SEO
On-Page SEO Checklist for 2024: A Comprehensive Guide

Want to make your pages rank high on Google? You wonât be able to do that if you donât know where or how to start your on-page SEO â and with each Google update, this pillar of SEO gets more and more complicated. To keep you updated with the best and most relevant practices when it comes to this aspect of your website, I have prepared an on-page SEO checklist for 2024.Â
On-Page SEO Factors
On-page SEO, in simple terms, is all the ways you can optimize your website take place on your website. Tweaking certain elements of your pages can enable them to climb very quickly up the ranks when done right. These elements include essentially everything you can see on your webpage, like its title tags, headers, and images.
Webmasterâs Note: This is part two of our SEO checklist series. Part one covers our technical SEO checklist, so go back if you havenât seen that yet. I also do deep dives into other aspects of on-page SEO in other articles, like the best content strategy for SEO, how to hack on-page factors, and ways to dominate niche keywords in your industry.
1. Identify Your Target Keyword
This is where any SEO effort should start. Identify which basic keywords you would like each page to rank for. From there, you can expand into common phrases, questions, and related words people use to find pages like yours through keyword research.Â
Key Aspects of Keyword Optimization:
- Keyword Research: Identifying the right keywords that your target audience is searching for.
- Keyword Placement: Sensibly incorporating keywords in titles, headings, the first paragraph, and throughout the content.
- Searcher Intent: Catering to why someone is performing a search, whether itâs to find information, make a purchase, etc.
Effective keyword optimization allows you to create pages that best meet user intent. This boosts your chances of ranking highly for your chosen keywords.Â
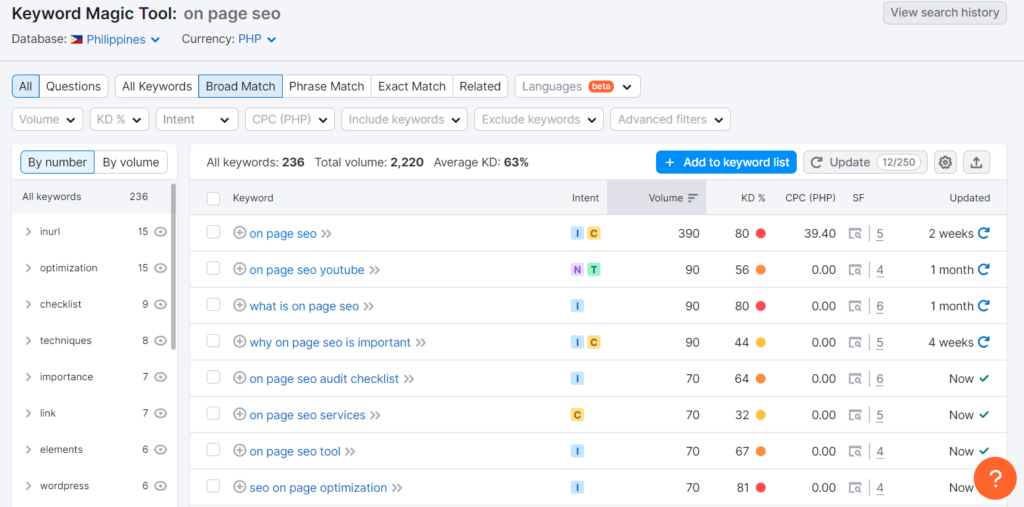

I have longer guides on the types of keywords you should look at, and another on how to do keyword research you can follow for this step.
2. High-Quality Content Creation
Quality content is the keystone of on-page SEO. It is, after all, fundamental to the selling point of Google â which is that it is the go-to place to find answers to your questions. Itâs why Google pushes Helpful Content Updates every so often.
So, your content must meet Googleâs standards of quality in order to make it to the top. To do that, your content must be authoritative, valuable to the reader, and deliver on the promises made by your meta tags and headings.
What Constitutes Quality Content:
- Originality: Your content must be unique and offer fresh insights.
- Relevancy: It should align with your target userâs intent and be updated regularly.
- Engagement: Content must encourage users to spend time on your site and interact with your offerings.
