SEO
15 Unique Ways to Check Competitor Website Traffic

You only need three tools to get sixteen highly actionable data points on your competitors’ traffic.
Before we dive in, let’s set the right expectations: no tool will give you your competitor’s exact traffic data. However, it’s still well enough to see what works for them, copy their best ideas, or set realistic benchmarks.
We’ll cover:
- Types of data you can access, such as traffic volume, trends, organic and paid keywords, and audience insights.
- Practical use cases, including benchmarking, tracking progress, identifying content gaps, boosting your SEO and SEM, and negotiating budgets.
- Last but not least, how this data is gathered and its reliability.
With these tools and insights, you’ll be well-equipped to understand and outperform your competitors’ website traffic.
We’ll start with organic search traffic — the source on which you’ll get the most data.
How to analyze competitor organic search traffic
Organic search traffic refers to the clicks a site gets from search engines, excluding search ads.
There’s a lot you can tell about your competitors’ organic traffic and a lot you can tell from it. Here are my favorite twelve use cases with detailed instructions.
You can check that in seconds for free, right now:
The tool will also show you where in the world the traffic is coming from, some of the top pages and keywords, and traffic value (i.e., the value of the organic search traffic, if it were to be acquired via PPC in Google Ads).
Organic competitors are the sites that compete with you for the same organic keywords in search engines.
Typically, you’ll have more organic competitors than your regular direct business competitors. For example, a 3D printer manufacturer may be competing for a fair share of keywords with a 3D printing magazine — completely different businesses, same keywords.
So by rounding up your top organic competitors, you gain a bigger pool of keyword ideas you can potentially target. Much bigger than if you’d just take into account your direct competitors.
Here’s how to identify all organic competitors.
- Open Ahrefs’ Site Explorer and enter your domain.
- Go to the Organic competitors report.
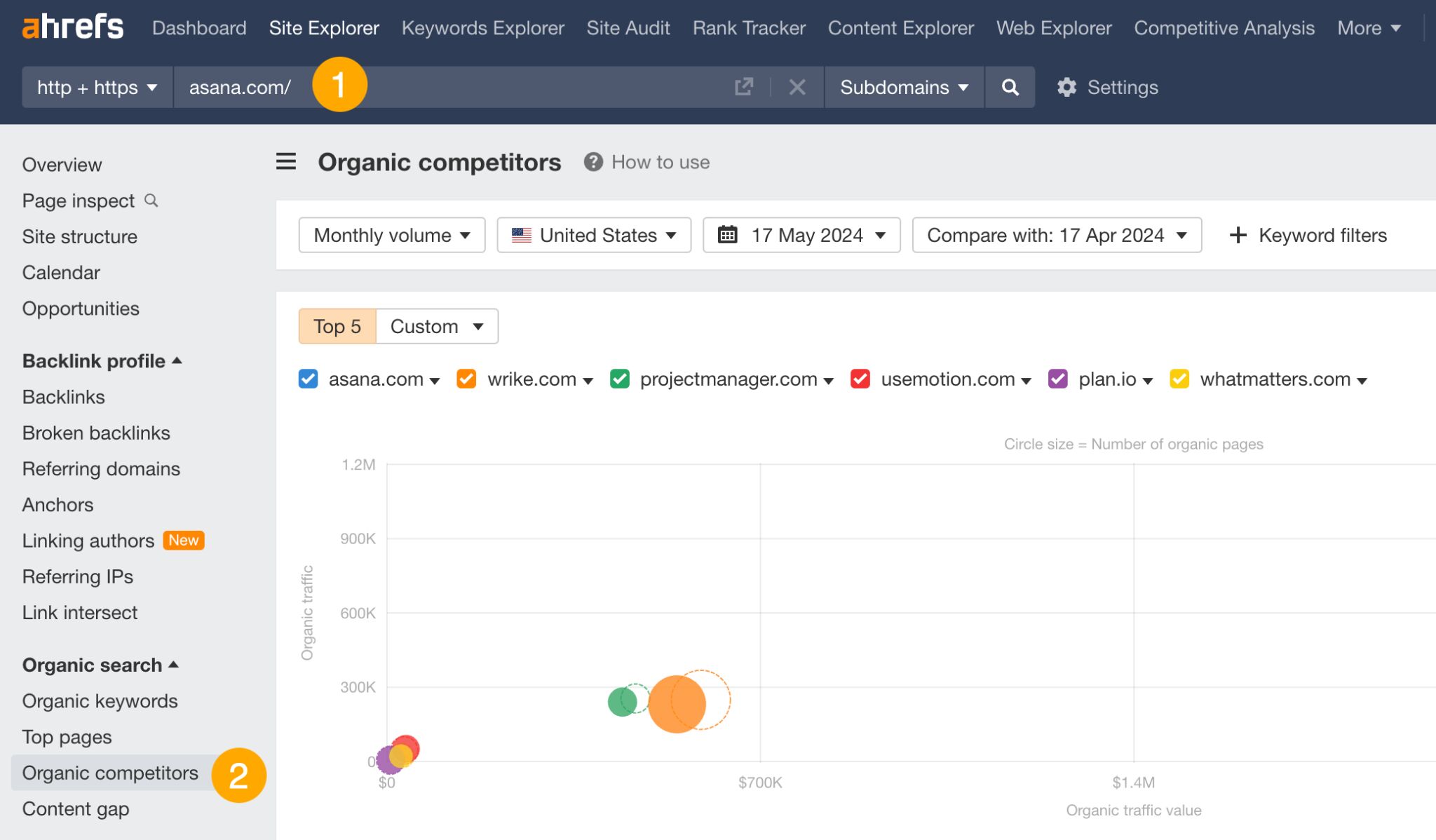

From there, you can look at the common keywords to see where they outrank you or click on Competitor’s keywords to see keywords you don’t rank for but they do (a.k.a. your content gap).
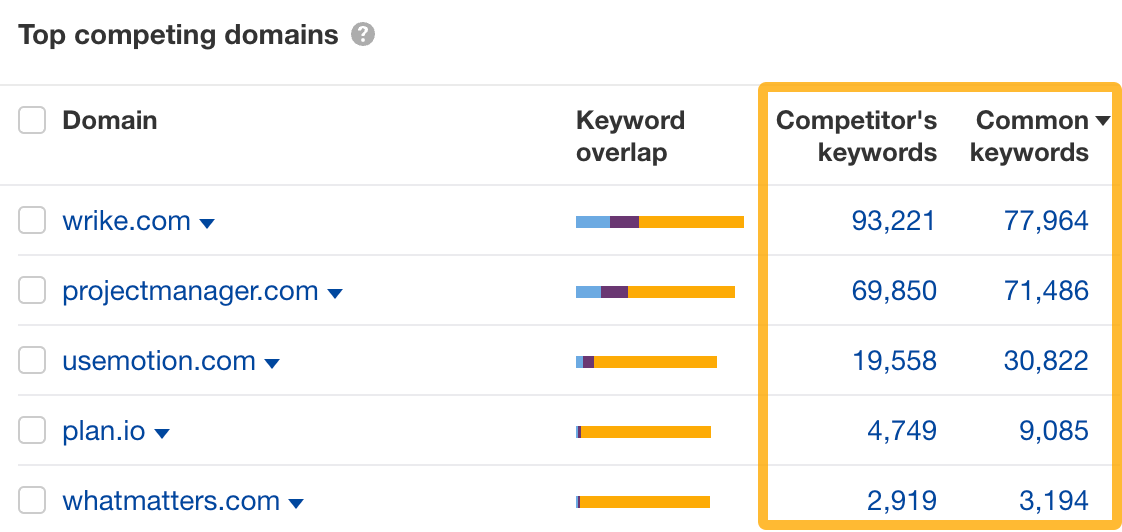

If your competitor is doing SEO, typically their blog will attract most of their organic traffic. But this is not always the case. They may have found other ways of getting clicks from Google, like free tools or free resources, and you could do the same.
- Open Site Explorer and enter your competitor’s domain.
- Go to the Site structure report.
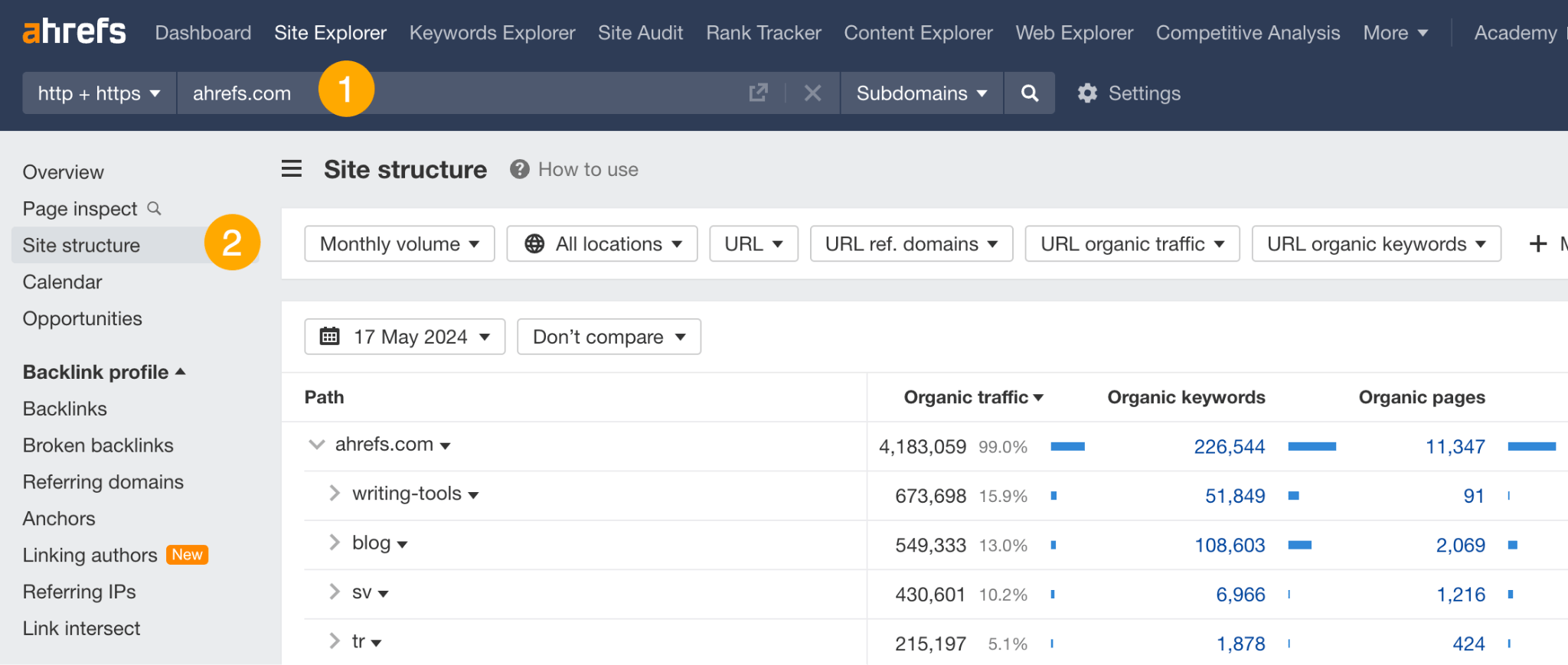

For example, someone analyzing our site could see that our free writing tools get more organic traffic than years of writing on the blog.
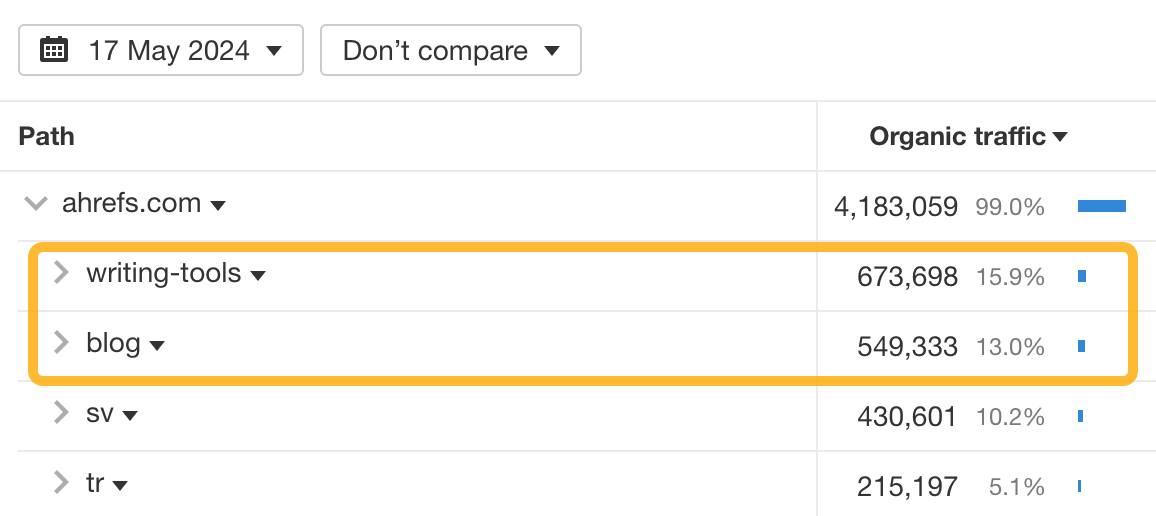

To see your competitor’s top performing pages:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter your competitor’s domain.
- Go to the Top pages report.
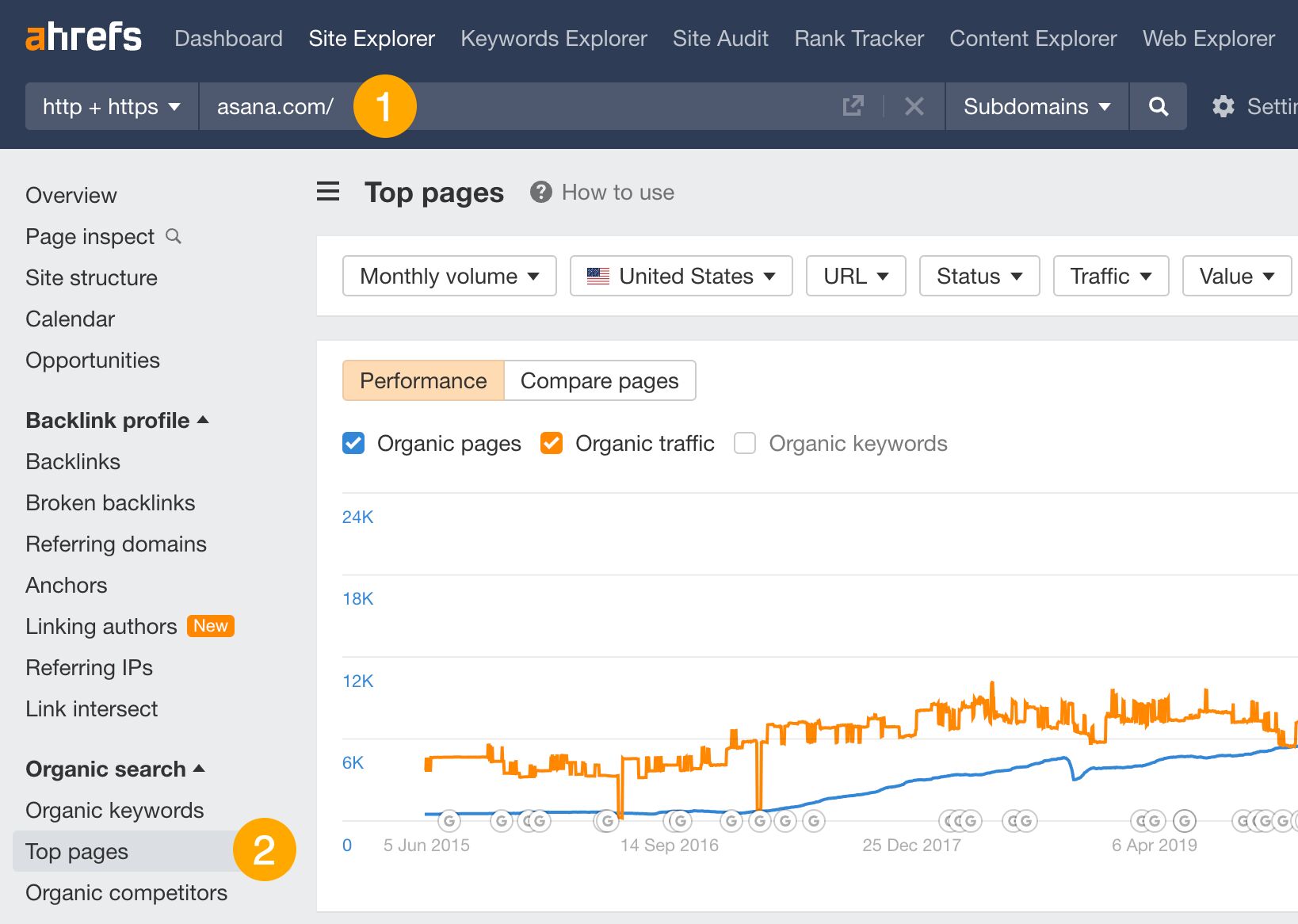

