MARKETING
How data clean rooms might help keep the internet open

Are data clean rooms the solution to what IAB CEO David Cohen has called the “slow-motion train wreck” of addressability? Voices at the IAB will tell you that they have a big role to play.
“The issue with addressability is that once cookies go away, and with the loss of identifiers, about 80% of the addressable market will become unknown audiences which is why there is a need for privacy-centric consent and a better consent-value exchange,” said Jeffrey Bustos, VP, measurement, addressability and data at the IAB.
“Everyone’s talking about first-party data, and it is very valuable,” he explained, “but most publishers who don’t have sign-on, they have about 3 to 10% of their readership’s first-party data.” First-party data, from the perspective of advertisers who want to reach relevant and audiences, and publishers who want to offer valuable inventory, just isn’t enough.
Why we care. Two years ago, who was talking about data clean rooms? The surge of interest is recent and significant, according to the IAB. DCRs have the potential, at least, to keep brands in touch with their audiences on the open internet; to maintain viability for publishers’ inventories; and to provide sophisticated measurement capabilities.
How data clean rooms can help. DCRs are a type of privacy-enhancing technology that allows data owners (including brands and publishers) to share customer first-party data in a privacy-compliant way. Clean rooms are secure spaces where first-party data from a number of sources can be resolved to the same customer’s profile while that profile remains anonymized.
In other words, a DCR is a kind of Switzerland — a space where a truce is called on competition while first-party data is enriched without compromising privacy.
“The value of a data clean room is that a publisher is able to collaborate with a brand across both their data sources and the brand is able to understand audience behavior,” said Bestos. For example, a brand selling eye-glasses might know nothing about their customers except basic transactional data — and that they wear glasses. Matching profiles with a publisher’s behavioral data provides enrichment.
“If you’re able to understand behavioral context, you’re able to understand what your customers are reading, what they’re interested in, what their hobbies are,” said Bustos. Armed with those insights, a brand has a better idea of what kind of content they want to advertise against.
The publisher does need to have a certain level of first-party data for the matching to take place, even if it doesn’t have a universal requirement for sign-ins like The New York Times. A publisher may be able to match only a small percentage of the eye-glass vendor’s customers, but if they like reading the sports and arts sections, at least that gives some directional guidance as to what audience the vendor should target.
Dig deeper: Why we care about data clean rooms
What counts as good matching? In its “State of Data 2023” report, which focuses almost exclusively on data clean rooms, concern is expressed that DCR efficacy might be threatened by poor match rates. Average match rates hover around 50% (less for some types of DCR).
Bustos is keen to put this into context. “When you are matching data from a cookie perspective, match rates are usually about 70-ish percent,” he said, so 50% isn’t terrible, although there’s room for improvement.
One obstacle is a persistent lack of interoperability between identity solutions — although it does exist; LiveRamp’s RampID is interoperable, for example, with The Trade Desk’s UID2.
Nevertheless, said Bustos, “it’s incredibly difficult for publishers. They have a bunch of identity pixels firing for all these different things. You don’t know which identity provider to use. Definitely a long road ahead to make sure there’s interoperability.”
Maintaining an open internet. If DCRs can contribute to solving the addressability problem they will also contribute to the challenge of keeping the internet open. Walled gardens like Facebook do have rich troves of first-party and behavioral data; brands can access those audiences, but with very limited visibility into them.
“The reason CTV is a really valuable proposition for advertisers is that you are able to identify the user 1:1 which is really powerful,” Bustos said. “Your standard news or editorial publisher doesn’t have that. I mean, the New York Times has moved to that and it’s been incredibly successful for them.” In order to compete with the walled gardens and streaming services, publishers need to offer some degree of addressability — and without relying on cookies.
But DCRs are a heavy lift. Data maturity is an important qualification for getting the most out of a DCR. The IAB report shows that, of the brands evaluating or using DCRs, over 70% have other data-related technologies like CDPs and DMPs.
“If you want a data clean room,” Bustos explained, “there are a lot of other technological solutions you have to have in place before. You need to make sure you have strong data assets.” He also recommends starting out by asking what you want to achieve, not what technology would be nice to have. “The first question is, what do you want to accomplish? You may not need a DCR. ‘I want to do this,’ then see what tools would get you to that.”
