SEO
How To Exclude Internal Traffic In Google Analytics 4

Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is rolling out in a rush, and if you’re reading this guide, you might be having a tough time figuring out how it works.
One area that might be causing you confusion is filtering out internal traffic.
If you’re like me, you’re already missing how user-friendly Universal Analytics (UA) was – especially when it came to filtering out traffic.
In UA, you had full control over how you could filter out traffic.
See the beauty it had.
-
Screenshot from Google UA, May 2023
Now, I find it hard to understand why GA4 has replaced such a vital function with only an IP-based rule.
The IP-based filter is useless when your company employees are remote as, in most cases, IPs are dynamic, and it is not practical to update the list of IPs daily.
This is why we have created this guide for you to help you filter out undesired traffic – and, most importantly, internal traffic – in GA4.
What Is Internal Traffic?
“Internal traffic” refers to the web traffic that originates from you and your employees accessing your website.
Your employees’ activity can reduce the quality of your data and make it harder for you to understand what real visitors are doing on the website, and how much traffic you have.
Even though IP-based filters may not be the best way to filter our internal traffic, I would like to start with that method as the easiest path to use – and as a basis to explain how new data filters work.
How To Filter Out Traffic Based On IP
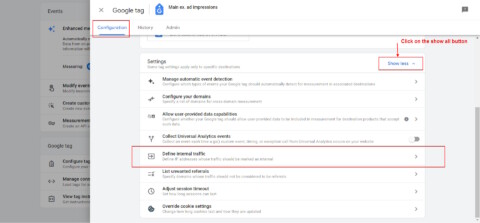
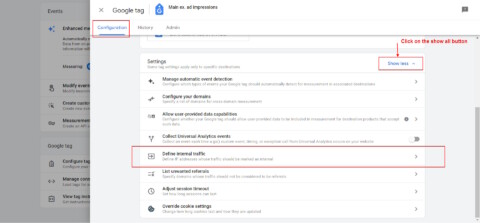
