MARKETING
How To Combine Machine and Human Input for More Effective Content

In 2023, marketers entered a new content battleground. Not only can brands and people become writers and publishers, but now machines can, too.
Together, people and machines create tens of millions of new web pages daily. Do your brand’s blog posts, white papers, videos, and fact sheets have any chance of being discovered and consumed?
You may already have an inbox full of pitches touting AI tools as a way to quickly create more – but will machine-generated content help you get your audience’s attention? Not necessarily.
Google’s position on AI-produced content is clear: “Using automation – including AI – to generate content with the primary purpose of manipulating ranking in search results is a violation of our spam policies.” Yet, Google acknowledges that not all AI content is spam, and AI can serve as “a critical tool to help people create great content for the web.”
Still, there you can put AI and machine learning tools to work in other areas, including content research, optimization, and promotion workflows. Let’s explore important ways to use both AI and human capital to improve your content marketing strategy effectively and sustainably.
Optimize content for people, but don’t ignore SEO
First, though, a few reminders about getting found by people using search engines.
Keep in mind that Google intends for all of its search engine updates (tens of thousands per year) to improve the search experience for human users. So optimizing for search engines isn’t all that different from optimizing for people. But when you optimize for search engines first, you risk doing things that can harm the human reader experience and perception of your brand.
For example, if you begin a piece of content with a list of 15 keywords you plan to use a certain number of times, you’ll likely end up with content that doesn’t read naturally.
Writing for people without a lens for SEO can also be problematic. For example, a great piece of content that lacks schema markup, image alt text, internal links, and headings won’t earn positive attention from search engines. Those elements help Google understand the page so it won’t designate the great content as worthless.
A great piece of #content that lacks schema markup, image alt text, internal links, and headings won’t earn attention from search engines, says @jimyu via @CMIContent. #AI #SEO Click To Tweet
Quality pieces optimized for a human audience ensure better indexing and online visibility from search engine crawlers.
Whether you use AI tools in the process or not, keep these guidelines in mind when creating quality content for people:
Those same steps will help you with search engines by communicating the content’s topical relevance, authority, and importance.
Now let’s look at ways AI can help you write for humans without landing you in hot water with search engines.
Some AI tools help in content research (but ChatGPT doesn’t)
AI content tools are not new. While ChatGPT’s capabilities seriously leveled up the conversation around AI content generation, marketers have used AI platforms like Frase, Clearscope, and other tools to help content marketing processes for years. You may have used them to research topics and create content briefs.
Features vary and new tools pop up regularly, but the best AI content research tools can:
- Analyze top-ranking content for a keyword term or topic and return insights on word count, subheadings, number of images, and internal and external links.
- Suggest related topics, keywords, and entities people often associate with the topic.
- Inspire title and meta-description writing, summarize information, and offer different ways to communicate the information.
- Provide frequently asked questions, commonly linked sources, and other insights to help you understand what your audience expects on the topic.
It’s important to note that ChatGPT isn’t ideal for content research because it uses a data set that ended in 2021.
#ChatGPT isn’t ideal for #content research because it uses a data set that ended in 2021, says @jimyu via @CMIContent. #AI #SEO Click To Tweet
So, while the aforementioned tools can analyze current results from the live web, ChatGPT cannot create content based on current information. You can use it to sort and categorize keywords by intent, for instance, but you won’t get the most updated list if you ask ChatGPT to create it.
ADVERTISEMENT
The Enterprise Marketer’s Content Creation Guide: A framework for developing content that attracts, engages, and converts
Elevate your content marketing creation with this 3-part framework based on our experience producing 100,000+ pieces of content. Perfect for enterprise marketers ready to scale. Download the e-book today.
AI can assist human writers (and already does)
Google acknowledges in its guidance about AI-generated content documentation that machine-generated content can be useful: “Automation has long been used to generate helpful content, such as sports scores, weather forecasts, and transcripts.”
AI does excellent work sorting and categorizing information, creating summaries, and analyzing data. The news wire service Reuters, for example, has been using AI since 2018 when it launched the Lynx Insight tool for its newsrooms. Its proprietary AI tool helped its journalists analyze data, generate story ideas, and write simple copy, acting as a sort of copywriting assistant who happens to have advanced data science skills.
