t updated their view of your site yet.”
Emphasizing Quality Over Links
The core update made notable changes to how Google ranks websites.
Most significantly, Google reduced the importance of links in determining a website’s ranking.
In contrast to the description of links as “an important factor in determining relevancy,” Google’s updated spam policies stripped away the “important” designation, simply calling links “a factor.”
This change aligns with Google’s Gary Illyes’ statements that links aren’t among the top three most influential ranking signals.
Instead, Google is giving more weight to quality, credibility, and substantive content.
Consequently, long-running campaigns favoring low-quality link acquisition and keyword optimizations have been demoted.
With the update complete, SEOs and publishers are left to audit their strategies and websites to ensure alignment with Google’s new perspective on ranking.
Core Update Feedback
Google has opened a ranking feedback form related to this core update.
You can use this form until May 31 to provide feedback to Google’s Search team about any issues noticed after the core update.
While the feedback provided won’t be used to make changes for specific queries or websites, Google says it may help inform general improvements to its search ranking systems for future updates.
Google also updated its help documentation on “Debugging drops in Google Search traffic” to help people understand ranking changes after a core update.
Featured Image: Rohit-Tripathi/Shutterstock
FAQ
After the update, what steps should websites take to align with Google’s new ranking criteria?
After Google’s March 2024 Core Update, websites should:
- Improve the quality, trustworthiness, and depth of their website content.
- Stop heavily focusing on getting as many links as possible and prioritize relevant, high-quality links instead.
- Fix any shady or spam-like SEO tactics on their sites.
- Carefully review their SEO strategies to ensure they follow Google’s new guidelines.
SEO
Google Declares It The “Gemini Era” As Revenue Grows 15%

Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, announced its first quarter 2024 financial results today.
While Google reported double-digit growth in key revenue areas, the focus was on its AI developments, dubbed the “Gemini era” by CEO Sundar Pichai.
The Numbers: 15% Revenue Growth, Operating Margins Expand
Alphabet reported Q1 revenues of $80.5 billion, a 15% increase year-over-year, exceeding Wall Street’s projections.
Net income was $23.7 billion, with diluted earnings per share of $1.89. Operating margins expanded to 32%, up from 25% in the prior year.
Ruth Porat, Alphabet’s President and CFO, stated:
“Our strong financial results reflect revenue strength across the company and ongoing efforts to durably reengineer our cost base.”
Google’s core advertising units, such as Search and YouTube, drove growth. Google advertising revenues hit $61.7 billion for the quarter.
The Cloud division also maintained momentum, with revenues of $9.6 billion, up 28% year-over-year.
Pichai highlighted that YouTube and Cloud are expected to exit 2024 at a combined $100 billion annual revenue run rate.
Generative AI Integration in Search
Google experimented with AI-powered features in Search Labs before recently introducing AI overviews into the main search results page.
Regarding the gradual rollout, Pichai states:
“We are being measured in how we do this, focusing on areas where gen AI can improve the Search experience, while also prioritizing traffic to websites and merchants.”
Pichai reports that Google’s generative AI features have answered over a billion queries already:
“We’ve already served billions of queries with our generative AI features. It’s enabling people to access new information, to ask questions in new ways, and to ask more complex questions.”
Google reports increased Search usage and user satisfaction among those interacting with the new AI overview results.
The company also highlighted its “Circle to Search” feature on Android, which allows users to circle objects on their screen or in videos to get instant AI-powered answers via Google Lens.
Reorganizing For The “Gemini Era”
As part of the AI roadmap, Alphabet is consolidating all teams building AI models under the Google DeepMind umbrella.
Pichai revealed that, through hardware and software improvements, the company has reduced machine costs associated with its generative AI search results by 80% over the past year.
He states:
“Our data centers are some of the most high-performing, secure, reliable and efficient in the world. We’ve developed new AI models and algorithms that are more than one hundred times more efficient than they were 18 months ago.
How Will Google Make Money With AI?
Alphabet sees opportunities to monetize AI through its advertising products, Cloud offerings, and subscription services.
Google is integrating Gemini into ad products like Performance Max. The company’s Cloud division is bringing “the best of Google AI” to enterprise customers worldwide.
Google One, the company’s subscription service, surpassed 100 million paid subscribers in Q1 and introduced a new premium plan featuring advanced generative AI capabilities powered by Gemini models.
Future Outlook
Pichai outlined six key advantages positioning Alphabet to lead the “next wave of AI innovation”:
- Research leadership in AI breakthroughs like the multimodal Gemini model
- Robust AI infrastructure and custom TPU chips
- Integrating generative AI into Search to enhance the user experience
- A global product footprint reaching billions
- Streamlined teams and improved execution velocity
- Multiple revenue streams to monetize AI through advertising and cloud
With upcoming events like Google I/O and Google Marketing Live, the company is expected to share further updates on its AI initiatives and product roadmap.
Featured Image: Sergei Elagin/Shutterstock
SEO
brightonSEO Live Blog

Hello everyone. It’s April again, so I’m back in Brighton for another two days of Being the introvert I am, my idea of fun isn’t hanging around our booth all day explaining we’ve run out of t-shirts (seriously, you need to be fast if you want swag!). So I decided to do something useful and live-blog the event instead.
Follow below for talk takeaways and (very) mildly humorous commentary. sun, sea, and SEO!
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days ago7 Best WooCommerce Points and Rewards Plugins (Free & Paid)
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago13 Best HubSpot Alternatives for 2024 (Free + Paid)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoBattling for Attention in the 2024 Election Year Media Frenzy
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoAdvertising in local markets: A playbook for success
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle Answers Whether Having Two Sites Affects Rankings
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Core Update Flux, AdSense Ad Intent, California Link Tax & More
-

 AFFILIATE MARKETING6 days ago
AFFILIATE MARKETING6 days agoGrab Microsoft Project Professional 2021 for $20 During This Flash Sale




![The Current State of Google’s Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] person typing on laptop with](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It.webp-400x240.webp)
![The Current State of Google’s Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] person typing on laptop with](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It.webp-80x80.webp)










You must be logged in to post a comment Login