How to Setup Google Analytics using Google Tag Manager?
Do you want to set up Google Tag Manager? If you already have a Google account, Google Tag Manager (GTM) is very easy to create and install. Here, in this blog, you will get a brief knowledge of how to manage Google Tags with each option highlighted.
But before going further, let us know some basics about GTM:
Google Tag Manager is a free tool that allows you to manage and deploy marketing tags ( tracking pixels) on your website and a mobile app without modifying the code. In simple words, it is a way you can easily update measurement codes and related code fragments collectively on your website or mobile applications.

Let’s consider the steps to install GTM (Google Tag Manager) today:
Step #1 Go To The GTM Account Page:
To get started, first create a GTM account. Go to the official website of Google Tag Manager “https://marketingplatform.google.com/about/tag-manager/“. And click on the main call-to-action to create a new Google Tag Manager account. If you already have on Gmail (Google Ads, Google Analytics, etc.), you will automatically log in to Google Tag Manager. Otherwise, you have to create a new account first.
Step #2 Create a GTM Account:
After logging in, you will be asked to create a new Google Tag Manager account. For this, follow the below process:
- First, in tag manager, click on accounts and then create an account.
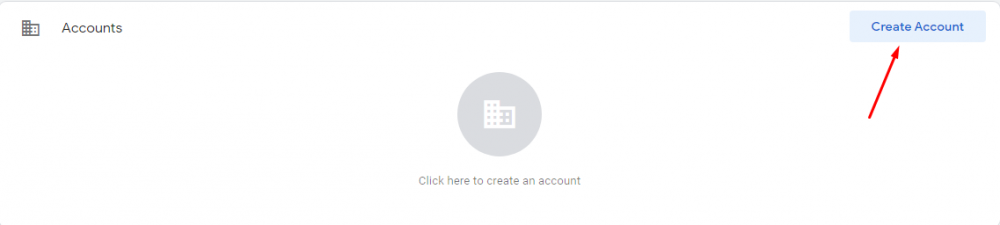
- Enter an account name and fill the other optionally indicate if you won’t share data with Google.
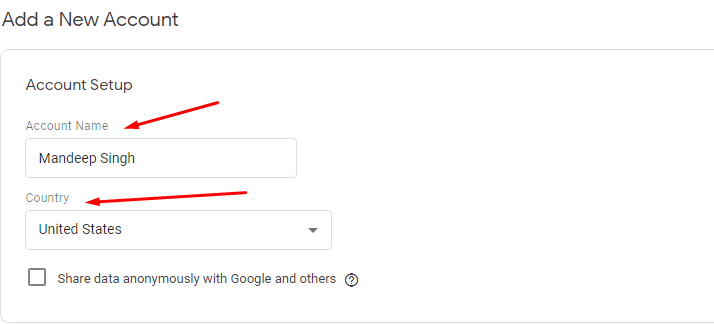
- After this, click on CONTINUE.
Step 3: Setup Your GTM Container
A container is where you will easily manage all your tags.
- After clicking on the CONTINUE Create container page will appear.
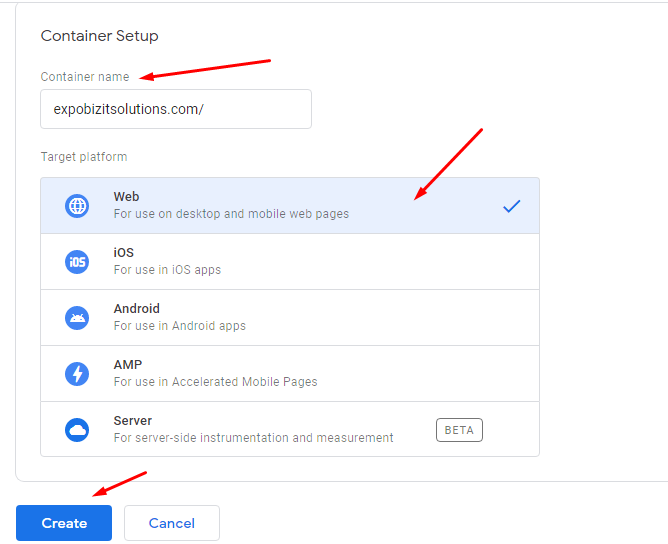
- Enter a descriptive container name with the name of your site (But make sure don’t use HTTPS:// or HTTPS://)
- Select the type of content where the container will use Web, AMP, Android, or iOS.
