SEO
Embracing AI Skills Amidst Job Market Turbulence

With the rapid pace of artificial intelligence (AI) news, it’s no surprise that six in ten Americans believe AI will significantly impact the labor force.
According to a report published by the U.S. White House, AI has the potential to increase productivity, efficiency, and innovation. Likewise, it can potentially displace workers who need help adapting to AI tools and skill sets.
An OpenAI study revealed the types of occupations which could be most affected by large language models (LLMs). Mathematicians, analysts, researchers, and writers could utilize GPT to reduce the time spent on tasks.
AI alone may not take most jobs. But the people who utilize AI in the right way will be the ones to take them as others become unable to meet new quotas and productivity expectations.
Reskilling Employees To Fill AI-Roles
A McKinsey survey of organizations worldwide found that almost half reskill internal resources to fill AI-related roles in addition to sourcing talent from tech companies and universities.
Organizations that chose to reskill employees used various training paths, including self-paced online courses and certifications.
It makes sense, considering employees know what their organization needs to succeed. AI allows employees willing to learn to boost their productivity and creative output to become valuable assets to their organization.
Continued Layoffs In Tech
Of course, not all companies will retrain employees for new opportunities. We’ve seen tech companies lay off hundreds to thousands of employees since the start of 2023. And the layoffs are not over yet.
Meta recently began another round of layoffs in its quest for efficiency.
According to Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) reports across the United States, many large companies in tech and beyond are planning more layoffs. U.S. employees can search Google for WARN notices in their employer’s state.
Increasing Jobs Listings Seek Talent With AI Skills
For those seeking a job in tech, Stanford revealed that the U.S., Canada, and Spain have the highest percentage of AI job postings in its AI Index Report.
John Mueller offered advice for those in search of a job in tech: “…my recommendation would be to take the time to get your skills & knowledge up to a high level, and then seriously look into a job once things start to pick up again.”
Comprehensive AI Courses To Enhance Your Skillset
Here are AI and machine learning online courses and certifications from tech companies and universities to work into your resume.
LinkedIn AI And Machine Courses
LinkedIn Learning made 100 AI and machine learning courses free until June 15, 2023. Topics covered include generative AI, AI and machine learning foundations, responsible AI, advanced AI, and applied AI.
IBM AI Foundations For Everyone Specialization
This introductory course on AI is designed for everyone, including those without a technical or programming background.
The specialization consists of three courses on AI uses and applications, using IBM Watson, and building AI chatbots.
IBM also offers AI Foundations for Business Specialization and professional certifications for applied AI, AI engineering, and machine learning.
Some courses are offered through Coursera. Coursera offers a seven-day free trial, after which it is $39 monthly to continue a single course.
If you find additional courses on Coursera, you can subscribe to the premium service that includes unlimited access to thousands of courses and certifications for $59 monthly.
Courses that offer certification or college credit may have additional prerequisites, requirements, and fees.
Google Machine Learning Crash Course
If you want a quick dive into the basics of machine learning, try this free Machine Learning Crash Course. It includes video lessons, case studies, and hands-on practice with TensorFlow APIs, an open-source platform for developing and training machine learning models.
Google AI offers more courses on various aspects of machine learning.
If you want to pursue a career as a data scientist or machine learning engineer, Google Cloud offers courses for a Professional Machine Learning Engineer Certification.
Google Advanced Data Analytics Professional Certificate
Recently introduced on The Keyword blog, the Google Advanced Data Analytics Professional Certificate is a self-paced course that prepares data analysts and scientists to use regression and machine learning models to collect and analyze data.
It could require approximately ten hours a week for three to six months to complete the course and earn a shareable certificate.
Microsoft Azure Data And AI Certifications
Microsoft offers several certifications for data analysts, developers, and engineers using AI and Microsoft Azure.
They also offer an Autonomous AI for Industry Specialization with the University of Washington.
Arizona State University MasterTrack® Certificate In AI & Machine Learning
If you already have a bachelor’s degree, you can complete three courses within an estimated six to nine months to earn a certificate in AI and machine learning.
You can choose from four courses on statistical machine learning, artificial intelligence, knowledge representation and reasoning, and an intro to deep learning.
The certificate program is $4,500 total or $1,500 per course.
If you meet specific ASU requirements, these credits will apply to an online Master of Computer Science program.
Stanford Artificial Intelligence Professional Program
Stanford’s AI Professional Program allows working professionals to dive into graduate-level AI and machine learning courses.
The program consists of seven courses. Each course costs $1,750 and takes 10 – 15 hours weekly for ten weeks.
Continuing Education
With the rapid developments in AI and machine learning, anyone interested in the field should stay current with the latest AI and machine learning news relevant to their industry.
Featured image: Chay_Tee/Shutterstock
SEO
Competing Against Brands & Nouns Of The Same Name

Establishing and building a brand has always been both a challenge and an investment, even before the days of the internet.
One thing the internet has done, however, is make the world a lot smaller, and the frequency of brand (or noun) conflicts has greatly increased.
In the past year, I’ve been emailed and asked questions about these conflicts at conferences more than I have in my entire SEO career.
