SEO
Bing Explains SEO For AI Search
AI search is inevitable so it’s vital for SEO to understand everything about it. An interview with Bing’s Fabrice Canel revealed interesting insights about this topic with some takeaways that offer some insights on the future of search.
Fabrice Canel is the Principal Product Manager at Bing and because of his position there he is in the position to know more about AI search from the search engine side, something we don’t get to see.
AI Search Clicks Are Valuable
Something of special interest for SEO professionals is his discussion about what host Jason Barnard calls the perfect click and what Fabrice referred to as qualified clicks.
I’ve noticed that contextual links are in some versions of Google SGE and is also a main feature of the search engine results pages (SERPs) of some of the newer AI search engines like Perplexity AI.
Bing AI search also shows citations to websites where users can dig deeper into the topic that is relevant to them at that moment.
Fabrice talks about how these links to websites that are shown to users from AI search are more valuable than standard links from a regular search engine.
He uses the phrase “qualified clicks” to refer to traffic to websites that originate from from AI search.
Fabrice (at the 6 minute mark of the video):
“Bing is all about satisfying the end user and sometimes it’s all about exploring the web.
But sometimes it’s all about understanding the web and providing this kind of experience where at the end we can learn the clicks to the website having extremely qualified clicks.
And this is something we’ve seen where clearly when people are clicking…
And this translates to a benefit for the end user, for the website more, certainly more, than [from a] search engine, typical search engine.”
What he’s saying is that there is more context in the interaction between users and Bing, which results in better answers and in turn better traffic, qualified clicks.
Why AI Search Clicks Are Better Than Normal Search Clicks
Fabrice explains in more detail why clicks from AI search are better than from a regular search engine.
He explains that user interaction provides Bing with more search query context, which in turn allows Bing to offer links to the exact site that offers the answers that the user is looking for.
Users provide so much query information that the click to the website is essentially a perfect click, the qualified click.
Fabrice answered:
“Yeah. So fundamentally, …we have abilities to do in Bing Chat what we don’t really have out of the box of in search.
It’s a little bit more time to really go deep in understanding the query, understanding what the query can return as results.
So this is all about at the end being able to have an orchestration between the queries itself and the ranking and the profile of a user to really go deeper in understanding what the user is looking for and retrieving from the set of content.”
These interactions are so rich in data about what users want that it allows Bing to make their search even better.
And the better Bing understands user queries the better the traffic that it sends.
What’s important about that insight is that it can very much apply to traffic from other AI search engines.
Let’s take that idea a little further.
If AI search engines understand what is asked of them, then they are better able to provide the correct answers. That makes offering ten blue links no longer necessary.
It very much resembles the interaction between humans, where one will ask the other something and receives a response.
Nobody needs to respond with ten answers, right? The same applies for AI search.
What’s extraordinary is that AI search not only helps users, but it allows Bing to become better in satisfying user queries.
Fabrice continued:
“…this new technology helps us to improve even faster and certainly better to satisfy even more users.
We see that the satisfaction of users at Bing has really improved even more in the last six months than before.
So this is continuous improvement of the technology.”
AI Search Is Not About Keyword Matching
Fabrice next speaks about keywords in AI Search.
He says that the technology is not in any way about matching keywords (terms) in the query to keywords on a webpage.
He noted:
“… the technology has evolved.
This is not about …term matching, this is really understanding the context of a query, the context of a user to really retrieve the best content on the internet.”
The AI search experience again resembles a conversation between humans, where when you provide an answer to a question, using the keywords in the question is not something you consciously do, right? Your focus is on providing an answer.
AI search understands the full context of the question and answers it, just like you would.
Ranking In AI Search – Role of Verbs And Keywords
Fabrice next says that keywords matter, not because the AI search engine is matching keywords to queries but rather, the keywords help Bing understand what the page is about.
This is an important insight. It reinforces one of the most important trends of the past several years about how SEOs need to be precise in communicating what a page is about.
Keywords matter to the extent that they tell the search engine what the page is about.
Fabrice explains [16:34 minute mark]:
“So the verbs of a user matter even more these days.
People want to say, I want to book a ticket to this thing and “book” maybe not really in the content of a page, but we know that it’s a booking activity.
So maybe this is all about retrieving the event itself where people then can book the concert.
So think technology really improve, don’t think about keyword …and so on, think about satisfying the user for a set of queries that they think they will do.
…obviously, if a customer specify a verb, this is important, but if a customer …do not specify a verb, then this is all about understanding the context of this query in this specific chat, of the ability to understand what the session was all about.
Because maybe you want to search, give me a restaurant…
Maybe we will give a list of restaurants near you and then you can say, hey, I want a vegetarian restaurant. Okay?
And then you have a list of vegetarian restaurants, or give me a vegetarian one and give me one that can accommodate 20 people.
So again, you don’t repeat the restaurant [can’t understand], you just continue the chat experience and we have a full context of the full session and helping to reply [to] your question.
And for search engine optimization, …It means at the end that you may care about keyword and you should care about keyword because we need to know that it’s a restaurant for vegetarian, we need to know that it can accommodate a large group of people.
But this is less about really matching this query. This is again, not really matching, this is matching what people are searching, looking for.”
