MARKETING
What It Is and How To Increase It

Is your website ready to attract and convert mobile website visitors into leads?
According to Adobe, companies with mobile-optimized sites triple their chances of increasing mobile conversation rate to 5% or above.
If that’s not enough to sell you on the importance of delivering a mobile-optimized experience, Google recently announced that more Google searches take place on mobile devices than on computers in 10 different countries including the United States and Japan.
All this talk of mobile got me thinking about how website visitors were accessing our offers. And after a closer look, I discovered that conversion rates on our landing pages were 20-30% lower from visitors coming from mobile. (As a lead generation geek, you can imagine how psyched I was to uncover such a huge opportunity for gathering more leads.)
With this information in tow, I set out to solve this problem — and I think you’ll be intrigued by what I found.
The Methodology
The hypothesis of this experiment was that by making content more easily digestible on mobile devices, it would increase conversion rate. However, getting inside the heads of our mobile visitors took a bit of reflection. I had to ask myself, “What would cause someone to bounce?”
Some answers I came up with were:
- The form is too long.
- There is too much text on the landing page to read.
- The design isn’t formatted for a mobile phone.
When presented with information that is not super mobile-friendly, a visitor won’t hesitate to bounce from your landing page.
Why?
Not only are poorly formatted pages time-consuming, but they also don’t appear very reputable, which often causes visitors to lose trust. With that decided, we knew we needed a way to condense all the information on the landing page to fit the size of a mobile screen.
The Experiment
To give you a better idea of what we were working with, check out what our landing pages looked like initially:

As you can see, it was quite long with a lot of content. So in order to improve the user experience on these landing pages, we leveraged smart content to shorten the display for mobile users. (To learn more about how smart content works, check out this resource.)
The first step we took was shortening the content and formatting the images for mobile:

Once that was completed, we tackled the form:
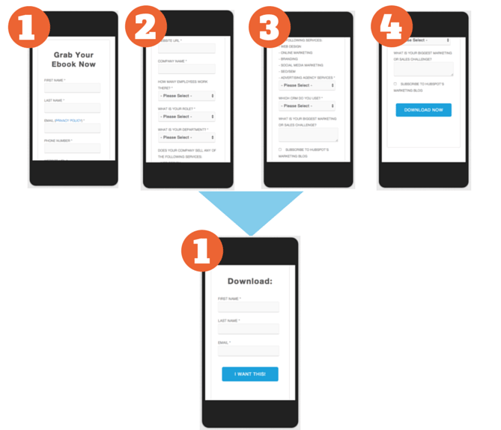
Voilà! With the help of smart content, mobile visitors are now shown a shorter, more digestible form.
The Analysis
With the changes in place, we decided that measuring the page’s bounce rate would help us determine if the mobile smart forms helped improve our conversion rates. Essentially, bounce rate refers to the percentage of people who only viewed a single page — it’s the number of people who visit our landing page and then “bounce” without converting on a form.
For this experiment specifically, we needed to figure out how many people filled out the form that came from a mobile device. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how we approached this:
- We used Google Analytics to find the number of “new users” to hubspot.com. I measured new people to hubspot.com on mobile (and not repeat visitors) because existing people in our database would not be net new prospects (which is what I’m solving for).
- I used HubSpot to determine the number of new prospects from the mobile smart form.
- I calculated the conversion rate using the following formula: Conversion Rate = New Prospects / New User PVs
- I calculated the bounce rate using the following formula: Bounce Rate = 100% – Conversion Rate
The Results
Results from Mobile Smart Form Test
By switching to mobile smart forms, we managed to decrease bounce rate (and therefore increase conversion rate) on each landing page tested by an average of 27%. Bounce rates that were previously between 50-90% are now between 20-50%.
Visitors now have a smoother experience and are less likely to leave the page before viewing and completing the form.
Results from Mobile Optimized Content Test
After optimizing the mobile smart forms, we tested shortening the content and optimizing the images for mobile. This produced a 10.7% decrease in bounce rate. (We expect this number will keep decreasing with continued optimization.)
The Takeaways
Through this experiment, I learned to solve for the user. I also learned the importance of placing myself into the shoes of the user to better determine why and how conversions happen (or don’t happen) in the first place.
While marketers don’t always think of UX, this experiment proved that there is no denying its importance. If your website is slow to load, visitors might leave. If the user has to scroll through six screens worth of content to reach a form, they might leave. If the form they arrive at has 10 tiny fields, they might leave.
See my point here? To improve the odds of a conversion actually taking place, always solve for the user.
MARKETING
Tinuiti Recognized in Forrester Report for Media Management Excellence

