MARKETING
How To Protect Your People and Brand

Your lack of social media guidelines could discourage employees from becoming brand advocates and even applicants from joining your company. I speak from personal experience.
When I first joined LinkedIn, my profile said I worked for a “Bay area Fortune 500 financial services company” instead of noting its name and linking to the company page. Soon, many of my colleagues’ profiles said the same thing.
You see, our organization was trying to figure out its social media policies within the confines of a highly regulated industry. It blocked access to any website with a social component — including YouTube. When employees were asked about using social media on their own time and devices, the company’s initial guidance was they didn’t want them using social media at all.
Well, that wasn’t going to happen. Instead, thanks to lengthy conversations with my legal and compliance colleagues, I hit upon a solution: I scrubbed any mention of my employer in all my public profiles.
Why employee social advocacy matters
Why do employee brand advocates matter? Because people are increasingly wary and distrustful of brand and government claims and prefer input from their peers.
The Edelman Trust Barometer underscored this message. In its 2024 iteration, it found people were concerned that the media (64%) and business leaders (61%) are purposely trying to mislead people by saying things they know are false or gross exaggerations.
This shift in trust becomes a competitive advantage for brands that cultivate thousands of eager brand ambassadors, but this requires documented employee social media guidelines to not only allow your team members to thrive on social but to protect your brand from legal risks.
Take a responsible approach to workplace social media policies
Whether you like it or not, employees will talk about your company on social media, and it’s their federally protected right to do so.
Many businesses react with fear and develop extensive restrictions around what employees can or cannot say online in their company social media guidelines. They require employees to agree to a list of don’ts and end the conversation.
However, innovative companies increasingly prioritize employee advocacy, seeing both employee retention and bottom-line advantages. A recent case study showed tech leader Salesforce activated about a third of its 73,000-person employee base as brand advocates, resulting in a 2,000% ROI on its social ambassador program.
Social media guidelines for employees serve as guardrails for online activity and show employees you want them to be engaged online, helping to build on your company’s social media success.
Follow the essentials for your guidelines
The length of your company’s social media guidelines is less important than their accessibility and quality. Ensure any employee can understand the guidelines. Create one-pagers or cheat sheets for specific activities, like training or unique campaigns.
At a minimum, all employee social media guidelines should include the following elements:
- Brand’s purpose on social media — Document the brand’s purpose for each social platform. Whether for recruitment, content amplification, customer advocacy, etc., the guidelines should explain why the company exists on each channel and how employees can support that purpose.
- Company style guide — List any trademark needs and spelling of company products and services so that employees correctly present the brand. You should also define your brand personality and any language considerations.
- Access to shared brand asset folder — Create a central folder employees can access for company logos, how-to’s, shared FAQs, branded profile headers for social sites, and more. Consider creating a list of preferred hashtags and their purposes, especially with company hashtags such as Dell’s #IWorkForDell or IBM’s #ProudIBMer. Keeping this information in one place increases the likelihood that employees will stay on brand.
For a deeper look at these areas, including resources to help you define your social media goals, check out my article, Why Social Media Guidelines are the Key to Unlocking Employee Brand Advocacy.
Use guidelines as a brand defense
The stakes can be high for enterprises when employees use their social media channels in unapproved ways, and savvy companies know the importance of developing extensive social media guidelines.
Get ahead of potential issues and address these all-too-common social media pitfalls in your employee social media guidelines:
- Legal concerns — Make it incredibly clear at the start of all projects what is and is not approved for social sharing. Also, while many people differ on the use of “views-are-my-own” disclaimers, large enterprises should discuss whether they want employees to have such a clause on their accounts.
- Unsanctioned brand accounts — When your company spans your country or the globe, employees may create localized accounts. Address this by listing all official corporate accounts in your social guidelines and asking team members to use only those for brand-related matters.
Consider having a social media request form that allows employees to suggest new accounts or content. This way, their enthusiasm can be better harnessed with a conversation versus an email request to delete the rogue account.
- Departed employees — As employees move on to different career opportunities, they may forget to update their profiles to note they are no longer with your company. This could cause confusion when they start posting content about their new companies or when customers search LinkedIn for staff. While you cannot force individuals to change their social account information, you can at least make the request a part of the exit or off-boarding process.