What’s The Connection Between AI And Search Algorithms?
Jason Barnard next asks if the Bing chat algorithm and the search algorithm are the same.
Fabrice answers [19:35 minute mark]:
“This is an excellent question.
So first of all, in Bing Chat and search we benefit obviously of a big index.
It’s not, let’s say, a large language model store that you interact here.
Here, we benefit from not only this new tech…, but also by having deep interaction with the index itself.
So mean that …we are doing multiple queries and retrieving from this query the best content on the Internet. It’s not a static set, it’s a dynamic set.
You benefit from having the latest content and index and we have technology for that to make sure that content can be indexed, latest content can be indexed in seconds.
But it’s really this kind of interaction with the best content on the Internet that we can retrieve and we do multiple queries to retrieve.
So overall I will share that the technology is the same, but in chat there is even more complex queries that are done to really retrieve the content, analyze the content.
Chat give us access to more time to do a little bit more things, understanding, also interacting deeper with the user via the chat experience and session, where we can also not only suggest text, suggest verbs that the customer can do to continue the discussion with a search engine to retrieve the best content on the Internet.”
Will Ten Blue Links Disappear?
The ten blue links have been going away as a standard in traditional search engines for many years, more than a decade.
Where does the ten blue links paradigm fit into AI search?
Surprisingly, ten blue links still have a place in AI search.
Fabrice answered [30:55 minute mark]:
“Yeah, again, personally I do not believe that.
Again, don’t know if mindset of people evolve and they really prefer chat, why not?
But again, I still feel that there is a set of queries where the ten blue links are really satisfying the user today.
And so this means again you query for specific query, navigational query.
You just certainly don’t want at least me, I don’t want to have an experience where there is asking me more questions.
No, no, I want to click this link, this is the link.
I know where I want to go. I don’t remember the domain names, but I want to go there.
And so this is kind of a directory address book where okay, I know this is perfect. Thank you. I’m done.
I am visiting the site now.
And this is then you don’t really need a huge experience and you need really this navigational… And so blue links satisfy your need.”
The takeaway then is that there are certain contexts where users need the ten blue links and that it doesn’t make sense to drag the full chat experience into those kinds of queries.
Two Things To Do For LLM Search
Fabrice later discusses what SEOs should do for AI search.
He basically says to make it easy to get indexed because building an index on the LLM side can take years.
The first thing is to adopt IndexNow for incredibly fast indexing. On the AI side, the LLM can take months to years to be up to date.
Fabrice said:
“…using IndexNow, you will get your content indexed in seconds.
…In LLM, it takes weeks, months, more likely years to build the new LLM tech.
So this is important for the SEO community because you have to do it right now, as soon as possible, to be a part of the next LLM version.”
The second thing that Fabrice suggested that the SEO community do is to make the content easily accessible by search engines.
Fabrice continued:
“Second is …have your content based on a basic template.
Don’t do the craziness things with plenty of Ajax calls to retrieve the content that the developer developing that says it will be great, but for a search engine it will be a disaster.
Machine learning is all about learning from a set of documents and then aligning to some judgment.
The more basic you are, the more standardized you are, the better it is for the search engine.
And as part of this you really want to help the content to be understood by search engines, means not only add HTML tags, the appropriate HTML title to differentiate the headings from the paragraph. And so on.
But add structured data to help the index and help the LLM to really understand what this is all about. What your content is all about.
So all this information is leveraged, real time as soon as we call the page for the index.
LLM has a different lifecycle. …LLM are not built at the same lifecycle as building an index.
Building an index is real-time. In an LLM it takes weeks, months, more likely years, to build the new LLM tech.
So this is important for the SEO community because you have to do it right now, as soon as possible to be a part of the next LLM version.
If you think of the old search engines, this is kind of the lifecycle that you need to target.
Fundamentally this about doing the right thing now, today.
And …doing the right things will benefit not only for search engine indexing, but also for LLMs.”
Bing Avoids Big Updates
Something interesting that Fabrice mentioned is that they try to avoid disruptive changes in rankings, which is different from the way Google’s core algorithm updates function. Instead, he described a process that is always changing.
Fabrice said:
“At Bing we in general avoid this kind of big change. Because this is constantly ongoing, meaning there are always improvements.
The lifecycle of a Bing engineer is to dream of a relevance improvement, to go to work in the morning to be able to code and test this experiment and in the afternoon this engineer will start to get feedback.
And the next day it’s good, then they can start …testing and rolling out the change.
So this is multiple hundreds of experiments that are done in the course of a day to really test things.
The ones that are good go live.
So this is continuous improvement, it’s not waves of improvement as we may see often in other search engines.”
Understanding SEO For AI Search
Learning what LLM search is about is critical because AI search is upon us right now. It may be in beta status like Google SGE or it may still be evolving, like Bing, as users figure out for themselves how to best use AI search.
As search professionals we need to get on board with certain ideas and practices:
- Don’t think in terms of keyword matching but rather use keywords to help the content become easy to understand what it’s about.
- Consider verbs that users may use to ask questions in order to better align your content to be relevant to their queries.
- Links from AI search are qualified, they’re on target.
- Use structured data.
- Use IndexNow in order to help your content get indexed fast.
- Avoid complex websites as best that you can.
- Blue links are not entirely going away.
Watch the video:
How does Generative AI in Search Work and What is Coming in 2024
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Freer
SEO
Is It Alternatives You’re Looking For?