Understand also that implementation is going to require talent. “It is a demanding project in terms of the set-up,” said Bustos, “and there’s been significant growth in consulting companies and agencies helping set up these data clean rooms. You do need a lot of people, so it’s more efficient to hire outside help for the set up, and then just have a maintenance crew in-house.”
Underuse of measurement capabilities. One key finding in the IAB’s research is that DCR users are exploiting the audience matching capabilities much more than realizing the potential for measurement and attribution. “You need very strong data scientists and engineers to build advanced models,” Bustos said.
“A lot of brands that look into this say, ‘I want to be able to do a predictive analysis of my high lifetime value customers that are going to buy in the next 90 days.’ Or ‘I want to be able to measure which channels are driving the most incremental lift.’ It’s very complex analyses they want to do; but they don’t really have a reason as to why. What is the point? Understand your outcome and develop a sequential data strategy.”
Trying to understand incremental lift from your marketing can take a long time, he warned. “But you can easily do a reach and frequency and overlap analysis.” That will identify wasted investment in channels and as a by-product suggest where incremental lift is occurring. “There’s a need for companies to know what they want, identify what the outcome is, and then there are steps that are going to get you there. That’s also going to help to prove out ROI.”
Dig deeper: Failure to get the most out of data clean rooms is costing marketers money
Get MarTech! Daily. Free. In your inbox.
MARKETING
How to create editorial guidelines that are useful + template

Before diving in to all things editorial guidelines, a quick introduction. I head up the content team here at Optimizely. I’m responsible for developing our content strategy and ensuring this aligns to our key business goals.
Here I’ll take you through the process we used to create new editorial guidelines; things that worked well and tackle some of the challenges that come with any good multi – stakeholder project, share some examples and leave you with a template you can use to set your own content standards.
What are editorial guidelines?
Editorial guidelines are a set of standards for any/all content contributors, etc. etc. This most often includes guidance on brand, tone of voice, grammar and style, your core content principles and the types of content you want to produce.
Editorial guidelines are a core component of any good content strategy and can help marketers achieve the following in their content creation process:
- Consistency: All content produced, regardless of who is creating it, maintains a consistent tone of voice and style, helping strengthen brand image and making it easier for your audience to recognize your company’s content
- Quality Control: Serves as a ‘North Star’ for content quality, drawing a line in the sand to communicate the standard of content we want to produce
- Boosts SEO efforts: Ensures content creation aligns with SEO efforts, improving company visibility and increasing traffic
- Efficiency: With clear guidelines in place, content creators – external and internal – can work more efficiently as they have a clear understanding of what is expected of them
Examples of editorial guidelines
There are some great examples of editorial guidelines out there to help you get started.
Here are a few I used:
1. Editorial Values and Standards, the BBC
Ah, the Beeb. This really helped me channel my inner journalist and learn from the folks that built the foundation for free quality journalism.
How to create editorial guidelines, Pepperland Marketing
After taking a more big picture view I recognized needed more focused guidance on the step by step of creating editorial guidelines.
I really liked the content the good folks at Pepperland Marketing have created, including a free template – thanks guys! – and in part what inspired me to create our own free template as a way of sharing learnings and helping others quickstart the process of creating their own guidelines.
3. Writing guidelines for the role of AI in your newsroom?… Nieman Lab

As well as provide guidance on content quality and the content creation process, I wanted to tackle the thorny topic of AI in our editorial guidelines. Specifically, to give content creators a steer on ‘fair’ use of AI when creating content, to ensure creators get to benefit from the amazing power of these tools, but also that content is not created 100% by AI and help them understand why we feel that contravenes our core content principles of content quality.
So, to learn more I devoured this fascinating article, sourcing guidance from major media outlets around the world. I know things change very quickly when it comes to AI, but I highly encourage reading this and taking inspiration from how these media outlets are tackling this topic.
Learn more: The Marketer’s Guide to AI-generated content
Why did we decide to create editorial guidelines?
1. Aligning content creators to a clear vision and process
Optimizely as a business has undergone a huge transformation over the last 3 years, going through rapid acquisition and all the joys and frustrations that can bring. As a content team, we quickly recognized the need to create a set of clear and engaging guidelines that helps content creators understand how and where they can contribute, and gave a clear process to follow when submitting a content idea for consideration.