When you share your brand name with another brand, town, or city, Google has to decide and determine the dominant user interpretation of the query – or at least, if there are multiple common interpretations, the most common interpretations.
Noun and brand conflicts typically happen when:
- A rebrand’s research focuses on other business names and doesn’t take into consideration general user search.
- When a brand chooses a word in one language, but it has a use in another.
- A name is chosen that is also a noun (e.g. the name of a town or city).
Some examples include Finlandia, which is both a brand of cheese and vodka; Graco, which is both a brand of commercial products and a brand of baby products; and Kong, which is both the name of a pet toy manufacturer and a tech company.
User Interpretations
From conversations I’ve had with marketers and SEO pros working for various brands with this issue, the underlying theme (and potential cause) comes down to how Google handles interpretation of what users are looking for.
When a user enters a query, Google processes the query to identify known entities that are contained.
It does this to improve the relevance of search results being returned (as outlined in its 2015 Patent #9,009,192). From this, Google also works to return related, relevant results and search engine results page (SERP) elements.
For example, when you search for a specific film or TV series, Google may return a SERP feature containing relevant actors or news (if deemed relevant) about the media.
This then leads to interpretation.
When Google receives a query, the search results need to often cater for multiple common interpretations and intents. This is no different when someone searches for a recognized branded entity like Nike.
When I search for Nike, I get a search results page that is a combination of branded web assets such as the Nike website and social media profiles, the Map Pack showing local stores, PLAs, the Nike Knowledge Panel, and third-party online retailers.
This variation is to cater for the multiple interpretations and intents that a user just searching for “Nike” may have.
Brand Entity Disambiguation
Now, if we look at brands that share a name such as Kong, when Google checks for entities and references against the Knowledge Graph (and knowledge base sources), it gets two closer matches: Kong Company and Kong, Inc.
The search results page is also littered with product listing ads (PLAs) and ecommerce results for pet toys, but the second blue link organic result is Kong, Inc.
Also on page one, we can find references to a restaurant with the same name (UK-based search), and in the image carousel, Google is introducing the (King) Kong film franchise.
It is clear that Google sees the dominant interpretation of this query to be the pet toy company, but has diversified the SERP further to cater for secondary and tertiary meanings.
In 2015, Google was granted a patent that included features of how Google might determine differences in entities of the same name.
This includes the possible use of annotations within the Knowledge Base – such as the addition of a word or descriptor – to help disambiguate entities with the same name. For example, the entries for Dan Taylor could be:
- Dan Taylor (marketer).
- Dan Taylor (journalist).
- Dan Taylor (olympian).
How it determines what is the “dominant” interpretation of the query, and then how to order search results and the types of results, from experience, comes down to:
- Which results users are clicking on when they perform the query (SERP interaction).
- How established the entity is within the user’s market/region.
- How closely the entity is related to previous queries the user has searched (personalization).
I’ve also observed that there is a correlation between extended brand searches and how they affect exact match branded search.
It’s also worth highlighting that this can be dynamic. Should a brand start receiving a high volume of mentions from multiple news publishers, Google will take this into account and amend the search results to better meet users’ needs and potential query interpretations at that moment in time.
SEO For Brand Disambiguation
Building a brand is not a task solely on the shoulders of SEO professionals. It requires buy-in from the wider business and ensuring the brand and brand messaging are both defined and aligned.
SEO can, however, influence this effort through the full spectrum of SEO: technical, content, and digital PR.
Google understands entities on the concept of relatedness, and this is determined by the co-occurrence of entities and then how Google classifies and discriminates between those entities.
We can influence this through technical SEO through granular Schema markup and by making sure the brand name is consistent across all web properties and references.
This ties into how we then write about the brand in our content and the co-occurrence of the brand name with other entity types.
To reinforce this and build brand awareness, this should be coupled with digital PR efforts with the objective of brand placement and corroborating topical relevance.
A Note On Search Generative Experience
As it looks likely that Search Generative Experience is going to be the future of search, or at least components of it, it’s worth noting that in tests we’ve done, Google can, at times, have issues when generative AI snapshots for brands, when there are multiple brands with the same name.
To check your brand’s exposure, I recommend asking Google and generating an SGE snapshot for your brand + reviews.
If Google isn’t 100% sure which brand you mean, it will start to include reviews and comments on companies of the same (or very similar) name.
It does disclose that they are different companies in the snapshot, but if your user is skim-reading and only looking at the summaries, this could be an accidental negative brand touchpoint.
More resources:
Featured Image: VectorMine/Shutterstock
SEO
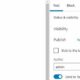
Google Rolls Out New ‘Web’ Filter For Search Results

Google is introducing a filter that allows you to view only text-based webpages in search results.
The “Web” filter, rolling out globally over the next two days, addresses demand from searchers who prefer a stripped-down, simplified view of search results.
Danny Sullivan, Google’s Search Liaison, states in an announcement:
“We’ve added this after hearing from some that there are times when they’d prefer to just see links to web pages in their search results, such as if they’re looking for longer-form text documents, using a device with limited internet access, or those who just prefer text-based results shown separately from search features.”