Creating content that exceeds user expectations can dramatically bolster your SEO as it can directly affect user engagement metrics and boost the credibility of your site.Â
Webmasterâs Note: Beyond making sure all new content is high-quality, however, is ensuring all of your existing content is also up to par. Iâll be covering that in part four of this series, so keep an eye out for that.Â
3. URL Structure
URLs are not only a ranking factor but also enhance the user experience when structured logically.Â
Features of an Effective URL Structure:
- Concise and Descriptive: A URL should be concise and explain your page content. No stop words.
- Keyword Inclusion: A relevant keyword can enhance a URLâs performance.
- Use Hyphens instead of Underscores: Conventional use dictates using hyphens to separate words.
A clear URL helps users and search engines make sense of the pageâs content before they even reach it.
Hereâs an example of a bad URL slug.Â


And hereâs an example of a good, optimized one.

4. Title Tag and Headings
I find that certain practices for these two elements give the most benefit to a pageâs SEO.Â
Best Practices for Title Tag and Heading Optimization:
- Use a Keyword-First Approach: Place keywords first in your title tag, as uninterrupted by stop-words as possible.
- Keep it Simple: Title tags should be concise to ensure the entire tag is displayed on the SERPs.
- Same Keyword, Different Phrasing: Use the same keyword in your title tag and heading 1. However, use different phrasing or wording for each.Â
- Insert Related Keywords: Do this for your heading 2, 3, and so on, where it makes sense.
- Avoid Duplicates: Use different title tags and headings for every unique page.
4. Meta Tags Enhancement
Meta tags, such as the meta description, serve as a brief pitch to users on search engine results pages. Other meta tags, like your image alt text and links, provide important context to both the user and crawlbot.
Tips for Enhanced Meta Tags:
- Compelling Copy: Write title tags and meta descriptions that accurately summarize the page content and entice clicks.
- Keyword Usage: Try to insert target keywords and/or related keywords effectively in your meta descriptions, and within the limit.
- Uniqueness: Each page should have unique meta tags.Â
- Be Descriptive: Your image alt text should not only include a related keyword but should also adequately describe what is seen on the image.Â
- Add internal and external links: Semantic search means Google can use the links in your pages to gain a better understanding of its content. Always add relevant internal links, and only include external links from trusted websites.Â
- Use Noindex Robots Meta Tag: Add this to prevent any pages with thin content, or pages with little value and no intent from appearing in the SERPs.
- Use rel=âcanonicalâ Link Tag: Use this for any duplicate pages you have on your website. Doing this can help you control which version of the page gets indexed and ranks for your targeted keywords.Â
- Set your Open Graph Meta Tags: This will let you optimize how your pages look when theyâre shared on social media.
- Set your Viewport Meta Tag: This configures how your pages are scaled and displayed on different devices and platforms, which is important for user experience (more on that later).Â
To get the most out of your SEO, donât neglect this part of your on-page SEO checklist. The small tweaks here can add up to the big picture.Â
Well-crafted meta tags have the potential to increase click-through rates, boost your visibility on organic search and image search, enhance user experience, and also distribute link equity throughout your pages. All these contribute to how well your page ranks.Â
5. Internal Linking
Internal linking spreads link equity throughout your site and can help search engines discover new pages. Always link back to pillar content, or other high-value content on your website.Â
Benefits of Strategic Internal Linking:
- Navigation: They guide users through other relevant pages on your website.
- Page Authority: Anchor text can help to convey what the linked-to page is about, which can aid in ranking for those terms.
- User Time on Site: Providing relevant links can keep users engaged on your site for longer periods.
Good internal linking can significantly increase your engagement rates and contribute to building a robust site architecture. I have a separate post on how to build topical authority through internal linking you can check out.
6. User Experience (UX)
User experience affects on-page SEO because search engines favor websites that provide a positive user experience.
UX Factors to Consider in Your Website Design:
- Mobile-Friendliness: The site must perform well across all devices â but especially on mobile-view, as most users use Google through their phones.
- Ease of Use: The site should be navigable and logical in its layout. Navigation bars and other menus should be intuitive and prioritize the most important pages of your website.
- Page Speed: Pages should load quickly to reduce bounce rates. Follow this guide to site speed optimization for this point.