2. Reinvigorated approach to brand and content
As a brand Optimizely is also going through a brand evolution – moving from a more formal, considered tone of voice to one that’s much more approachable, down to earth and not afraid to use humor, different in content and execution.
See, our latest CMS campaign creative:

It’s pretty out there in terms of creative and messaging. It’s an ad campaign that’s designed to capture attention yes, but also – to demonstrate our abilities as a marketing team to create this type of campaign that is normally reserved for other more quote unquote creative industries.
We wanted to give guidance to fellow content creators outside the team on how they can also create content that embraces this evolved tone of voice, while at the same time ensuring content adheres to our brand guidelines.
3. Streamline content creation process
Like many global enterprises we have many different content creators, working across different time zones and locations. Documenting a set of guidelines and making them easily available helps content creators quickly understand our content goals, the types of content we want to create and why. It would free up content team time spent with individual contributors reviewing and editing submissions, and would ensure creation and optimization aligns to broader content & business goals.
It was also clear that we needed to document a process for submitting content ideas, so we made sure to include this in the guidelines themselves to make it easy and accessible for all contributors.
4. 2023 retrospective priority
As a content team we regularly review our content strategy and processes to ensure we’re operating as efficiently as possible.
In our last retrospective. I asked my team ‘what was the one thing I could do as a manager to help them be more impactful in their role?’
Editorial guidelines was the number 1 item on their list.
So off we went…
What we did
- Defined a discrete scope of work for the first version of the editorial guidelines, focusing on the Blog and Resources section of the website. This is where the content team spends most of its time and so has most involvement in the content creation process. Also where the most challenging bottlenecks have been in the past
- Research. Reviewed what was out there, got my hands on a few free templates and assembled a framework to create a first version for inputs and feedback
- Asked content community – I put a few questions out to my network on LinkedIn on the topic of content guidelines and content strategy, seeking to get input and guidance from smart marketers.
