SEO
Technical SEO Checklist for 2024: A Comprehensive Guide

With Google getting a whopping total of six algorithmic updates and four core updates in 2023, you can bet the search landscape is more complicated (and competitive) to navigate nowadays.
To succeed in SEO this year, you will need to figure out what items to check and optimize to ensure your website stays visible. And if your goal is to not just make your website searchable, but have it rank at the top of search engine results, this technical SEO checklist for 2024 is essential.
Webmaster’s Note: This is part one of our three-part SEO checklist for 2024. I also have a longer guide on advanced technical SEO, which covers best practices and how to troubleshoot and solve common technical issues with your websites.
Technical SEO Essentials for 2024
Technical SEO refers to optimizations that are primarily focused on helping search engines access, crawl, interpret, and index your website without any issues. It lays the foundation for your site to be properly understood and served up by search engines to users.
1. Website Speed Optimization
A site’s loading speed is a significant ranking factor for search engines like Google, which prioritize user experience. Faster websites generally provide a more pleasant user experience, leading to increased engagement and improved conversion rates.
Server Optimization
Often, the reason why your website is loading slowly is because of the server it’s hosted on. It’s important to choose a high-quality server that ensures quick loading times from the get-go so you skip the headache that is server optimization.
Google recommends keeping your server response time under 200ms. To check your server’s response time, you need to know your website’s IP address. Once you have that, use your command prompt.
In the window that appears, type ping, followed by your website’s IP address. Press enter and the window should show how long it took your server to respond.
If you find that your server goes above the recommended 200ms loading time, here’s what you need to check:
- Collect the data from your server and identify what is causing your response time to increase.
- Based on what is causing the problem, you will need to implement server-side optimizations. This guide on how to reduce initial server response times can help you here.
- Measure your server response times after optimization to use as a benchmark.
- Monitor any regressions after optimization.
If you work with a hosting service, then you should contact them when you need to improve server response times. A good hosting provider should have the right infrastructure, network connections, server hardware, and support services to accommodate these optimizations. They may also offer hosting options if your website needs more server resources to run smoothly.
Website Optimization
Aside from your server, there are a few other reasons that your website might be loading slowly.
Here are some practices you can do:
- Compressing images to decrease file sizes without sacrificing quality
- Minimizing the code, eliminating unnecessary spaces, comments, and indentation.
- Using caching to store some data locally in a user’s browser to allow for quicker loading on subsequent visits.
- Implementing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute the load, speeding up access for users situated far from the server.
- Lazy load your web pages to prioritize loading the objects or resources only your users need.
A common tool to evaluate your website speed is Google’s PageSpeed Insights or Google Lighthouse. Both tools can analyze the content of your website and then generate suggestions to improve its overall loading speed, all for free. There are also some third-party tools, like GTMetrix, that you could use as well.
Here’s an example of one of our website’s speeds before optimization. It’s one of the worst I’ve seen, and it was affecting our SEO.
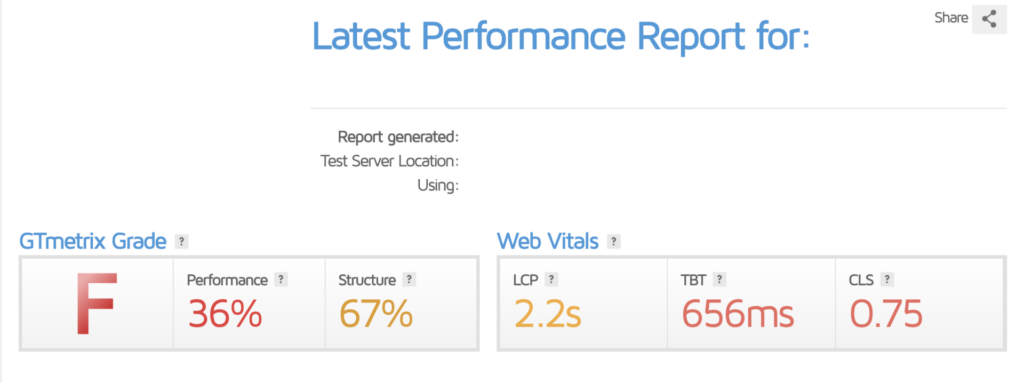

