The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
Gravatar “Breach” Exposes Data of 100+ Million Users

The security alert company HaveIBeenPwned notified users that the profile information of 114 million Gravatar users had been leaked online in what they characterized as a data breach. Gravatar denies that it was hacked.
Here’s a screenshot of the email that was sent to HaveIBeenPwned users that characterized the Gravatar event as a data breach:
![]()
I hate getting emails from this guy 😭 pic.twitter.com/rkZrmzU7hp
— Troy Hunt (@troyhunt) December 6, 2021
Gravatar Enumeration Vulnerability
The user information of every person with a Gravatar account was open to being downloaded using software that “scrapes” the data.
While technically that is not a breach, the manner in which user information was stored by Gravatar made it easy for a person with malicious intent to obtain user information which could then be used as part of another attack to gain passwords and access.
Gravatar accounts are public information. However the individual user profile accounts are not publicly listed in a way that can easily be browsed. Ordinarily a person would have to know account information like the username in order to find the account and all the publicly available information.
A security researcher discovered in late 2020 that Gravatar user account information was recorded in numerical order. A news report from the time described how the security researcher peeked into a JSON file linked in the profile page revealed an ID number that corresponded to the numerical number assigned to that user.
The problem with that user identification number is that the profile could be reached with that number.
Because the number was not randomly generated but in numerical order, anyone wishing to access the all of the Gravatar usernames could access that information by requesting and scraping the user profiles in numerical order.
Data Scraping Event
A data breach is defined as when an unauthorized person gains access to information that is not publicly available.
The Gravatar information was publicly available but an outsider would have to know the username of the Gravatar user in order to gain access to the Gravatar user profile. Additionally the email address of that user was stored in an insecure encrypted manner (called an MD5 hash).
An MD5 hash is insecure and can easily be unencrypted (also known as cracked). Storing email addresses in the MD5 format provided only minor security protection.
That means that once an attacker downloaded the usernames and the email MD5 hash it was then a simple matter for the user’s email address to be extracted.
According to the security researcher who initially discovered the username enumeration vulnerability, Gravatar only had “virtually no rate limiting” which means that a scraper bot could request millions of user profiles without being stopped or challenged for suspicious behavior.
According to the news report from October 2020 that originally divulged the vulnerability:
“While data provided by Gravatar users on their profiles is already public, the easy user enumeration aspect of the service with virtually no rate limiting raises concerns with regards to the mass collection of user data.”
Gravatar Minimizes User Data Collection
Gravatar tweeted public statements that minimized the impact of the user information collection.
Gravatar helps establish your identity online with an authenticated profile. We’re aware of the conversation online that claims Gravatar was hacked, so we want to clear up the misinformation. (1/4)
— Gravatar.com (@gravatar) December 6, 2021
Gravatar was not hacked. Our service gives you control over the data you want to share online. The data you choose to share publicly is made available via our API. Users can choose to share their full name, display name, location, email address, and a short biography.
(2/4)— Gravatar.com (@gravatar) December 6, 2021
Last year, a security researcher scraped public Gravatar data – usernames and MD5 hashes of email addresses used to reference users’ avatars by abusing our API. We immediately patched the ability to harvest the public profile data en masse. (3/4)
— Gravatar.com (@gravatar) December 6, 2021
The last tweet in the series from Gravatar encouraged readers to learn how Gravatar works:
“If you want to learn more about how Gravatar works or adjust the data shared on your profile, please visit http://Gravatar.com.”