Navigate to Data Streams in GA4.
-
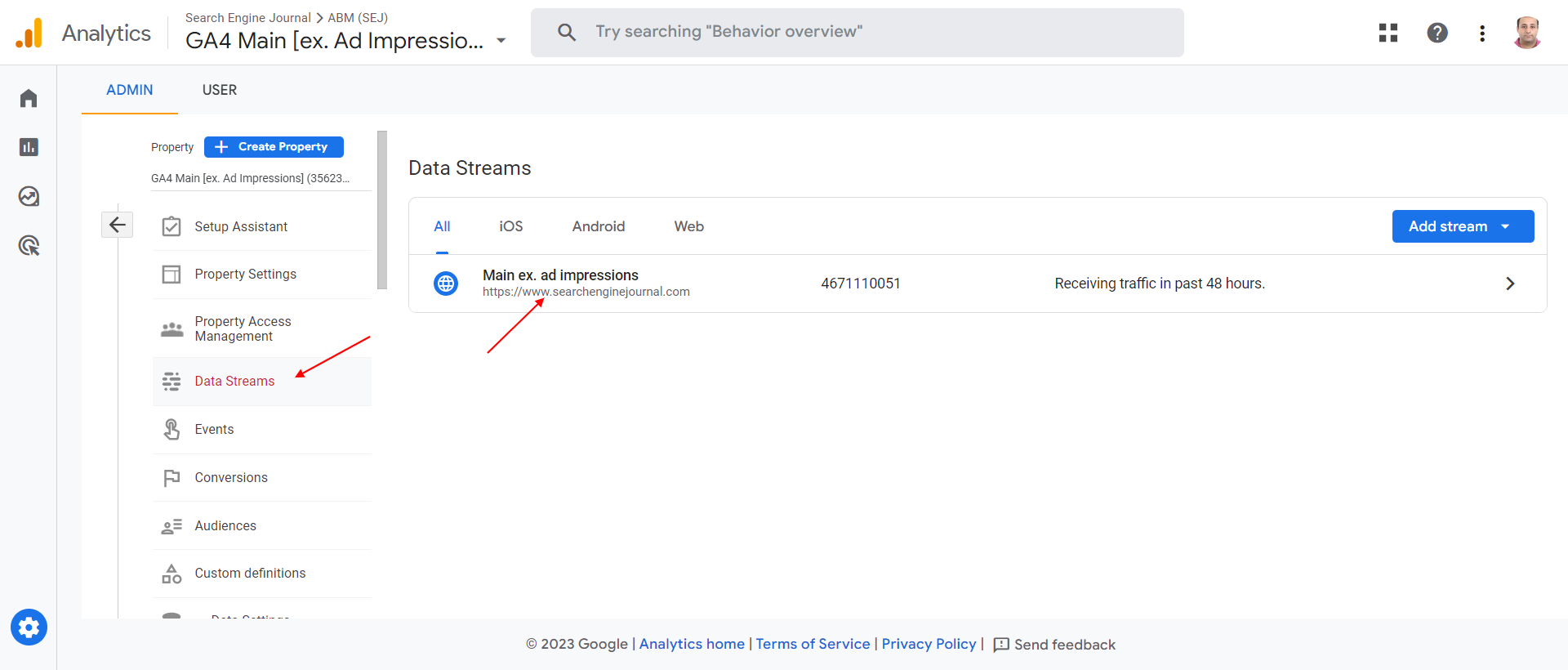 Screenshot from GA4, May 2023
Screenshot from GA4, May 2023
Go to Configure tag settings, click on the Show all button, and then click on Define Internal Traffic Rule.
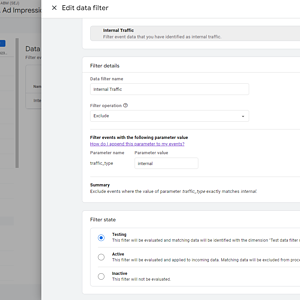
On the popup dialog, click the Create button, and you will see a screen where you can enter the IP addresses you want to exclude.
Please note the “traffic_type=internal” parameter in the dialog.
When you create a rule, whenever it applies, it does append to the Google Analytics hits the parameter “tt=internal” which is saved in the GA4 database.

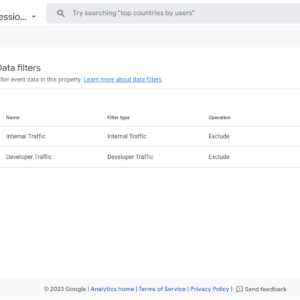
Add data filters by navigating to Data Settings then Data Filters, and clicking Create Filter button.
The basic idea is straightforward: You need to assign a value of your choice to the “traffic_type” parameter and then use data filters to remove any hits that have that same value assigned to the “traffic_type” parameter.
There are two options: The “Developer” filter and the “Internal Traffic” filter.
What Is The Internal Traffic Data Filter?
This filters out any traffic with the traffic_type parameter set to “internal” by default. The value of the parameter and filter name can be anything.
How Does The Internal Traffic Data Filter Work?
For example, you can create an IP filter rule with a parameter traffic_type=europe_headquarters and set a different IP range for your EU office.
You can create as many rules as you want with different traffic_type parameter values, and it will be sent in the hit payload (as tt a parameter) when the visitor IP matches the rule.