Whatever the reason, in this article, I’ll share some alternatives to HARO and a few extra ways to get expert quotes and backlinks for your website.
Disclaimer: I am not a PR expert. I did a bit of outreach a few years ago, but I have only been an occasional user of HARO in the past year or so.
So, rather than providing my opinion on the best alternatives to HARO, I thought it would be fun to ask users of the “new HARO” what they thought were the best alternatives.
I wanted to give the “new HARO”—Connectively—the benefit of the doubt.
Still, a few minutes after my pitch was accepted, I got two responses that appeared to be AI-generated from two “visionary directors,” both with “extensive experience.”
My experience of Connectively so far mirrored Josh’s experience of old HARO: The responses were most likely automated.
Although I was off to a bad start, looking through most of the responses afterward, these two were the only blatant automated pitches I could spot.
These responses weren’t included in my survey, and anyone who saw my pitch would have to copy and paste the survey link to complete it—increasing the chance of genuine human responses—hopefully.
So, without further ado, here are the results of the survey.

Sidenote.
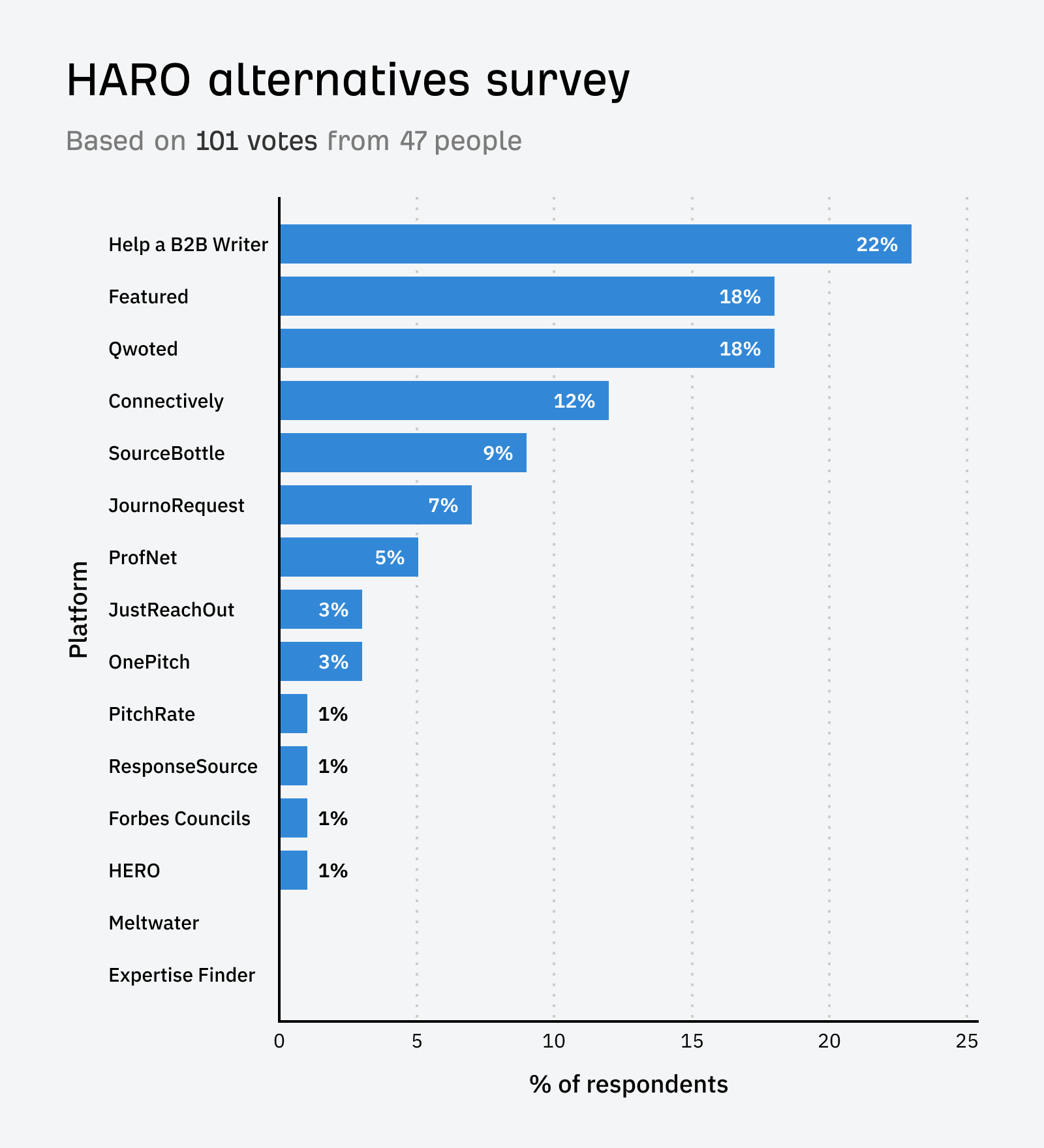
The survey on Connectively ran for a week and received 101 votes. Respondents could vote for their top three HARO alternatives.
Price: Free.
Help a B2B Writer was the #1 alternative platform respondents recommended. In my survey it got 22% of the vote.
Help a B2B Writer is a platform run by Superpath that is similar to HARO but focused on connecting business-to-business (B2B) journalists with industry experts and sources for their stories.


Price: Free and paid plans. Paid plans start at $99 per month.
Coming in joint second place, Featured was popular, scoring 18% of the vote.
Featured connects journalists with experts and thought leaders. It allows experts to create profiles showcasing their expertise and helps journalists find suitable sources for their stories.


Price: Free and paid plans. Paid plans start at $99 per month.
Qwoted is another platform that I’ve heard talked about a lot. It came in joint second place, scoring 18% of the vote.
Qwoted matches journalists with expert sources, allowing them to collaborate on creating high-quality content. It streamlines the process of finding and connecting with relevant sources.