So we followed our technical SEO checklist. After working on the images, removing render-blocking page elements, and minifying code, the score greatly improved — and we saw near-immediate improvements in our page rankings.
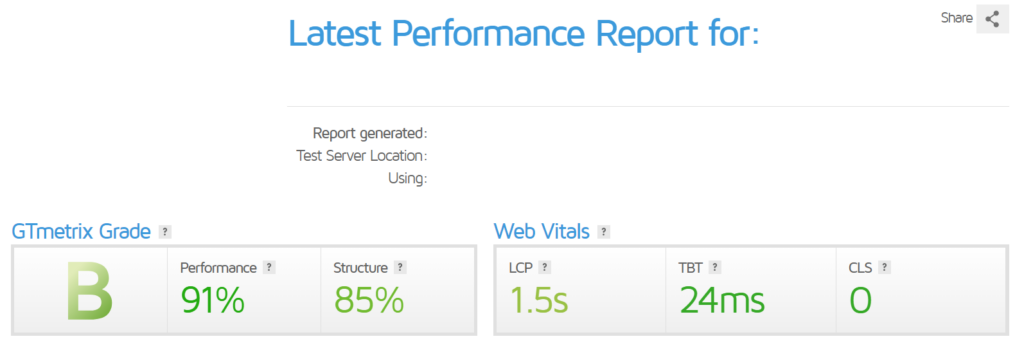

That said, playing around with your server settings, coding, and other parts of your website’s backend can mess it up if you don’t know what you’re doing. I suggest backing up all your files and your database before you start working on your website speed for that reason.
2. Mobile-First Indexing
Mobile-first Indexing is a method used by Google that primarily uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking.
It’s no secret that Google places a priority on the mobile users’ experience, what with mobile-first indexing being used. Beyond that, optimizing your website for mobile just makes sense, given that a majority of people now use their phones to search online.
This change signifies that a fundamental shift in your approach to your website development and design is needed, and it should also be part of your technical SEO checklist.
- Ensuring the mobile version of your site contains the same high-quality, rich content as the desktop version.
- Make sure metadata is present on both versions of your site.
- Verify that structured data is present on both versions of your site.
Tools like Google’s mobile-friendly test can help you measure how effectively your mobile site is performing compared to your desktop versions, and to other websites as well.
3. Crawlability & Indexing Check
Always remember that crawlability and Indexing are the cornerstones of SEO. Crawlability refers to a search engine’s ability to access and crawl through a website’s content. Indexing is how search engines organize information after a crawl and before presenting results.
- Utilizing a well-structured robots.txt file to communicate with web crawlers about which of your pages should not be processed or scanned.
- Using XML sitemaps to guide search engines through your site’s content and ensure that all valuable content is found and indexed. There are several CMS plugins you can use to generate your sitemap.
- Ensuring that your website has a logical structure with a clear hierarchy, helps both users and bots navigate to your most important pages easily.
Google Search Console is the tool you need to use to ensure your pages are crawled and indexed by Google. It also provides reports that identify any problems that prevent crawlers from indexing your pages.
4. Structured Data Markup
Structured Data Markup is a coding language that communicates website information in a more organized and richer format to search engines. This plays a strategic role in the way search engines interpret and display your content, enabling enhanced search results through “rich snippets” such as stars for reviews, prices for products, or images for recipes.
Doing this allows search engines to understand and display extra information directly in the search results from it.
Key Takeaway
With all the algorithm changes made in 2023, websites need to stay adaptable and strategic to stay at the top of the search results page. Luckily for you, this technical SEO checklist for 2024 can help you do just that. Use this as a guide to site speed optimization, indexing, and ensuring the best experience for mobile and desktop users.



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













