Threads: What to Know About Instagram’s ‘Twitter Killer’ App
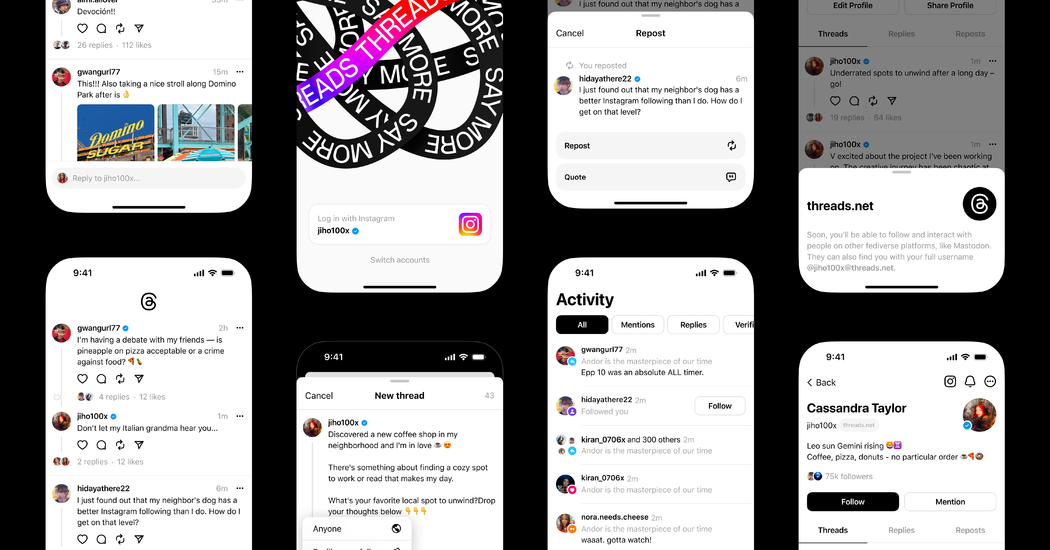
After months of speculation and secrecy, Mark Zuckerberg’s long-rumored competitor app to Twitter is here.
The new app, Threads, was unveiled on Wednesday as a companion to Instagram, the popular photo-sharing network that Mr. Zuckerberg’s company, Meta, bought more than a decade ago. If Instagram executives get their way, Threads will also replace rival Twitter, with some techies referring to it as a “Twitter killer.”
The rollout of Threads ramps up the rivalry between Mr. Zuckerberg and Elon Musk, who bought Twitter last year. Mr. Musk has changed the experience of Twitter by tinkering with its algorithm and other features, and most recently imposed temporary limits on how many tweets people could read when using the app, inciting outrage.
Many tech companies have tried capitalizing on Twitter’s turmoil in recent months. But Threads has a leg up, backed by Meta’s deep pockets and Instagram’s enormous user base of more than two billion monthly active users around the world.
In a post to his Threads account on Wednesday, Mr. Zuckerberg said he wanted the new app to be “friendly as it expands,” which was an area where “Twitter never succeeded” as much as he believed it should have. “We want to do it differently,” he said.
Here’s what to know about Threads.
What is Threads and how does it work?
Built by Instagram, Threads is positioned as an app where people can have real-time, public conversations with one another. Threads also helps boost Instagram, which is a marquee app in Meta’s family of products.
“The idea is to hopefully build an open, friendly space for communities,” Adam Mosseri, head of Instagram, said in an interview.
Instagram has tied Threads closely to itself. Those interested in signing up for the new app are required to have an Instagram account for now. A user’s Instagram handle must also be their Threads user name.
And people will be able to directly import the list of those they follow on Instagram to Threads if they wish. Instagram’s verified users will also be verified on the new app. Users can set their Threads account to be private or public.
How is Threads similar to or different from Twitter?
Threads looks nearly identical to Twitter in many ways. Users can post mostly text-based messages to a scrolling feed, where people who follow them and whom they follow can reply. People can also post photos or video to the app.
But Threads is also different from Twitter. It does not currently support direct messaging, a feature that Twitter offers. Instagram said it may add features to Threads if new users ask for them.
How did Instagram come up with Threads?
Instagram has made a concerted effort to simplify its app over the past few years, Mr. Mosseri said. As part of that effort, he said, Threads was spun out into a separate app. That way, Instagram would not be too cluttered by trying to make public conversations work inside its existing app.
The choice to create a new app was also hard to resist, Mr. Mosseri added, especially at a tumultuous moment in the social media landscape.
“There was an opportunity or demand for more people to play in the public space,” he said, referring to the changes around Twitter under Mr. Musk. Mr. Mosseri added that the chance to challenge Twitter came about “not just because of the ownership, but because of product changes and decisions” that Mr. Musk and others made to how the social platform works.