Price: Free for ten pitches per month
Despite being the “new HARO,” Connectively came 4th on my list, scoring 12% of the vote—surprisingly, it wasn’t even the top choice for most users on its own platform.
Connectively connects journalists with sources and experts. It helps journalists find relevant sources for their stories and allows experts to gain media exposure.


Price: Free and paid plans. Paid plans start at $5.95 per month.
SourceBottle is an online platform that connects journalists, bloggers, and media professionals with expert sources. It allows experts to pitch their ideas and insights to journalists looking for story sources. It scored 9% of the vote in my survey.

Price: Free.
JournoRequest is an X account that shares journalist requests for sources. UK-based journalists and experts often use it, but it can sometimes have international reach. It scored 7% of the vote in my survey.


Price: Paid. Plans start at $1,150 per year.
ProfNet connects journalists to expert sources. It helps journalists find knowledgeable sources for their articles, interviews, and other media content. It helps subject matter experts gain media exposure and share their expertise. It scored 5% of the vote in my survey.


Price: 7-day free trial and paid plans. Paid plans start at $147 per month.
JustReachOut is a PR and influencer outreach platform that helps businesses find and connect with relevant journalists and influencers. It provides tools for personalized outreach and relationship management. It scored 3% of the vote in my survey.


Price: 14-day free trial and paid plans. Paid plans start at $50 per month.
OnePitch is a platform that simplifies the process of pitching story ideas to journalists. Businesses and PR professionals can create and send targeted pitches to relevant media outlets. It scored 3% of the vote in my survey.

Price: Free.
PitchRate is a free PR tool that connects journalists and highly rated experts. Useful for subject matter experts looking for free PR leads, media coverage, or publicity. Or journalists looking for credible sources. It scored 1% of the vote in my survey.


Price: Free and paid plans. Paid plans start at ~$105 per month.
A UK service that connects media professionals with expert sources, press releases, and PR contacts. It scored 1% of the vote in my survey.


Price: Invitation-only platform.
Forbes Councils is an invitation-only community for executives and entrepreneurs. Members can contribute expert insights and thought leadership content to Forbes.com and gain media exposure. It scored 1% of the vote in my survey.


Price: Free.
Yes, you read that right.
HERO was created by Peter Shankman, the original creator of HARO, who said the platform will always be free. It scored 1% of the vote in my survey.
Peter set up the platform after receiving over 2,000 emails asking him to build a new version of HARO.

Price: Paid. Sign up for details.
Meltwater received no votes in my survey, but I included it because I’d seen it shared on social media as a paid alternative to HARO.
It’s a media intelligence and social media monitoring platform. It provides tools for tracking media coverage, analyzing sentiment, and identifying influencers and journalists for outreach.


Price: Free.
Expertise Finder also received no votes in my survey, but it was included as I saw it had been recommended as an HARO alternative on LinkedIn. It’s a platform that helps journalists find and connect with expert sources from universities.
HARO had a dual purpose for SEOs: it was a place to acquire links, but it also was a place to get expert quotes on topics for your next article.
Here are a few more free methods outside the platforms we’ve covered that can help you get expert quotes and links.
We’ve already seen that JournoRequest is a popular X account that shares journalist requests for sources.
But you can also follow hashtags on X to access even more opportunities.
Here are my favorite hashtags to follow:
I used to track the #journorequest hashtag to find opportunities for my clients when I worked agency-side, so I know it can work well for quotes and link acquisition.
Here are two opportunities I found just checking the #journorequest hashtag:
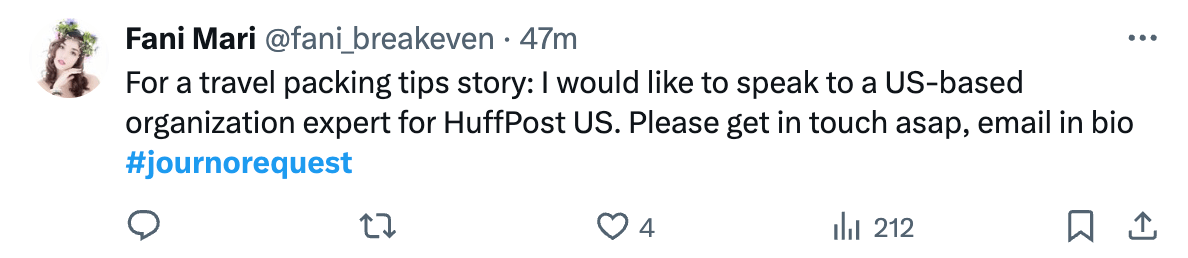

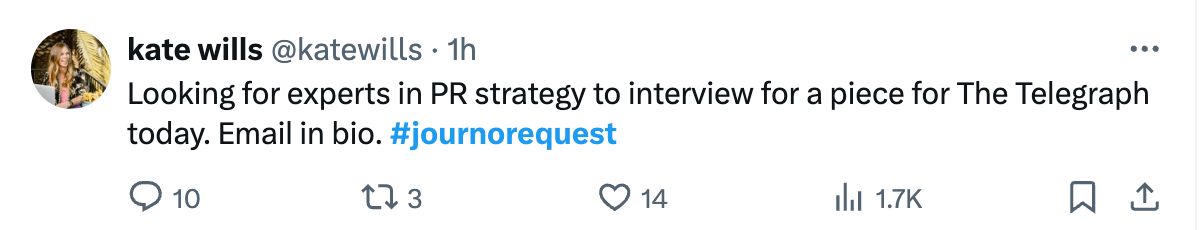
Here’s another example from the Telegraph—a DR 92 website:

