SEO
Best AI Search Engines To Try Right Now

AI-powered search engines are a new breed redefining the search experience as we know it.
And when we talk about AI-powered search engines, Bing and Google SGE (Search Generative Experience) are currently the two that rise to the top.
For some time, they have been the most popular and widely recognizable names in AI search engines – and, as such, the ones that get the most attention.
But as with most things, the landscape is far from stagnant. Today, there are many other AI search engines out there that are just as useful as Bing and Google – and, in some ways, even better.
From privacy-focused search engines to those that prioritize publisher sourcing, we have curated a list of the six best AI search engines that exist right now and what you need to know about them.
Notably, at least one of them boasts a paid version with such a generous number of queries per day that some argue it surpasses the offerings of OpenAI’s ChatGPT Plus.
Let’s dive in.
1. Andi Search
Andi Search is a startup AI search engine that offers an interpretation of a better way to explore the Internet and obtain knowledge.
After a while of using Andi, one gets a sense that there really is a better way to present information.
It also becomes apparent that Bing and Google SGE haven’t strayed far from the old 10 blue links paradigm.
There are three things that make Andi stand out:
- The interface uses AI throughout the entire search results, not just at the top of the page the way Bing and Google SGE do.
- Images, summaries, and options are offered in a way that makes sense contextually.
- All on-page elements work together to communicate the information users are seeking.
Andi Is More Than A Text-Based Search Engine
Humans are highly visual, and Andi does a good job of presenting information not just with text but with images, too.
Using Andi, it becomes apparent that both Bing and Google SGE are traditional search engines with an AI chatbox at the top of the page.
What Is Andi AI Search?
Andi is a factually grounded AI search engine that was purposely created to offer trustworthy answers while avoiding hallucinations that are common to GPT-based apps.
It offers keyword search results, answers complex multi-part questions, and fully understands natural language input.
Technology Used By Andi
Andi Search uses a mix of technologies.
In a 2022 Q&A, Andi Search engineers said they use several commercial and open-source Large Language Models (LLMs), knowledge graphs, and Google, Bing, and other search engines (50% of the time in 2022).
Andi AI Search Results
I asked Andi a complex question:
"Please tell me about the fictional star wars character Ahsoka and also explain if she is one of the most skilled Jedi of all time."
The answer was in the form of a short summary and a link to the source of the information, with an option to show the full search results or to summarize an answer to the question.
The summary provided correctly answered my complex question, even the part about whether the fictional character Ahsoka Tano is the most skilled Jedi of all time.
Video Of Search Results From Websites
On a desktop, the right-hand side contains a panel with the search results.
The results are not in the form of a standard 10 blue links, but rather, they consist of the featured image with text from the webpage.
Andi is currently in a Beta testing stage, but it is freely available to use – no need to sign up or have an account.
Andi Search And Privacy
Andi is a privacy-first AI company. It doesn’t store cookies, doesn’t share data, and no information is available to any employee of the company.
It even blocks Google’s FLoC tracking technology so that Google can’t follow you onto Andi.
Controversial Feature
Andi is a fine search engine in many ways, but there is one feature called Reader that publishers may not appreciate.
Screenshot Of Andi Reader Button
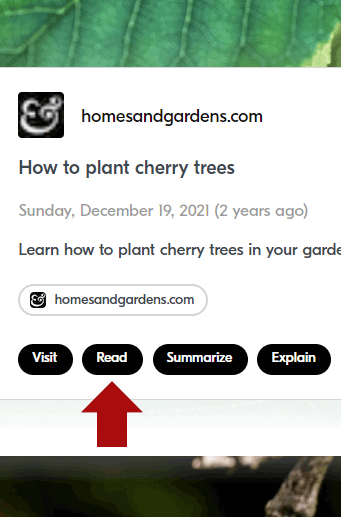
Clicking on the Read button reveals the entire webpage for users to read without visiting the website.