Enterprise social media guidelines examples
Many brands make their company’s social media guidelines public. These examples can serve as great models for your company’s guidelines. Keep in mind, though, that these are just public-facing documents. The organizations may have more expansive guides for internal audiences.
Each of these three examples has unique elements, but they boil down to address the same point — not everyone knows how to act online.
- Stanford University: These extensive guidelines have a small yet informative section on an individual employee’s social media use. The main points cover how employees are responsible for what they say on social and how they should think about how their social engagement may affect the organization’s reputation. While this may seem general, the policy also links to the university’s information security and privacy policies. What truly sets this social policy apart is its thoroughness in discussing using social on behalf of the organization.
- IBM: What stands out in this guide (no longer available on IBM’s public site) is that employees are clearly encouraged to engage in industry conversations online and have their own blogs. “Bring your own personality to the forefront” is part of the company’s guidelines, with the necessary caveat to not use offensive or harmful language.
- Dell: This policy is distilled into five easy-to-digest bullet points for employees and directs them to the Dell social media team email for additional questions. It tackles the issue of rogue accounts, noting that an account created for Dell may be considered Dell property and that accounts cannot be created to ride on the success of Dell’s corporate accounts.
Educate employees on the social media guidelines
As part of every employee’s onboarding, a member of the social team should discuss the company’s social media policies and guidelines and help any new hires set up their channels in a brand-relevant way.
To maintain and grow awareness of the company’s social media policies, get creative:
- Host lunch-and-learn conversations. These informational meetings allow employees to enjoy their food while you discuss topics relevant to your company’s social media channels. If your company has multiple offices, hold a video meeting. Record the conversation to provide a playback file for those who cannot attend.
- Post social media office hours. If employees are hesitant to ask questions during meetings or regular day-to-day operations, give them a safe place for in-depth, one-on-one time by hosting regular social media office hours. This strategy establishes your social team as a helpful resource rather than the brand police.
- Send social media amplification emails. Email employees regularly to share content you want them to amplify. Include suggested text for easy plug-and-play for busy employees. You cannot rely solely on email, though, as internal emails have an average open rate of 76%.
- Create a social media Slack or Teams channel. If Slack or Microsoft Teams is where work happens in your organization, share all your social content there as well.
- Hold employee meetings. Create regular update/reminder slides employees can include in presentation decks during company all-hands, all-team meetings, or individual group or office meetings.
- Use the company intranet. An intranet can be a great resource for increasing productivity and distributing information to employees. Share updates to the social media policies and use it as a hub for all your social resources.
- Develop training videos. With more internal resources available, enterprises can explore using video to educate employees on topics related to social. Research has found that viewers retain 95% of a message when they watch it in a video compared to just text, so the time commitment to create a video could pay off in message retention.
Continue success with employee social media guidelines
In addition to the core company social media guidelines, ensure that employees can access the brand voice so they can mirror your brand’s language and engage with content that you think best emulates what you want to see your employees doing on social media platforms.
Ongoing monitoring and education are the keys to getting the most out of your guidelines. But with an eager brand advocate base on your side, you’re more likely to see the social ROI you need to achieve your goals.
Updated from a January 2020 article.
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
MARKETING
Profit More, Work Less: 4 Steps to Niching Down For Your Agency


Ever wonder what the most successful agencies did differently than everyone else?
Was it luck, skill, hard work, the industry they chose, or something else?
Through my consulting work at Revenue Boost, I’ve worked with and taught over 400+ agencies how to scale their business.
From this, I’ve seen consistent patterns & traits in the ones who grow effortlessly…
Versus the ones who stay stuck for years – no matter how hard they work.
One key difference in approach stuck out to me.
I’ll illustrate what this one difference was with a story.
Once upon a time…
Two marketers graduated from business school with big plans to start their own agency.
Ready to conquer the world, they started cold calling, cold emailing, and doing everything under the sun to get clients.
And although they had the SAME levels of work ethic and talent…
One of them now has an 8-figure agency.
The other one of them is still freelancing odd jobs, barely making ends meet.
What did the successful one do differently?
He took a big risk and started turning down clients and projects.
Instead of offering everything to everyone, like most agency owners…
And being a jack of all trades but a master of none…
He decided only to serve Plumbers and be the best dang’ plumbing marketer on the planet.
With a goal to make their pipeline fuller than a broken toilet pipe.