Certain types of content are more likely to be shared by journalists and PRs than others.
One of these types of content is statistics-based content. The reason? Journalists often use statistics to support their points.
Once they have included your statistic in their post, they often add a backlink back to your post.
We tested this with our SEO statistics post, and as you can see, it still ranks number one in Google.
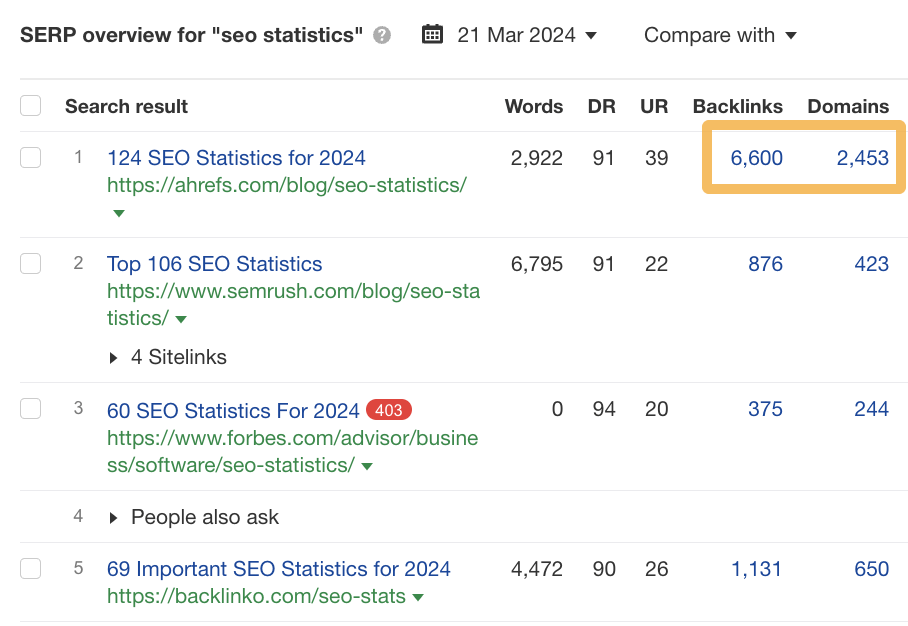

Another method is to use the Linking authors report in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. This report shows the authors’ names who link to any website you enter.
You can see which authors link to their site by entering your competitor’s domain. Some of these authors may represent outreach opportunities for your website as well.
- Head to Site Explorer, click on Linking authors
- Type in your competitor’s URL
- Contact any authors that you think may be interested in your website and its content
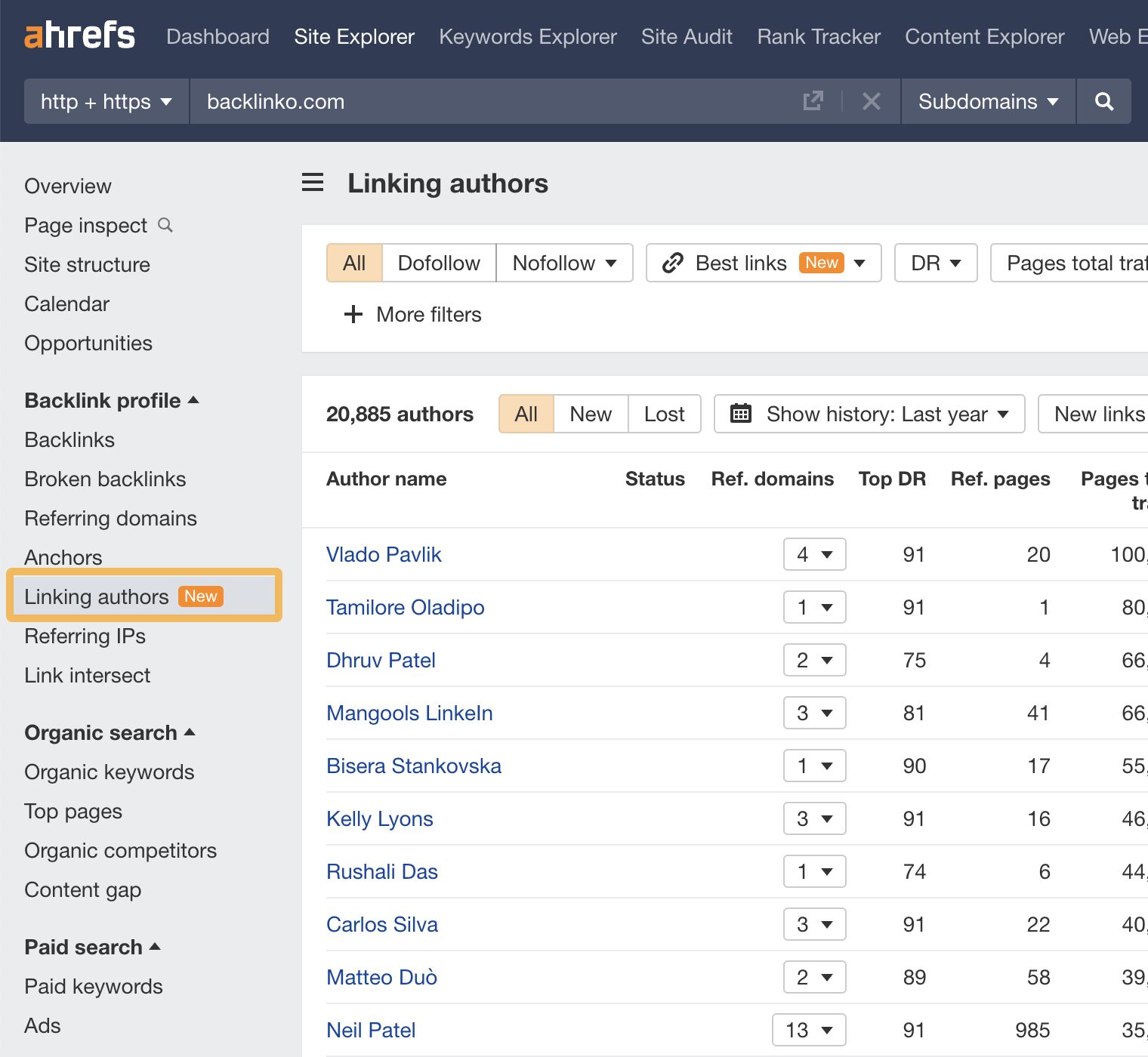