- Invited feedback: Over the course of a few weekswe invited collaborators to comment in a shared doc as a way of taking iterative feedback, getting ideas for the next scope of work, and also – bringing people on the journey of creating the guidelines. Look at all those reviewers! Doing this within our Content Marketing Platform (CMP) ensured that all that feedback was captured in one place, and that we could manage the process clearly, step by step:
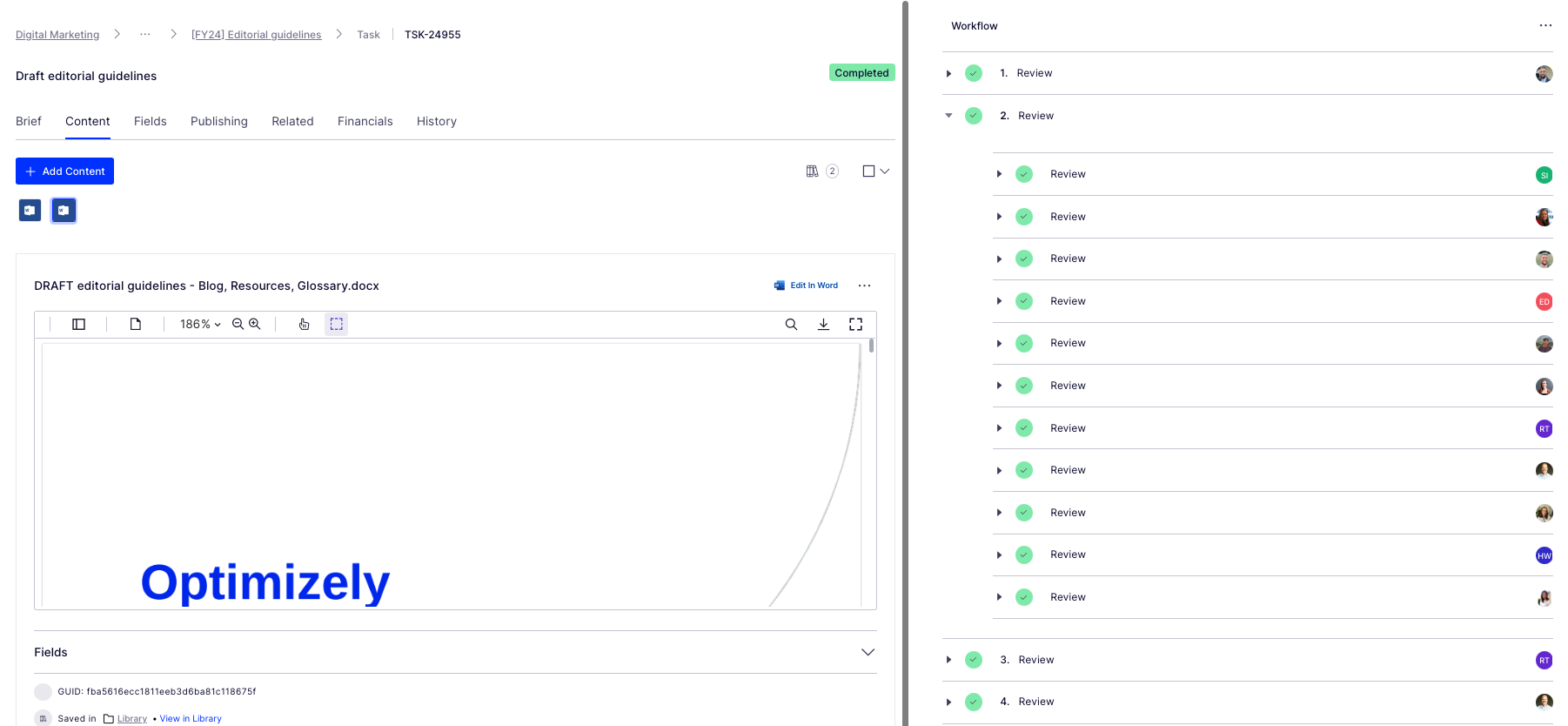
Look at all those collaborators! Thanks guys! And all of those beautiful ticks, so satisfying. So glad I could crop out the total outstanding tasks for this screen grab too (Source – Optimizely CMP)
- Updated content workflow: Now we have clear, documented guidance in place, we’ve included this as a step – the first step – in the workflow used for blog post creation:
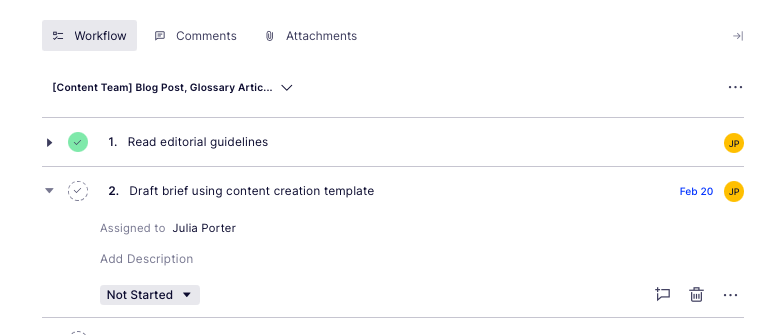
Source: Optimizely CMP
Results
It’s early days but we’re already seeing more engagement with the content creation process, especially amongst the teams involved in building the guidelines (which was part of the rationale in the first place :))
Source: My Teams chat
It’s inspired teams to think differently about the types of content we want to produce going forwards – for the blog and beyond.
I’d also say it’s boosted team morale and collaboration, helping different teams work together on shared goals to produce better quality work.
What’s next?
We’re busy planning wider communication of the editorial guidelines beyond marketing. We’ve kept the original draft and regularly share this with existing and potential collaborators for ongoing commentary, ideas and feedback.
Creating guidelines has also sparked discussion about the types of briefs and templates we want and need to create in CMP to support creating different assets. Finding the right balance between creative approach and using templates to scale content production is key.
We’ll review these guidelines on a quarterly basis and evolve as needed, adding new formats and channels as we go.
Key takeaways
- Editorial guidelines are a useful way to guide content creators as part of your overall content strategy
- Taking the time to do research upfront can help accelerate seemingly complex projects. Don’t be afraid to ask your community for inputs and advice as you create
- Keep the scope small at first rather than trying to align everything all at once. Test and learn as you go
- Work with stakeholders to build guidelines from the ground up to ensure you create a framework that is useful, relevant and used
And lastly, here’s that free template we created to help you build or evolve your own editorial guidelines!