How can you use AI to assist rather than replace human writers? Here are a few ideas:
If you work for a B2B SaaS company, you could use an AI tool to analyze anonymized customer data to create performance benchmarks for your clients. If you work for a retail or e-commerce brand, try using AI to write product descriptions, then send them through human editors for quality control.
Using AI in these ways can expand your human writers’ capabilities and help them scale their efforts.
AI in data reporting
When you pull together data manually for your reporting, it can be a time-consuming, confusing, and uncomfortable task. In fact, 43% of CMOs believe their teams spend more time compiling data than using it to drive decisions. A typical SEO and content practitioner can spend up to four hours a day manually researching, reporting, and analyzing.
On the other hand, AI-automated reporting can simplify reporting operations and empower you with real-time insights into complex performance metrics. AI-powered reporting also can revolutionize the way different stakeholders receive it with dashboards customized for what each business unit wants. Plus, the speed of reporting insights can give your business an edge in responding to changes driven by consumers or competitors. Custom-built dashboards can help with reporting to different business units in your company when they need or want it.
You can integrate AI-automated reporting in several ways, from your CRM to your Google Analytics. You can use many tools, from Google’s Google Looker and Data Studio to my employer BrightEdge’s AI tool.
This AI-automated data report compiles data from traffic based on device, organic search appearances, and content listings on a universal search to glean insights for a content team:
“We are seeing an uptick in demand for instructions and how-to content for our products. Right now, social channels and editorials are winning share of voice. These queries represent an opportunity to help customers and potentially cross-sell products. Let’s discuss how we could prioritize how-to content in the calendar in our meeting.”
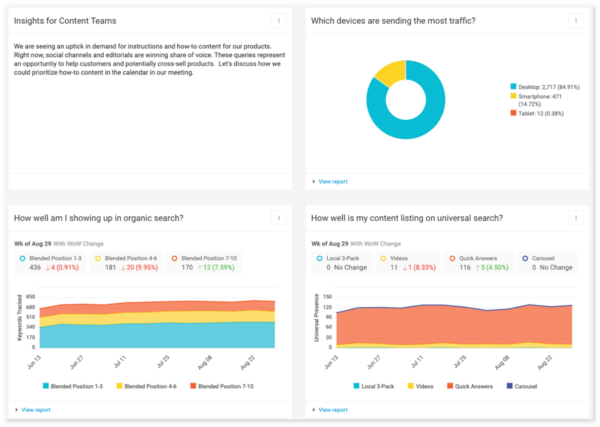
Using AI to analyze the data to identify common opportunities and recurring optimizations frees up your content team’s time to focus on more creative initiatives. But, of course, the old adage “garbage in, garbage out” still applies. Your human team must ensure the data it’s fed is most purposeful.
What’s ahead?
We’re not yet in a state of symbiosis between human marketers and AI, but the possibilities ahead are exciting.
Both humans and machines will still make errors, fail in some respects, and have biases to overcome. So, make 2023 all about balance. AI is best used with human input and supervision. Determine how and where it best augments your content team’s skills, knowledge, and capabilities.
Provide your team time and opportunity to explore how AI can help scale their processes, extend their skills, and focus now on developing best practices for your organization. Give your team permission to try and fail. Today’s lessons will drive your content marketing success into tomorrow and beyond.
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
MARKETING
YouTube Ad Specs, Sizes, and Examples [2024 Update]
![YouTube Ad Specs, Sizes, and Examples [2024 Update] YouTube Ad Specs, Sizes, and Examples](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/YouTube-Ad-Specs-Sizes-and-Examples.jpg)
Introduction
With billions of users each month, YouTube is the world’s second largest search engine and top website for video content. This makes it a great place for advertising. To succeed, advertisers need to follow the correct YouTube ad specifications. These rules help your ad reach more viewers, increasing the chance of gaining new customers and boosting brand awareness.
Types of YouTube Ads
Video Ads
- Description: These play before, during, or after a YouTube video on computers or mobile devices.
- Types:
- In-stream ads: Can be skippable or non-skippable.
- Bumper ads: Non-skippable, short ads that play before, during, or after a video.
Display Ads
- Description: These appear in different spots on YouTube and usually use text or static images.
- Note: YouTube does not support display image ads directly on its app, but these can be targeted to YouTube.com through Google Display Network (GDN).