Tip
If you download your website’s linking authors and your competitors into a spreadsheet and put them into separate tabs, you can compare the lists to see which authors are only linking to your competitor’s website.
When I was about to wrap up this article, I was contacted by Greg Heilers of Jolly SEO on LinkedIn.
He said he’d sent 200,000+ pitches over the years and wanted to share the results with me.
These are his top three platforms over the last 1,000 pitches he sent. Interestingly, we can see that it’s similar to my much smaller-scale survey.
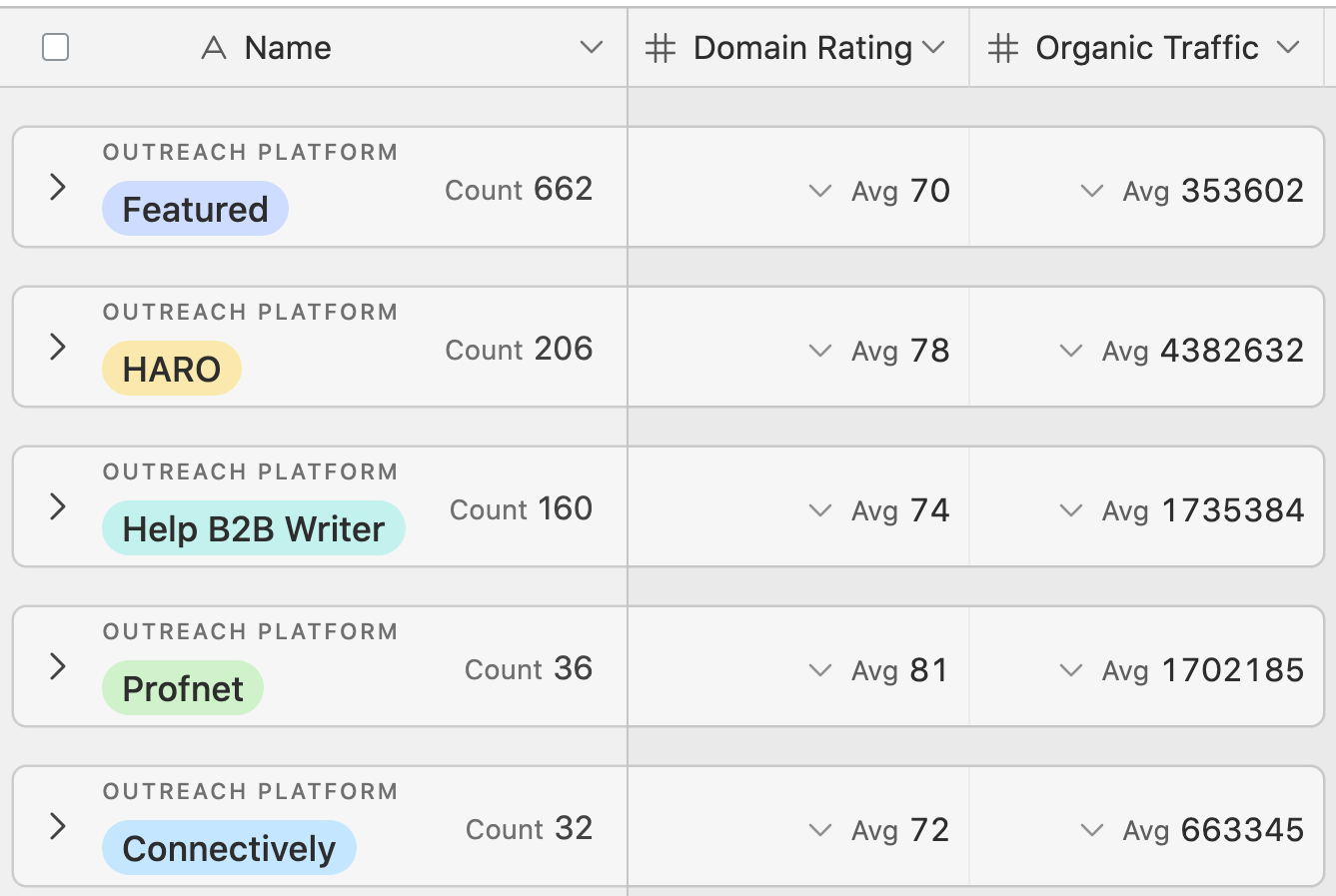