- Then click on “CREATE”.
Step 4: Accept the Data Processing Terms Required by GTM:
Here you have to read all the terms and conditions of the services agreement. Click “yes” by scroll down to the very bottom of the page and then click on the checkbox.
“I accept the Data Processing Terms As Required By GDPR, Learn More.”
Step 5: Open GTM Container:
In this step, click on your container’s name, which you create, and click on your GTM tracking code ID. Once you click, you would see the code for installing a tag manager.
Step 6: Install GTM:
Important consideration:
“Before moving further to the next steps, make sure that you audit the current tags installed in the code of your website, app, or AMP pages. Plus, create an analytics migration plan”.
To install the GTM, you have to copy (highlighted below) code and paste it within the <head> section of every page of your site. And click on the “ok” button. Here, you will see the GTM user interface. But, sometimes, not all vendor tags are currently supported by GTM, and for those that are not for this, you might want to check with the vendor’s technical support to make sure their tracking code works with GTM.
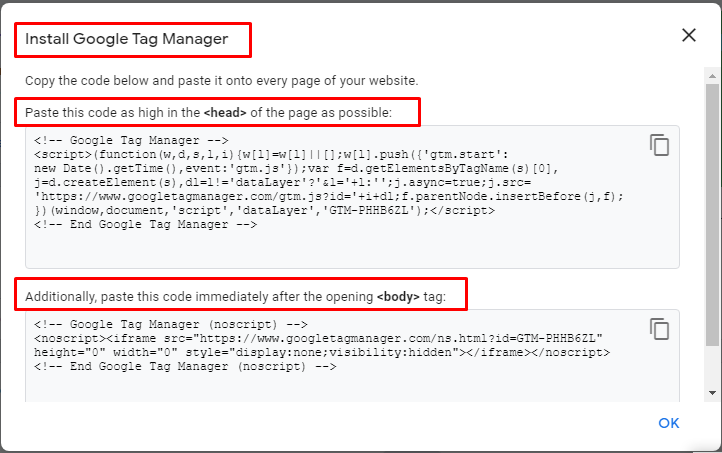
Step 6: Analyze the Coverage of GTM Container Tracking Code:
Once you install the code, now it’s time to test that code is running on every page. Several tools that you can use for this process, but one of these is Google Tag Assistant Legacy. A free tool commonly used by several professionals to analyze small sites!
Congratulations! You have successfully installed your GTM Google Tag Manager!!

How to Setup Google Analytics with Google Tag Manager
Once you are successfully entering the code snippet on your website, you will need to set a tag.
Start by clicking on the new tag.
By clicking on the untitled field, you can rename the tag. Then click on the big icon where it says choose a tag type to start setup.
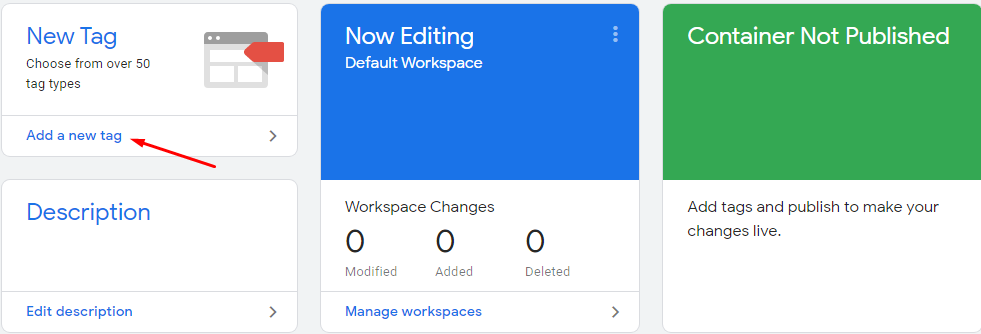
Once you click, there are different types of tags that will appear on-page. You have to select “Google Analytics: Universal Analytics.”