The first use case here is targeting the same keywords as their top pages to channel some of that traffic your way.
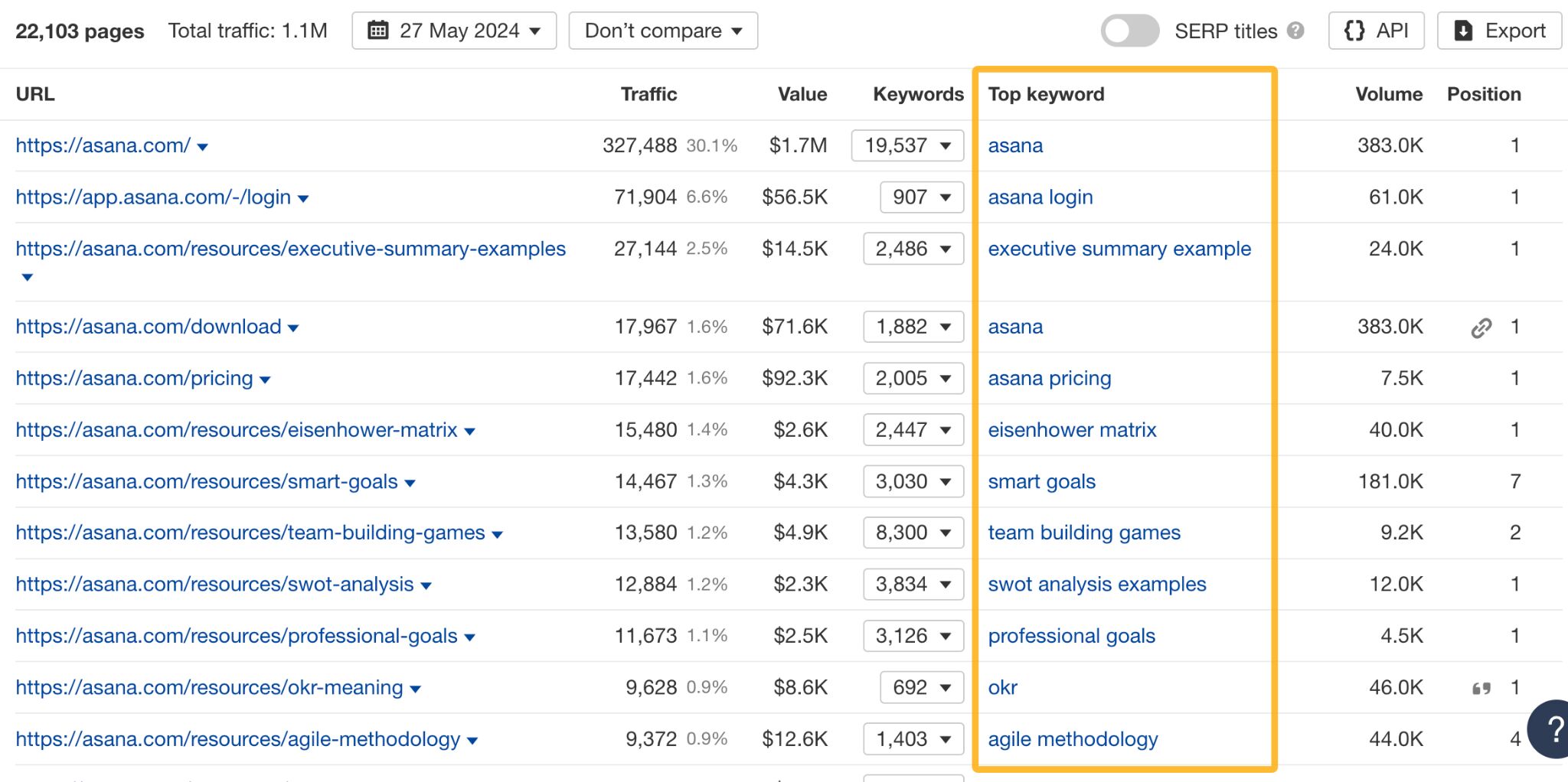

There’s more. You can use the report to see which pages contributed to an uptrend or downtrend in your competitor’s traffic.
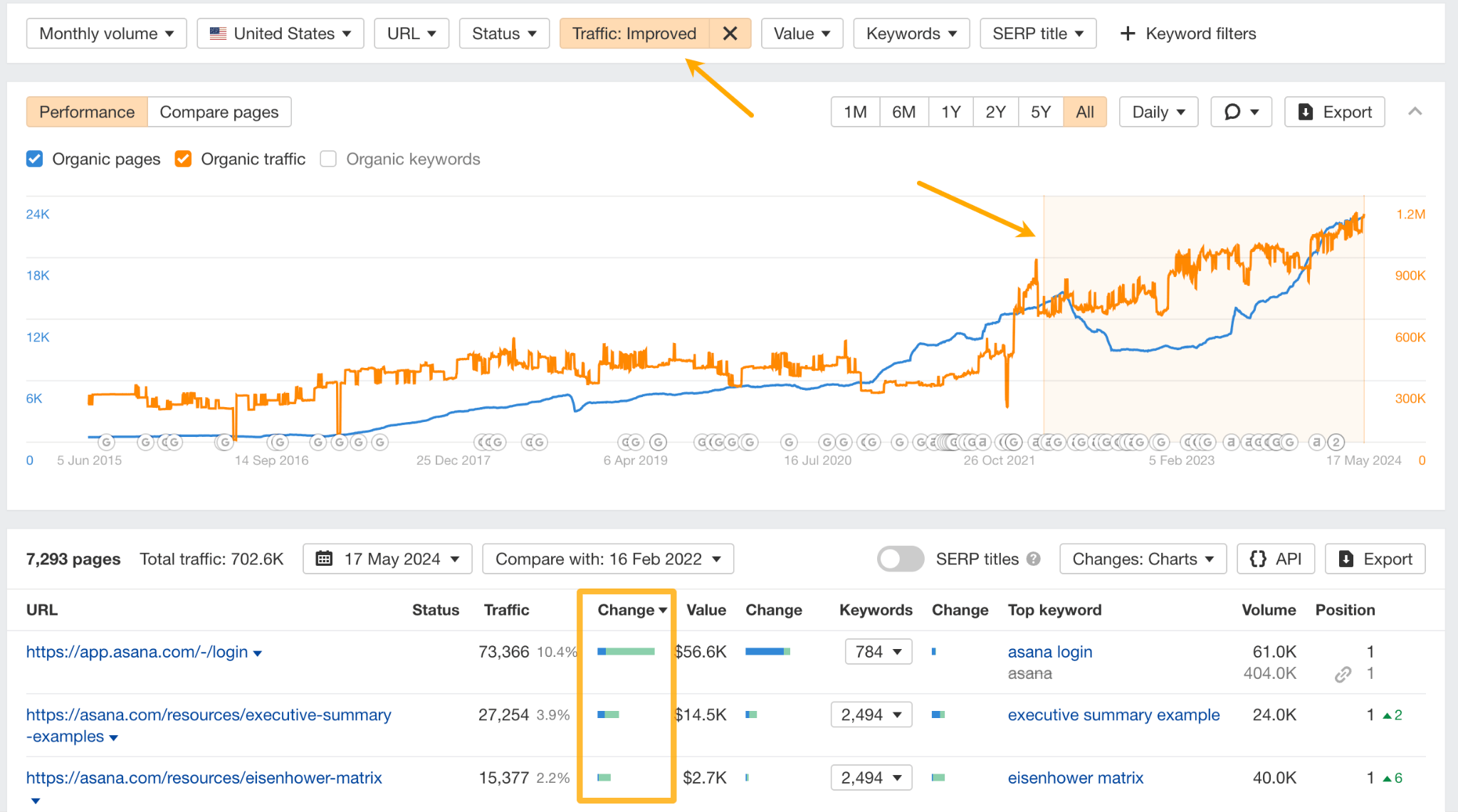

Or, focus on top-performing pages and use the Compare pages view to see when those pages started to pick up traffic.
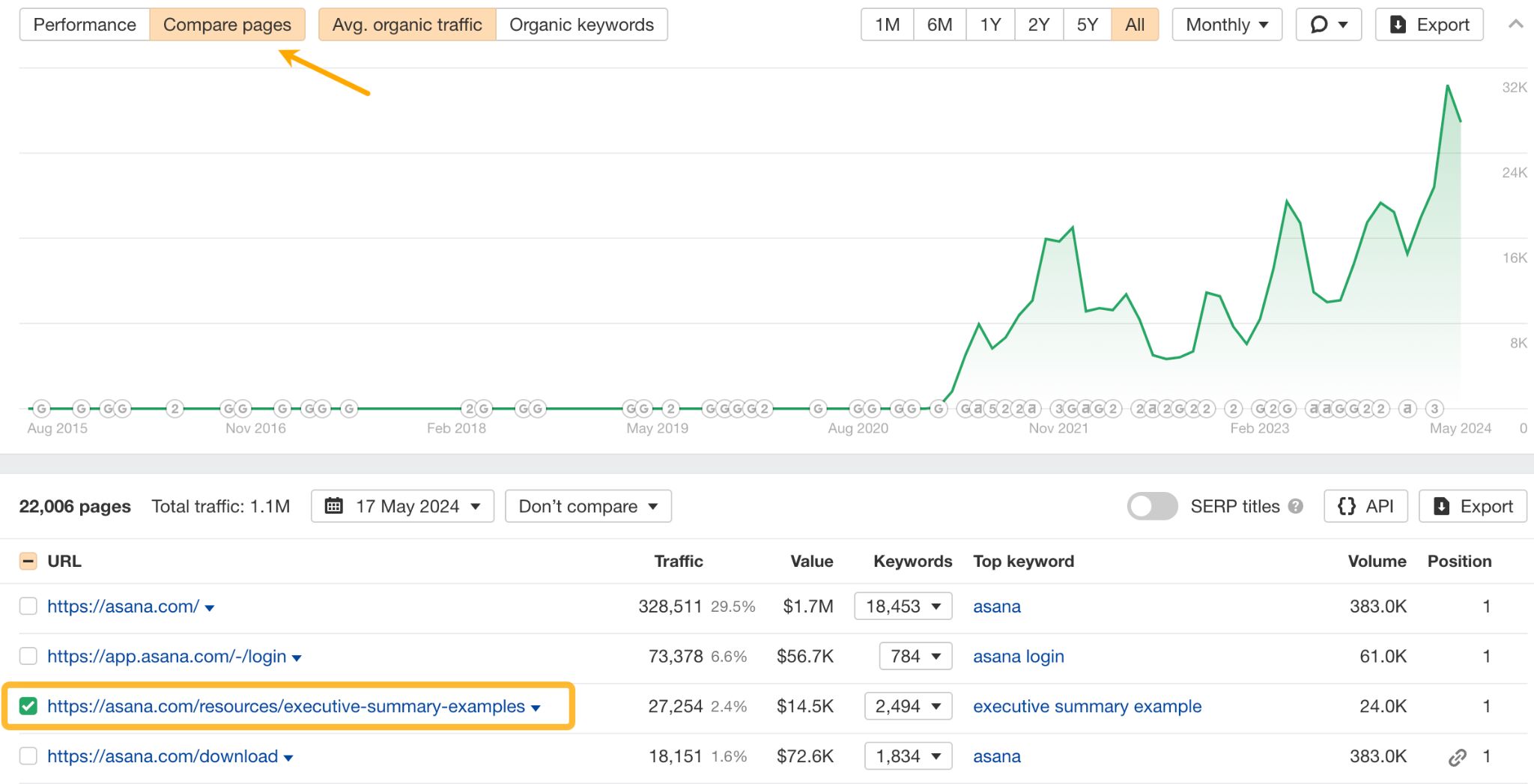

Now to see what the competitors did to improve the pages, click on the caret next to the page and click Inspect.
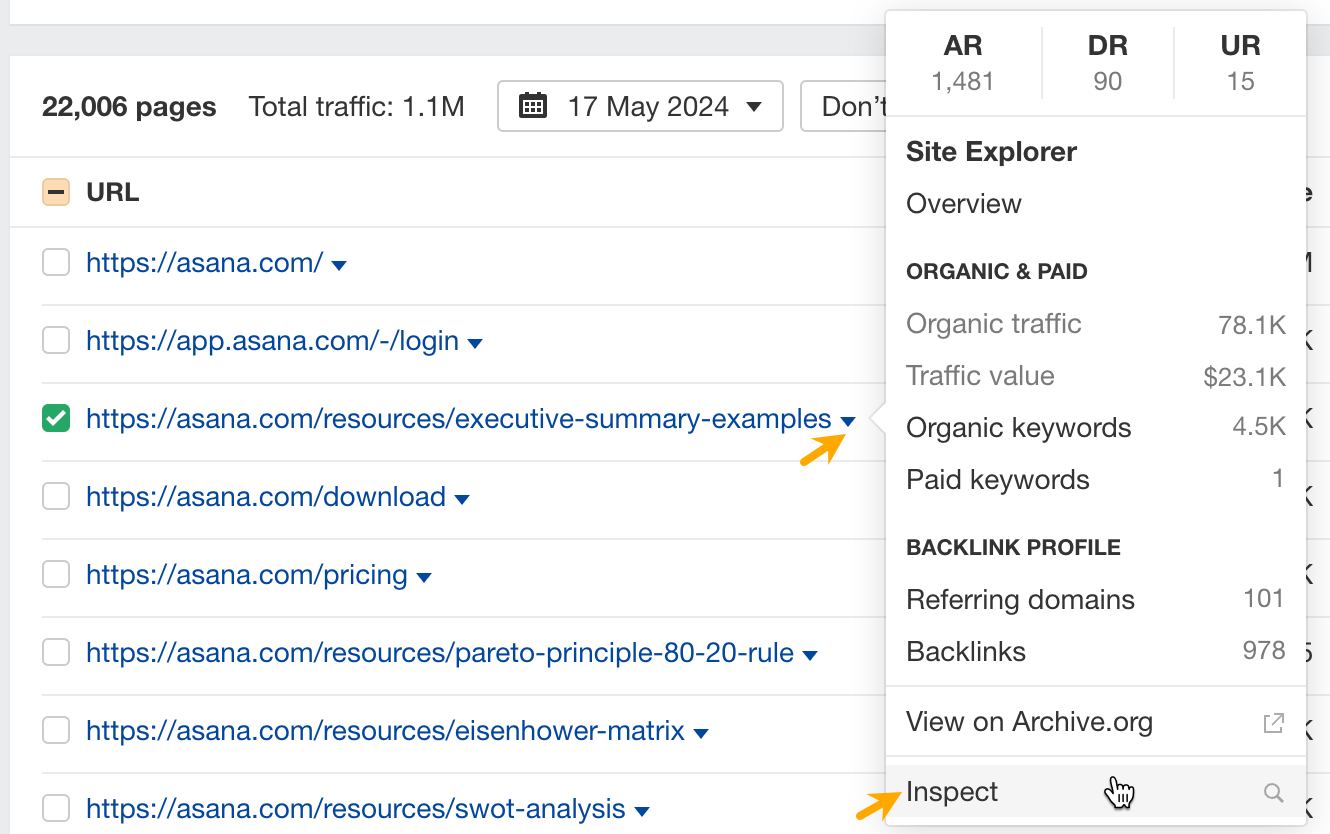