He mastered the art of niching down and realized it would be easier to be the biggest fish in a small pond.
And you should too – and in this article, you’ll learn exactly how to define your own niche.
Now it may seem scary to turn down clients…and it may feel like you’re limiting yourself by focusing on only one client-type.
But it’s exactly the opposite. You’re actually limiting yourself by being everything for everybody.
Niching Down Can Help 2x-3x Your Revenues
One of my clients Lauren ran a digital agency offering everything under the sun.
Social media, paid ads, web dev, SEO, and she offered it to clients from many different industries.
Because of this, her agency stayed stuck at $25,000 a month and she couldn’t break through.
On top of that, she and her team worked so much harder than they had to and operations were messy.
Every client needed different things, required customization, and nothing was standardized.
We sat together to audit all her past clients, and we found that Medical practices were her best clients.
They were easy to sell, stayed the longest, and gave her the least amount of headaches and complaints.
So, she changed her entire business model to ONLY service this industry.
Then, she developed a standardized offer for that industry, rather than customizing everything.
One offer, to one target market. Afterwards, she started cold emailing businesses in her niche with her new offer.
The Results?
She 2X’d her revenues and grew to $52,000 in monthly revenue in not even four months time.
All from making one simple shift. One decision that can make everything easier, and you can do the same.
See, most agency owners and marketers start out with one or two clients, and then they get referred new clients from various industries.
Before they know it, they’re marketing everything for everyone and have NO idea who their ideal client is.
The Problem with Running a Business This Way Is That It Becomes Impossible to Scale.
Every single new client requires a ton of research, thought, and brainpower.


Because each new client has different needs, it leads to having no standardized processes and systems.
Which keeps the founder stuck in the business and unable to hire a team.
The other problem that arises is acquisition.
There are hundreds of thousands of agencies on the planet, and it’s really hard to stand out.
UNLESS you specialize.
When you specialize in a niche – let’s say, SEO for plumbers…
Then you aren’t competing with every other agency on the planet. You don’t look and sound just like them anymore.
Now, you’ve created your own tiny pond in which you can be a big fish.
There are way fewer agencies that specialize in plumbers or SEO, let alone both. So, you’ve eliminated the competition with one decision.
If a plumber was looking at two agencies – one that was a general digital agency and one that specializes in helping plumbers…
They almost always choose the agency that specializes in their industry and has testimonials from people just like them.
Not to mention, it’s easier to market when you have a clear niche in mind.
You know who you’re writing your content for…
You know who to send emails and social media DMs too…
You know exactly who to target in your ads….
You know what podcasts you should get booked on
And so on and so on.
Plus, you can charge whatever prices you want. Because you aren’t compared to the hundreds of thousands of agencies out there – you have a unique offer now.
Committing to one niche makes marketing easier, it makes selling easier, and it makes scaling easier.
You only have to be good at doing 1 thing for 1 person, and you can build systems and processes around it. This way, you can hire a team to take it over and be able to work less.


Become a Certified Analytics & Data Master
At Last, You’ll Have A Powerful Analytics Dashboard That Will Help You Make Smart Business Decisions
Now how do you do it? What if you don’t know who your ideal client is?
Step 1: Audit Your Current + Past Client List.
Write down every single client you’ve ever served, and group them by niche. Industry, location, size and so on.
Once you group them together, one niche might stick out for you already as your favorite type of client.
If it doesn’t, use my 7-Point checklist and rank each niche on a 1-5 scale.
These 7 criteria points are what makes a great niche.
#1 – Total Addressable Market:
How many businesses are in this market? Is it large enough to support your bigger goals? Is the market shrinking or growing? Make sure the niche is big enough for you and that it’s not declining.
#2 – Purchasing Power
Is this market (or at least a segment of it) able to afford what you want to charge?
Think back to if you’ve received a lot of pricing objections when you’ve sold to these people in the past.
#3 – Lifetime Value
How long did these clients stay? Were they one-and-done projects or did they stay with me for eternity?
The bigger the life-time value, the more money and time you can spend to acquire a client.
If the niche typically churns in a few months or only works with you for quick, one-off projects…
Then you’ll have to spend so much energy on sales and marketing to keep the business alive.
#4 – Strong Need & Pain
Does this market have an important problem to solve, one that they have to fix? Or, is what you sell just a “nice to have”?