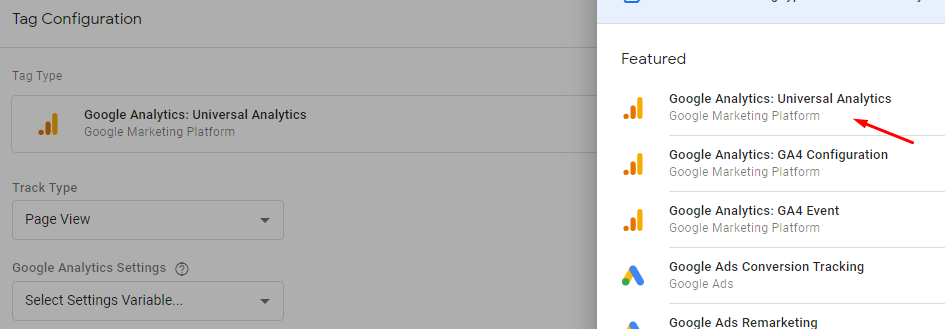
Now, under Google Analytics settings, click on the dropdown menu and select a “NEW VARIABLE.”
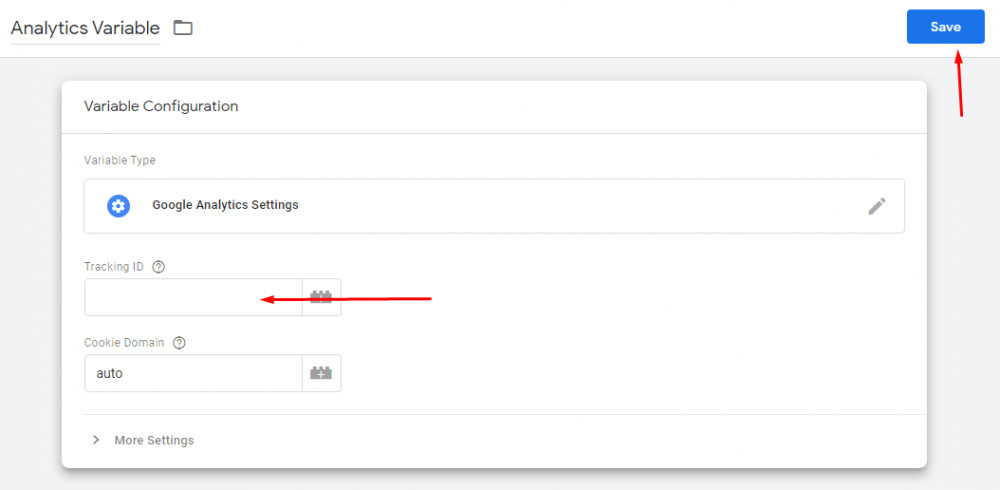
Here, give a name to your variable and enter your Google Analytics “TRACKING ID” After that, click “SAVE” when you are done.
In the next step, you will have to set up a trigger. For this, click on the big icon where it says “choose a trigger to make this tag fire.”
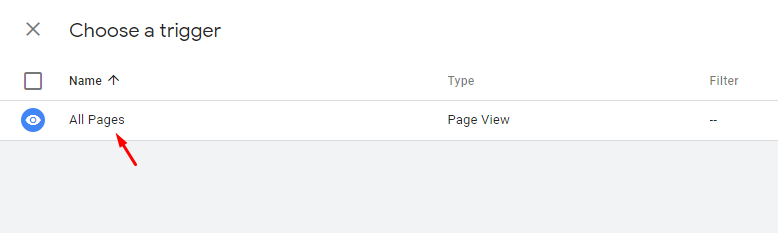
Here select All Pages for basic Google analytic implementation and click on the Save button at the top.
Now, you are ready to publish your Google Analytics tag.
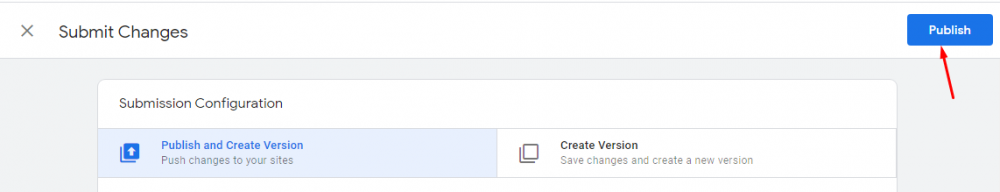
After that, you will have to submit a Newly Created Tag. For this, select tag from the left appearing options. Then select Google Analytics Tag and click on the submit button.
That’s all! You have successfully implemented Google Analytics with Google Tag Manager. And now, it will execute on every page. Now, all you will have to do is wait for a few hours for Google Analytics to collect your website’s data. Then, you can log in to your Google Analytics account and analyze or view your website’s reports.



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