Tinuiti, the largest independent full-funnel performance marketing agency, has been included in a recent Forrester Research report titled, “The Media Management Services Landscape, Q2 2024.” In an overview of 37 notable providers, this comprehensive report focuses on the value B2C marketing leaders can expect from a media management service provider, and analyzes key factors to consider when looking for a media management partner such as size and business scenarios. B2C marketing executives rely on media management services to:
- Augment the efficacy of media investments
- Bridge media impressions to commerce transactions
- Enhance ad campaigns to drive performance
Report authors, VP, Principal Analyst Jay Pattisall and Senior Analyst Nikhil Lai call attention to the pressing need for providers to prove their value, deliver profitable ROAS, and drive alignment between CMOs and CFOs and thus liberate strained marketing budgets.
Our Always-On Incrementality tool – which is a part of our patented tech, Bliss Point by Tinuiti – empowers marketers to validate the incrementality of their spend on each ad set, media channel, and marketing tactic so marketers can create stronger, more focused campaigns that get the job done without sacrificing the bottomline.
B2C marketing leaders often seek and expect key business scenarios from media management service providers including media measurement and attribution, data strategy, and marketing mix modeling. MMM’s adaptability to the post-cookie/ post-IDFA world positions it as an essential tool for marketers. As businesses seek to connect the dots, leverage data, and make strategic decisions, MMM is a crucial ally in the dynamic realm of mixed media advertising. Our Rapid Media Mix Modeling sets a new standard in the market with its exceptional speed, precision, and transparency.
According to the Forrester report, “46% of senior B2C marketing and advertising decision-makers say they plan to integrate performance and brand media assignments with a single media agency in the next 12 months…”
In our quest to better understand all revenue-driving aspects of a given campaign, we have started on a process to quantify the impact of Brand Equity, which we believe is one of the largest missing pieces in more accurate and complete measurement.
Learn more about Bliss Point by Tinuiti, our use cases, and our approach to performance and brand equity.
The Landscape report is available online to Forrester customers or for purchase here.
MARKETING
Let’s Start Treating Content More Like We Treat Code