Then choose the date on the calendar and view changes made to the text in that time.
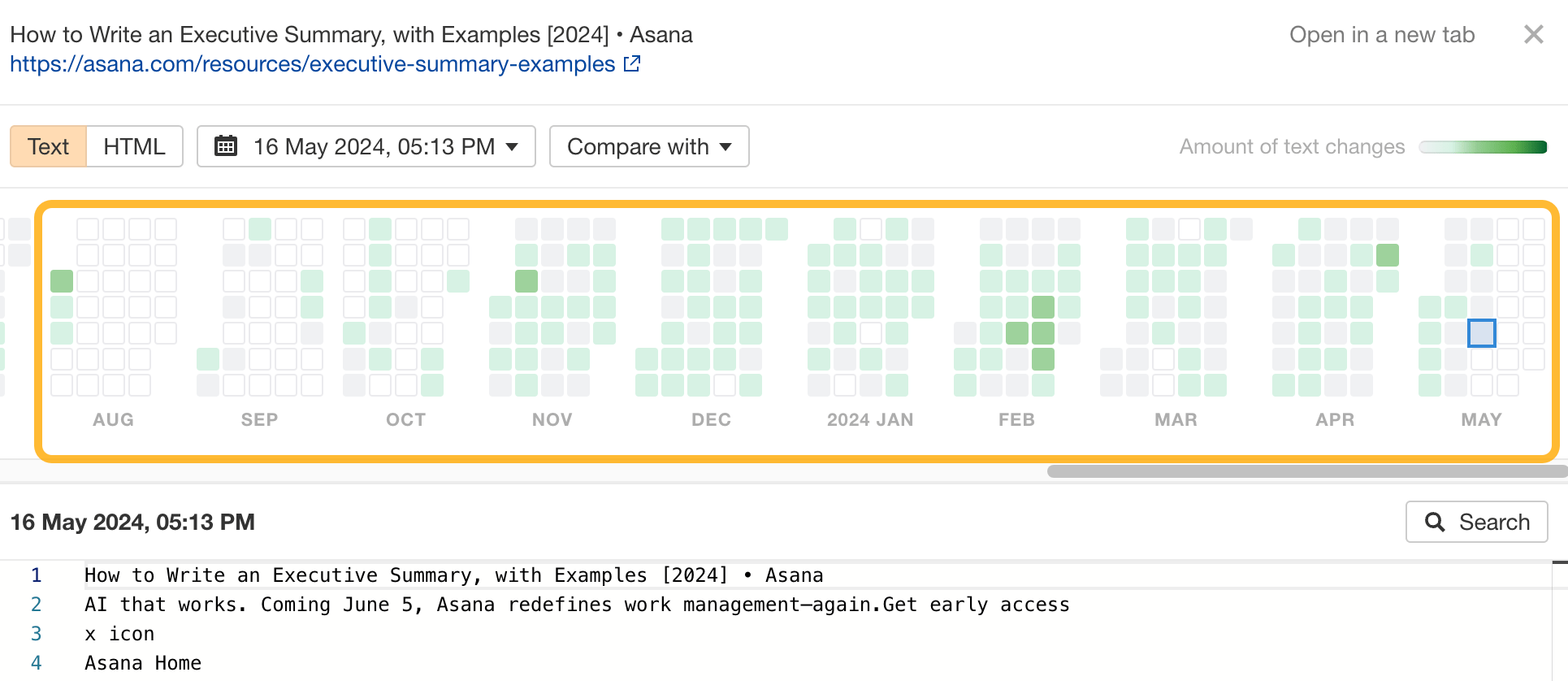

If you’re already doing SEO or considering it, seeing a list of your competitors’ keywords is almost like they’ve shared their keyword research with you.
You can use keyword data to find:
- Top-performing keywords and “steal” some of their traffic with your own content.
- Top-performing keywords in specific countries.
- Keywords with specific terms to find content ideas around certain topics or phrases.
- Low-difficulty keywords (typically, faster to rank).
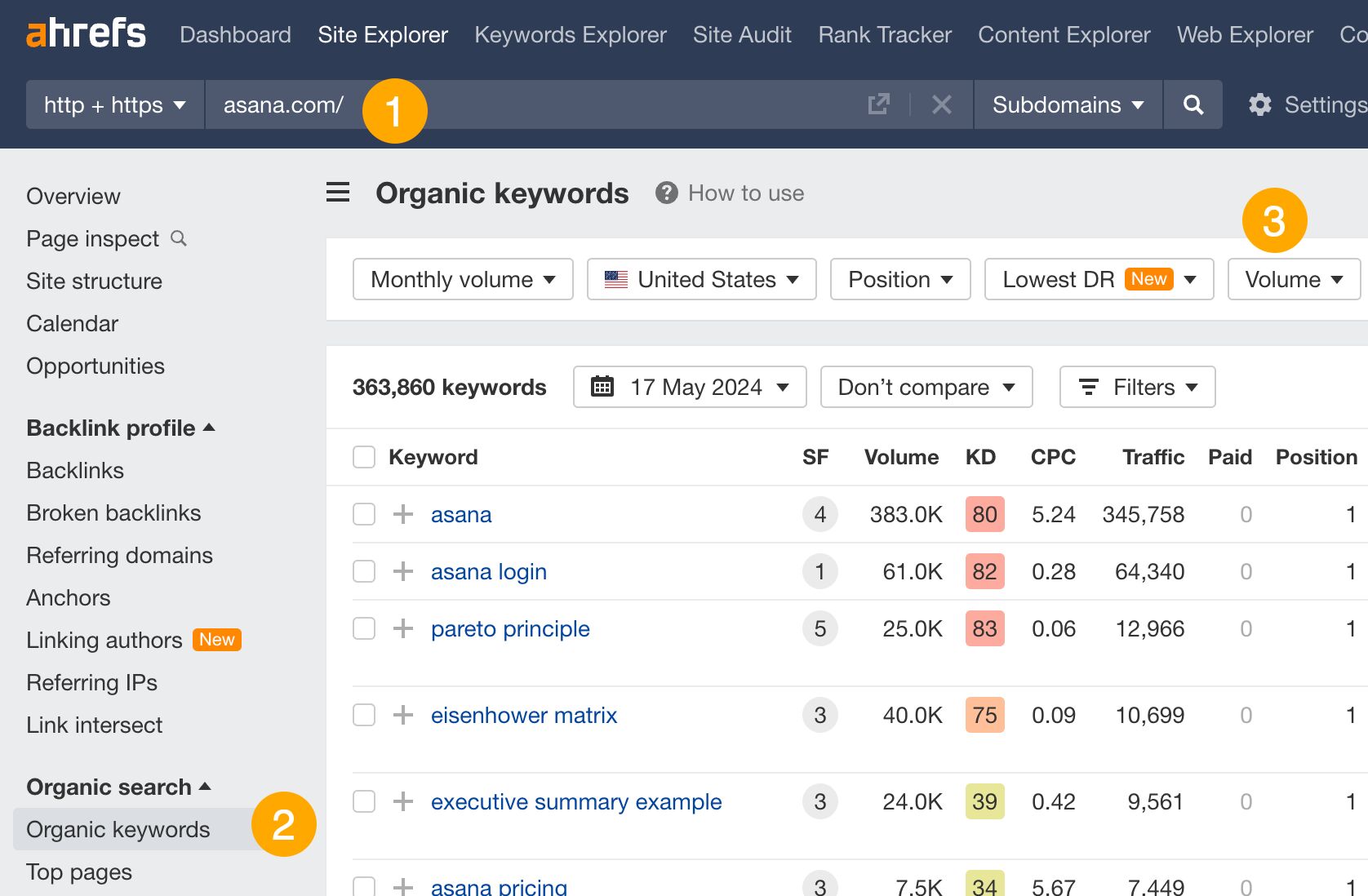
To see your competitors’ keywords:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter your competitor’s domain.
- Go to the Organic keywords report.
- Use the filters to find what you need. For instance, use the KD filter to find low-competition keywords.

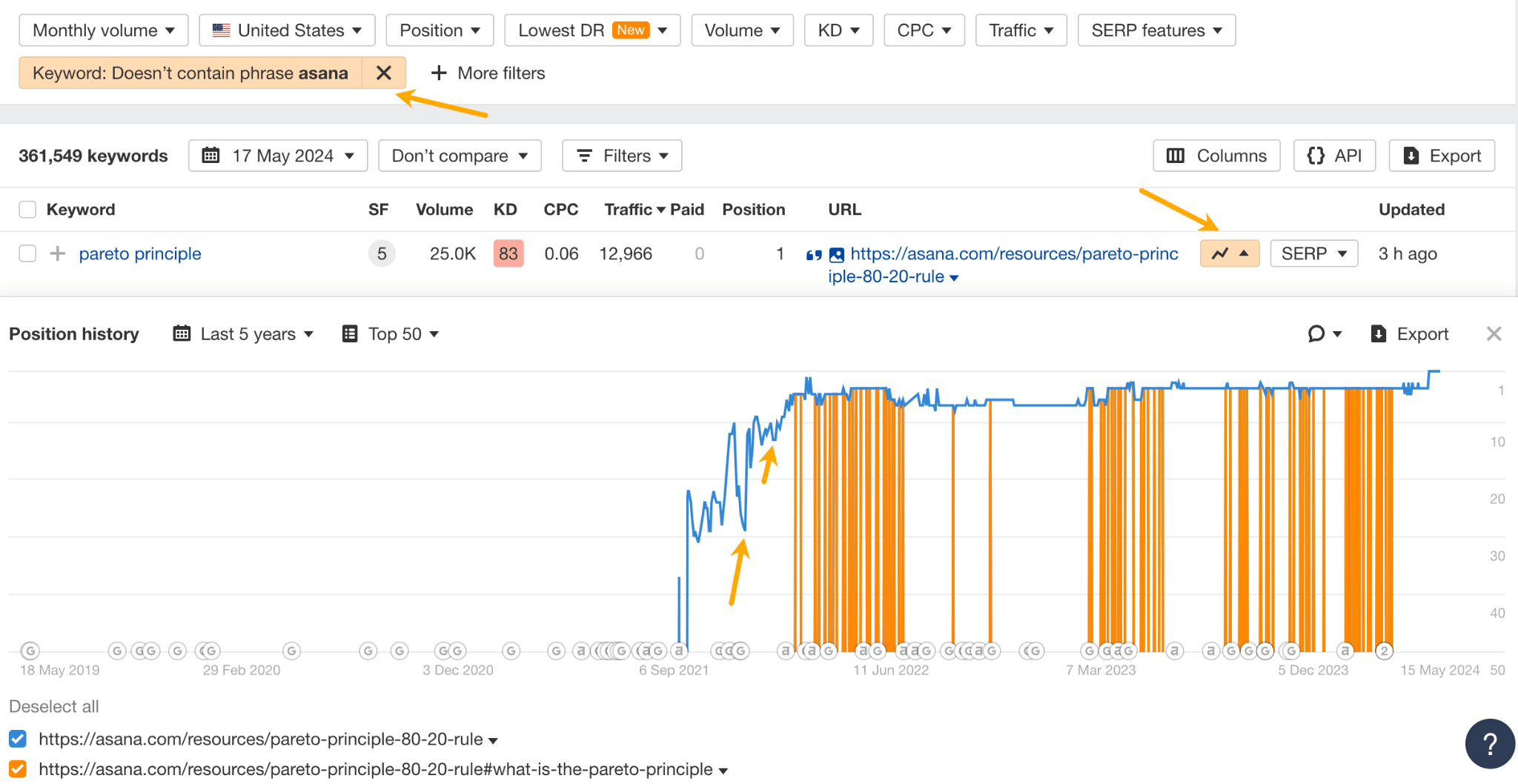
For example, you can track the ranking history of your competitor’s top traffic-generating keywords. If you see sudden spikes, it likely means they’ve updated the content to increase ranking. By using the calendar feature mentioned above, you can learn how they did it.

One of the best ways to find organic traffic you’re potentially missing out on is to do a content gap analysis. In SEO, it means identifying the keywords that your competitors rank for but you don’t. Some of those keywords can make perfect topics for you to cover.
In Ahefs, you can do a content gap analysis automatically:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Competitive Analysis tool.
- Enter your domain in the Target section.
- Enter your competitors’ domains in the Competitors section.
- Hit “Compare”.
- Click the Content Gap report.
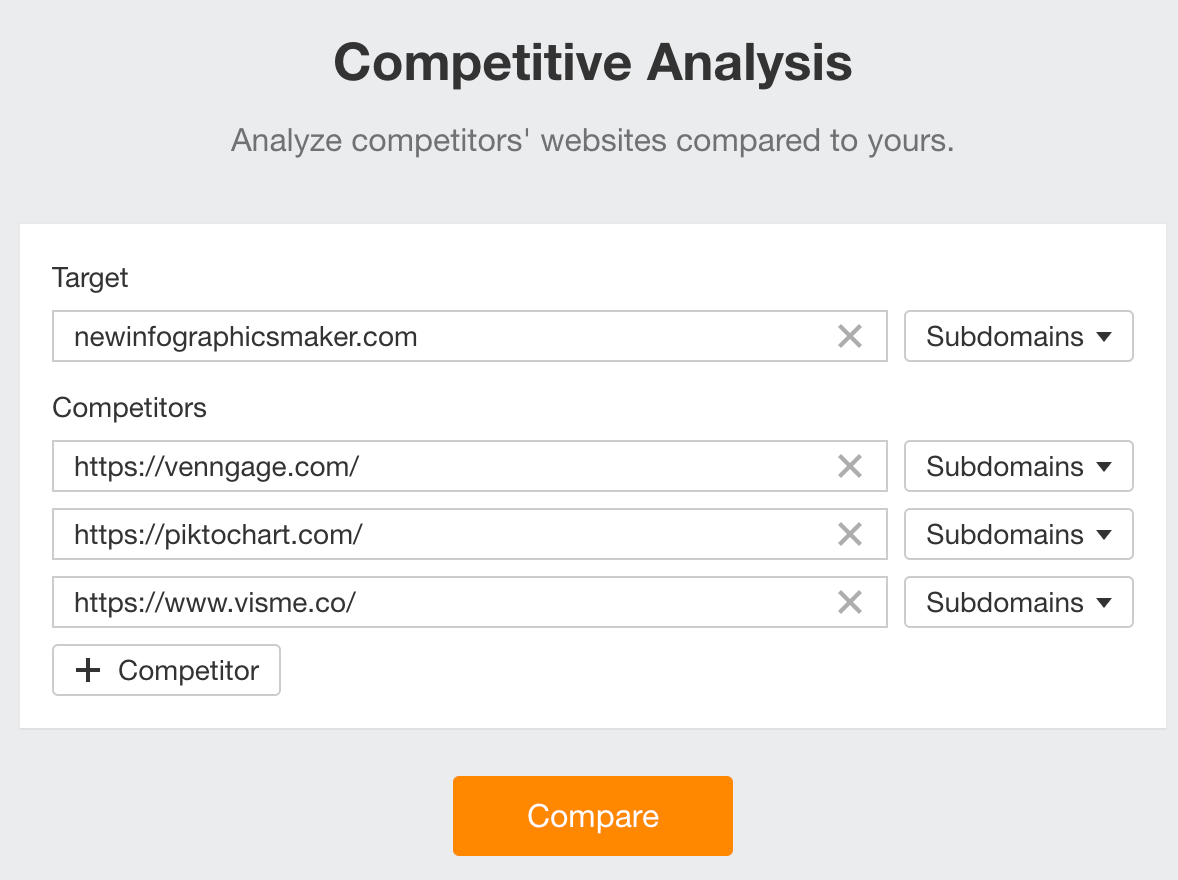

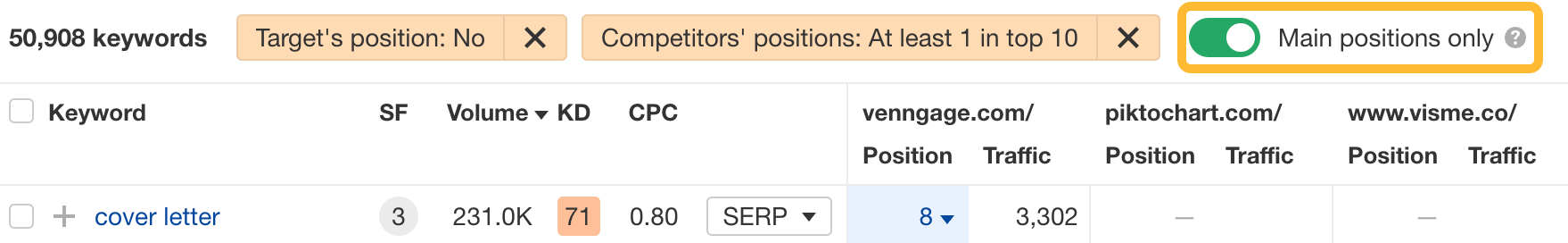
Toggle Main positions to exclude your competitors’ rankings in SERP features like “Top stories” and “Image packs.”