Below is a screenshot that shows how Andi publishes a snapshot of the webpage (content blurred by me):
Screenshot Of Andi Search Reader
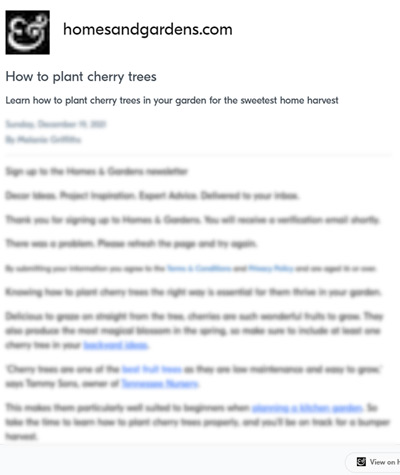 Screenshot from Andi Reader, September 2023
Screenshot from Andi Reader, September 2023
Summary Of Andi Search
Andi is truly a rethink of how the search engines of today should function. It encourages users to rediscover the best that the web has to offer.
On the other hand, the engineers behind Andi may want to consider that publishers and search engines are an ecosystem that are dependent on each other.
2. Metaphor AI Search
There are many AI startups that are visualizing different ways to surface internet data that leverage the power of AI. That approach does away with traditional crawlers and indexers.
Metaphor is an example of the out-of-the-box use of large language models.
A Q&A on Y Combinator/Hacker News reveals that the engineer behind Metaphor uses what he calls next link prediction.
The intuition underlying the approach is that training LLMs and indexing websites are somewhat similar.
What they did was create a model architecture that had the concept of links baked in.
An interesting feature of Metaphor is that growing the index of sites doesn’t require retraining the entire language model. It’s simply a matter of adding the additional data.
How Metaphor AI Search Works
Approaching Metaphor, it’s important to keep in mind that this isn’t a traditional style search engine.
It’s surfacing links.
Furthermore, users can select what kinds of links to show.
The user-selectable categories are:
- Tweets.
- Wiki.
- News.
- Research Papers.
- Podcasts.
- Events.
- Blogs.
- GitHub.
- Companies.
- Recipes.
- All of the Above.
Metaphor Search Results
Searching for recipes shows results that are different from Google and Bing, in a good way.
A search for authentic Spanish rice recipes as well as authentic mujadara recipes. Metaphor surfaced links to websites with authentic recipes.
The quality of the sites was different from the dumbed-down and inauthentic recipes sometimes shown on Google.
Searches on Metaphor sometimes don’t generate what you’re looking for. For example, searching for SEO in the News category yielded irrelevant results.
Summary Of Metaphor
Metaphor is worth giving a try because it may be useful for certain kinds of searches.
It’s not a general search engine, and it doesn’t claim to be. It’s something different, and that can be refreshing sometimes.
Nevertheless, Metaphor is still in the early stages of development, and it shows in some searches.
3. Brave AI Search Summarizer
 Screenshot from Brave, September 2023
Screenshot from Brave, September 2023
Brave Search is a privacy-first search engine.
AI is deployed in a way that complements search and does not attempt to be a chatbot – it simply serves the goal of offering information.
Brave uses its own LLMs to assess the ranked webpages and offer a summarization. This function is called the Summarizer, which users can opt out of if they wish.
The Summarizer isn’t invoked for every search, only about 17% of searches will spawn the feature.
What’s great about the Summarizer is that it links to sources.
The screenshot below has the links circled in red.
Screenshot Of Brave Summarizer
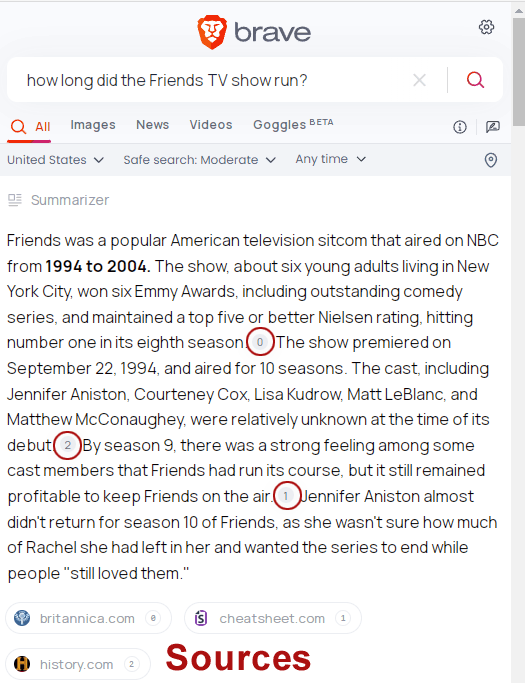 Screenshot from Brave Summarizer, September 2023
Screenshot from Brave Summarizer, September 2023
Another use of AI is to generate webpage descriptions so that users can read a brief of what’s contained on the webpage.