The technology space is pretty obsessed with preventing code defects from getting to production. We take great pains to make sure that a mistake doesn’t make it from the developer’s fingertips all the way through to the product system.
There’s an entire field called DevOps (short for “development operations”). This is something like a $5 billion industry. There are entire market segments filled with companies that tightly control the movement and testing of code.
Search for “DevOps diagram” sometime. You’ll be amazed at what you find—detailed schematics showing exactly how code should be copied, packaged, tested, and deployed. Developers who don’t have an artistic bone in their bodies suddenly turn into Da Vinci when describing in exacting detail how they want to orchestrate code deployments.
All of this is in search of one goal: prevent bad code from reaching production. A lofty goal, to be sure.
…but why don’t we care so much about content?
Where we have majestic acrobatics on the code side, when it comes to content, the process is usually something like, “Well, Alice writes something in Word, then emails it to Bob, and he copies it into the rich text editor” then presses publish.
Congratulations, you have the tightest, most reliable codebase serving up terrible content. A+. Great job.
Content defects are a thing, and we don’t do enough to prevent them. In particular, we don’t look at content development as a process to be managed. We think it’s some kind of magic, not a flow of work with checkpoints, trackable assignments, and review gateways. We’re somehow convinced this would take the “soul” out of it or something.
So, while our developers get six figures worth of toys to make sure they can swap every line of code instantly without spilling their coffee, our content creators are copying and pasting things into Slack and yelling “I swear sent that to you last week!” over the cubicle wall.
We need to do better.
Content creation isn’t magic—no more than code is magic. It’s a process that can and should be managed just like code deployments, and it deserves the same level of regard.
Your content creators need:
- Library services. Your developers have source code management. They know where code is, all the time. They probably have versions of it dating back to when they were teenagers. These things exist for content as well—they’re called content marketing platforms (CMPs) and digital asset management systems (DAMs). They’re designed to store, organize, and version content assets so creators know where everything is.
- Change management, in the form of editorial calendaring. Your developers know when code will be released (note: don’t do it on Fridays). They plan these things long in advance. But ask a content creator when Content Item X for the new campaign is launching, and they can only say something like, “I don’t know. I showed it to Bob. It’s in his court now…”
- Workflow. Developers have detailed ticket management systems that can tie their actions down to the exact line of source code they changed to resolve a defect. These systems exist so that everyone knows, at all times, who is responsible for what. Meanwhile, the content editors can only shrug when someone asks who was supposed to edit the CEO’s blog post that she just announced from the keynote stage.
- Content preview. I promise you that your development team has a graduated system of environments where they test code. They probably spend hundreds of hours maintaining it, so they can run code in isolation and know exactly how it works before they deploy it. Think of that fondly next time when your image caption is published in 30pt bold-faced font because no one told you that it wouldn’t be. (Incidentally, I’ve been thinking about preview a lot lately.)
Here’s why this is important:
Content defects matter. They can be far more damaging than code defects, while being so much harder to detect. By the time you realize something is wrong, the problem may have been existing in public for a long time, doing a lot of damage.
Imagine that you have a software company, and you’ve been trying to get an analyst to include your software in one of their reports. Your Analyst Relations staff has been consistently courting, cajoling, and hinting to this analyst that your software fits their segment exactly, and would be a great addition to the report.
The analyst finally decides to check things out. They go to your website, looking for evidence of all the things you told them about. They expected to find reinforcement of that information, that energy, that…vibe.
But, they didn’t. Their experience fell flat. They gave you a 20-minute chance, but then clicked away and didn’t look back.
Oh sure, you had plans. You were going to revamp that part of the website, and you had mentioned it to Gary just before he went on vacation. You heard some rumors that people were working on it, and some content got changed, but you never saw and never had a chance to guide it. Content development seemingly happened in a far-off land somewhere. Normally, when something changed on the website, you were as surprised as anyone.
This is a content defect. The whole thing. One big defect.
Why don’t we categorize like this? Why don’t we call it what it is?
Maybe because it’s not…binary? With code, things often either work, or explode spectacularly, so we can stand back and confidently say, “Yup, that’s busted.”
But with content, there’s a spectrum—there’s a range. People can look at it and say, “yeah, that’s fine” even when it’s not.
The only solution here is process. You need a way to make sure that content is seen by the right people, and at the right time, and has a way of reflecting the right input.
This happens with code all the time. We handle code exactingly, rigorously, and with due process and care.
We need to demand the same for content. And we need to start acknowledging that poor content is a failure of process, a failure of planning, and a failure of tooling.
The tools are available to avoid this. We need to implement them and use them.
Interested in learning how Optimizely Content Marketing Platform can better support your content creation process? See how it works in this quick video.
MARKETING
Generative Engine Optimization Framework Introduced in New Research