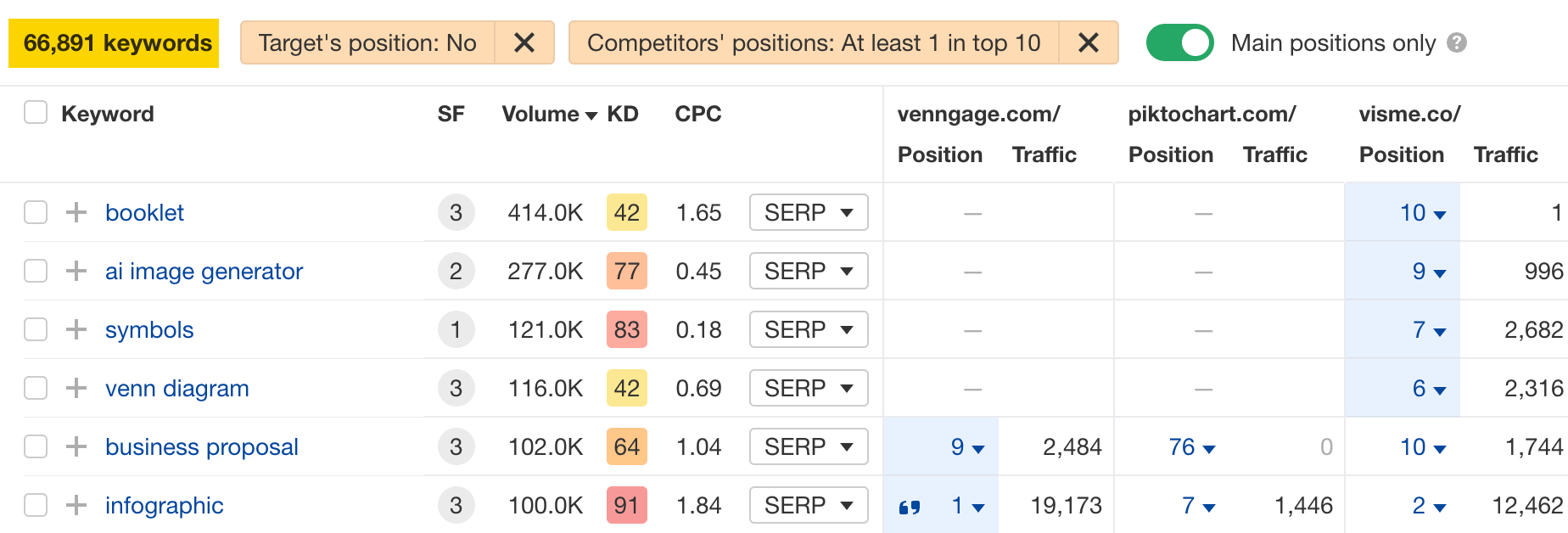
Now look through the report and identify keywords that are relevant for your site. The volume column will show you which keywords are likely to send the most traffic.

Short-term organic traffic performance can inform you of the latest developments in your competitors’ rankings (say, within the last 24 hours to a couple of weeks).
For example, you can observe the impact of the latest Google Update on their site, see how much traffic they gained or lost last month, or check if any of their newly launched pages are already picking up traffic.
To see short-term organic traffic performance:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter your competitor’s domain.
- In the Overview report, choose a timeframe in the Changes mode.
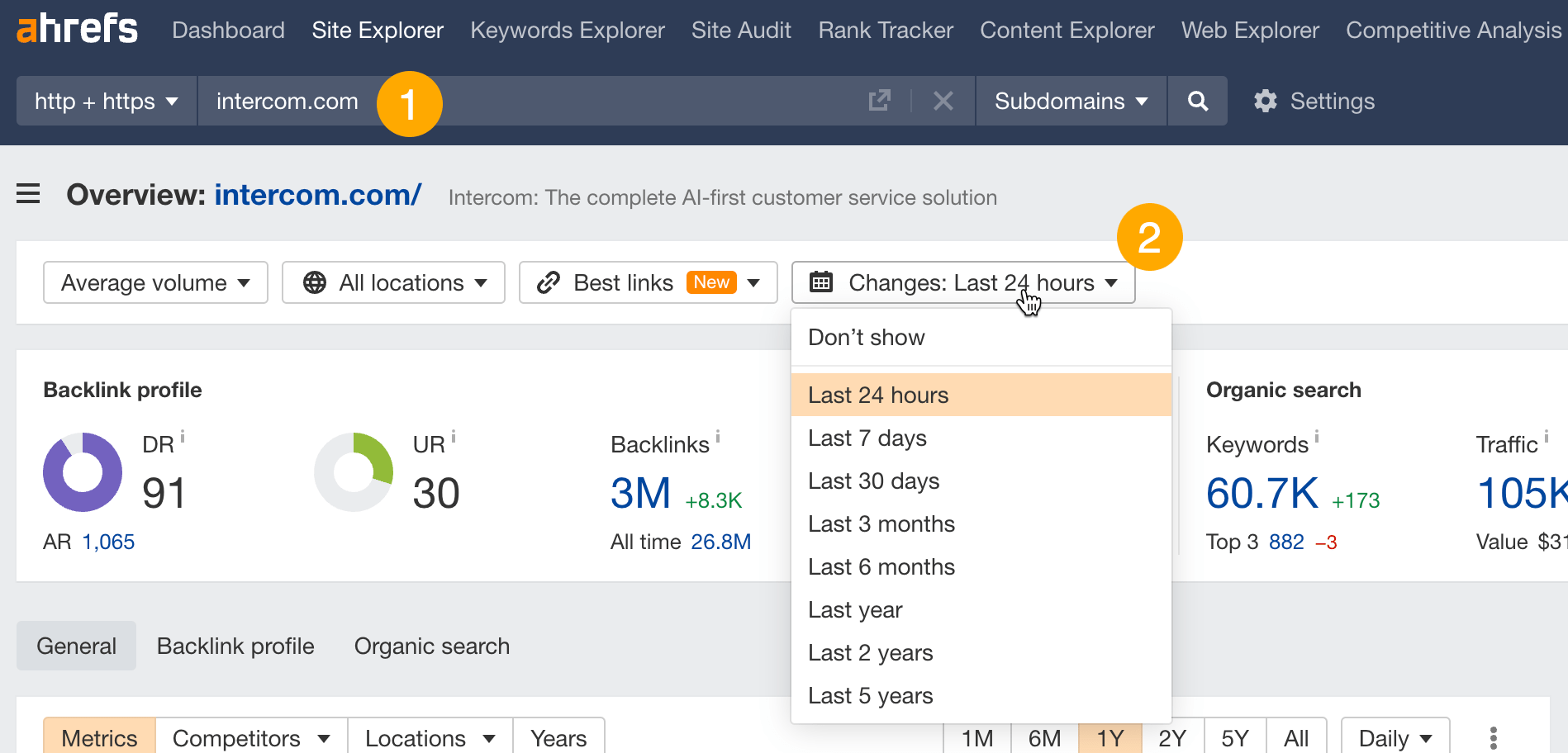

This will adjust the top-level metrics and traffic by location panel and show you the changes over the specified period.
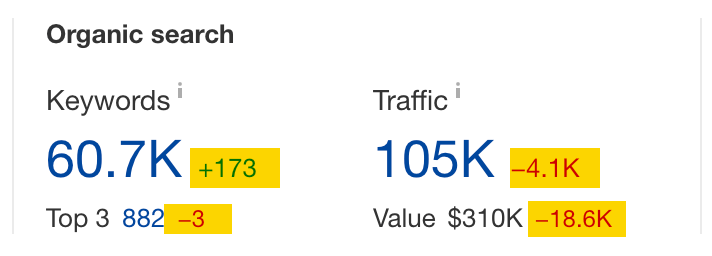

You can go as deep as day-to-day traffic changes — a very helpful thing if you want to see Google’s update impact on your competitors’ traffic.
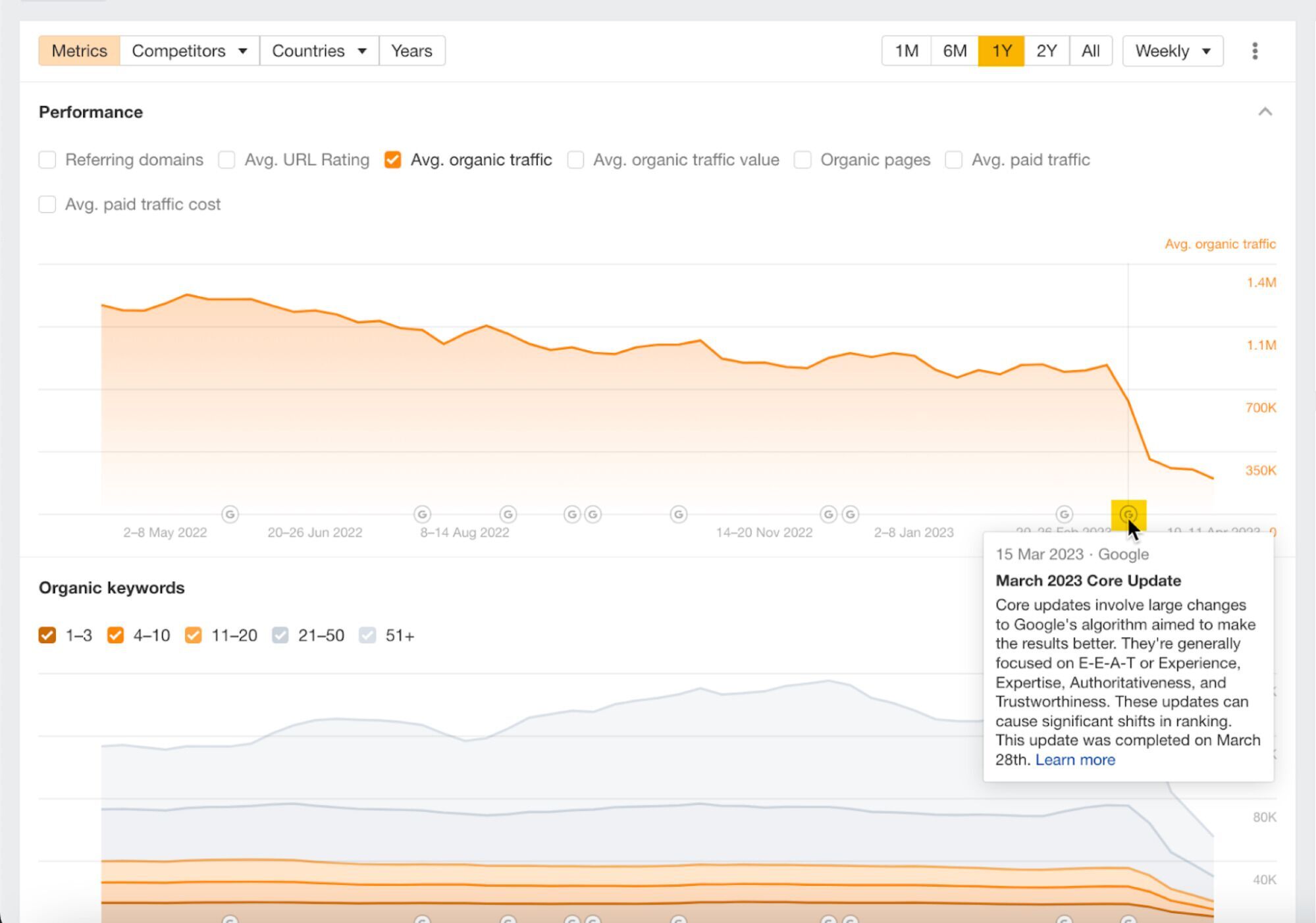

Date comparison is available in multiple tools and reports across Ahrefs.
As for long-term traffic performance, this allows to set a traffic goal to match or overtake your competitor’s traffic, and plan your budget based on competitor’s performance. You can also use it to forecast your competitors’ traffic.
To see long-term traffic performance:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter your competitor’s domain.
- Turn on the Years mode in the traffic graph.
- Adjust the time frame and export the data if needed.
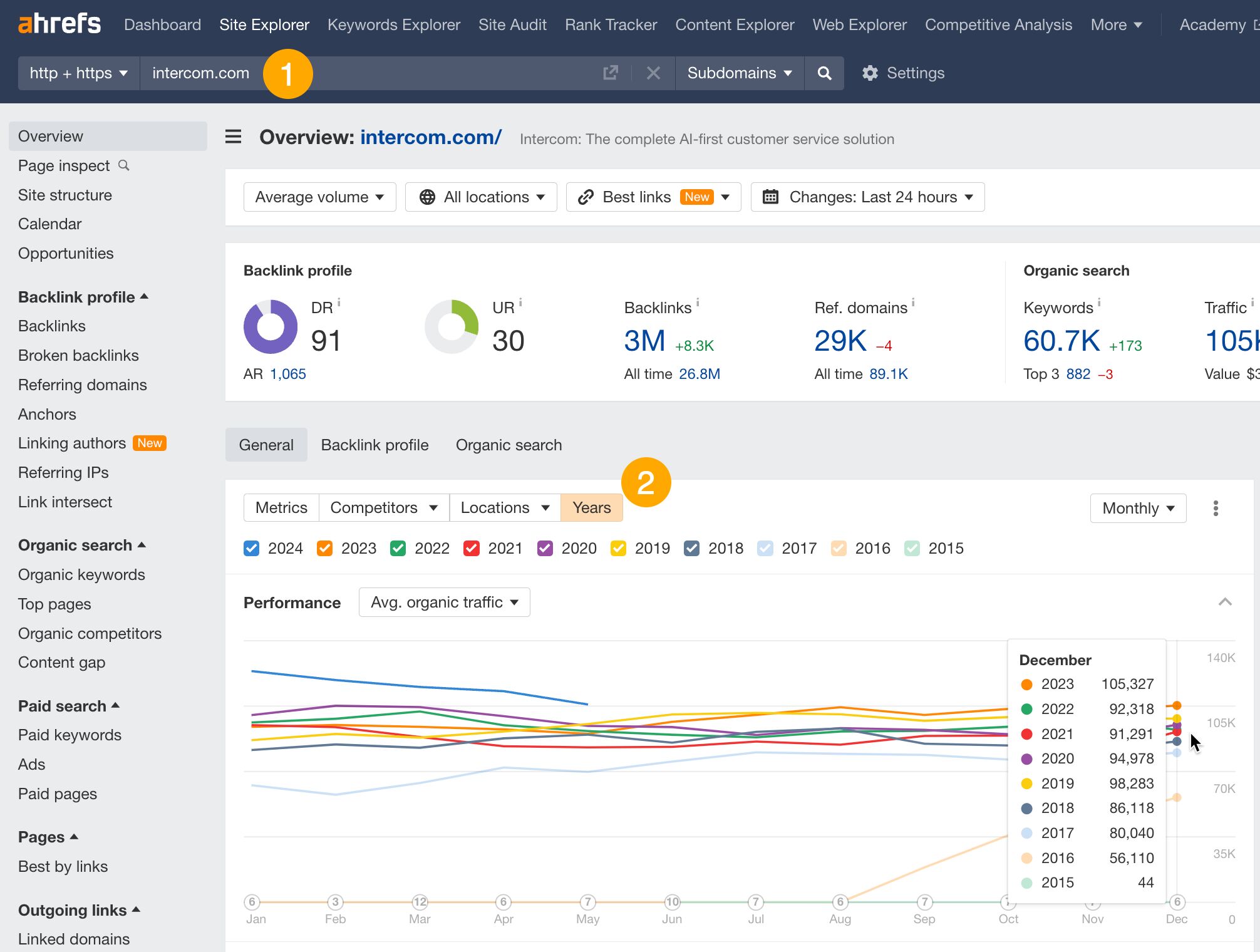