The technology powering Brave consists of three LLMs trained for:
- Question answering and improving search results.
- Classification to weed out undesirable search results.
- Summarizer and paraphrasing model add the final touches.
Brave Search Language Models
Brave Search uses two open-source language models that are available at Hugging Face.
The first language model is called BART (not to be confused with BERT, which is something different).
The second language model used by Brave is DeBERTa, which is a hybrid model based on Google’s BERT and Meta’s RoBERTa. DeBERTa is said to be an improvement over BERT and ROBERTa.
Brave Search does not use Bing or Google search, it has its own webpage index.
Brave Search Summary
Brave Search is perfect for users who want a search engine that respects privacy, is easy to use, and is useful.
4. YOU AI Search Engine
YOU is an AI search engine that combines a large language model with up-to-date citations to websites, which makes it more than just a search engine.
You.com calls itself YouChat, a search assistant that’s in the search engine.
Notable about YouChat is that, while it’s a privacy-first search assistant, it claims that it also gets better the more you use it.
Another outstanding feature is that YouChat can respond to the latest news and recent events.
YouChat can write code, summarize complex topics, generate images, write code, and create content (in any language).
You.com features YouAgent, an AI agent that writes code and can run it in its own environment, then take further action based on the output.
It’s available at You.com and available as an app for Android and iPhone and as a Chrome extension.
All versions of You.com respect privacy and do not sell user data to advertisers.
The web version of You.com answers questions with answers summarized from websites that are linked to from the answer.
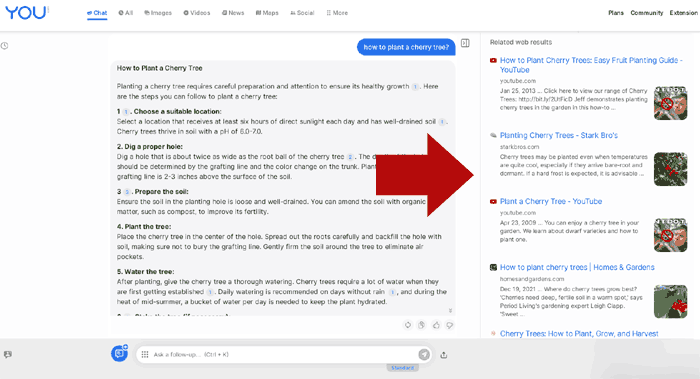
You.com SERPs With Links To Websites


There are traditional search results in a right-hand panel, which consists of links to videos and websites.
Links To Webpages & Videos On Side Panel

YOU is available in a free and paid version.
The free version of You offers unlimited chat-based searches. It also provides a limited amount of AI image and writing generations (ten each).
The paid versions, You Pro for $9.99/month and YouPro for Educational for $6.99/month, offer unlimited AI image and writing generations, personalized machine learning, and priority access.
Subscriptions are available at a lower price when paid on a yearly basis.
You.com Summary
You.com is a unique personalized search destination tuned to help users not just research topics but get things done.
The AI search engine answers questions in natural language while also citing links to websites and videos that offer comprehensive coverage of the topic.
You.com also provides chat-based AI tools that are capable of taking that research and creating something new with it.
5. Phind.com
Phind calls itself a generative AI search engine for developers.
On August 28, 2023, it announced a new LLM called Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2 that outperforms GPT-4 on a benchmark called HumanEval.
The technology underpinning Phind is a serious contender.
While it self-describes as AI search for developers, it does a great job of surfacing answers from trustworthy websites.
A drop down menu next to the search box allows users to choose from GPT-3.5 Turbo or the Phind Model (unlimited uses) and limited use of GPT-4.
Phind can answer complex questions such as, “How did Facebook become so popular?” or “What marketing lessons can be learned from how Shein promotes itself?” It can also respond to follow-up questions.
But the search results aren’t always perfect.