MARKETING
Effective Communication in Business as a Crisis Management Strategy

Everyday business life is full of challenges. These include data breaches, product recalls, market downturns and public relations conflicts that can erupt at any moment. Such situations pose a significant threat to a company’s financial health, brand image, or even its further existence. However, only 49% of businesses in the US have a crisis communications plan. It is a big mistake, as such a strategy can build trust, minimize damage, and even strengthen the company after it survives the crisis. Let’s discover how communication can transform your crisis and weather the chaos.
The ruining impact of the crisis on business
A crisis can ruin a company. Naturally, it brings losses. But the actual consequences are far worse than lost profits. It is about people behind the business – they feel the weight of uncertainty and fear. Employees start worrying about their jobs, customers might lose faith in the brand they once trusted, and investors could start looking elsewhere. It can affect the brand image and everything you build from the branding, business logo, social media can be ruined. Even after the crisis recovery, the company’s reputation can suffer, and costly efforts might be needed to rebuild trust and regain momentum. So, any sign of a coming crisis should be immediately addressed. Communication is one of the crisis management strategies that can exacerbate the situation.
The power of effective communication
Even a short-term crisis may have irreversible consequences – a damaged reputation, high employee turnover, and loss of investors. Communication becomes a tool that can efficiently navigate many crisis-caused challenges:
- Improved trust. Crisis is a synonym for uncertainty. Leaders may communicate trust within the company when the situation gets out of control. Employees feel valued when they get clear responses. The same applies to the customers – they also appreciate transparency and are more likely to continue cooperation when they understand what’s happening. In these times, documenting these moments through event photographers can visually reinforce the company’s messages and enhance trust by showing real, transparent actions.
- Reputation protection. Crises immediately spiral into gossip and PR nightmares. However, effective communication allows you to proactively address concerns and disseminate true information through the right channels. It minimizes speculation and negative media coverage.
- Saved business relationships. A crisis can cause unbelievable damage to relationships with employees, customers, and investors. Transparent communication shows the company’s efforts to find solutions and keeps stakeholders informed and engaged, preventing misunderstandings and painful outcomes.
- Faster recovery. With the help of communication, the company is more likely to receive support and cooperation. This collaborative approach allows you to focus on solutions and resume normal operations as quickly as possible.
It is impossible to predict when a crisis will come. So, a crisis management strategy mitigates potential problems long before they arise.
Tips on crafting an effective crisis communication plan.
To effectively deal with unforeseen critical situations in business, you must have a clear-cut communication action plan. This involves things like messages, FAQs, media posts, and awareness of everyone in the company. This approach saves precious time when the crisis actually hits. It allows you to focus on solving the problem instead of intensifying uncertainty and panic. Here is a step-by-step guide.
Identify your crisis scenarios.
Being caught off guard is the worst thing. So, do not let it happen. Conduct a risk assessment to pinpoint potential crises specific to your business niche. Consider both internal and external factors that could disrupt normal operations or damage the online reputation of your company. Study industry-specific issues, past incidents, and current trends. How will you communicate in each situation? Knowing your risks helps you prepare targeted communication strategies in advance. Of course, it is impossible to create a perfectly polished strategy, but at least you will build a strong foundation for it.
Form a crisis response team.
The next step is assembling a core team. It will manage communication during a crisis and should include top executives like the CEO, CFO, and CMO, and representatives from key departments like public relations and marketing. Select a confident spokesperson who will be the face of your company during the crisis. Define roles and responsibilities for each team member and establish communication channels they will work with, such as email, telephone, and live chat. Remember, everyone in your crisis response team must be media-savvy and know how to deliver difficult messages to the stakeholders.
Prepare communication templates.
When a crisis hits, things happen fast. That means communication needs to be quick, too. That’s why it is wise to have ready-to-go messages prepared for different types of crises your company may face. These messages can be adjusted to a particular situation when needed and shared on the company’s social media, website, and other platforms right away. These templates should include frequently asked questions and outline the company’s general responses. Make sure to approve these messages with your legal team for accuracy and compliance.
Establish communication protocols.