Hopefully, the data here speaks for itself. The high-quality links and traffic from HARO alternatives is considerable.
This research shows that Featured gained the most link placements in this campaign.
We have compiled some helpful content related to link building that you can get your teeth into. These hand-picked guides will take you from beginner to expert in no time.
Here are my favorite resources on this topic:
Final thoughts
There are many options for sourcing expert quotes and getting links for your next marketing campaigns. HARO may be dead, but its legacy lives on.
My highly unscientific survey suggests that most “new HARO” users liked Help a B2B Writer the most, but for HARO purists, there really is only one choice—HERO.
Give your favorites from this list a whirl, and let me know if you have any success. Got more questions? Ping me on X. 🙂
SEO
OpenAI To Show Content & Links In Response To Queries

OpenAI content deal will enhance ChatGPT with the ability to show real-time content with links in response to queries. OpenAI quietly took steps to gaining more search engine type functionality as part of a content licensing deal that may have positive implications for publishers and SEO.
Content Licensing Deal
OpenAI agreed to content licensing with the Financial Times, a global news organization with offices in London, New York, across continental Europe and Asia.
Content licensing deals between AI organizations and publishers are generally about getting access to high quality training data. The training data is then used by language models to learn connections between words and concepts. This deal goes far beyond that use.
ChatGPT Will Show Direct Quotes With Attribution
What makes this content licensing deal between The Financial Times and OpenAI is that there is a reference to giving attribution to content within ChatGPT.
The announced licensing deal explicitly mentions the use of the licensed content so that ChatGPT could directly quote it and provide links to the licensed content.
Further, the licensing deal is intended to help improve ChatGPT’s “usefulness”, which is vague and can mean many things, but it takes on a slightly different meaning when used in the context of attributed answers.
The Financial Times agreement states that the licensing deal is for use in ChatGPT when it provides “attributed content” which is content with an attribution, commonly a link to where the content appeared.
This is the part of the announcement that references attributed content:
“The Financial Times today announced a strategic partnership and licensing agreement with OpenAI, a leader in artificial intelligence research and deployment, to enhance ChatGPT with attributed content, help improve its models’ usefulness by incorporating FT journalism, and collaborate on developing new AI products and features for FT readers. “
And this is the part of the announcement that mentions ChatGPT offering users attributed quotes and links:
“Through the partnership, ChatGPT users will be able to see select attributed summaries, quotes and links to FT journalism in response to relevant queries.”
The Financial Times Group CEO was even more explicit about OpenAI’s intention to show content and links in ChatGPT:
“This is an important agreement in a number of respects,” said FT Group CEO John Ridding. “It recognises the value of our award-winning journalism and will give us early insights into how content is surfaced through AI. …this partnership will help keep us at the forefront of developments in how people access and use information.
OpenAI understands the importance of transparency, attribution, and compensation…”
Brad Lightcap, COO of OpenAI directly referenced showing real-time news content in ChatGPT but more important he referenced OpenAI exploring new ways to show content to its user base.
Lastly, the COO stated that they embraced disruption, which means innovation that creates a new industry or paradigm, usually at the expense of an older one, like search engines.
Lightcap is quoted:
“We have always embraced new technologies and disruption, and we’ll continue to operate with both curiosity and vigilance as we navigate this next wave of change.”
Showing direct quotes of Financial Times content with links to that content is very similar to how search engines work. This is a big change to how ChatGPT works and could be a sign of where ChatGPT is going in the future, a functionality that incorporates online content with links to that content.
Something Else That Is Possibly Related
Someone on Twitter recently noticed a change that is related to “search” in relation to ChatGPT.
This change involves an SSL security certificate that was added for a subdomain of ChatGPT.com. ChatGPT.com is a domain name that was snapped up by someone to capitalize on the 2022 announcement of ChatGPT by OpenAI. OpenAI eventually acquired the domain and it’s been redirecting to ChatGPT.
The change that was noticed is to the subdomain: search.chatgpt.com.
This is a screenshot of the tweet:
Big News For SEO and Publishers
This is significant news for publishers and search marketers ChatGPT will become a source of valuable traffic if OpenAI takes ChatGPT in the direction of providing attributed summaries and direct quotes.
How Can Publishers Get Traffic From ChatGPT?
Questions remain about attributed quotes with links in response to relevant queries. Here are X unknowns about ChatGPT attributed links.
- Does this mean that only licensed content will be shown and linked to in ChatGPT?
- Will ChatGPT incorporate and use most web data without licensing deals in the same way that search engines do?
- OpenAI may incorporate an Opt-In model where publishers can use a notation in Robots.txt or in meta data to opt-in to receiving traffic from ChatGPT.
- Would you opt into receiving traffic from ChatGPT in exchange for allowing your content to be used for training?
- How would SEOs and publisher’s equation on ChatGPT change if their competitors are all receiving traffic from ChatGPT?
Read the original announcement:
Financial Times announces strategic partnership with OpenAI
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Photo For Everything
SEO
Google’s John Mueller On Website Recovery After Core Updates