We’ve added this after hearing from some that there are times when they’d prefer to just see links to web pages in their search results, such as if they’re looking for longer-form text documents, using a device with limited internet access, or those who just prefer text-based…
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) May 14, 2024
The new functionality is a throwback to when search results were more straightforward. Now, they often combine rich media like images, videos, and shopping ads alongside the traditional list of web links.
How It Works
On mobile devices, the “Web” filter will be displayed alongside other filter options like “Images” and “News.”
If Google’s systems don’t automatically surface it based on the search query, desktop users may need to select “More” to access it.
 Screenshot from: twitter.com/GoogleSearchLiaison, May 2024.
Screenshot from: twitter.com/GoogleSearchLiaison, May 2024.More About Google Search Filters
Google’s search filters allow you to narrow results by type. The options displayed are dynamically generated based on your search query and what Google’s systems determine could be most relevant.
The “All Filters” option provides access to filters that are not shown automatically.
Alongside filters, Google also displays “Topics” – suggested related terms that can further refine or expand a user’s original query into new areas of exploration.
For more about Google’s search filters, see its official help page.
Featured Image: egaranugrah/Shutterstock
SEO
Why Google Can’t Tell You About Every Ranking Drop

In a recent Twitter exchange, Google’s Search Liaison, Danny Sullivan, provided insight into how the search engine handles algorithmic spam actions and ranking drops.
The discussion was sparked by a website owner’s complaint about a significant traffic loss and the inability to request a manual review.
Sullivan clarified that a site could be affected by an algorithmic spam action or simply not ranking well due to other factors.
He emphasized that many sites experiencing ranking drops mistakenly attribute it to an algorithmic spam action when that may not be the case.
“I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a algorithmic spam action against them, but they don’t. “
Sullivan’s full statement will help you understand Google’s transparency challenges.
Additionally, he explains why the desire for manual review to override automated rankings may be misguided.
Two different things. A site could have an algorithmic spam action. A site could be not ranking well because other systems that *are not about spam* just don’t see it as helpful.
I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a…
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) May 13, 2024
Challenges In Transparency & Manual Intervention
Sullivan acknowledged the idea of providing more transparency in Search Console, potentially notifying site owners of algorithmic actions similar to manual actions.
However, he highlighted two key challenges:
- Revealing algorithmic spam indicators could allow bad actors to game the system.
- Algorithmic actions are not site-specific and cannot be manually lifted.
Sullivan expressed sympathy for the frustration of not knowing the cause of a traffic drop and the inability to communicate with someone about it.
However, he cautioned against the desire for a manual intervention to override the automated systems’ rankings.
Sullivan states:
“…you don’t really want to think “Oh, I just wish I had a manual action, that would be so much easier.” You really don’t want your individual site coming the attention of our spam analysts. First, it’s not like manual actions are somehow instantly processed. Second, it’s just something we know about a site going forward, especially if it says it has change but hasn’t really.”
Determining Content Helpfulness & Reliability
Moving beyond spam, Sullivan discussed various systems that assess the helpfulness, usefulness, and reliability of individual content and sites.
He acknowledged that these systems are imperfect and some high-quality sites may not be recognized as well as they should be.
“Some of them ranking really well. But they’ve moved down a bit in small positions enough that the traffic drop is notable. They assume they have fundamental issues but don’t, really — which is why we added a whole section about this to our debugging traffic drops page.”
Sullivan revealed ongoing discussions about providing more indicators in Search Console to help creators understand their content’s performance.
“Another thing I’ve been discussing, and I’m not alone in this, is could we do more in Search Console to show some of these indicators. This is all challenging similar to all the stuff I said about spam, about how not wanting to let the systems get gamed, and also how there’s then no button we would push that’s like “actually more useful than our automated systems think — rank it better!” But maybe there’s a way we can find to share more, in a way that helps everyone and coupled with better guidance, would help creators.”
Advocacy For Small Publishers & Positive Progress
In response to a suggestion from Brandon Saltalamacchia, founder of RetroDodo, about manually reviewing “good” sites and providing guidance, Sullivan shared his thoughts on potential solutions.
He mentioned exploring ideas such as self-declaration through structured data for small publishers and learning from that information to make positive changes.
“I have some thoughts I’ve been exploring and proposing on what we might do with small publishers and self-declaring with structured data and how we might learn from that and use that in various ways. Which is getting way ahead of myself and the usual no promises but yes, I think and hope for ways to move ahead more positively.”
Sullivan said he can’t make promises or implement changes overnight, but he expressed hope for finding ways to move forward positively.
Featured Image: Tero Vesalainen/Shutterstock
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoHow to Use Keywords for SEO: The Complete Beginner’s Guide
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoAdvertising on Hulu: Ad Formats, Examples & Tips
-
 MARKETING2 days ago
MARKETING2 days ago18 Events and Conferences for Black Entrepreneurs in 2024
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoBest WordPress Plugins of All Time: Updated List for 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoUpdates to data build service for better developer experiences
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoShopify Could Be Undervalued Based On A Long-Term Horizon
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoThe Ultimate Guide to Email Marketing
-
 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoLow Risk, High Reward YouTube Ads alexking