Companion Banners
- Description: Appears to the right of the YouTube player on desktop.
- Requirement: Must be purchased alongside In-stream ads, Bumper ads, or In-feed ads.
In-feed Ads
- Description: Resemble videos with images, headlines, and text. They link to a public or unlisted YouTube video.
Outstream Ads
- Description: Mobile-only video ads that play outside of YouTube, on websites and apps within the Google video partner network.
Masthead Ads
- Description: Premium, high-visibility banner ads displayed at the top of the YouTube homepage for both desktop and mobile users.
YouTube Ad Specs by Type
Skippable In-stream Video Ads
- Placement: Before, during, or after a YouTube video.
- Resolution:
- Horizontal: 1920 x 1080px
- Vertical: 1080 x 1920px
- Square: 1080 x 1080px
- Aspect Ratio:
- Horizontal: 16:9
- Vertical: 9:16
- Square: 1:1
- Length:
- Awareness: 15-20 seconds
- Consideration: 2-3 minutes
- Action: 15-20 seconds
Non-skippable In-stream Video Ads
- Description: Must be watched completely before the main video.
- Length: 15 seconds (or 20 seconds in certain markets).
- Resolution:
- Horizontal: 1920 x 1080px
- Vertical: 1080 x 1920px
- Square: 1080 x 1080px
- Aspect Ratio:
- Horizontal: 16:9
- Vertical: 9:16
- Square: 1:1
Bumper Ads
- Length: Maximum 6 seconds.
- File Format: MP4, Quicktime, AVI, ASF, Windows Media, or MPEG.
- Resolution:
- Horizontal: 640 x 360px
- Vertical: 480 x 360px
In-feed Ads
- Description: Show alongside YouTube content, like search results or the Home feed.
- Resolution:
- Horizontal: 1920 x 1080px
- Vertical: 1080 x 1920px
- Square: 1080 x 1080px
- Aspect Ratio:
- Horizontal: 16:9
- Square: 1:1
- Length:
- Awareness: 15-20 seconds
- Consideration: 2-3 minutes
- Headline/Description:
- Headline: Up to 2 lines, 40 characters per line
- Description: Up to 2 lines, 35 characters per line
Display Ads
- Description: Static images or animated media that appear on YouTube next to video suggestions, in search results, or on the homepage.
- Image Size: 300×60 pixels.
- File Type: GIF, JPG, PNG.
- File Size: Max 150KB.
- Max Animation Length: 30 seconds.
Outstream Ads
- Description: Mobile-only video ads that appear on websites and apps within the Google video partner network, not on YouTube itself.
- Logo Specs:
- Square: 1:1 (200 x 200px).
- File Type: JPG, GIF, PNG.
- Max Size: 200KB.
Masthead Ads
- Description: High-visibility ads at the top of the YouTube homepage.
- Resolution: 1920 x 1080 or higher.
- File Type: JPG or PNG (without transparency).
Conclusion
YouTube offers a variety of ad formats to reach audiences effectively in 2024. Whether you want to build brand awareness, drive conversions, or target specific demographics, YouTube provides a dynamic platform for your advertising needs. Always follow Google’s advertising policies and the technical ad specs to ensure your ads perform their best. Ready to start using YouTube ads? Contact us today to get started!
MARKETING
Why We Are Always ‘Clicking to Buy’, According to Psychologists

Amazon pillows.
MARKETING
A deeper dive into data, personalization and Copilots

Salesforce launched a collection of new, generative AI-related products at Connections in Chicago this week. They included new Einstein Copilots for marketers and merchants and Einstein Personalization.
To better understand, not only the potential impact of the new products, but the evolving Salesforce architecture, we sat down with Bobby Jania, CMO, Marketing Cloud.
Dig deeper: Salesforce piles on the Einstein Copilots
Salesforce’s evolving architecture
It’s hard to deny that Salesforce likes coming up with new names for platforms and products (what happened to Customer 360?) and this can sometimes make the observer wonder if something is brand new, or old but with a brand new name. In particular, what exactly is Einstein 1 and how is it related to Salesforce Data Cloud?