As UX becomes an even more important ranking factor, I find it is necessary to add to this on-page SEO checklist. Sites that deliver a high-quality user experience will dominate search engine results pages.
Key Takeaway
Mastering this pillar of SEO is crucial for achieving high rankings on Google, and staying updated with evolving best practices is essential. But with every update, what works best changes.Â
My 2024 on-page SEO checklist provides basically the most up-to-date practices for the elements on your website. Follow it, and you should be able to boost your websiteâs authority, credibility, and long-term SEO performance.
SEO
Google Rolls Out New ‘Web’ Filter For Search Results

Google is introducing a filter that allows you to view only text-based webpages in search results.
The “Web” filter, rolling out globally over the next two days, addresses demand from searchers who prefer a stripped-down, simplified view of search results.
Danny Sullivan, Google’s Search Liaison, states in an announcement:
“We’ve added this after hearing from some that there are times when they’d prefer to just see links to web pages in their search results, such as if they’re looking for longer-form text documents, using a device with limited internet access, or those who just prefer text-based results shown separately from search features.”
We’ve added this after hearing from some that there are times when they’d prefer to just see links to web pages in their search results, such as if they’re looking for longer-form text documents, using a device with limited internet access, or those who just prefer text-based…
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) May 14, 2024
The new functionality is a throwback to when search results were more straightforward. Now, they often combine rich media like images, videos, and shopping ads alongside the traditional list of web links.
How It Works
On mobile devices, the “Web” filter will be displayed alongside other filter options like “Images” and “News.”
If Google’s systems don’t automatically surface it based on the search query, desktop users may need to select “More” to access it.
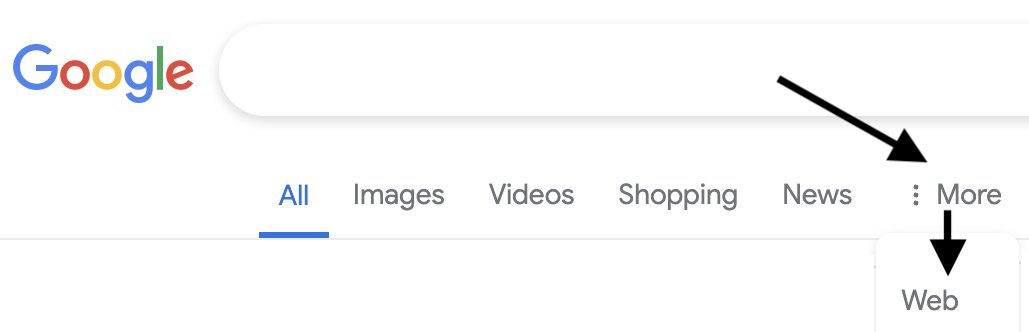 Screenshot from: twitter.com/GoogleSearchLiaison, May 2024.
Screenshot from: twitter.com/GoogleSearchLiaison, May 2024.More About Google Search Filters
Google’s search filters allow you to narrow results by type. The options displayed are dynamically generated based on your search query and what Google’s systems determine could be most relevant.
The “All Filters” option provides access to filters that are not shown automatically.
Alongside filters, Google also displays “Topics” – suggested related terms that can further refine or expand a user’s original query into new areas of exploration.
For more about Google’s search filters, see its official help page.
Featured Image: egaranugrah/Shutterstock
SEO
Why Google Can’t Tell You About Every Ranking Drop

In a recent Twitter exchange, Google’s Search Liaison, Danny Sullivan, provided insight into how the search engine handles algorithmic spam actions and ranking drops.
The discussion was sparked by a website owner’s complaint about a significant traffic loss and the inability to request a manual review.
Sullivan clarified that a site could be affected by an algorithmic spam action or simply not ranking well due to other factors.
He emphasized that many sites experiencing ranking drops mistakenly attribute it to an algorithmic spam action when that may not be the case.
“I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a algorithmic spam action against them, but they don’t. “
Sullivan’s full statement will help you understand Google’s transparency challenges.
Additionally, he explains why the desire for manual review to override automated rankings may be misguided.
Two different things. A site could have an algorithmic spam action. A site could be not ranking well because other systems that *are not about spam* just don’t see it as helpful.