If the latter, it’s going to be very hard to get clients.
If they can’t live without your solution, then getting clients will be a breeze.
#5 – Desire to Solve that Pain
It’s one thing for a market to have a problem, but they must also have a desire to solve that problem.
Even if they have the need that you fulfill, that’s not enough – they also have to care about fulfilling that need.
#6 – Easy to Reach
Is the market fairly easy to find online? Can you reach them via most advertising platforms and social channels? Are their groups and communities online?
If you’re targeting businesses that are hard to reach online, you’re creating one extra barrier to your success.
Step 2: Choose 1 Niche After Ranking Each of Your Past Clients.


Tally up all the rankings and pick the 1 with the highest score.
Don’t worry about making the wrong decision.
Consider this an experiment.
You aren’t married to your new niche, you can always change back in a few months if it doesn’t work out.
Step 3: Create a Pre-Packaged Offer for Your New Niche
The whole point of niching down is to create more focus and simplicity in your business
Part of this is about WHO you sell, part of this is about WHAT you sell them.
Start out by choosing 1 problem to solve for them, and 1 solution to that problem.
List out what the deliverables will be and what you want to charge.
Keep it simple! You can build upon this later.
Step 4: Test the Waters and Go Land 5 New Clients.
Before you make any drastic changes to your business, such as letting go of clients, changing your branding and website…
Test the waters first, and verify if this new niche is the direction you want to go.
Go land another 5 clients or so, and that’ll be enough to identify if these are really our ideal clients or not.
You might think they are at first but you’ll know for sure once you serve more of them.
Wrapping Up…
You know now the problems of being a jack-of-all-trades with no clear focus.
Every new client is a ton of work and requires customization…
And getting new clients is difficult because there’s nothing that stands out about your agency. You’ll look and sound like everyone else.
This means when you do niche down, and sell 1 offer to 1 target market…
Your workload will decrease. Each new client will be easier to serve than the previous one.
You’ll become world-class at helping your clients from all the focused repetition
You’ll quickly develop a reputation and become a big fish in a small pond.
In every way, it’ll become easier to grow, scale, attract, and retain clients.
Plus, you’ll have more fun and the business will be simpler & easier to run.
And with this knowledge…
You’ve learned the 5 simple steps to niching down.
So…
Time to get to work!
Put this into practice and watch it transform your business.
MARKETING
Unlocking AMC Insights Series: Leveraging Media Overlap Analysis for Enhanced Conversions

In today’s data-driven marketing landscape, the ability to ask the right questions is paramount. Amazon Marketing Cloud (AMC) emerges as the magic 8-ball of advertising solutions, offering advertisers a robust platform for precise analytics and strategic decision-making. If you’re new to AMC, it’s a secure, privacy-friendly, dedicated cloud-based measurement and analytics solution introduced in 2021.
Understanding the Value of Amazon Marketing Cloud
Built on Amazon Web Services (AWS), AMC provides a flexible environment that empowers advertisers with customizable reporting capabilities based on event-level data across various data sets. These data sets can encompass both advertiser data and Amazon Advertising data, granting advertisers a comprehensive view of campaign performance. In essence, AMC equips advertisers with transparent, cross-channel data essential for making informed marketing decisions, a necessity in today’s marketing landscape.
For a comprehensive understanding of AMC basics, Tinuiti’s AMC overview provides all the essential information about the Amazon Marketing Cloud.
This article marks the first of a 3-part series where we dive into specific AMC use cases. In this installment, we focus on the Media Overlap analysis, guiding you through utilizing this report to address critical business questions, pinpoint key metrics, and strategically apply derived insights.
What is the Media Overlap Analysis?
The Media Overlap analysis determines the collective impact of Amazon ads and isolates the incremental impact of a specific media type. The metrics provided by this report analyze reach and performance across a full-funnel strategy, including DSP Display, Streaming TV, and Sponsored Ads.
To utilize this report, it is required to have data from at least two of the aforementioned ad types in a single AMC instance. The same products must be advertised in each ad type, and each ad product must have been running for at least one week during the same time period. It is recommended to wait 14 days after the query’s end date to use this analysis to capture all conversions due to Amazon’s 14-day attribution window. This use case is designed to help answer business questions surrounding how to best leverage the array of Amazon Ad products.