-
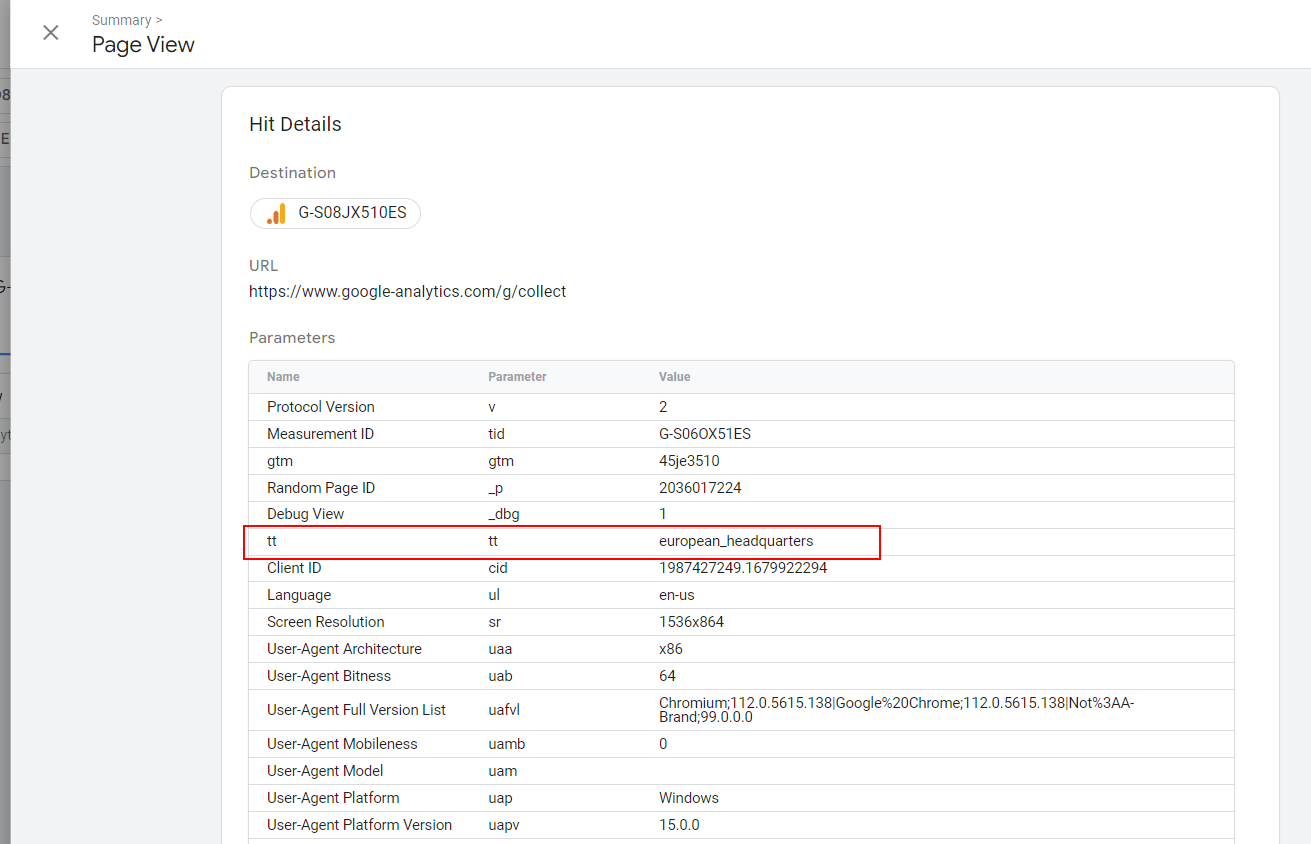 tt parameter in the hit payload
tt parameter in the hit payload
Then, by adding a data filter for each IP rule you’ve created, GA4 will exclude hits when traffic_type the data filter setting value matches the tt parameter of the payload –(tt is simply an abbreviation of “traffic type”).
What Is The Developer Traffic Data Filter?
This filter excludes traffic from developers or internal traffic from a company or organization.
Similarly to the internal traffic data filter, it eliminates only data from being recorded in GA’s database, with the difference that you can still see your activity in the Debug View and its real-time reports.
That is why it is called a developer data filter.
In contrast, you can’t see events from internal traffic in Debug View when internal data filters are active.
How Does The Developer Data Filter Work?
When debug mode is enabled _dbg payload parameter is included in hits.
Then, the developer data filter eliminates all hits with _dbg the parameter being recorded in the GA4 database.
Debug mode parameter is added when using the preview mode of Google Tag Manager, or when Google Analytics Debugger is used.