There are several AI chatbot-like features available in the current search engines, including Bing Copilot, Google, Bard, and Gemini. They help to optimize the content visibility in the search results with the help of an AI-powered Search engine known as a Generative engine or AI Search.
A traditional search engine like Bing, Google, or Yahoo ranks and displays information in the SERPs based on the search terms a user inputs. 🔎
The generative engine, on the other hand, generates comprehensive, accurate, and relevant results and information with the help of Generative AI or Large Language Models (LLMs) such as chatGPT, Gemini, and Claude. They understand and integrate information from various sources for the user’s queries.
In this blog, We will discuss the GEO that is introduced in the new research, its framework, and how it can change traditional Search engine optimization (SEO) practices and optimize content for visibility.
The Key Components of the GEO Framework and How They Transform Traditional SEO Practices
GEO is described in the research paper as: “A novel paradigm to aid content creators in improving the visibility of their content in Generative Engine responses through a black-box optimization framework for optimizing and defining visibility metrics. We facilitate systematic evaluation in this new paradigm by introducing GEO-bench, a benchmark of diverse user queries across multiple domains, coupled with sources required to answer these queries.”
Traditional SEO depends upon the keyword volume, difficulty, and optimization for the specific search terms, which focus less on an interpretation relationship between the concepts of keywords or user queries. SEO practices prioritize text-based source content over other sources of content format where regular updating of fresh content is not a primary focus. Also, metrics like impression and click rates affect ranking system results in traditional methods.
GEO encourages detailed information over just the keyword, addressing the related main queries by creating depth content and potential subtopics with the understanding of concept and relationship, encouraging the other formats, such as visual, audio, and images, not just text-based. Moreover, it emphasizes the latest updated content information with continuous accuracy and relevance to provide the most accurate and up-to-date details.
The Impact of Introducing GEO on Website Ranking and Content Relevancy
A generative engine relies on traditional SEO practices like user intent and algorithms for ranking to a degree, such as keyword stuffing. Although it focuses on keywords, it tries to find connections and meanings beyond the keywords in order to create high-quality content.
GEO doesn’t directly indicate the web visibility or page ranking in the Search Engine Result Page. However, it can optimize the overall website visibility and indirectly drive user traffic to your websites through generated responsive data and information.
GEO-optimized content provides the AI Search or a Large Language Model (LLM) with reliable and completely detailed information, enabling them to generate the most accurate and relevant information for responses to user questions or inputs.
These AI-powered engines can deliver a vibrant user experience using optimized content for user engagement and interactive experiences. Furthermore, It also builds trust with a user as it relies on renowned and credible sources, which enhances the effectiveness and reliability of the generated response data and provides synthesizing information.
Comparison with Existing SEO Models: Why GEO Stands Out in Enhancing Search Engine Performance
GEO utilizes auto-generative algorithms for content generation based on predetermined objectives and standards where generated content can cover a broader range of keywords and related topics in various formats like image and visual.
A generative search engine uses modern optimization techniques that involve cognitive SEO, NLP (natural language processing), and structured data markup to maintain and improve content leverage, relevancy, and search engine visibility. In addition, it introduces new methods for determining citations’ importance and website visibility, as well as improving user-centric content by using impression metrics.
Traditional SEO models rely upon and use specific keywords to optimize and rank manually in search results. It uses traditional optimization techniques like link building, meta tags, and URLs.
In traditional search optimization, content creation and optimization can be slow and have low content scalability compared to AI-powered, requiring manual effort for generation and optimization. Constant monitoring and adaptation to platform algorithms are needed to produce the latest and updated information for dynamic user behavior.
Both are equally responsible for improving the brand or website’s online visibility; traditional SEO models require the manual touch for content creation and optimization. GEO tends to use generative responses automatically for content generation as per user queries, making it more effective for user-centric content creation, optimization, and stability in related topics or keywords.
9 Test research findings to improve the website content in GEO
The researchers from Princeton University, Georgia Tech, Allen Institute for AI, and IIT Delhi tested nine various GEO approaches to improve site content for generative engines. Techniques that have been tried and tested over 10,000 search queries, nine optimization strategies were tested on something that “closely resembles the design of BingChat”:

- Authoritative: The content was altered to be more compelling while conveying definitive claims.
- Keyword Stuffing: More keywords were added to match the query.
- Statistics Addition: Instead of a qualitative conversation, quantitative statistics were included.
- Sources: Relevant citations have been added. Like quotes statistics
- Quotation Addition: Quotations from reliable sources have been included.
- Easy-to-understand: Simplified the language.
- Fluency Optimisation: Improved fluency.
- Unique Words: Used in the text whenever possible.
- Technical terms: Technical terms have been incorporated into the content.
The data set for search queries was obtained from Google, Microsoft Bing, and Perplexity. Sources include AI Discover, GPT-4, and others.
So, focus on creating detailed and comprehensive blogs or articles by defining the relation and highlighting the context for deeper meaning. Utilize the various formats for content creation to enrich information and diversify the learning perspective.
Also, update your content with the latest information and trends to maintain regular effectiveness and relevancy in the generative engines.
Conclusion:
In the end, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) provides a more automated, scalable, and adaptive method of content creation and optimization than traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO) approaches, which need manual and constant work for the optimization and ranking. Compared to traditional search engines, generative engines give instant and detailed personalized information to users’ queries for improved engagement.
Conventional SEO uses metrics like impression, session duration, and click-through rate (CTR), whereas GEO proposes new metrics to measure the relevance and visibility of citations within generative engine responses, making users eliminate the need to visit individual websites for information as it generates the responses on users queries from the reliable, relevant, and various sources.
AI-powered search optimization is still developing and becoming popular since most users and business owners are using generative AI as their source of information and improved visibility with universally applicable diverse content formats.
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoNavigating the Video Marketing Maze: Short-Form vs. Long-Form
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 26, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 29, 2024
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoOffline For Last Days Of Passover 5784
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoMicrosoft unveils a new small language model
-
 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoThe Best Option for Online Stores
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoStudio By WordPress & Other Free Tools
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoHow to Promote Your Digital Marketing Agency: 4 Growth Strategies
