Here are a few examples of the types of questions the Media Overlap analysis addresses:
- When shoppers are exposed to any combination of Display, Streaming TV, Sponsored Ads, what is the impact on conversion rates?
- What impact does each ad type have on conversion beyond ROAS or last-touch attribution?
- What is the average order value when shoppers are exposed to a combination of ad types?
The following metrics tend to be the most useful in addressing the business questions above:
- Purchase rate: Percentage of unique users who purchased at least one time compared to unique users reached
- Reach: Number of unique users reached
- Users that purchased: Number of unique users who purchased at least one time.
- Purchases: Number of times any amount of a promoted product or products are included in a purchase event. Purchase events include video rentals and new Subscribe & Save subscriptions.
- Order value: Total amount resulting from a single purchase event
Below is a sample case study used to address the following question: When shoppers are exposed to any combination of Display, Streaming TV, Sponsored Ads, what is the impact on conversion rates?
Here is an example of a what a finalized report looks like:
Top 7 Media Type Mixes based on Purchase Volume (CE Advertiser)
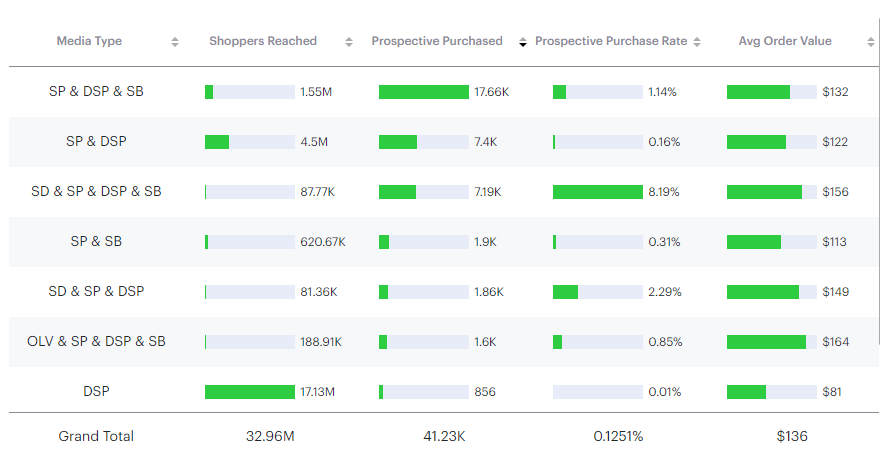
To answer the original question, the key metric to review here is the Prospective Purchase Rate (PPR). When exposed to fewer than three ad types, the PPR is significantly lower. However, when exposed to three or more ad types, the PPR increases. For users who were exposed to Sponsored Display (SD), Sponsored Products (SP), Demand Side Platform (DSP), and Sponsored Brands (SB) ads, the PPR was 8.19%, demonstrating the correlation between the number of ad types shoppers were exposed to and an increased Prospective Purchase Rate.
As a result of these findings, two prominent potential opportunities to improve performance emerge:
- Continuing to invest, or increasing investments, in DSP and video as they are key drivers in a user’s path to conversion. The advertiser should diversify their media mix with these ad products.
- Due to the correlation between Sponsored Products ads in combination with other ad products and higher conversion rates, there is an additional opportunity to build an AMC audience retargeting SP clickers. This will ensure advertisers are capitalizing on shoppers moving through the lower to upper funnel in their shopping journey.
AMC’s Media Overlap Analysis: Key Takeaways and Next Steps for Enhanced Conversions
AMC’s Media Overlap analysis highlights the impact of middle and upper funnel ads on conversion rates. Tinuiti’s teams observe many brands prioritizing Sponsored Products due to their perceived low risk and high returns under Amazon’s last-touch attribution model. However, this approach overlooks the influence of other ad types. Data from this analysis underscores the effectiveness of a holistic strategy. While a Sponsored Products ad may lead to a sale, it doesn’t consider other ad exposures that shape purchase decisions. The Overlap analysis underscores the value of a full-funnel strategy and the impact of DSP media on overall performance. Advertisers should consider adjusting budget allocations to DSP and streaming video based on these insights.
Furthermore, a full-funnel strategy can drive higher average order value.
The average order value significantly increases when exposed to a media mix of three or more ad types. While each advertiser should analyze their own business, Tinuiti consistently observes that users exposed to a greater number of ad products typically correlate with higher conversion rates and higher order values.