-
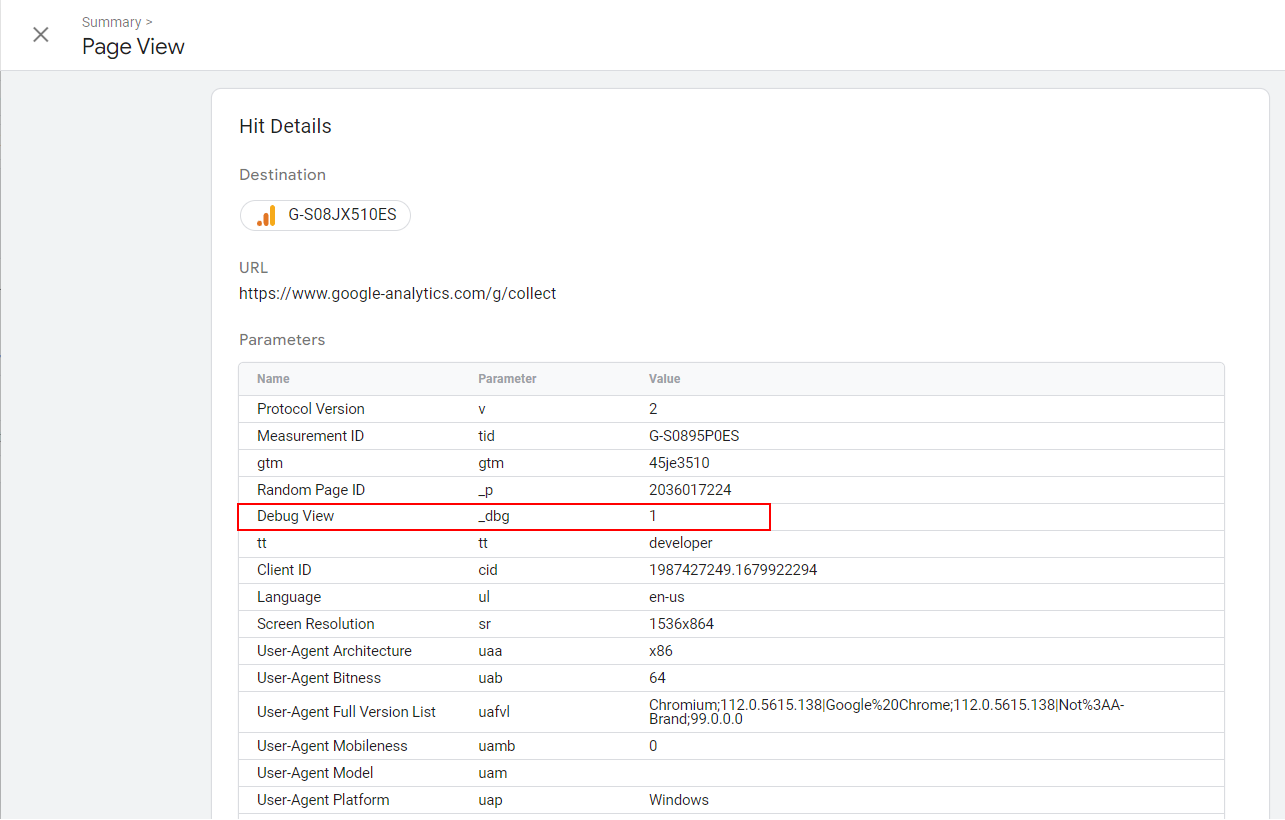 _dbg debug view parameter in the payload
_dbg debug view parameter in the payload
Data Filter States
Data filters have three different states:
- Testing.
- Active.
- Inactive.
Active and inactive states are self-explanatory, but you might be wondering what the testing state is.
In the testing mode, you can apply a filter in GA’s reports using the automatically added custom dimension “Test data filter name” equal to your data filter name.
Testing mode is a great feature that allows you to test if your filters work properly before activating them because applying a data filter permanently impacts your data.
It means the data you exclude will not be processed and won’t be accessible in Analytics.
We’ve learned how data filters work by using built-in IP filter rules.
But as I mentioned, this will not work with remote teams – and in that case, it’s better to use a cookie-based approach where you send your team a URL they can open, and their successive visits will be excluded based on the cookies.