I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a…
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) May 13, 2024
Challenges In Transparency & Manual Intervention
Sullivan acknowledged the idea of providing more transparency in Search Console, potentially notifying site owners of algorithmic actions similar to manual actions.
However, he highlighted two key challenges:
- Revealing algorithmic spam indicators could allow bad actors to game the system.
- Algorithmic actions are not site-specific and cannot be manually lifted.
Sullivan expressed sympathy for the frustration of not knowing the cause of a traffic drop and the inability to communicate with someone about it.
However, he cautioned against the desire for a manual intervention to override the automated systems’ rankings.
Sullivan states:
“…you don’t really want to think “Oh, I just wish I had a manual action, that would be so much easier.” You really don’t want your individual site coming the attention of our spam analysts. First, it’s not like manual actions are somehow instantly processed. Second, it’s just something we know about a site going forward, especially if it says it has change but hasn’t really.”
Determining Content Helpfulness & Reliability
Moving beyond spam, Sullivan discussed various systems that assess the helpfulness, usefulness, and reliability of individual content and sites.
He acknowledged that these systems are imperfect and some high-quality sites may not be recognized as well as they should be.
“Some of them ranking really well. But they’ve moved down a bit in small positions enough that the traffic drop is notable. They assume they have fundamental issues but don’t, really — which is why we added a whole section about this to our debugging traffic drops page.”
Sullivan revealed ongoing discussions about providing more indicators in Search Console to help creators understand their content’s performance.