John Mueller, a Google Search Advocate, provided guidance this week regarding the path forward for websites impacted by recent search algorithm updates.
The discussion started on X (formerly Twitter) by SEO professional Thomas Jepsen.
Jepsen tagged Mueller, asking:
“Google has previously said Google doesn’t hold a grudge and sites will recover once issues have been solved. Is that still the case after HCU?”
Mueller’s response offered hope to site owners while being realistic about the challenges ahead.
Addressing Recovery Timelines
Mueller affirmed Google’s stance on not holding grudges, stating, “That’s still the case.”
However, he acknowledged the complexity of rankings, saying:
“…some things take much longer to be reassessed (sometimes months, at the moment), and some bigger effects require another update cycle.”
That’s still the case. That said, some things take much longer to be reassessed (sometimes months, at the moment), and some bigger effects require another update cycle. https://t.co/WDy7Q4dpzb has some more.
— John 🧀 … 🧀 (@JohnMu) April 29, 2024
Mueller pointed to a Google help document explaining the nuances. The document reads:
“Broad core updates tend to happen every few months. Content that was impacted in Search or Discover by one might not recover—assuming improvements have been made—until the next broad core update is released.
Do keep in mind that improvements made by site owners aren’t a guarantee of recovery, nor do pages have any static or guaranteed position in our search results. If there’s more deserving content, that will continue to rank well with our systems.”
The Comments Sparking Debate
Jepsen probed further, asking, “Is a core update what’s needed for HCU-affected sites to recover (assuming they’ve fixed their issues)?”
Mueller’s response highlighted how situations can differ:
“It depends on the situation… I realize there’s a big space between the situations, but generalizing doesn’t help. Sometimes it takes a lot of work on the site, a long time, and an update.”
It depends on the situation. https://t.co/F9s3Hli9t7 and https://t.co/pLdm29PjPD has some on that. I realize there’s a big space between the situations, but generalizing doesn’t help. Sometimes it takes a lot of work on the site, a long time, and an update.
— John 🧀 … 🧀 (@JohnMu) April 29, 2024
The thread grew as user @selectgame raised concerns about Google Discover traffic, to which Mueller replied:
“Google Discover is affected by core updates as well as other parts of Search (and there are more policies that apply to Discover).”
Google Discover is affected by core updates as well as other parts of Search (and there are more policies that apply to Discover). If you’re seeing these changes when a core update rolled out, that might be what you’re seeing.
— John 🧀 … 🧀 (@JohnMu) April 29, 2024
Growing Frustrations
Prominent industry figure Lily Ray voiced mounting frustrations, stating,
“…many HCU-affected websites – which have been making all kinds of improvements over the last 7 months – have only seen further declines with the March Core Update.
I have seen some sites lose 90% or more of their SEO visibility since the HCU, with the last few weeks being the nail in the coffin, despite making significant improvements.”
Ray continued:
“And in my professional opinion, many of these sites did not deserve anywhere near that level of impact, especially the further declines over the past month.”
Mueller hasn’t responded to Ray’s tweet at this time.
John, any chance you can comment on the fact that many HCU-affected websites – which have been making all kinds of improvements over the last 7 months – have only seen further declines with the March Core Update?
I have seen some sites lose 90% or more of their SEO visibility… https://t.co/lvYRAScRQQ
— Lily Ray 😏 (@lilyraynyc) April 29, 2024
Looking Ahead
As the search community awaits Google’s next moves, the path to recovery appears arduous for many impacted by recent algorithm reassessments of “Helpful Content.”
Site improvements don’t guarantee immediate recovery, so publishers face an uphill battle guided only by Google’s ambiguous public advice.
Why SEJ Cares
The March 2024 core update has proven disastrous for many websites, with severe traffic losses persisting even after sites try to improve low-quality content, address technical issues, and realign with Google’s guidelines.
Having clear, actionable guidance from Google on recovering from core update updates is invaluable.
As evidenced by the frustrations expressed, the current communications leave much to be desired regarding transparency and defining a straightforward recovery path.
How This Can Help You
While Mueller’s comments provide some insights, the key takeaways are:
- Regaining previous rankings after an algorithm hit is possible if sufficient content/site quality improvements are made.
- Recovery timelines can vary significantly and may require a future core algorithm update.
- Even with enhancements, recovery isn’t guaranteed as rankings depend on the overall pool of competing content.
The path is undoubtedly challenging, but Mueller’s comments underscore that perseverance with substantial site improvements can eventually pay off.
FAQ
Can SEO professionals predict recovery time for a website hit by core updates?
SEO professionals can’t pinpoint when a site will recover after a core Google algorithm update.
Reasons for this include:
- Google releases core updates every few months, so sites may need to wait for the next one.
- It can take months for Google to reassess and adjust rankings.
- How competitive the query is also impacts if and when a site recovers.
Does making site improvements after a core update ensure recovery in rankings and visibility?
After making improvements following a Google algorithm update, regaining your previous rankings isn’t guaranteed.
Reasons why include:
- Your impacted content may not recover until the next core update, provided you’ve implemented enough site improvements.
- Google’s search results are dynamic, and rankings can fluctuate based on the quality of competitor content.
- There’s no fixed or guaranteed position in Google’s search results.
What is the relationship between Google Discover traffic and core search updates?
Google’s core algorithm updates that impact regular search results also affect Google Discover.
However, Google Discover has additional specific policies that determine what content appears there.
This means:
- Improving your content and website quality can boost your visibility on Google Discover, just like regular searches.
- You may see changes in your Discover traffic when Google rolls out core updates.
- Your SEO and content strategy should account for potential impacts on regular searches and Google Discover.
Featured Image: eamesBot/Shutterstock
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEffective Communication in Business as a Crisis Management Strategy
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Won’t Change The 301 Signals For Ranking & SEO
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agobrightonSEO Live Blog
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days ago9 Ecommerce Trends to Boost Your Business in 2024
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days agoGoogle March 2024 Core Update Officially Completed A Week Ago
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days ago9 Best WooCommerce Multi Vendor Plugins (Compared)
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 25, 2024
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoYour New Favorite Way to Develop WordPress Locally – WordPress.com News