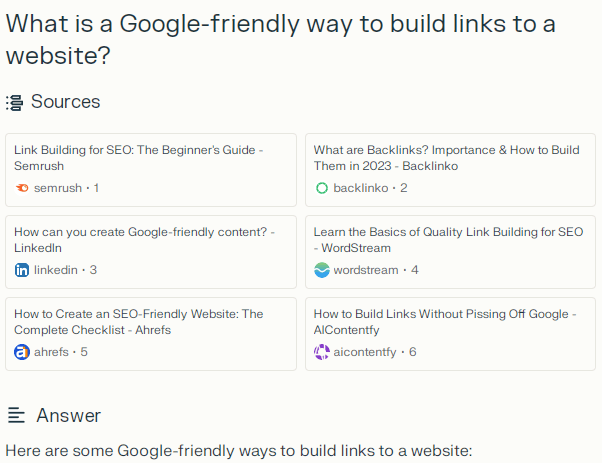
A query for “What is a Google-friendly way to build links to a website?” resulted in several valid suggestions but also the recommendation of guest posting for links.
A follow-up question resulted in a response that backtracked on the guest posting suggestion.
Summary Of Phind
Phind is a fine way to interact with a GPT-3.5-based search engine that can also output essays and solve other problems.
Users can sign in to save their chats.
6. Perplexity.ai
Perplexity.ai is a self-described answer engine.
It offers natural language answers to questions that are up to date, including being able to answer questions about the weather.
Perplexity is powered by LLMs, Internet data, and its updated version of Google’s PageRank, which creates a link graph of trustworthy websites.
Perplexity.ai is a serious contender in AI Search.
It was founded by people with links to DeepMind and OpenAI and is funded by leading Silicon Valley investors.
The search engine itself offers in-depth answers and suggests follow-up questions to dig even deeper.
Perplexity is even able to mix different kinds of information and come up with perfect answers.
For example, I asked it to write an article about SEO that corresponds to Ernest Hemingway’s writing style.
"Please create an informational article about search engine optimization, that is done in the style of Ernest Hemingway"
It offered suggestions like:
“Keep it simple: Hemingway’s writing style is known for its simplicity and clarity.
Similarly, when it comes to SEO, it’s important to keep your content simple and easy to understand.
Avoid using overly technical jargon or complex sentence structures that might confuse your readers.
…Hemingway’s writing style can be a useful guide for creating SEO-friendly content. By focusing on simplicity, readability, and clarity, you can create content that is both engaging and optimized for search engines.”
It’s not perfect, though.
I asked it about former Googler Matt Cutts, and it provided a comprehensive answer that also cited Matt as the founder of an SEO consultancy.
The wrong answer came from a LinkedIn page where the name of the consultancy was found in a sidebar containing people who are connected to him on LinkedIn.
What I think may have happened is that the Perplexity.ai crawler may not yet be able to separate the main content of a webpage from the rest of the content.
I asked it the link building question, “What is a Google-friendly way to build links to a website?” and it gave a reasonable answer.
A useful feature, as mentioned earlier, is the suggested follow-up topics. Perplexity labels them as “Related.”
The related topics offered for the link building question were:
- “What are some effective link building strategies for SEO.”
- How to find high-quality websites to link to your site.
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when building links for SEO.”
Screenshot Of Related Topics Suggestions
 Screenshot from Perplexity.ai, September 2023
Screenshot from Perplexity.ai, September 2023
Perplexity.ai Is Publisher-Friendly
Something that should be mentioned is that Perplexity.ai is publisher-friendly.
It does a great job of linking to the websites from which the answers were sourced.
 Screenshot from Perplexity.ai, September 2023
Screenshot from Perplexity.ai, September 2023
Perplexity.ai Summary
Perplexity is much more than a search engine, it’s a true answer engine.
It reimagines what question answering can be and does a great job of providing answers and also encouraging exploration with suggestions for related topics.
AI Search Engine Future Is Now
It’s been decades since users had such a vast choice in search engines.
There have never been so many viable alternatives to Google as there are today.
Generative AI is creating new ways to discover accurate and up-to-date information.
The “organic” 10 blue links are increasingly becoming a thing of the past.
Give some of these free AI search engines a try, because many are every bit as good as the top two.
More resources:
Featured image by Shutterstock/SvetaZi








![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)