“Another thing I’ve been discussing, and I’m not alone in this, is could we do more in Search Console to show some of these indicators. This is all challenging similar to all the stuff I said about spam, about how not wanting to let the systems get gamed, and also how there’s then no button we would push that’s like “actually more useful than our automated systems think — rank it better!” But maybe there’s a way we can find to share more, in a way that helps everyone and coupled with better guidance, would help creators.”
Advocacy For Small Publishers & Positive Progress
In response to a suggestion from Brandon Saltalamacchia, founder of RetroDodo, about manually reviewing “good” sites and providing guidance, Sullivan shared his thoughts on potential solutions.
He mentioned exploring ideas such as self-declaration through structured data for small publishers and learning from that information to make positive changes.
“I have some thoughts I’ve been exploring and proposing on what we might do with small publishers and self-declaring with structured data and how we might learn from that and use that in various ways. Which is getting way ahead of myself and the usual no promises but yes, I think and hope for ways to move ahead more positively.”
Sullivan said he can’t make promises or implement changes overnight, but he expressed hope for finding ways to move forward positively.
Featured Image: Tero Vesalainen/Shutterstock
SEO
56 Google Search Statistics to Bookmark for 2024

If you’re curious about the state of Google search in 2024, look no further.
Each year we pick, vet, and categorize a list of up-to-date statistics to give you insights from trusted sources on Google search trends.
- Google has a web index of “about 400 billion documents”. (The Capitol Forum)
- Google’s search index is over 100 million gigabytes in size. (Google)
- There are an estimated 3.5 billion searches on Google each day. (Internet Live Stats)
- 61.5% of desktop searches and 34.4% of mobile searches result in no clicks. (SparkToro)
- 15% of all Google searches have never been searched before. (Google)
- 94.74% of keywords get 10 monthly searches or fewer. (Ahrefs)
- The most searched keyword in the US and globally is “YouTube,” and youtube.com gets the most traffic from Google. (Ahrefs)