How To Exclude Traffic In GA4 By Using Cookies
I want to be honest at the outset: Setting this up requires many steps.
You need to remember the principle.
We need to send the hits with the traffic_type parameter that we’ve set in data filters when creating them.
This means we will set a cookie on employees’ browsers and check every visit. Whenever that cookie is set, we will set the traffic_type parameter to “internal.”
Let’s say we are going to use the exclude_user query parameter.
When employees visit the URL “https://example.com/?exclude_user=1” with the query parameter “exclude_user” set to “1”, a sample cookie exclude_user will be set up.
You can send that URL to your employees to use once to open the website and set up cookies.
Please note: Keeping the names of variables the same is important for the codes below to function, and since client-side set cookies expire in seven days in Safari, your employees may need to open that URL once a week – or you can set cookies when they are logged in to your website server side.
To set up a cookie when one opens the URL https://example.com/?exclude_user=1, we need to add a “custom HTML” tag in GTM with the following script and choose the firing trigger “Pageviews All Pages.”
(Hint: You can use ChatGPT for coding.)
<script>
var urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
//check if exclude_user query parameter exists and set cookie
if (urlParams.has("exclude_user")) {
if (urlParams.get("exclude_user") === "1") {
set_cookie('exclude_user');
} else {
delete_cookie('exclude_user');
}
}
function set_cookie(cookie_name) {
var date = new Date();
date.setTime(date.getTime() + (2 * 365 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000));
var expires = "expires=" + date.toUTCString();
document.cookie = cookie_name + "=1; " + expires + "; path=/";
}
function delete_cookie(cookie_name) {
document.cookie = cookie_name + "=; expires=Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 UTC; path=/;";
}
</script>
-
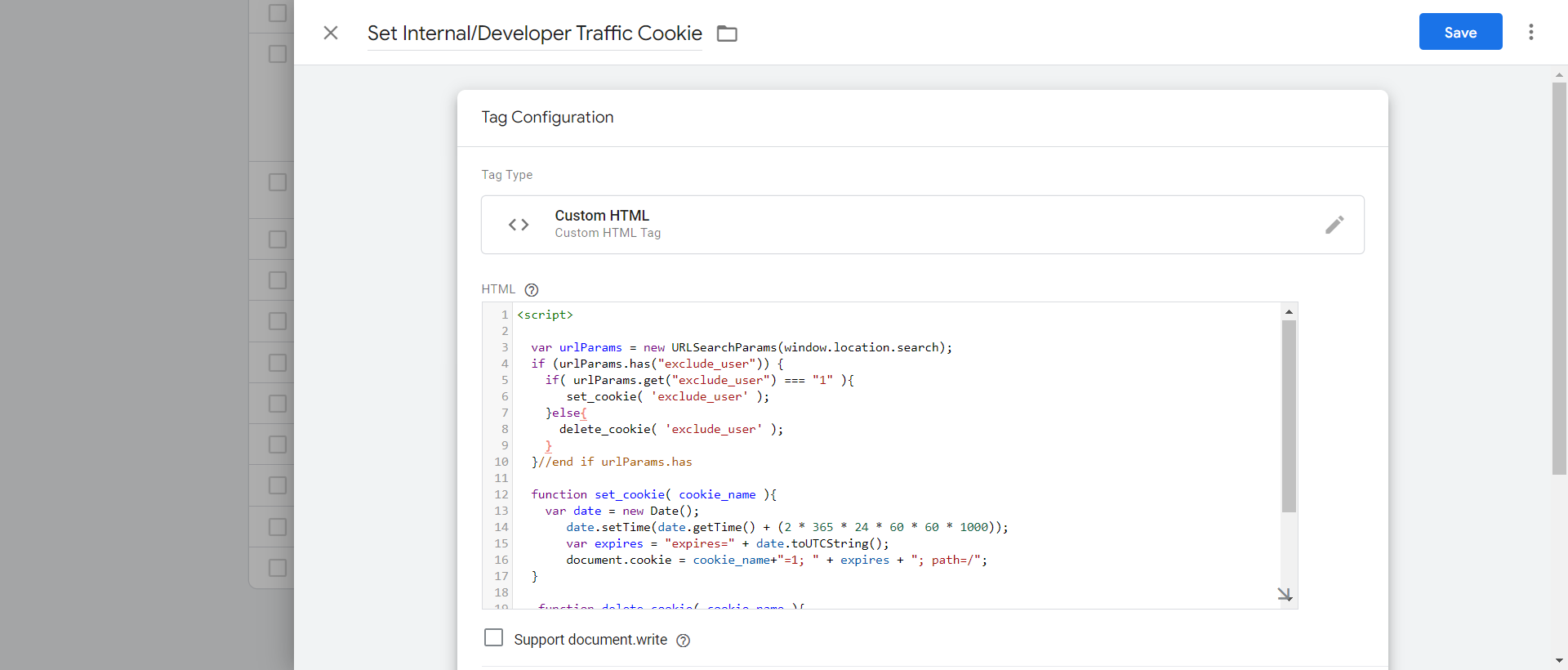 Custom HTML tag in GTM
Custom HTML tag in GTMAdd the “1st Party Cookie” type of variable with the name “Internal Cookie” and set the cookie name setting as exclude_user.
-
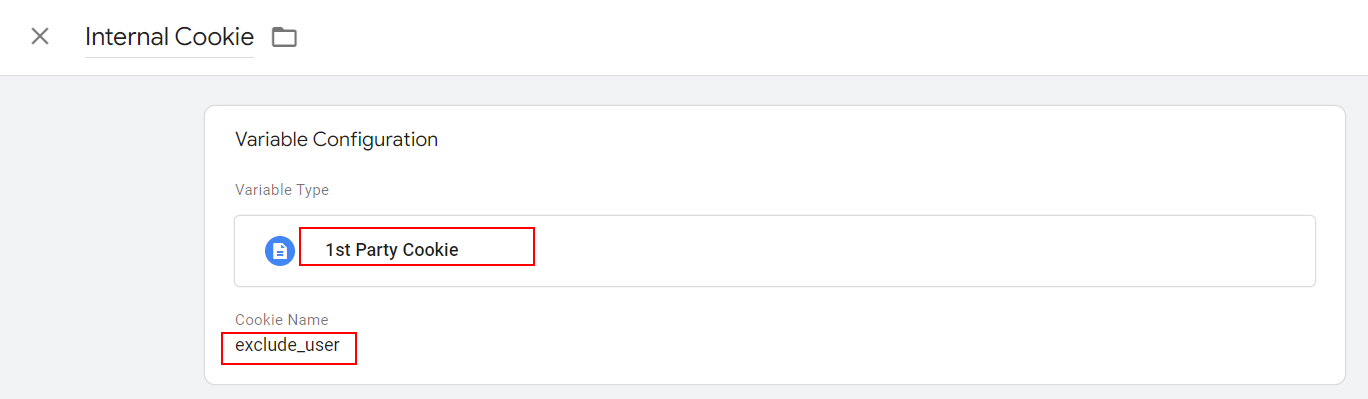 1st Party Cookie Variable
1st Party Cookie VariableIt will return the value of the exclude_user cookie if it is set, or a special value undefined (not the same as the string “undefined”) if the cookie doesn’t exist.
Add a built-in “Debug Mode” variable named “Debug Mode.”