“Data Cloud is built on the Einstein 1 platform,” Jania explained. “The Einstein 1 platform is our entire Salesforce platform and that includes products like Sales Cloud, Service Cloud — that it includes the original idea of Salesforce not just being in the cloud, but being multi-tenancy.”
Data Cloud — not an acquisition, of course — was built natively on that platform. It was the first product built on Hyperforce, Salesforce’s new cloud infrastructure architecture. “Since Data Cloud was on what we now call the Einstein 1 platform from Day One, it has always natively connected to, and been able to read anything in Sales Cloud, Service Cloud [and so on]. On top of that, we can now bring in, not only structured but unstructured data.”
That’s a significant progression from the position, several years ago, when Salesforce had stitched together a platform around various acquisitions (ExactTarget, for example) that didn’t necessarily talk to each other.
“At times, what we would do is have a kind of behind-the-scenes flow where data from one product could be moved into another product,” said Jania, “but in many of those cases the data would then be in both, whereas now the data is in Data Cloud. Tableau will run natively off Data Cloud; Commerce Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud — they’re all going to the same operational customer profile.” They’re not copying the data from Data Cloud, Jania confirmed.
Another thing to know is tit’s possible for Salesforce customers to import their own datasets into Data Cloud. “We wanted to create a federated data model,” said Jania. “If you’re using Snowflake, for example, we more or less virtually sit on your data lake. The value we add is that we will look at all your data and help you form these operational customer profiles.”
Let’s learn more about Einstein Copilot
“Copilot means that I have an assistant with me in the tool where I need to be working that contextually knows what I am trying to do and helps me at every step of the process,” Jania said.
For marketers, this might begin with a campaign brief developed with Copilot’s assistance, the identification of an audience based on the brief, and then the development of email or other content. “What’s really cool is the idea of Einstein Studio where our customers will create actions [for Copilot] that we hadn’t even thought about.”
Here’s a key insight (back to nomenclature). We reported on Copilot for markets, Copilot for merchants, Copilot for shoppers. It turns out, however, that there is just one Copilot, Einstein Copilot, and these are use cases. “There’s just one Copilot, we just add these for a little clarity; we’re going to talk about marketing use cases, about shoppers’ use cases. These are actions for the marketing use cases we built out of the box; you can build your own.”
It’s surely going to take a little time for marketers to learn to work easily with Copilot. “There’s always time for adoption,” Jania agreed. “What is directly connected with this is, this is my ninth Connections and this one has the most hands-on training that I’ve seen since 2014 — and a lot of that is getting people using Data Cloud, using these tools rather than just being given a demo.”
What’s new about Einstein Personalization
Salesforce Einstein has been around since 2016 and many of the use cases seem to have involved personalization in various forms. What’s new?
“Einstein Personalization is a real-time decision engine and it’s going to choose next-best-action, next-best-offer. What is new is that it’s a service now that runs natively on top of Data Cloud.” A lot of real-time decision engines need their own set of data that might actually be a subset of data. “Einstein Personalization is going to look holistically at a customer and recommend a next-best-action that could be natively surfaced in Service Cloud, Sales Cloud or Marketing Cloud.”
Finally, trust
One feature of the presentations at Connections was the reassurance that, although public LLMs like ChatGPT could be selected for application to customer data, none of that data would be retained by the LLMs. Is this just a matter of written agreements? No, not just that, said Jania.
“In the Einstein Trust Layer, all of the data, when it connects to an LLM, runs through our gateway. If there was a prompt that had personally identifiable information — a credit card number, an email address — at a mimum, all that is stripped out. The LLMs do not store the output; we store the output for auditing back in Salesforce. Any output that comes back through our gateway is logged in our system; it runs through a toxicity model; and only at the end do we put PII data back into the answer. There are real pieces beyond a handshake that this data is safe.”
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle’s Revamped Documentation Shows 4 Reasons To Refresh Content
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: August 26, 2024
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Ranking Bug Fixed, August Core Update Swings, AI Overviews, Google Ads Bug & More
-
SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: August 27, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoHow to Secure Your WordPress Store
-

 AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days ago
AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days agoBusiness Owners are Batting 1,000 With This All-in-One Management Hub
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Migrating All To Google Merchant Center Next By September
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days ago9 Best Elementor Alternatives 2024 (Faster Page Builders)