- 96.55% of all pages get zero search traffic from Google. (Ahrefs)
- 50-65% of all number-one spots are dominated by featured snippets. (Authority Hacker)
- Reddit is the most popular domain for product review queries. (Detailed)
- Google is the most used search engine in the world, with a mobile market share of 95.32% and a desktop market share of 81.95%. (Statista)

- Google.com generated 84.2 billion visits a month in 2023. (Statista)
- Google generated $307.4 billion in revenue in 2023. (Alphabet Investor Relations)
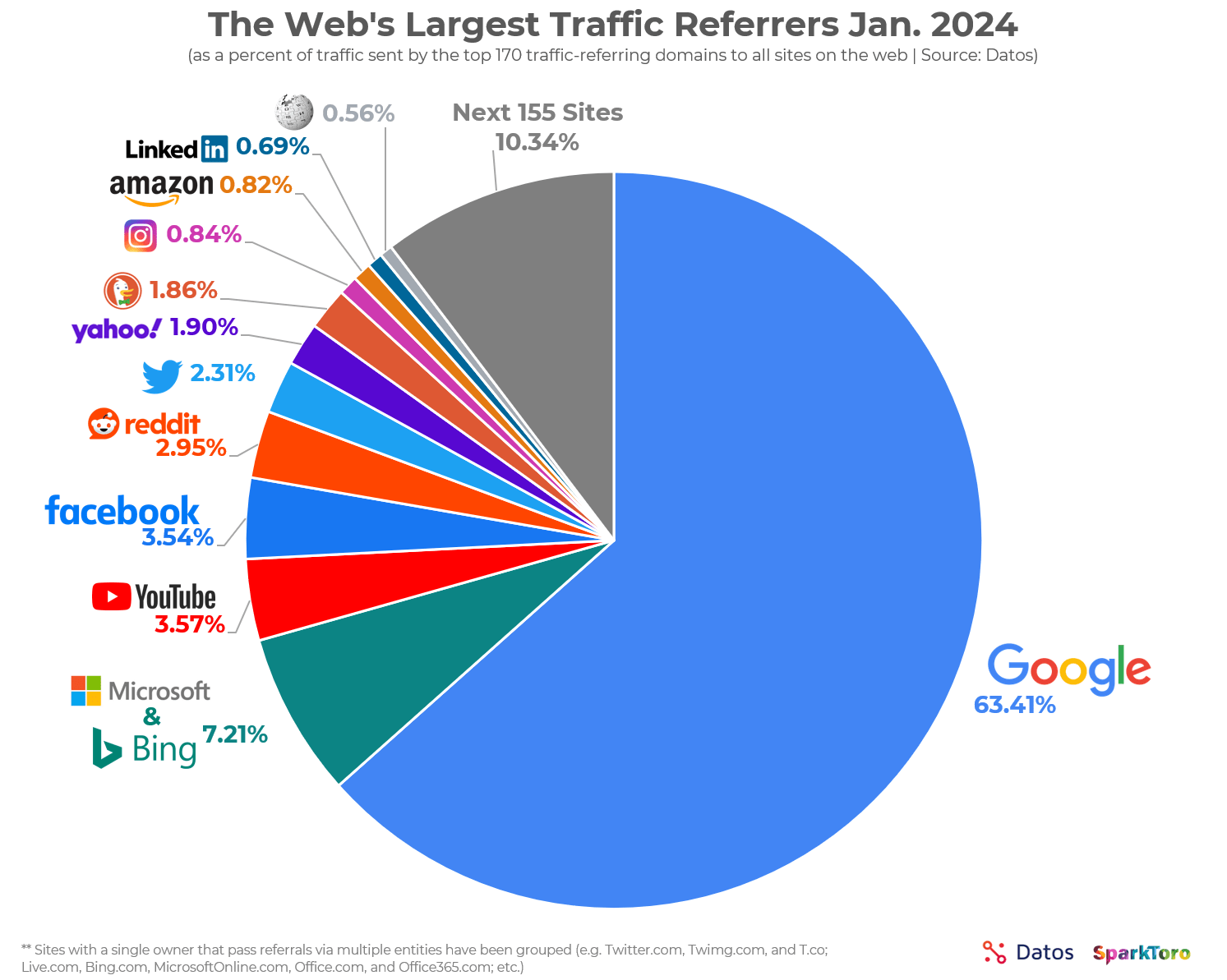
- 63.41% of all US web traffic referrals come from Google. (SparkToro)
- 92.96% of global traffic comes from Google Search, Google Images, and Google Maps. (SparkToro)
- Only 49% of Gen Z women use Google as their search engine. The rest use TikTok. (Search Engine Land)
- 58.67% of all website traffic worldwide comes from mobile phones. (Statista)
- 57% of local search queries are submitted using a mobile device or tablet. (ReviewTrackers)
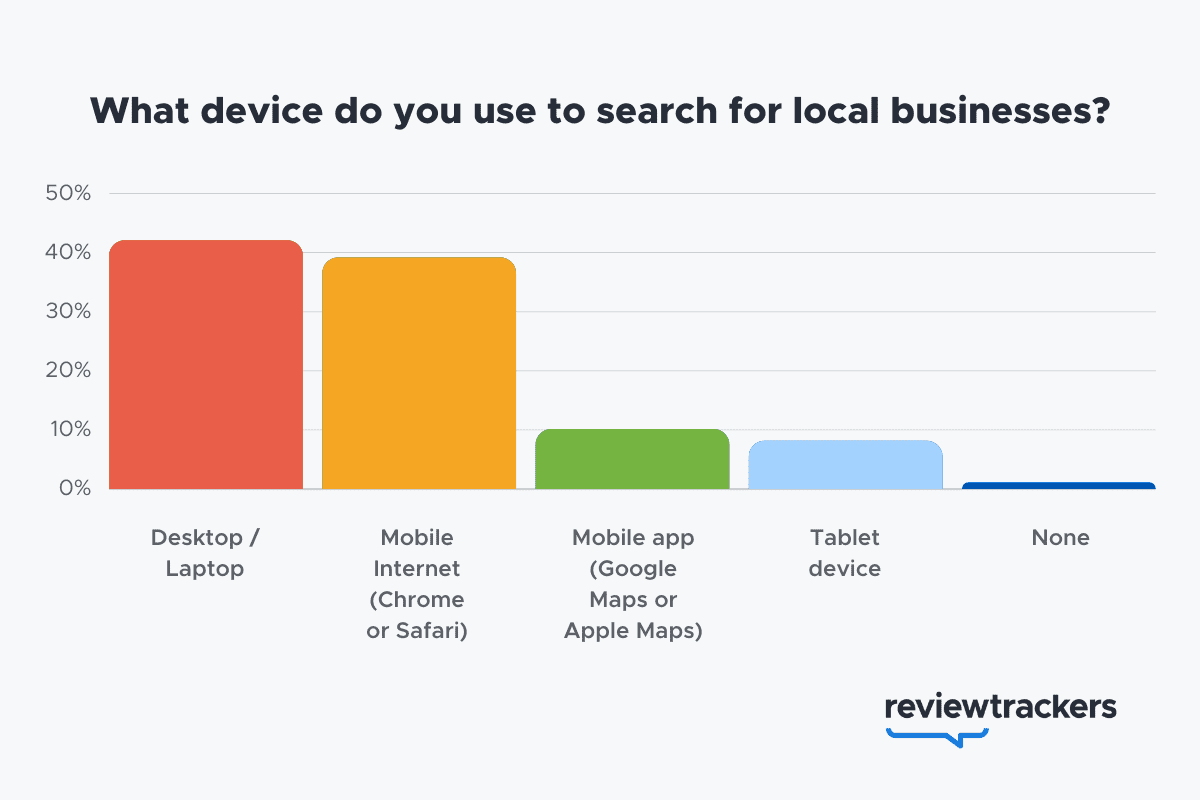

- 51% of smartphone users have discovered a new company or product when conducting a search on their smartphones. (Think With Google)
- 54% of smartphone users search for business hours, and 53% search for directions to local stores. (Think With Google)
- 18% of local searches on smartphones lead to a purchase within a day vs. 7% of non-local searches. (Think With Google)
- 56% of in-store shoppers used their smartphones to shop or research items while they were in-store. (Think With Google)
- 60% of smartphone users have contacted a business directly using the search results (e.g., “click to call” option). (Think With Google)
- 63.6% of consumers say they are likely to check reviews on Google before visiting a business location. (ReviewTrackers)
- 88% of consumers would use a business that replies to all of its reviews. (BrightLocal)
- Customers are 2.7 times more likely to consider a business reputable if they find a complete Business Profile on Google Search and Maps. (Google)