-
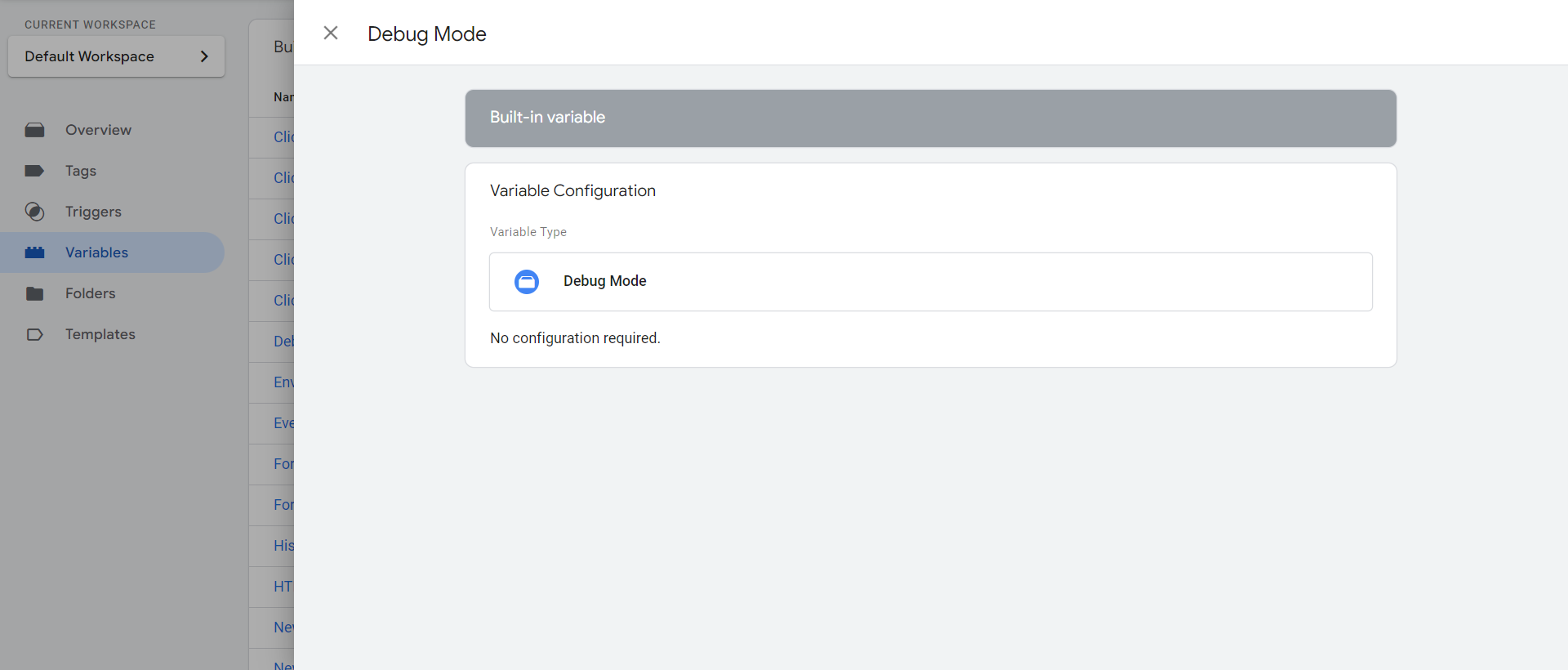 Debug mode variable
Debug mode variable
Create a JavaScript type of variable named “Internal Traffic,” copy and paste the code below into it, and save.
This JavaScript variable will return values “internal” or “developer_view” (could be anything different than “internal”) to be set up for traffic_type parameter.
function getTrackingType() {
var developer_mode = {{Debug Mode}};
var urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
var excludeUserParam = urlParams.get('exclude_user');
//if exclude_user query parameter exists, override the return value.