Seeing multiple sites on one graph is useful if you want to identify the leader in your niche, compare your site to a few competitors simultaneously, and determine if you are catching up to the leader or if someone is catching up to you.
Here’s how:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter your domain.
- Add competitors using the Competitors tab.
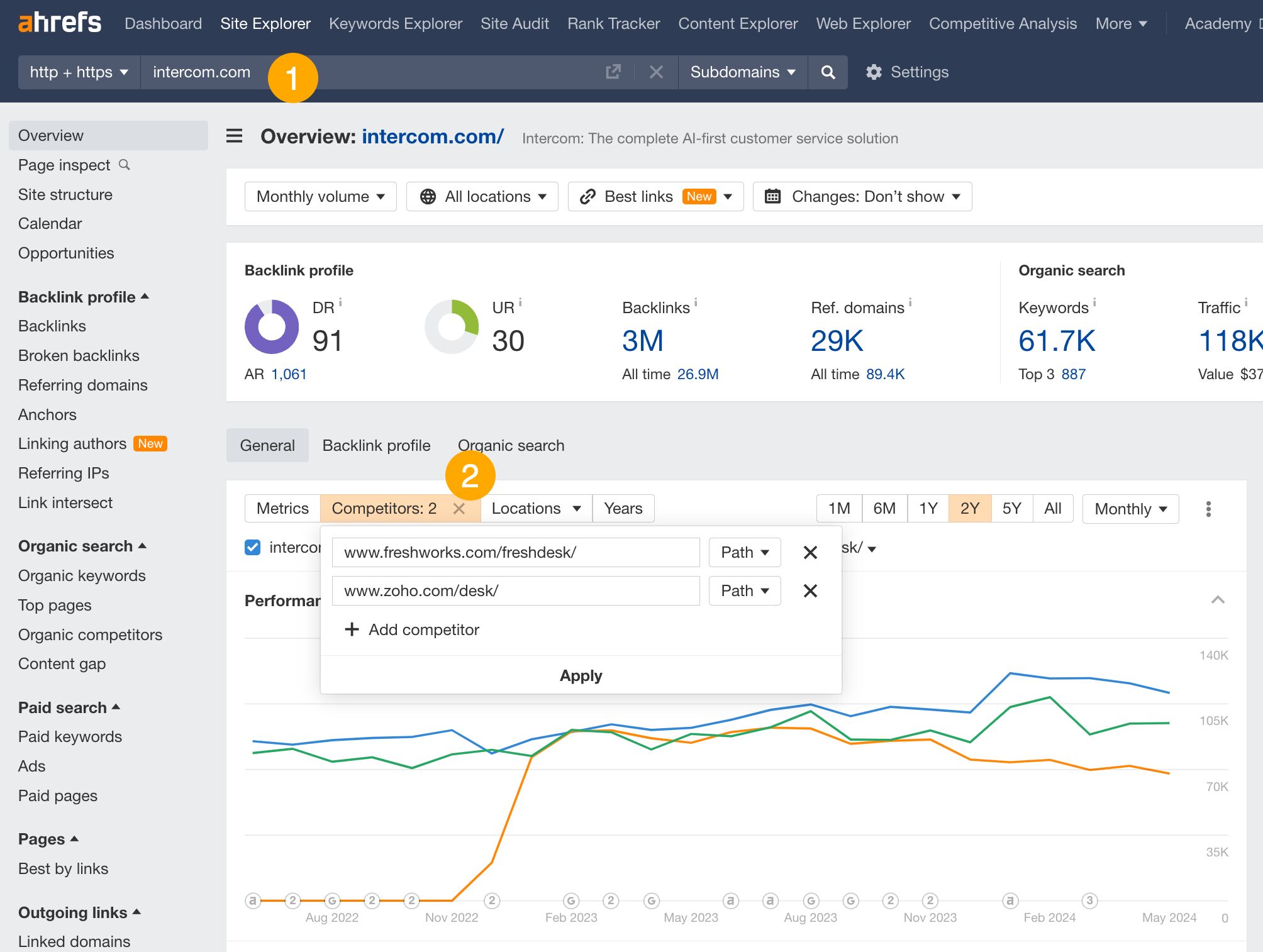

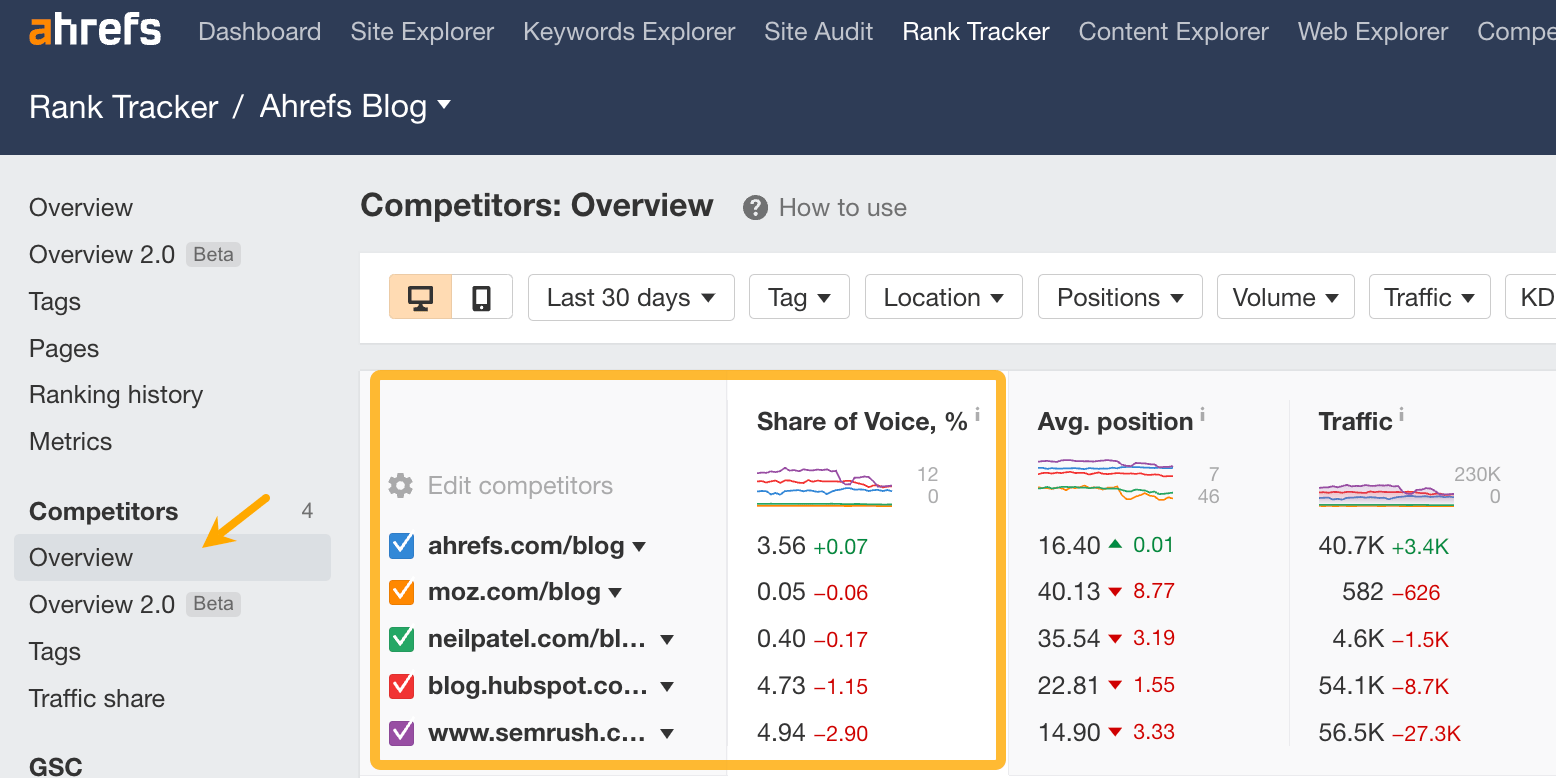
Organic share of voice (SOV) is an SEO metric that shows how much traffic goes to your pages compared to competitors’.
In other words, if you want to see your overall organic search traffic share in the market, and eventually increase it, this is the metric you’d want to use.
SOV is based on tracked keywords, so you first need to add them to the tool. These can be keywords you target on your blog, your product pages, or even all of your important keywords together.
- Go to Ahrefs’ Rank Tracker.
- Start a New project.
- Select keywords to track. You can use the filters to refine the list suggested by the tool and add some keywords later on. Make sure to choose only important locations for your site.
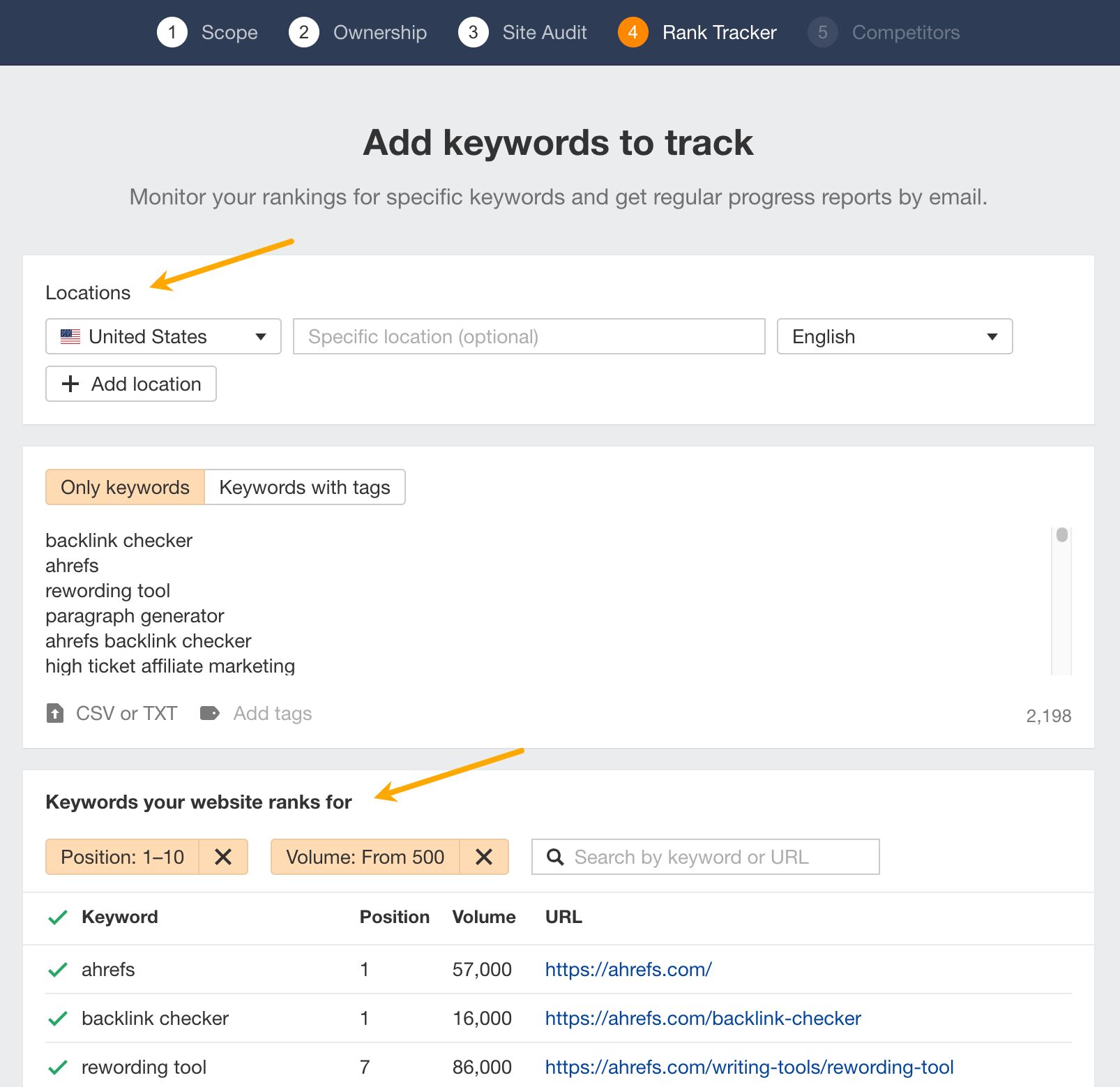

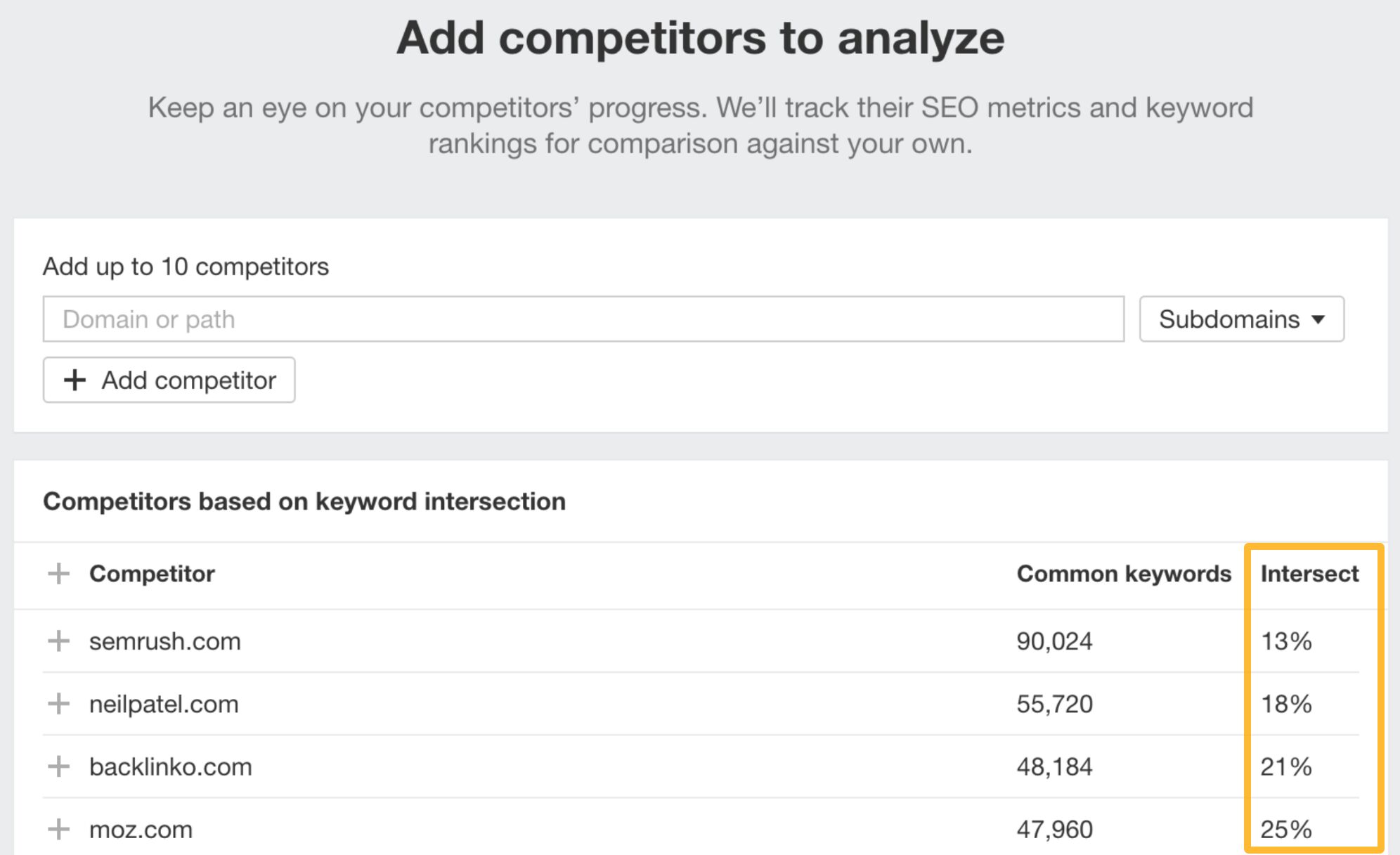
- Add competitors. You can add specific sites or choose from the ones suggested by the tool. Notice the keyword intersect — the higher the number, the “closer” the competitor.

Once you finish the set-up, you will be able to see and regularly track SOV in the Competitors Overview section in Rank Tracker.