- Customers are 70% more likely to visit and 50% more likely to consider purchasing from businesses with a complete Business Profile. (Google)
- 76% of people who search on their smartphones for something nearby visit a business within a day. (Think With Google)
- 28% of searches for something nearby result in a purchase. (Think With Google)
- Mobile searches for “store open near me” (such as, “grocery store open near me” have grown by over 250% in the last two years. (Think With Google)
- People use Google Lens for 12 billion visual searches a month. (Google)
- 50% of online shoppers say images helped them decide what to buy. (Think With Google)
- There are an estimated 136 billion indexed images on Google Image Search. (Photutorial)
- 15.8% of Google SERPs show images. (Moz)
- People click on 3D images almost 50% more than static ones. (Google)
- More than 800 million people use Google Discover monthly to stay updated on their interests. (Google)
- 46% of Google Discover URLs are news sites, 44% e-commerce, 7% entertainment, and 2% travel. (Search Engine Journal)
- Even though news sites accounted for under 50% of Google Discover URLs, they received 99% of Discover clicks. (Search Engine Journal)
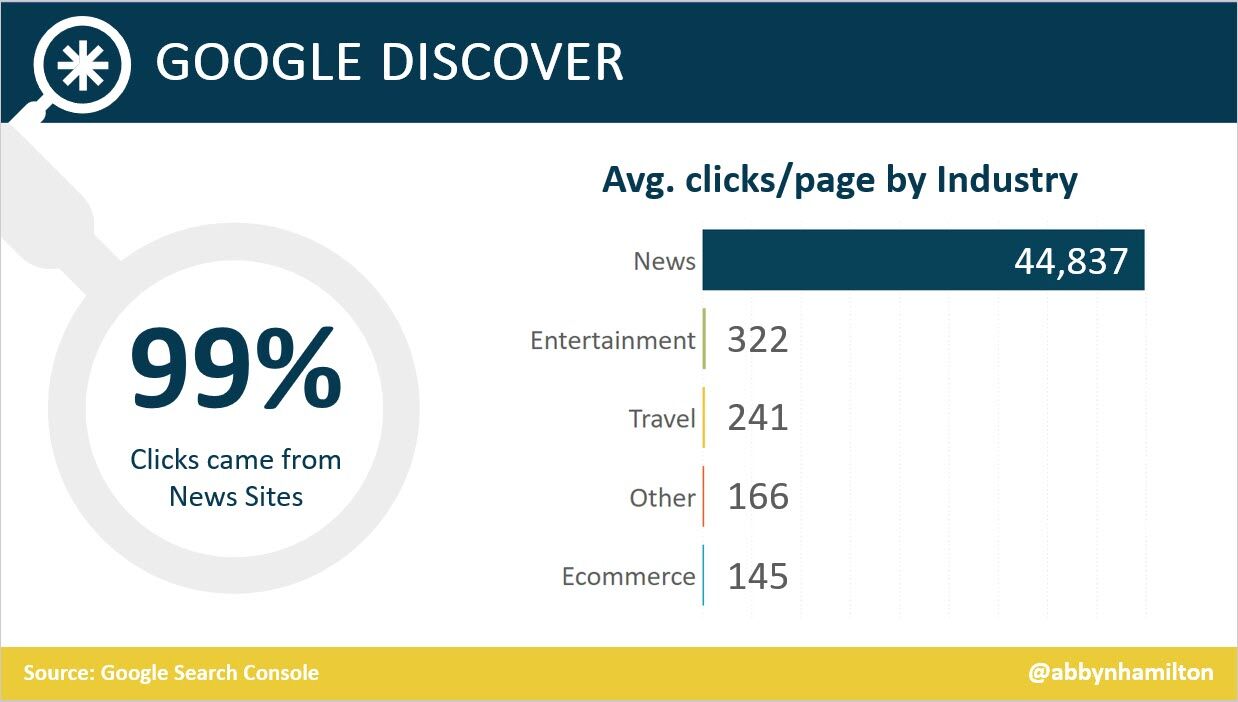

- Most Google Discover URLs only receive traffic for three to four days, with most of that traffic occurring one to two days after publishing. (Search Engine Journal)
- The clickthrough rate (CTR) for Google Discover is 11%. (Search Engine Journal)
- 91.45% of search volumes in Google Ads Keyword Planner are overestimates. (Ahrefs)
- For every $1 a business spends on Google Ads, they receive $8 in profit through Google Search and Ads. (Google)
- Google removed 5.5 billion ads, suspended 12.7 million advertiser accounts, restricted over 6.9 billion ads, and restricted ads from showing up on 2.1 billion publisher pages in 2023. (Google)
- The average shopping click-through rate (CTR) across all industries is 0.86% for Google Ads. (Wordstream)
- The average shopping cost per click (CPC) across all industries is $0.66 for Google Ads. (Wordstream)