Instagram began its effort to take on Twitter late last year, with dozens of engineers, product managers and designers pitching ideas on what a rival app could look like. Among the notions Meta’s workers talked over at the time was a more extensive rollout of a feature called Instagram Notes, where people can share short messages on the site, and a text-focused app using Instagram’s technology.
Ultimately, Mr. Mosseri said, he and other managers decided they should “make a bet” in the space and leaned into building what became Threads.
How will Threads work with other apps?
Instagram’s goal is to ultimately have Threads work across multiple apps in what it calls the Fediverse, which is shorthand for a federated universe of services that share communication protocols. Other apps like Mastodon, another social network, also function in this way.
This might sound like a lot of tech speak. What it means, essentially, is that Instagram wants to make it easier for Threads to operate seamlessly with other platforms, which could appeal to creators and influencers so they do not have to start from scratch on each app.
If a creator builds up a sizable number of followers on Threads, for instance, they could ostensibly take those followers with them to other platforms that are built on the same technology. That would make it less risky for creators and could free them from feeling like they are “stuck” on one platform, Mr. Mosseri said.
Has Instagram cloned other apps?
Mr. Zuckerberg’s Meta, which also owns Facebook and WhatsApp, has an extensive history of trying to stamp out social media rivals, partly by copying their features. Mr. Zuckerberg is fiercely competitive and has long wanted to own a product that accomplishes what Twitter does.
That strategy does not always guarantee success. Facebook’s early attempts to clone the ephemeral messaging app Snapchat, for example, did not initially gain much traction.
Even so, Meta has continued to imitate rivals. In 2020, Meta released a TikTok copycat called Reels, which focuses on short videos and has since become widely used.
Where will Threads be available?
Threads is available for download for free from Apple’s App Store and the Google Play store in the United States and roughly 100 other countries beginning on Wednesday. It has plans to expand further.
But Meta said Threads will not initially be available in the European Union, one of the company’s largest markets. A new E.U. law called the Digital Markets Act is taking effect in the coming months and limits how the largest tech companies share data across services. Meta said it was waiting to get more specifics about the law’s implementation before introducing Threads across the 27-nation bloc.
Adam Satariano contributed reporting.
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
Christian family goes in hiding after being cleared of blasphemy

LAHORE, Pakistan — A court in Pakistan granted bail to a Christian falsely charged with blasphemy, but he and his family have separated and gone into hiding amid threats to their lives, sources said.
Haroon Shahzad, 45, was released from Sargodha District Jail on Nov. 15, said his attorney, Aneeqa Maria. Shahzad was charged with blasphemy on June 30 after posting Bible verses on Facebook that infuriated Muslims, causing dozens of Christian families in Chak 49 Shumaali, near Sargodha in Punjab Province, to flee their homes.
Lahore High Court Judge Ali Baqir Najfi granted bail on Nov. 6, but the decision and his release on Nov. 15 were not made public until now due to security fears for his life, Maria said.
Shahzad told Morning Star News by telephone from an undisclosed location that the false accusation has changed his family’s lives forever.
“My family has been on the run from the time I was implicated in this false charge and arrested by the police under mob pressure,” Shahzad told Morning Star News. “My eldest daughter had just started her second year in college, but it’s been more than four months now that she hasn’t been able to return to her institution. My other children are also unable to resume their education as my family is compelled to change their location after 15-20 days as a security precaution.”
Though he was not tortured during incarceration, he said, the pain of being away from his family and thinking about their well-being and safety gave him countless sleepless nights.
“All of this is due to the fact that the complainant, Imran Ladhar, has widely shared my photo on social media and declared me liable for death for alleged blasphemy,” he said in a choked voice. “As soon as Ladhar heard about my bail, he and his accomplices started gathering people in the village and incited them against me and my family. He’s trying his best to ensure that we are never able to go back to the village.”
Shahzad has met with his family only once since his release on bail, and they are unable to return to their village in the foreseeable future, he said.
“We are not together,” he told Morning Star News. “They are living at a relative’s house while I’m taking refuge elsewhere. I don’t know when this agonizing situation will come to an end.”
The Christian said the complainant, said to be a member of Islamist extremist party Tehreek-e-Labbaik Pakistan and also allegedly connected with banned terrorist group Lashkar-e-Jhangvi, filed the charge because of a grudge. Shahzad said he and his family had obtained valuable government land and allotted it for construction of a church building, and Ladhar and others had filed multiple cases against the allotment and lost all of them after a four-year legal battle.