One of the ways your competitors could be getting traffic is from links from other sites (a.k.a. referral traffic).
Knowing who links to your competitors allows you to pursue the same or similar links which can help you not only get more referral traffic but also boost your SEO and increase your brand awareness.
To find pages with a high probability of sending traffic to your competitors, look for backlinks from pages with significant organic traffic. Here’s how:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter your competitor’s domain.
- Open Backlinks report. Pages with the most traffic will be displayed on top by default.
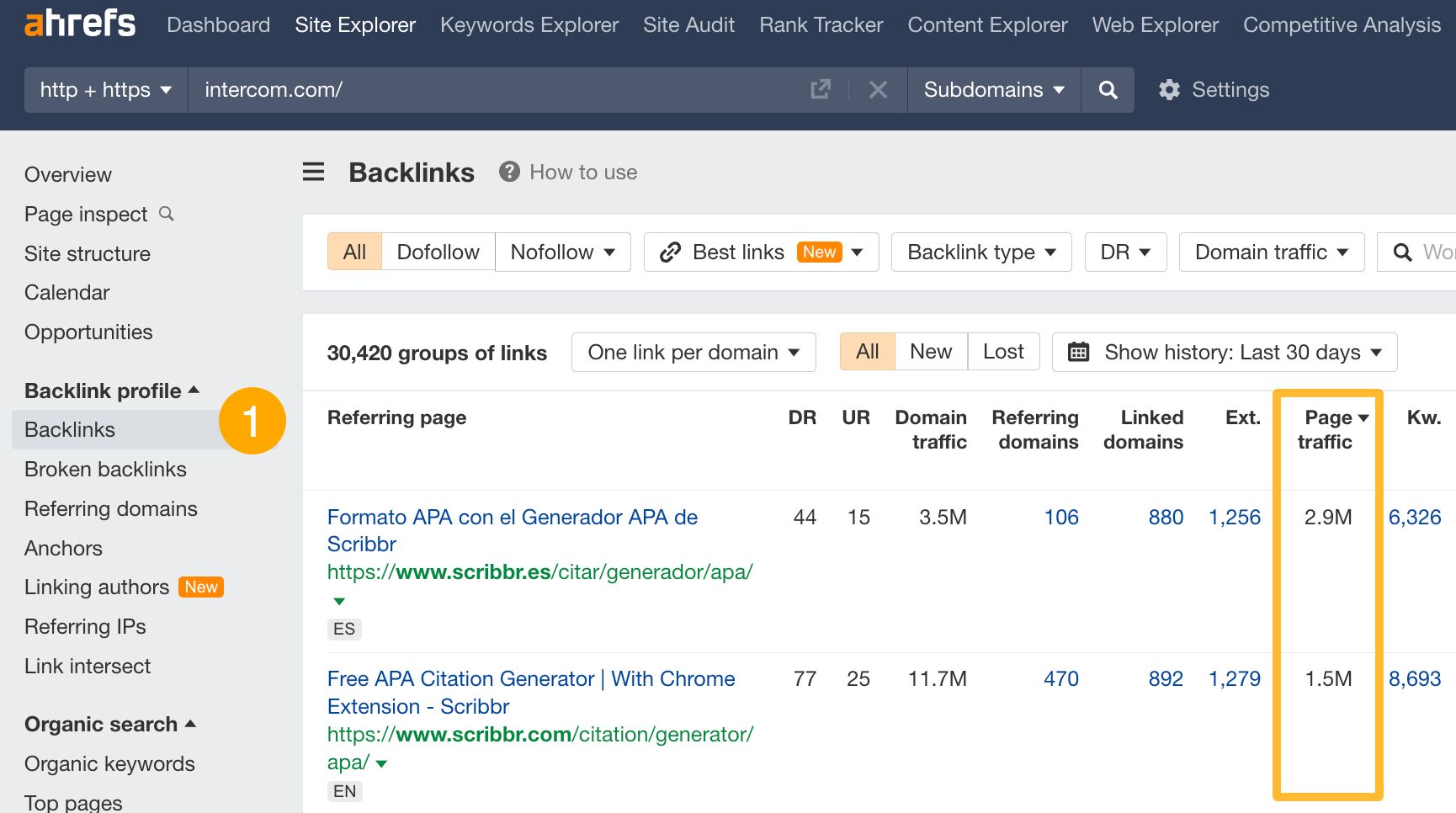

From there you can use the Referring page title filter to see only reviews or rankings where you could be listed, too. Simply add in words like “vs, review, tool, tools, top” as a way to identify these pages.
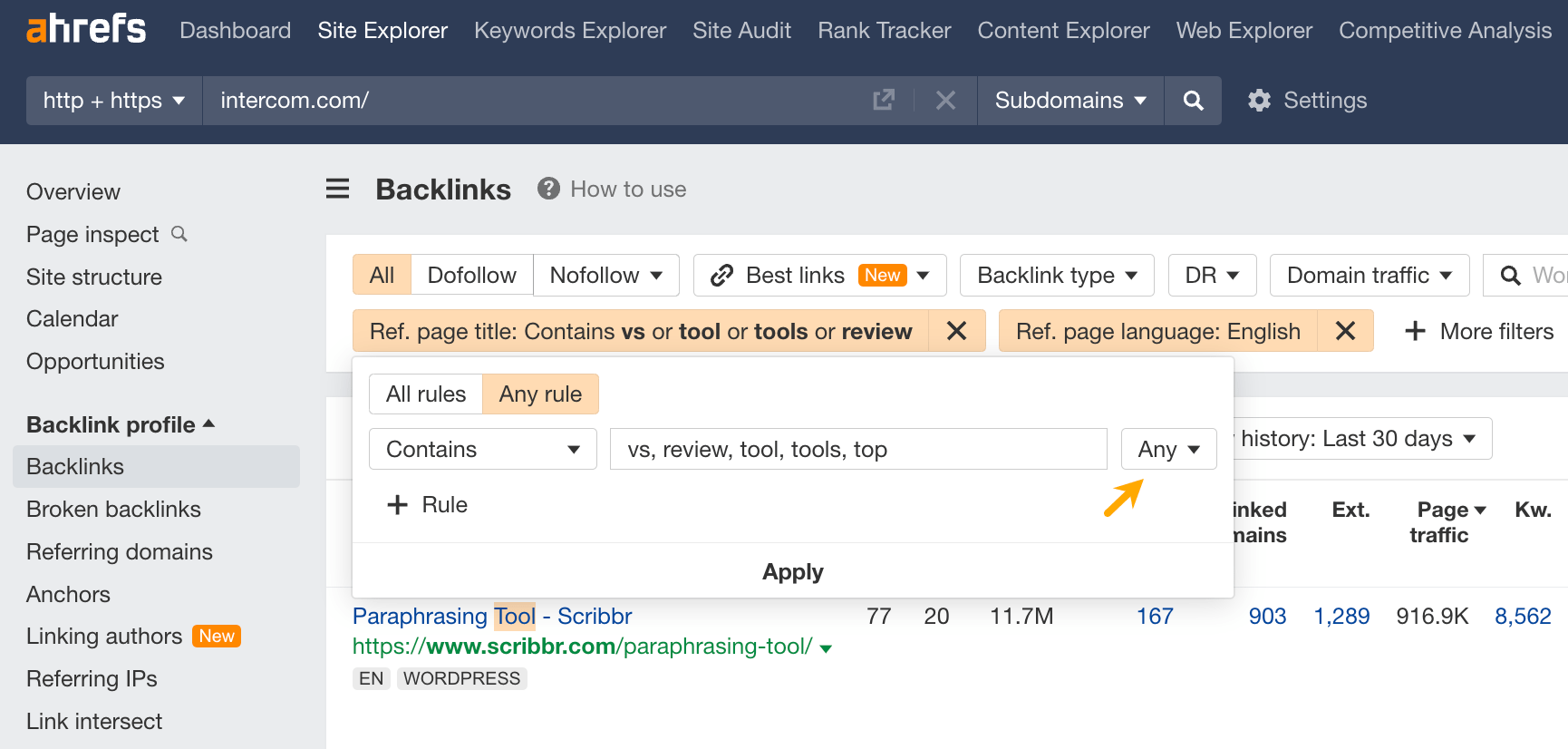

Here’s an example of such a page:


Another way to analyze your competitors’ traffic is to treat them as one entity. This allows you to:
- Benchmark your site traffic trend to your competitors as a market segment.
- Identify broader industry trends and seasonal patterns in traffic.
- Assess the collective impact of major events, such as changes in search engine algorithms or economic shifts.
- Monitor the overall health and growth rate of your industry.
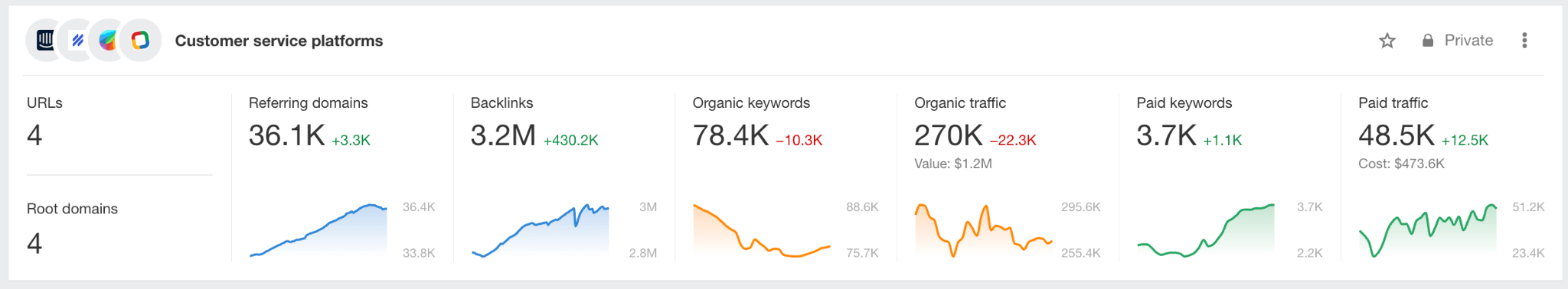
For this, use the Portfolios feature in Ahrefs. The image below shows aggregated data for four sites, including organic traffic and paid traffic (from Google Search Ads).

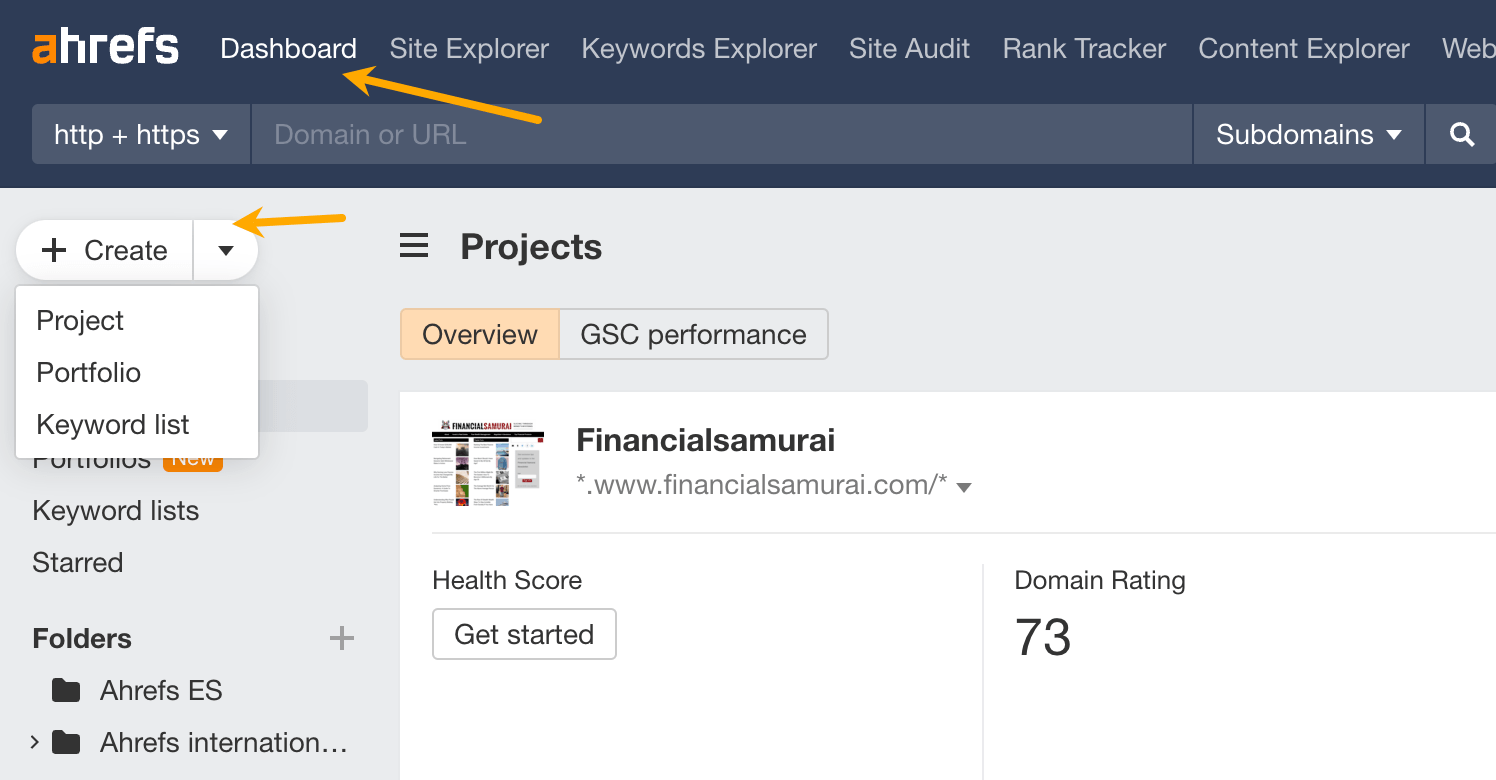
Here’s how to set it up:
- Dashboard and click Create > Portfolio.

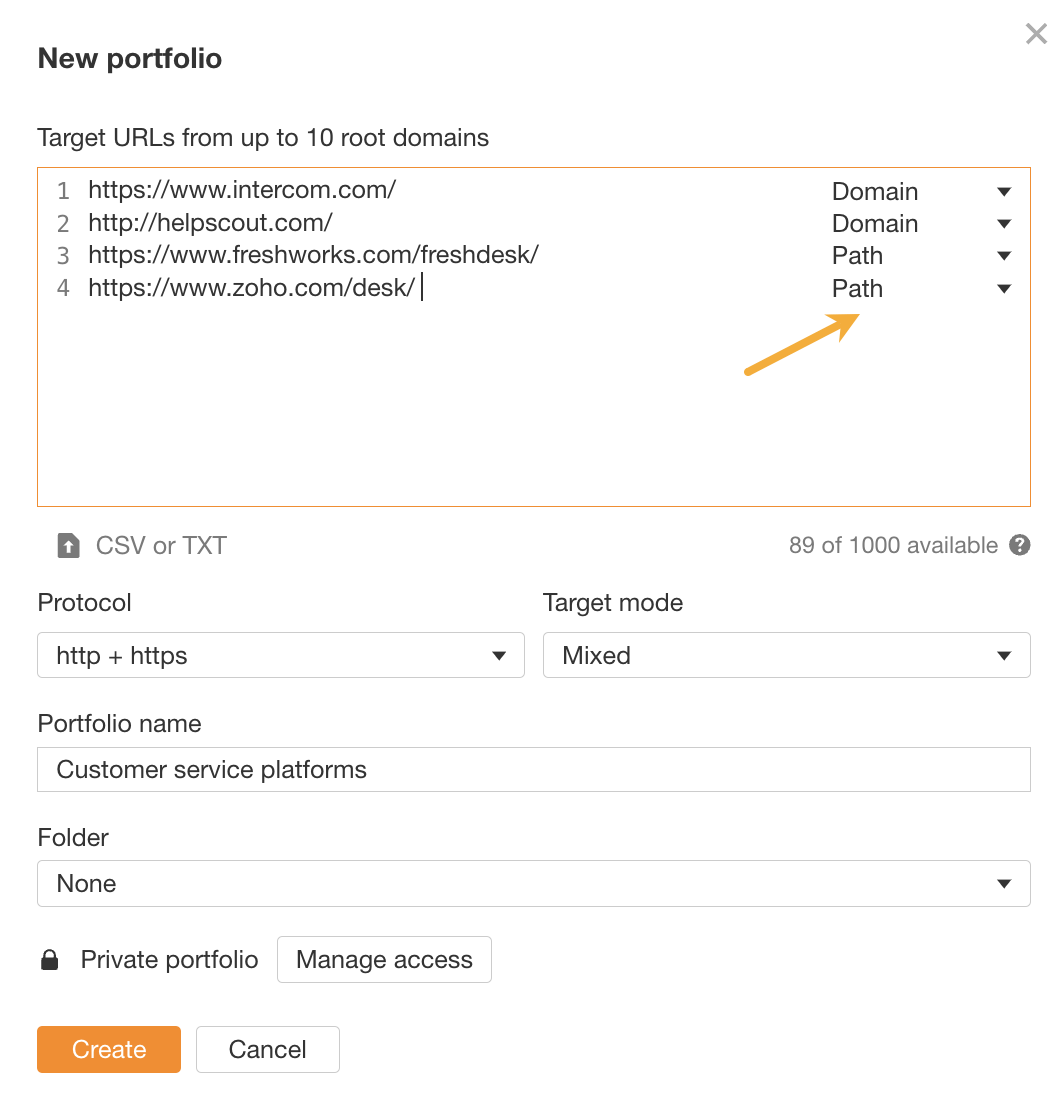
- Fill in the URLs you want to track. Note the URL mode selector. Use “Domain” to track the entire domain with subdomains, “Path” for folders, and “Exact URL” for single pages.