A crisis is always chaotic, so clear communication protocols are a must-have. Define trigger points – specific events that would launch the crisis communication plan. Establish a clear hierarchy for messages to avoid conflicting information. Determine the most suitable forms and channels, like press releases or social media, to reach different audiences. Here is an example of how you can structure a communication protocol:
- Immediate alert. A company crisis response team is notified about a problem.
- Internal briefing. The crisis team discusses the situation and decides on the next steps.
- External communication. A spokesperson reaches the media, customers, and suppliers.
- Social media updates. A trained social media team outlines the situation to the company audience and monitors these channels for misinformation or negative comments.
- Stakeholder notification. The crisis team reaches out to customers and partners to inform them of the incident and its risks. They also provide details on the company’s response efforts and measures.
- Ongoing updates. Regular updates guarantee transparency and trust and let stakeholders see the crisis development and its recovery.
Practice and improve.
Do not wait for the real crisis to test your plan. Conduct regular crisis communication drills to allow your team to use theoretical protocols in practice. Simulate different crisis scenarios and see how your people respond to these. It will immediately demonstrate the strong and weak points of your strategy. Remember, your crisis communication plan is not a static document. New technologies and evolving media platforms necessitate regular adjustments. So, you must continuously review and update it to reflect changes in your business and industry.
Wrapping up
The ability to handle communication well during tough times gives companies a chance to really connect with the people who matter most—stakeholders. And that connection is a foundation for long-term success. Trust is key, and it grows when companies speak honestly, openly, and clearly. When customers and investors trust the company, they are more likely to stay with it and even support it. So, when a crisis hits, smart communication not only helps overcome it but also allows you to do it with minimal losses to your reputation and profits.
MARKETING
Should Your Brand Shout Its AI and Marketing Plan to the World?

To use AI or not to use AI, that is the question.
Let’s hope things work out better for you than they did for Shakespeare’s mad Danish prince with daddy issues.
But let’s add a twist to that existential question.
CMI’s chief strategy officer, Robert Rose, shares what marketers should really contemplate. Watch the video or read on to discover what he says:
Should you not use AI and be proud of not using it? Dove Beauty did that last week.
Should you use it but keep it a secret? Sports Illustrated did that last year.
Should you use AI and be vocal about using it? Agency giant Brandtech Group picked up the all-in vibe.
Should you not use it but tell everybody you are? The new term “AI washing” is hitting everywhere.
What’s the best option? Let’s explore.
Dove tells all it won’t use AI
Last week, Dove, the beauty brand celebrating 20 years of its Campaign for Real Beauty, pledged it would NEVER use AI in visual communication to portray real people.
In the announcement, they said they will create “Real Beauty Prompt Guidelines” that people can use to create images representing all types of physical beauty through popular generative AI programs. The prompt they picked for the launch video? “The most beautiful woman in the world, according to Dove.”
I applaud them for the powerful ad. But I’m perplexed by Dove issuing a statement saying it won’t use AI for images of real beauty and then sharing a branded prompt for doing exactly that. Isn’t it like me saying, “Don’t think of a parrot eating pizza. Don’t think about a parrot eating pizza,” and you can’t help but think about a parrot eating pizza right now?
Brandtech Group says it’s all in on AI
Now, Brandtech Group, a conglomerate ad agency, is going the other way. It’s going all-in on AI and telling everybody.
This week, Ad Age featured a press release — oops, I mean an article (subscription required) — with the details of how Brandtech is leaning into the takeaway from OpenAI’s Sam Altman, who says 95% of marketing work today can be done by AI.
A Brandtech representative talked about how they pitch big brands with two people instead of 20. They boast about how proud they are that its lean 7,000 staffers compete with 100,000-person teams. (To be clear, showing up to a pitch with 20 people has never been a good thing, but I digress.)
OK, that’s a differentiated approach. They’re all in. Ad Age certainly seemed to like it enough to promote it. Oops, I mean report about it.
False claims of using AI and not using AI
Offshoots of the all-in and never-will approaches also exist.
The term “AI washing” is de rigueur to describe companies claiming to use AI for something that really isn’t AI. The US Securities and Exchange Commission just fined two companies for using misleading statements about their use of AI in their business model. I know one startup technology organization faced so much pressure from their board and investors to “do something with AI” that they put a simple chatbot on their website — a glorified search engine — while they figured out what they wanted to do.