Ironically, Gravatar linked to an insecure protocol of the URL, using HTTP. Upon reaching the URL there was no redirect on Gravatar to a secure (HTTPS) version of the web page, which only undermined their efforts to project a sense of security.
Twitter Users React
One Twitter user objected to the use of the word “breach” because the information was publicly available.
I think it was unfair of @troyhunt to classify that as a breach. It was screen scraping, they didn’t get anything that wasn’t already publicly available.
— Peter Morris #BlackLivesMatterToo (@MrPeterLMorris) December 6, 2021
The person behind the HaveIBeenPwned website responded:
That’s why it says “scraped data”. But you could also argue that “breach” is appropriate when the data is obtained and misused outside the intended scope with which it was provided.https://t.co/FwiqpUFSsp
— Troy Hunt (@troyhunt) December 6, 2021
Why Gravatar Scraping Event Is Important
Troy Hunt, the person behind the HaveIBeenPwned website explained in a series of tweets why the Gravatar scraping event is important.
Troy asserted that the data that users entrusted to Gravatar was used in a way that was unexpected.
Gravatar User Trust Eroded
The argument of “well, it’s public data anyway” is a view held by the minority. The vast majority of people consistently say “I didn’t expect my data to be used in this way and I’m unhappy it’s now out there and being passed around in this format”.
— Troy Hunt (@troyhunt) December 6, 2021
What can you actually do about it? People often request that the impacted service delete their data. That obviously doesn’t put the genie back in the bottle, but it’s a reasonable action once trust is eroded.
— Troy Hunt (@troyhunt) December 6, 2021
Users Want Control Over Their Gravatar Information
Troy asserted that users want to be aware of how their information is used and accessed.
At the very least, it’s awareness. I want to know – *most* people want to know – when our personal data appears in places we didn’t expect it to, and that’s precisely what @haveibeenpwned does.
— Troy Hunt (@troyhunt) December 6, 2021
Were Gravatar Users Pwned?
An argument could be made that a Gravatar account can be public but not easily harvested as Step One of a hacking event by people with malicious intent.
Gravatar asserted that after the enumeration attack vulnerability was disclosed that they took steps to close it to prevent further downloading of user information.
So on the one hand Gravatar took steps to prevent those with malicious intent from harvesting user information. But on the other hand they said reports of Gravatar being hacked is misinformation.
But the fact is that HaveIBeenPwned did not call it a hacking event, they called it a breach.
An argument could be made that Gravatar’s use of the MD5 hash for storing email data was insecure and the moment hackers cracked the insecure encryption, the abnormal scraping of “public information” became a breach.
Many Gravatar users aren’t particularly happy and are looking for answers:
Will you be publishing this info on your site?
People who received the Gravatr notice from Have I been Pwned will visit your site for the latest information.
I checked, there’s nothing on your site.
Gravatar users shouldn’t be forced to contact support for answers.
— Deborah Edwards-Oñoro (@redcrew) December 6, 2021
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
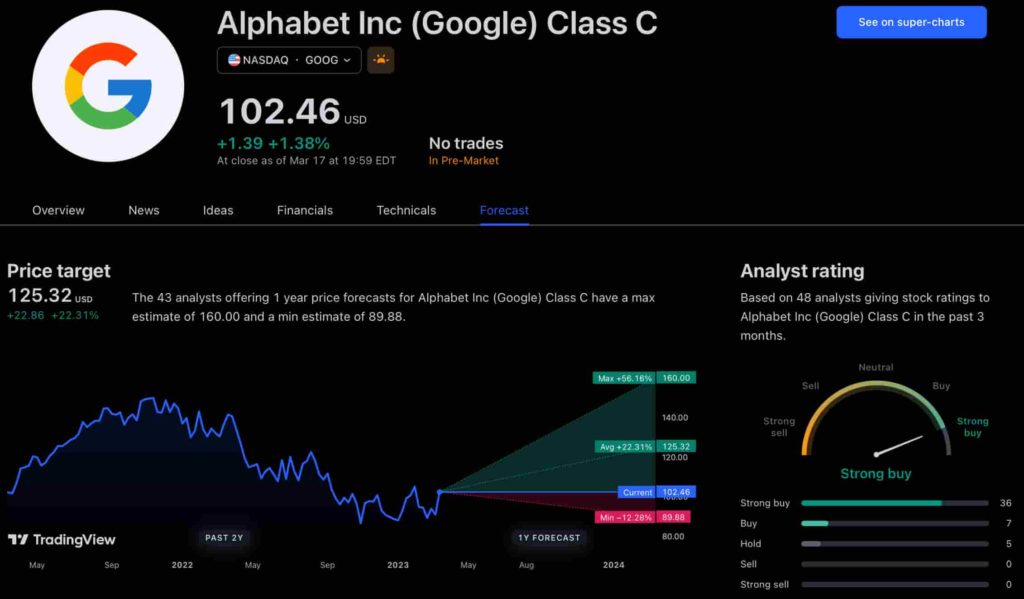
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress





![Astra Theme Coupon 2024 (Apr) [40% Discount, Save $400] Astra Pricing Plans on discounts](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/1713797772_611_Astra-Theme-Coupon-2024-Apr-40-Discount-Save-400-400x240.png)
![Astra Theme Coupon 2024 (Apr) [40% Discount, Save $400] Astra Pricing Plans on discounts](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/1713797772_611_Astra-Theme-Coupon-2024-Apr-40-Discount-Save-400-80x80.png)
![Elementor Pro Discount (Apr 2024) [70% OFF, Save $150] Elementor Coupon](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/1713729377_Elementor-Pro-Discount-Apr-2024-70-OFF-Save-150-400x240.png)
![Elementor Pro Discount (Apr 2024) [70% OFF, Save $150] Elementor Coupon](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/1713729377_Elementor-Pro-Discount-Apr-2024-70-OFF-Save-150-80x80.png)




You must be logged in to post a comment Login