How to analyze competitor paid search traffic
Paid search traffic refers to the clicks a site gets from search ads on search engine result pages. Here’s how to check your competitors’s paid search traffic and how to use that knowledge to your advantage.
If you’re running search ads, checking out your competitors’ paid keywords can give you ready-made keyword research. This lets you see which keywords are working for them and helps you fine-tune your own ad strategy to target those high-performing keywords.
What’s more, you can reveal paid search data Google Keyword Planner hides by default: search volume for a particular keyword instead of a search volume range for a group of keywords.
And even if you’re not investing in ads, this info can still be super useful. It usually means these keywords are important to your competitors because they know these keywords bring in customers. Chances are, these keywords could be important for your business, too.
To find your competitors’ paid keywords:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter your competitor’s domain.
- Open Paid keywords report.
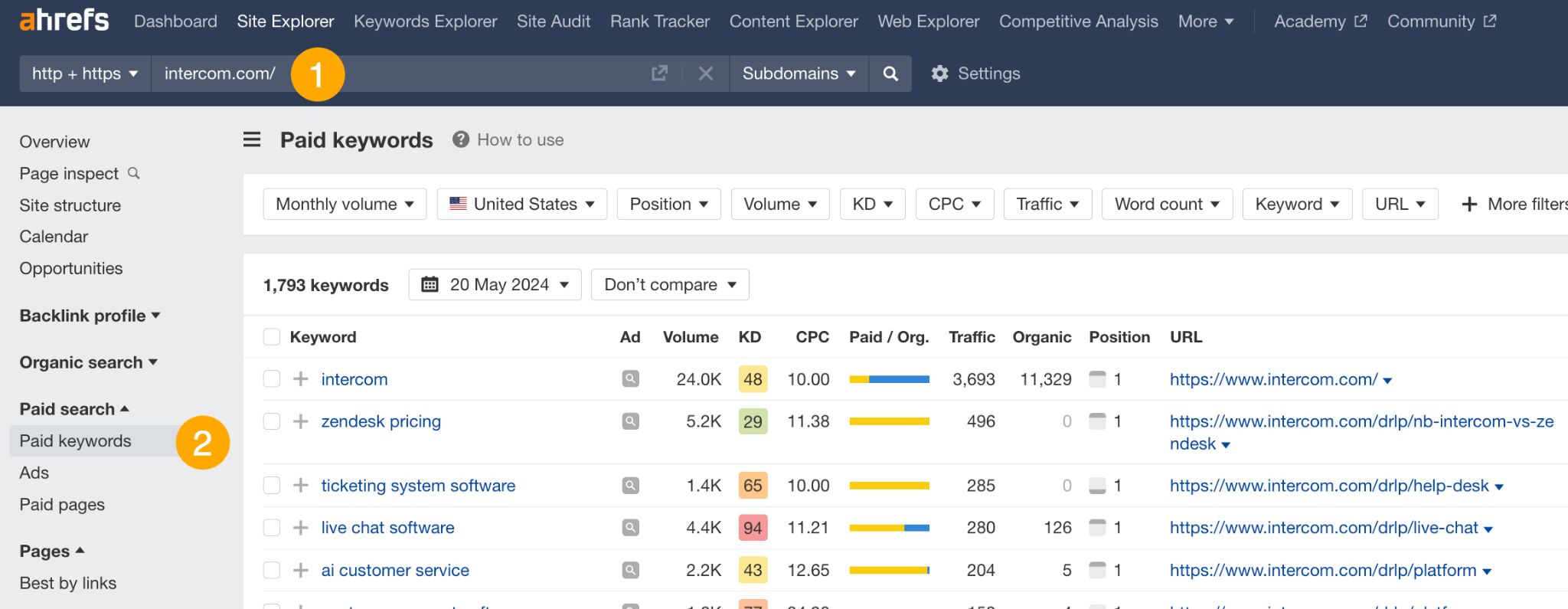

From here, you can use filters to find keywords that meet your CPC, traffic, or relevance criteria, and sort the data to see the keywords which bring the most traffic.
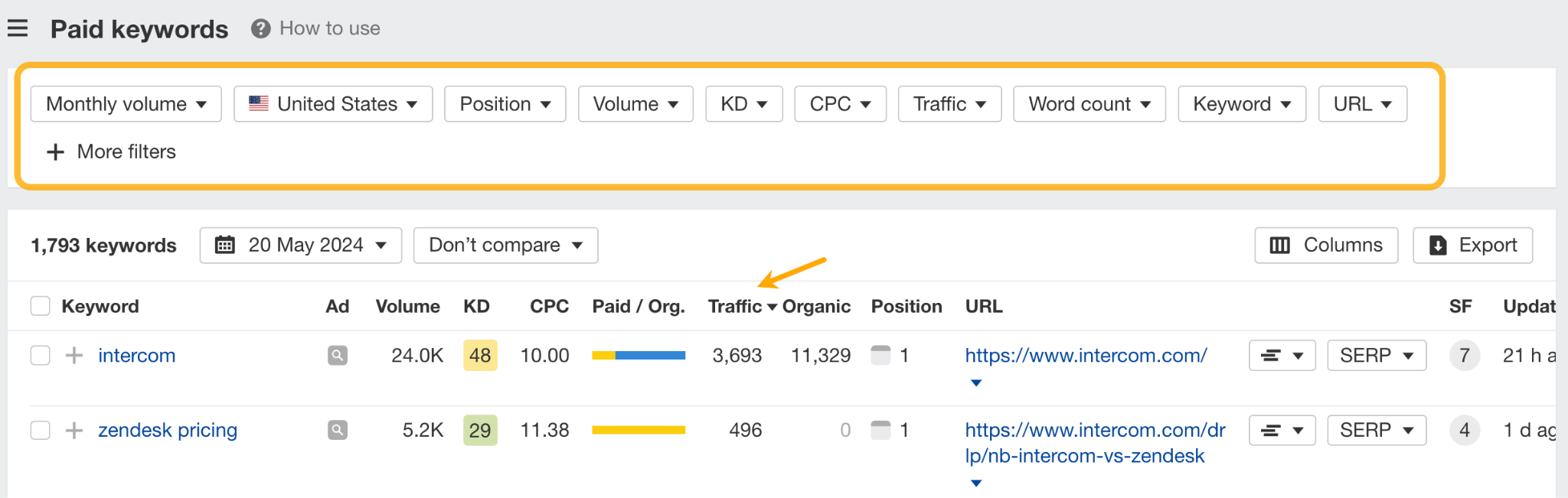

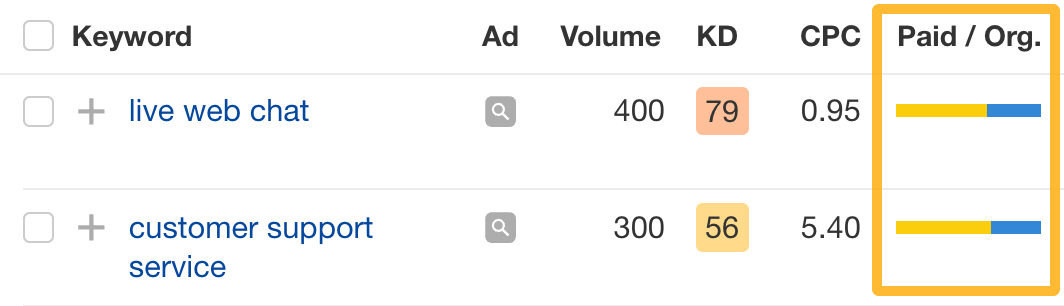
Notice the Paid/organic traffic share bar. If you see both blue and yellow color, that means your competitor has invested in the keyword twice (through content and ads) and is trying to get as much SERP real estate as possible — consider pursuing these keywords as well.

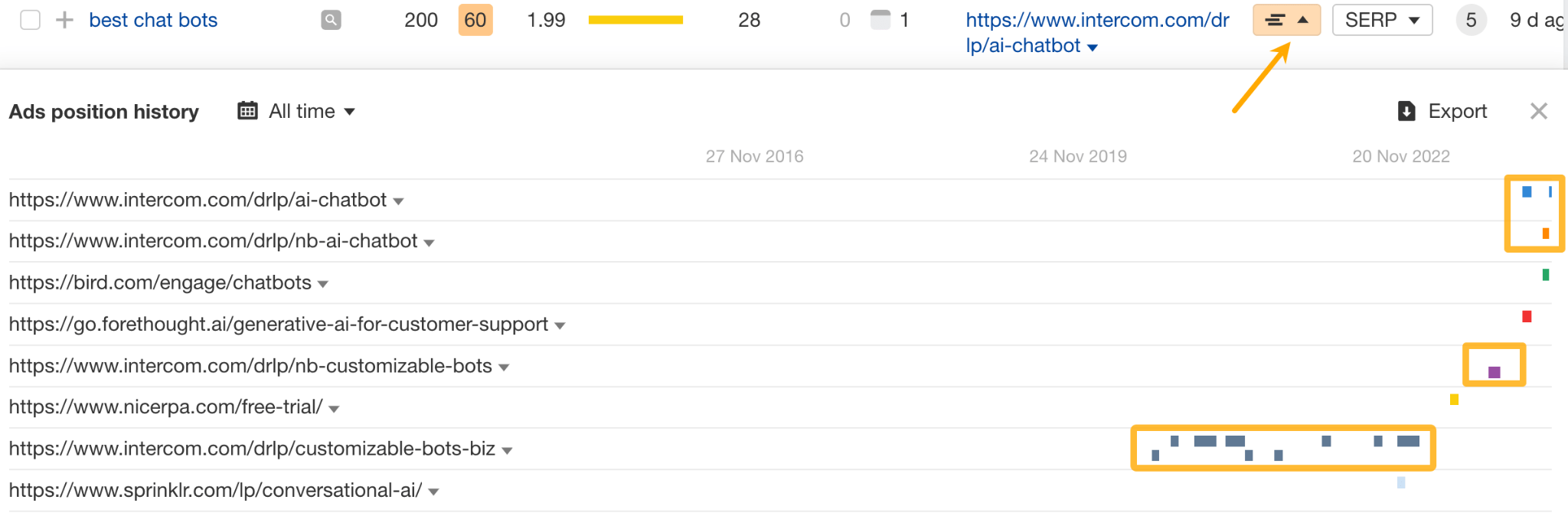
Another way to gauge a keyword’s importance is to look at its ad position history. A long and consistent history suggests it’s likely a valuable ‘money’ keyword, while a short history might indicate your competitor is just experimenting with it.

Want to check out their ad copy and landing pages? Head to the Ads report. You can set the location where your competitor runs their ads and see the landing pages and keywords associated with each ad.
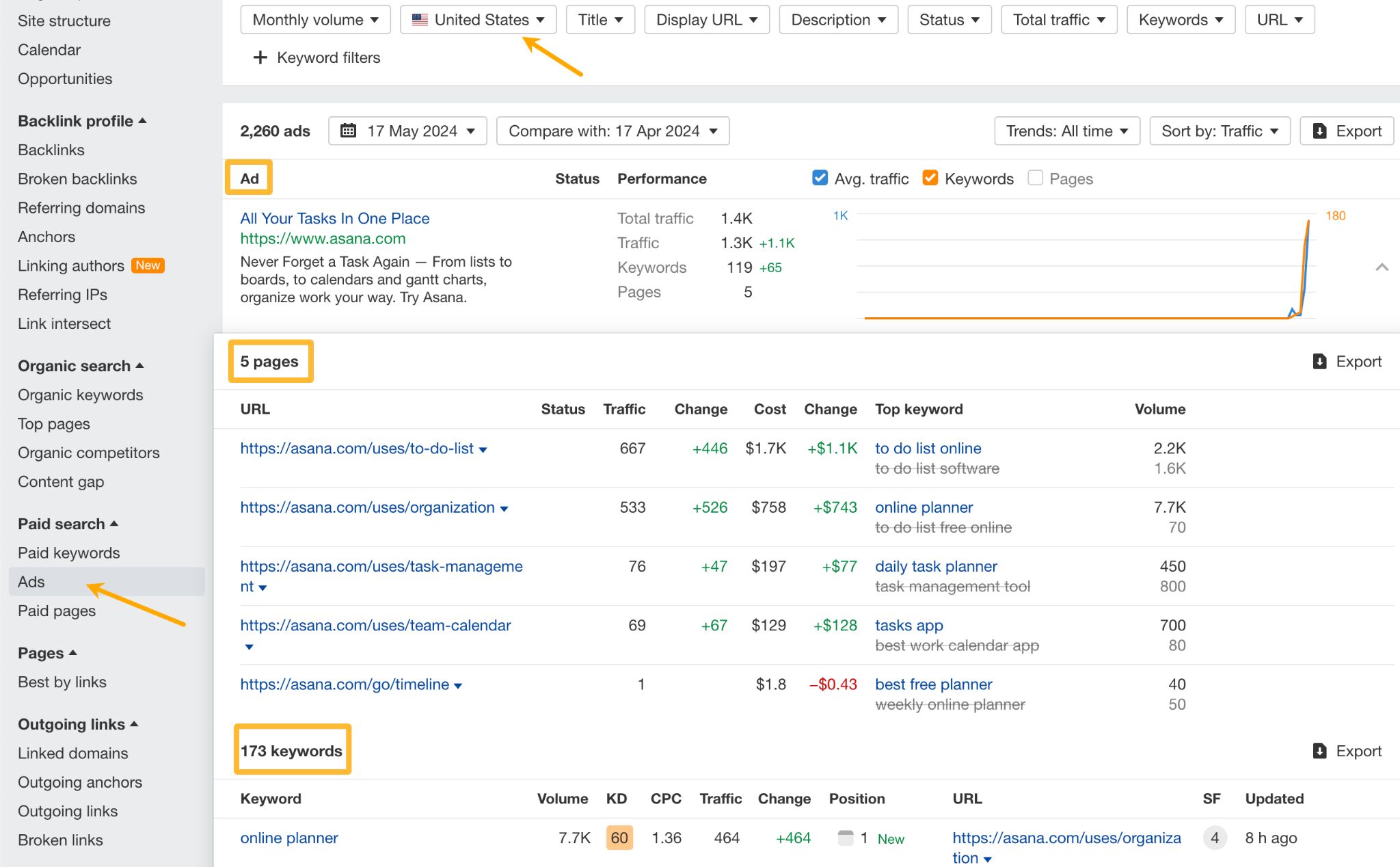