Lastly and perhaps most interestingly, companies have and will use AI for much of what they create but remain quiet about it or desire to keep it a secret. A recent notable example is the deepfake ad of a woman in a car professing the need for people to use a particular body wipe to get rid of body odor. It was purported to be real, but sharp-eyed viewers suspected the fake and called out the company, which then admitted it. Or was that the brand’s intent all along — the AI-use outrage would bring more attention?
This is an AI generated influencer video.
Looks 100% real. Even the interior car detailing.
UGC content for your brand is about to get really cheap. ☠️ pic.twitter.com/2m10RqoOW3
— Jon Elder | Amazon Growth | Private Label (@BlackLabelAdvsr) March 26, 2024
To yell or not to yell about your brand’s AI decision
Should a brand yell from a mountaintop that they use AI to differentiate themselves a la Brandtech? Or should a brand yell they’re never going to use AI to differentiate themselves a la Dove? Or should a brand use it and not yell anything? (I think it’s clear that a brand should not use AI and lie and say it is. That’s the worst of all choices.)
I lean far into not-yelling-from-mountaintop camp.
When I see a CEO proudly exclaim that they laid off 90% of their support workforce because of AI, I’m not surprised a little later when the value of their service is reduced, and the business is failing.
I’m not surprised when I hear “AI made us do it” to rationalize the latest big tech company latest rounds of layoffs. Or when a big consulting firm announces it’s going all-in on using AI to replace its creative and strategic resources.
I see all those things as desperate attempts for short-term attention or a distraction from the real challenge. They may get responses like, “Of course, you had to lay all those people off; AI is so disruptive,” or “Amazing. You’re so out in front of the rest of the pack by leveraging AI to create efficiency, let me cover your story.” Perhaps they get this response, “Your company deserves a bump in stock price because you’re already using this fancy new technology.”
But what happens if the AI doesn’t deliver as promoted? What happens the next time you need to lay off people? What happens the next time you need to prove your technologically forward-leaning?
Yelling out that you’re all in on a disruptive innovation, especially one the public doesn’t yet trust a lot is (at best) a business sugar high. That short-term burst of attention may or may not foul your long-term brand value.
Interestingly, the same scenarios can manifest when your brand proclaims loudly it is all out of AI, as Dove did. The sugar high may not last and now Dove has itself into a messaging box. One slip could cause distrust among its customers. And what if AI gets good at demonstrating diversity in beauty?
I tried Dove’s instructions and prompted ChatGPT for a picture of “the most beautiful woman in the world according to the Dove Real Beauty ad.”
It gave me this. Then this. And this. And finally, this.
She’s absolutely beautiful, but she doesn’t capture the many facets of diversity Dove has demonstrated in its Real Beauty campaigns. To be clear, Dove doesn’t have any control over generating the image. Maybe the prompt worked well for Dove, but it didn’t for me. Neither Dove nor you can know how the AI tool will behave.
To use AI or not to use AI?
When brands grab a microphone to answer that question, they work from an existential fear about the disruption’s meaning. They do not exhibit the confidence in their actions to deal with it.
Let’s return to Hamlet’s soliloquy:
Thus conscience doth make cowards of us all;
And thus the native hue of resolution
Is sicklied o’er with the pale cast of thought,
And enterprises of great pith and moment
With this regard their currents turn awry
And lose the name of action.
In other words, Hamlet says everybody is afraid to take real action because they fear the unknown outcome. You could act to mitigate or solve some challenges, but you don’t because you don’t trust yourself.
If I’m a brand marketer for any business (and I am), I’m going to take action on AI for my business. But until I see how I’m going to generate value with AI, I’m going to be circumspect about yelling or proselytizing how my business’ future is better.
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days ago13 Best HubSpot Alternatives for 2024 (Free + Paid)
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoBattling for Attention in the 2024 Election Year Media Frenzy
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days ago25 WordPress Alternatives Best For SEO
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago7 Best WooCommerce Points and Rewards Plugins (Free & Paid)
-

 AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days ago
AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days agoAI Will Transform the Workplace. Here’s How HR Can Prepare for It.
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login