“Another probable reason for Ladhar’s jealousy could be that we were financially better off than most Christian families of the village,” he said. “I was running a successful paint business in Sargodha city, but that too has shut down due to this case.”
Regarding the social media post, Shahzad said he had no intention of hurting Muslim sentiments by sharing the biblical verse on his Facebook page.
“I posted the verse a week before Eid Al Adha [Feast of the Sacrifice] but I had no idea that it would be used to target me and my family,” he said. “In fact, when I came to know that Ladhar was provoking the villagers against me, I deleted the post and decided to meet the village elders to explain my position.”
The village elders were already influenced by Ladhar and refused to listen to him, Shahzad said.
“I was left with no option but to flee the village when I heard that Ladhar was amassing a mob to attack me,” he said.
Shahzad pleaded with government authorities for justice, saying he should not be punished for sharing a verse from the Bible that in no way constituted blasphemy.
Similar to other cases
Shahzad’s attorney, Maria, told Morning Star News that events in Shahzad’s case were similar to other blasphemy cases filed against Christians.
“Defective investigation, mala fide on the part of the police and complainant, violent protests against the accused persons and threats to them and their families, forcing their displacement from their ancestral areas, have become hallmarks of all blasphemy allegations in Pakistan,” said Maria, head of The Voice Society, a Christian paralegal organization.
She said that the case filed against Shahzad was gross violation of Section 196 of the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC), which states that police cannot register a case under the Section 295-A blasphemy statute against a private citizen without the approval of the provincial government or federal agencies.
Maria added that Shahzad and his family have continued to suffer even though there was no evidence of blasphemy.
“The social stigma attached with a blasphemy accusation will likely have a long-lasting impact on their lives, whereas his accuser, Imran Ladhar, would not have to face any consequence of his false accusation,” she said.
The judge who granted bail noted that Shahzad was charged with blasphemy under Section 295-A, which is a non-cognizable offense, and Section 298, which is bailable. The judge also noted that police had not submitted the forensic report of Shahzad’s cell phone and said evidence was required to prove that the social media was blasphemous, according to Maria.
Bail was set at 100,000 Pakistani rupees (US $350) and two personal sureties, and the judge ordered police to further investigate, she said.
Shahzad, a paint contractor, on June 29 posted on his Facebook page 1 Cor. 10:18-21 regarding food sacrificed to idols, as Muslims were beginning the four-day festival of Eid al-Adha, which involves slaughtering an animal and sharing the meat.
A Muslim villager took a screenshot of the post, sent it to local social media groups and accused Shahzad of likening Muslims to pagans and disrespecting the Abrahamic tradition of animal sacrifice.
Though Shahzad made no comment in the post, inflammatory or otherwise, the situation became tense after Friday prayers when announcements were made from mosque loudspeakers telling people to gather for a protest, family sources previously told Morning Star News.
Fearing violence as mobs grew in the village, most Christian families fled their homes, leaving everything behind.
In a bid to restore order, the police registered a case against Shahzad under Sections 295-A and 298. Section 295-A relates to “deliberate and malicious acts intended to outrage religious feelings of any class by insulting its religion or religious beliefs” and is punishable with imprisonment of up to 10 years and fine, or both. Section 298 prescribes up to one year in prison and a fine, or both, for hurting religious sentiments.
Pakistan ranked seventh on Open Doors’ 2023 World Watch List of the most difficult places to be a Christian, up from eighth the previous year.
Morning Star News is the only independent news service focusing exclusively on the persecution of Christians. The nonprofit’s mission is to provide complete, reliable, even-handed news in order to empower those in the free world to help persecuted Christians, and to encourage persecuted Christians by informing them that they are not alone in their suffering.
Free Religious Freedom Updates
Join thousands of others to get the FREEDOM POST newsletter for free, sent twice a week from The Christian Post.
Individual + Team Stats: Hornets vs. Timberwolves
CHARLOTTE HORNETS MINNESOTA TIMBERWOLVES You can follow us for future coverage by liking us on Facebook & following us on X: Facebook – All Hornets X – …
Source link
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoBattling for Attention in the 2024 Election Year Media Frenzy
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago13 Best HubSpot Alternatives for 2024 (Free + Paid)
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoAdvertising in local markets: A playbook for success
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Core Update Flux, AdSense Ad Intent, California Link Tax & More
-

 AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days ago
AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days agoGrab Microsoft Project Professional 2021 for $20 During This Flash Sale
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Needs Very Few Links To Rank Pages; Links Are Less Important
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days ago10 Most Effective Franchise Marketing Strategies
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoHow to Use AI For a More Effective Social Media Strategy, According to Ross Simmonds