- The average shopping conversion rate (CVR) across all industries is 1.91% for Google Ads. (Wordstream)
- 58% of consumers ages 25-34 use voice search daily. (UpCity)
- 16% of people use voice search for local “near me” searches. (UpCity)
- 67% of consumers say they’re very likely to use voice search when seeking information. (UpCity)
- Active users of the Google Assistant grew 4X over the past year, as of 2019. (Think With Google)
- Google Assistant hit 1 billion app installs. (Android Police)
- AI-generated answers from SGE were available for 91% of entertainment queries but only 17% of healthcare queries. (Statista)
- The AI-generated answers in Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) do not match any links from the top 10 Google organic search results 93.8% of the time. (Search Engine Journal)
- Google displays a Search Generative element for 86.8% of all search queries. (Authoritas)
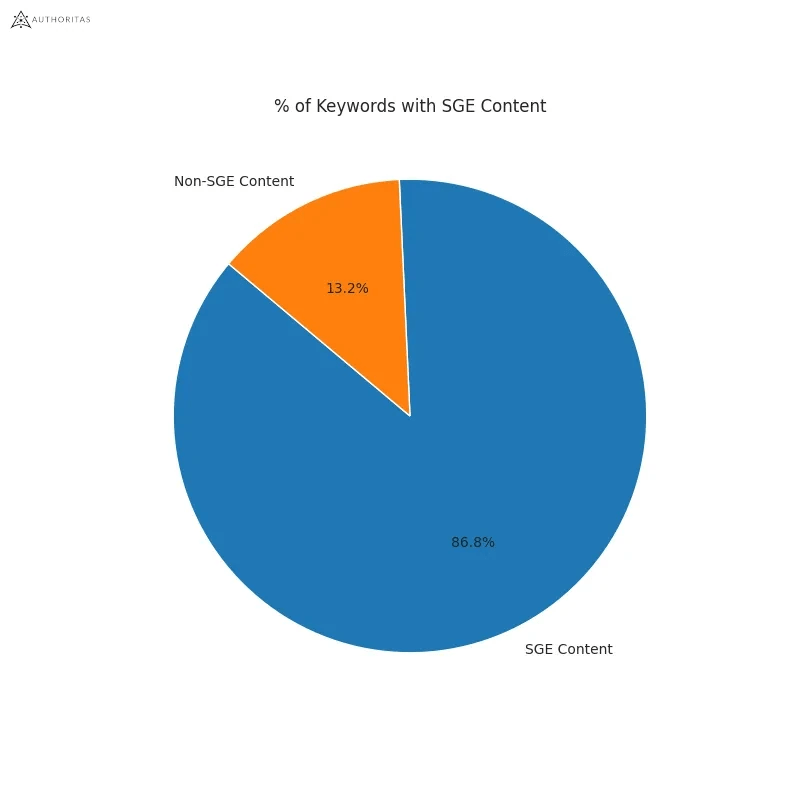

- 62% of generative links came from sources outside the top 10 ranking organic domains. Only 20.1% of generative URLs directly match an organic URL ranking on page one. (Authoritas)
- 70% of SEOs said that they were worried about the impact of SGE on organic search (Aira)
Learn more
Check out more resources on how Google works:
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoHow to Use Keywords for SEO: The Complete Beginner’s Guide
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoHow To Protect Your People and Brand
-

 MARKETING4 days ago
MARKETING4 days agoAdvertising on Hulu: Ad Formats, Examples & Tips
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoUpdates to data build service for better developer experiences
-
 MARKETING2 days ago
MARKETING2 days ago18 Events and Conferences for Black Entrepreneurs in 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoThe Ultimate Guide to Email Marketing
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoBest WordPress Plugins of All Time: Updated List for 2024
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoShopify Could Be Undervalued Based On A Long-Term Horizon