The Media Overlap analysis is part of the Instructional Query Library (IQL), which offers pre-built templates by Amazon to get started with the basics. If you’re seeking deeper insights with the guidance of experts who understand AMC’s unique landscape, reach out to Tinuiti today.
Liked this article? Don’t miss Part 2 of our AMC use case series on Tinuiti’s blog next month!
This post was authored by Averie Lynch, Specialist of Strategic Services at Tinuiti.
MARKETING
Introducing Variation Generator for Web Experimentation

If you attended Opticon ’23, you saw first-hand how Optimizely has been investing in AI. Optimizely introduced Opal, an AI assistant designed to accelerate the entire marketing lifecycle. Opal is ever-present across Optimizely One, providing generative AI, smart insights, and recommendations to transform how our customers create, test and personalize digital experiences.
Now, our latest AI capability is here: Variation Generator. Available for all Web Experimentation customers, Variation Generator helps experiment authors expedite the ideation and creation of test variations.
What does it do?
Variation Generator leverages generative artificial intelligence to create a list of phrasing suggestions based on a site’s text elements like headlines, product descriptions, or call-to-action (CTA) wording, ultimately making it easier and faster for experimenters to plan multiple variations for their tests, which can be quite time-consuming.
Who is it for?
Based on our research, around 30% of experiments include text changes. So, experiment authors like optimization managers or digital marketers are spending a lot of time ideating/brainstorming multiple versions of the original copy to decide which should be tested. Variation Generator empowers users to add more variations in an experiment, which we strongly suggest after our Experimentation Benchmark research found that experiments with more variations (4+) tend to see higher win rates and return higher uplifts on the metrics tracked.
Cool…but generative AI is popping up everywhere, why does it matter here?
- Directly embedded into our UI: No separate tools or tabs to click out to…No typing out a prompt to a chatbot…just click the text element you want suggestions for, and click “generate.” All interaction stays within our Visual Editor.
- Reduce time and effort in variation ideation: Shorten the time it takes to come up with new experiment variations, allowing experiment authors to get more time back into their day.
- Optimize each variation in an experiment: Variation Generator provides unbiased and creative alternatives to experiment authors so they can make sure that each variation is different enough to avoid duplicative messaging, yet effective enough captures visitors’ attention.
- Increase a test’s chances of winning: Our Benchmark research shows that experiments with 4+ variations are ~90% more likely to win than experiments with just 2 variations. Variation Generator helps experiment authors create more variations, leading to higher lifts.
- Fine-tune brand positioning: Improve existing headlines, product descriptions, CTA buttons, and more, ensuring a consistent and impactful brand message across digital properties.
Increase a test’s chances of winning
This outcome is important enough to highlight a second time. Mentioned earlier, we know from our Experimentation Benchmark research that tests with more variations (4+) are more likely to produce a winning (statistically significant) result versus a traditional A/B test that pits a baseline (original version) against a single variation. Variation Generator can help experiment authors get into the habit of testing more variations and producing more winning results.
Future enhancements
Optimizely is committed to continuous innovation and improvement. Potential enhancements for Variation Generator include generating suggestions for other content types like images, icons, HTML, and CSS, as well as giving users more control over output fine-tuning, such as adjusting length, tone, and other fields.
At the end of the day…
Optimizely’s Variation Generator is a simple yet powerful feature that empowers experiment authors to create more effective and winning experiments. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, this feature saves time, optimizes variations, and fine-tunes brand positioning, ultimately leading to better results, stronger brand presence, and an effortless workflow.
Want more info? If you’re an existing customer, ask your account manager about Variation Generator, and if you’re a future customer, contact us to learn more.
-
 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days ago18 Events and Conferences for Black Entrepreneurs in 2024
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoIAB Podcast Upfront highlights rebounding audiences and increased innovation
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoGoogle Ads Benchmarks 2024: New Trends & Insights for Key Industries
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoWhy Google Can’t Tell You About Every Ranking Drop
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoHow To Use ChatGPT For Keyword Research
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days agoThe Ultimate Guide to Click Fraud
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago86 Summer-Ready June Content Ideas
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago56 Google Search Statistics to Bookmark for 2024