Interested to see how much your competitors spend to get all of that paid traffic?
- Go to Site Explorer.
- Enter your competitor’s domain.
- Open Paid pages report.
- Set the preferred location to see the budget per country (leave it set to all locations to see the total ad spend).
- Set the Performance report to Paid traffic cost set and adjust the timeframe.
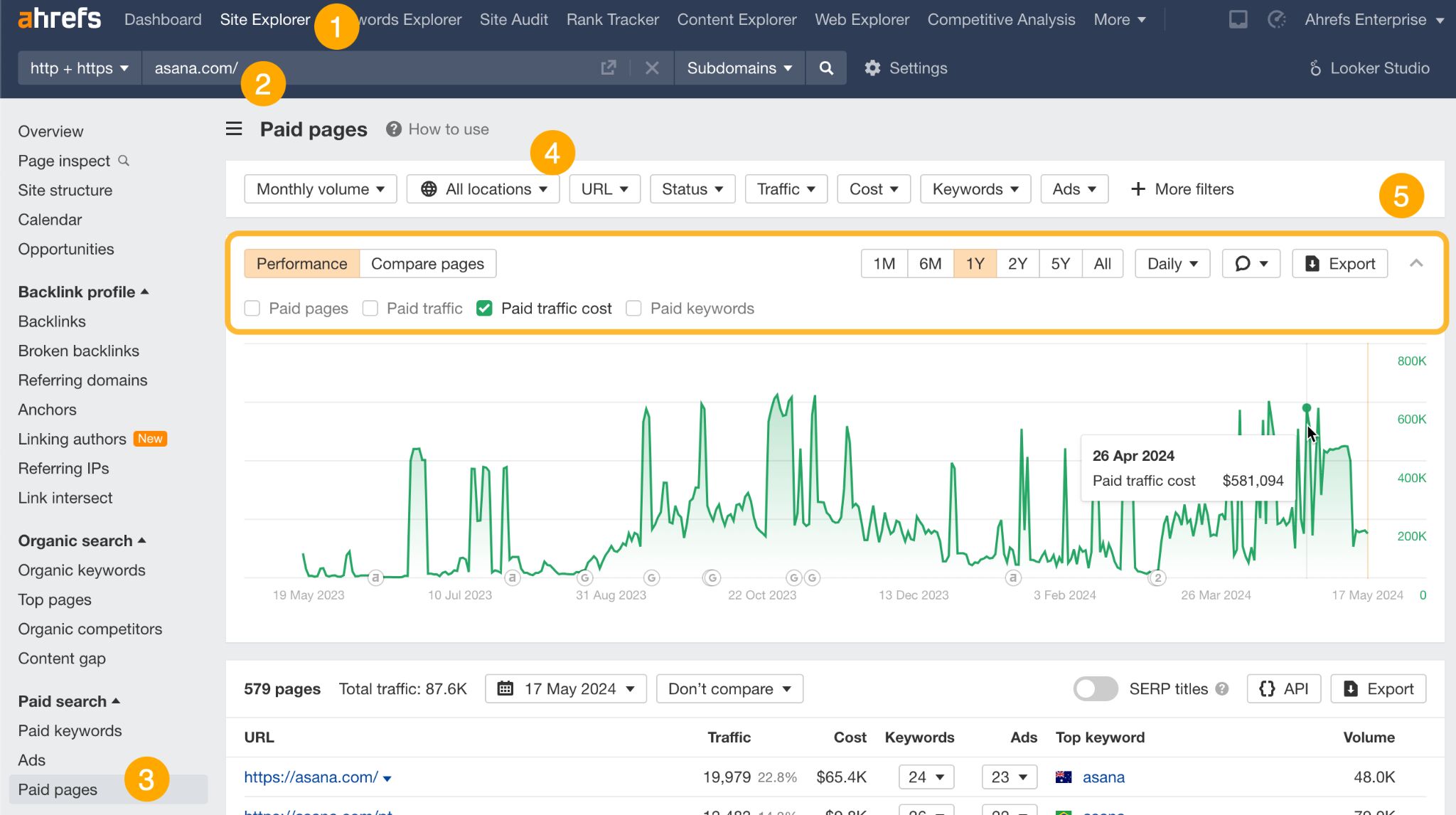

Use this data to set a benchmark for traffic performance relative to ad spend and to negotiate the budget for your campaigns.
How to analyze other traffic sources
If you’re interested in the overall competitor traffic performance, here’s where to look.
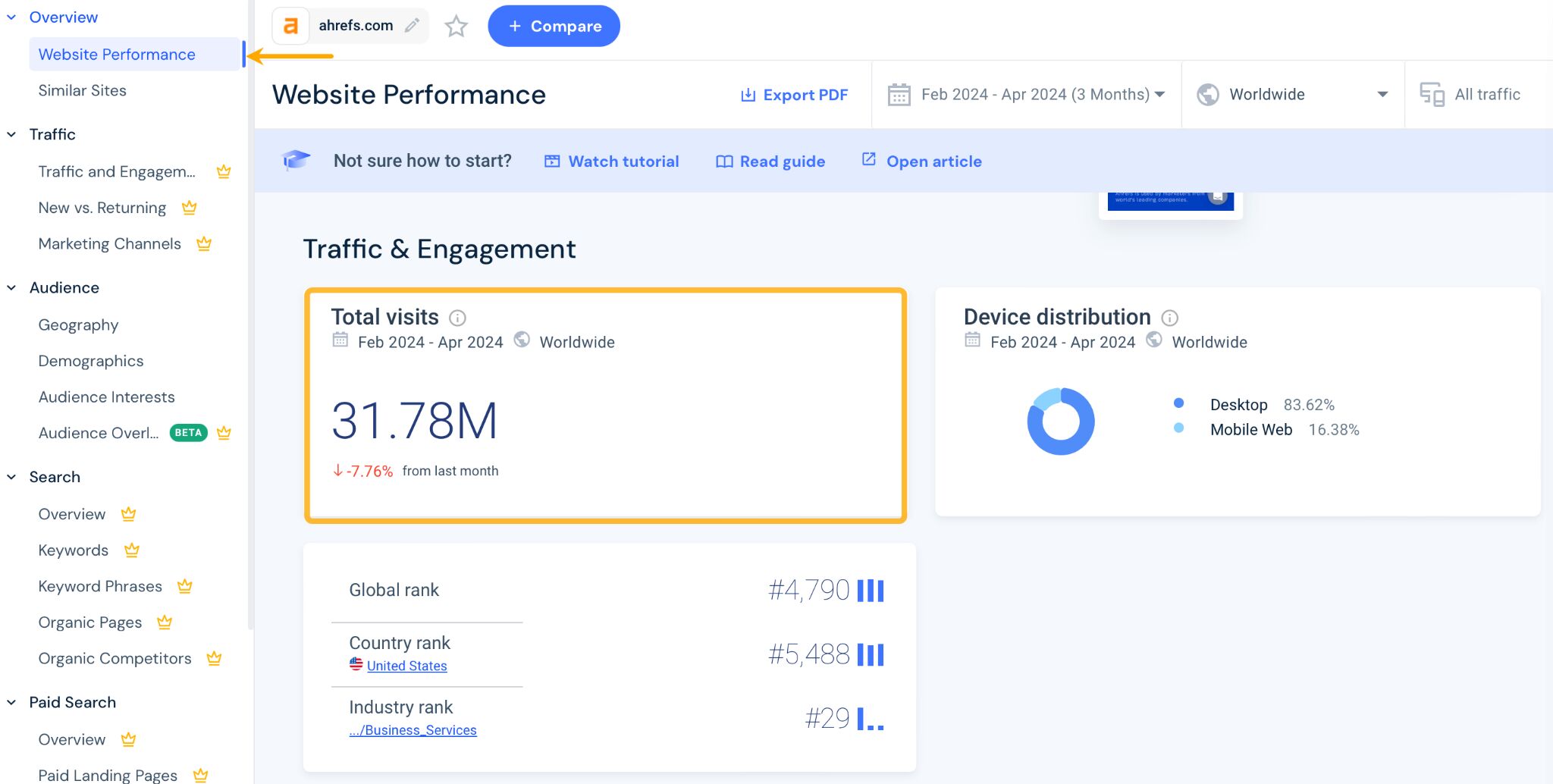
To get a quick answer to how much traffic your competitors get overall (from all traffic sources), you can get that information for free with Similarweb.
Once you set up a free account, simply go to Website analysis > Website performance report.

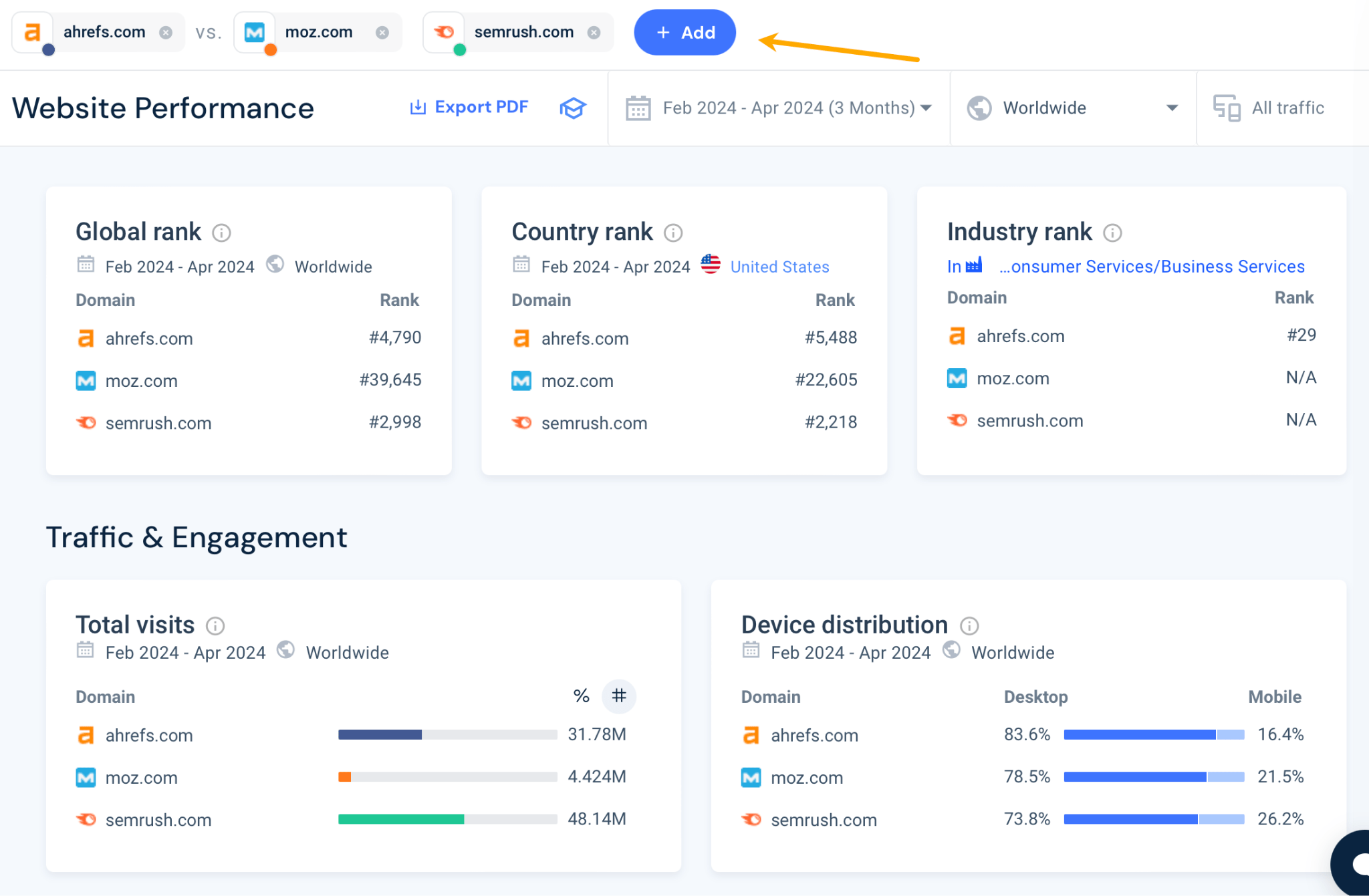
Arguably, the best way to use Similarweb is in comparison mode. This approach ensures that the data is directionally accurate: whether the data is overestimated or underestimated, it is consistently so across all sites. By comparing your traffic with your competitors, you can identify the relative differences that set you apart.

Similarweb is not the only tool with general traffic insights. Another one is Sparktoro, an audience research tool.
What’s great about Sparktoro is that its data and functionality revolve around the users behind the clicks. So you can use Similarweb to understand how popular the site is and then Sparktoro to get to know the people who visit it. Take that data and use it for persona development, fine-tuning your messaging, and looking up influencers to partner with or sites to advertise on.
Simply set up an account at Sparktoro and type your competitor’s domain in the search bar. Make sure the “Visit the website” mode is on.
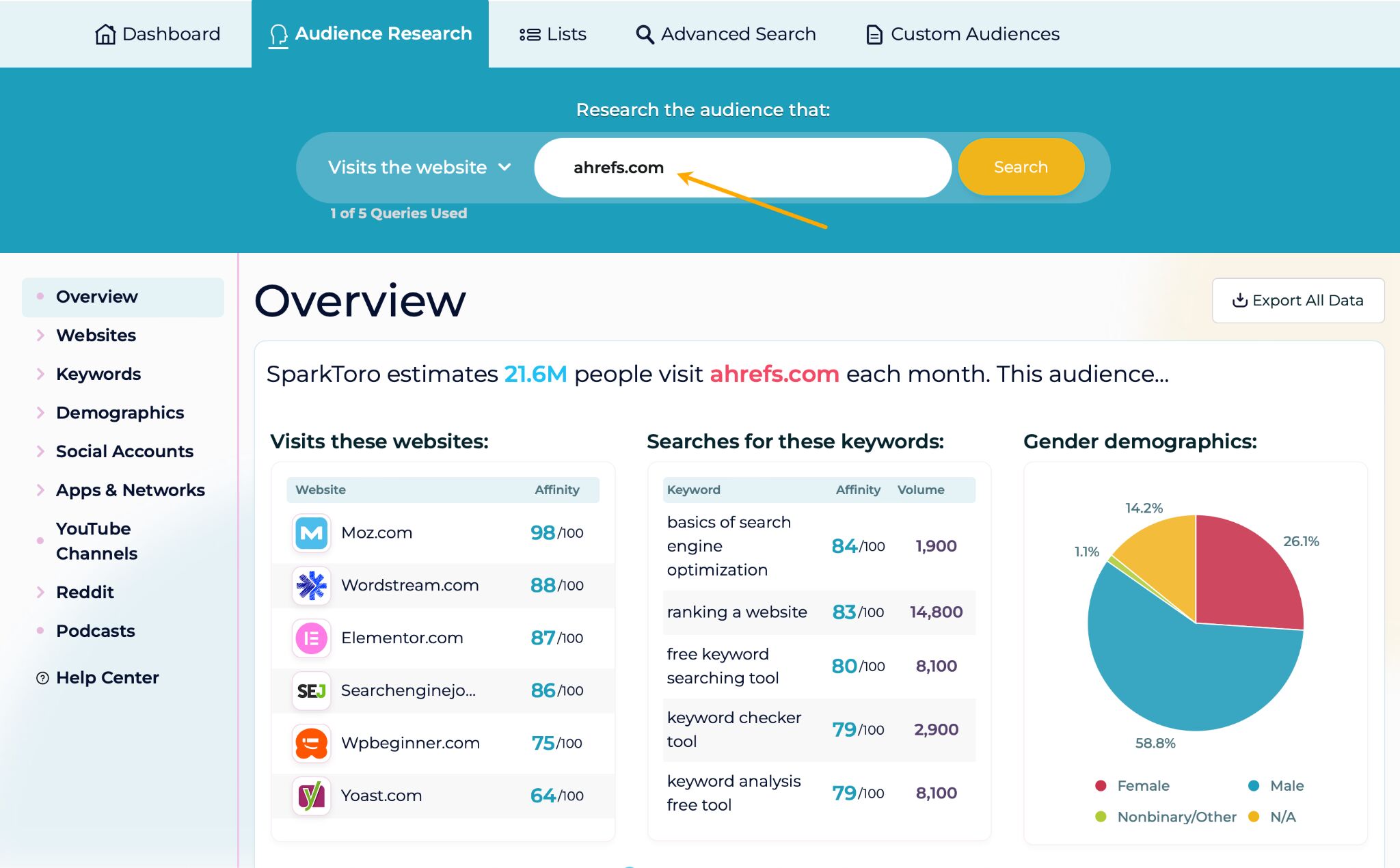

From there go to:
- Social networks: scroll down a bit and see which social network the brand uses the most. This not only tells which social networks likely send the most traffic but also which proved to be the most engaging.
- Demographics tab: see data like gender, age, geography and interests. What’s unique about this data is that it comes from social media profiles.
- Social accounts tab: to see what social media accounts site visitors are likely to follow and engage with. This is a great source of potential influencers to work with.
- YouTube channels, Reddit, and Podcast tabs: see where it’s highly likely to meet your competitors’ (and possibly yours) audience.
Where does the data come from? Is it accurate?
Depending on the tool, the data on your competitors will mostly come from:
- Web crawlers. Also known as spiders or bots. They are automated programs that browse the internet to gather information. For example, Ahrefs’ crawler is called AhrefsBot, one of the most active ones around.
- Clickstream data. Clickstream data refers to the recording of a user’s online activity as they navigate through websites. This data is anonymized and aggregated.
- Google Keyword Planner and Search Console. These tools provide valuable data on search engine performance and keyword usage. Also, this data is anonymized and aggregated.
- Social media APIs. Some social media platforms allow third-party tools to access their data.
This means that, in most cases, the data is estimated instead of actual data taken from your competitors and handed over to you.
So, when it comes to the data’s accuracy, you should expect a blend of estimated accuracy and directional accuracy. Despite best efforts, the data will be approximated and designed to give you an idea of relative performance because there’s no other way.
This also means that if you’re interested in a particular type of traffic, say traffic from search engines, it’s probably best to get a dedicated tool for that. You’ll get access to bigger data sets and more capable functionality, allowing you to do more.
Final thoughts
Want to go deeper into competitor analysis? Check out our other guides to go beyond traffic data:



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)