if( excludeUserParam !== null ){
var filter_type_overrdie = (excludeUserParam === null || excludeUserParam === '1');
//if exclude_user paramter is set don't check cookies
if( filter_type_overrdie ){
return 'internal';
}else{
return 'developer_view';
}
}
var internalCookie = {{Internal Cookie}};
if ( internalCookie === "1" ) {
return 'internal';
}
if (developer_mode) {
return 'developer_view';
}
return undefined;
}
-
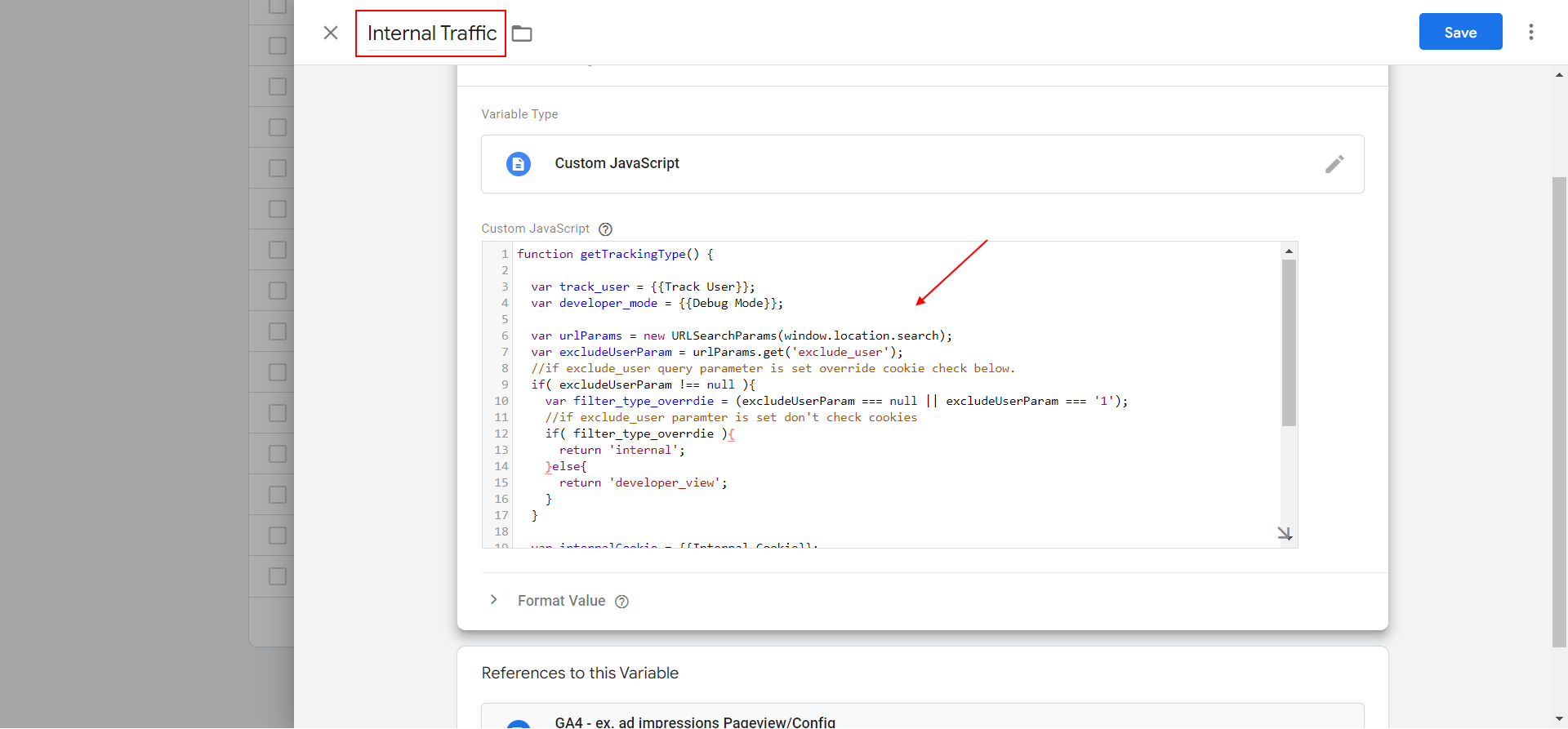 GTM JavaScript variable where we set traffic_type parameter value
GTM JavaScript variable where we set traffic_type parameter value
It will have a different value than the internal, thus our data filter will not be filtering out our developer views, and we can debug our setup while still having an exclude_user cookie setup.
The purpose of this setup is to exclude developers from website visits when they are not testing while still allowing them to perform debugging when necessary because you need to be able to debug the setup occasionally.
Set the traffic_type parameter to populate from the newly created {{Internal Traffic}} variable in your GA4 configuration tag.
-
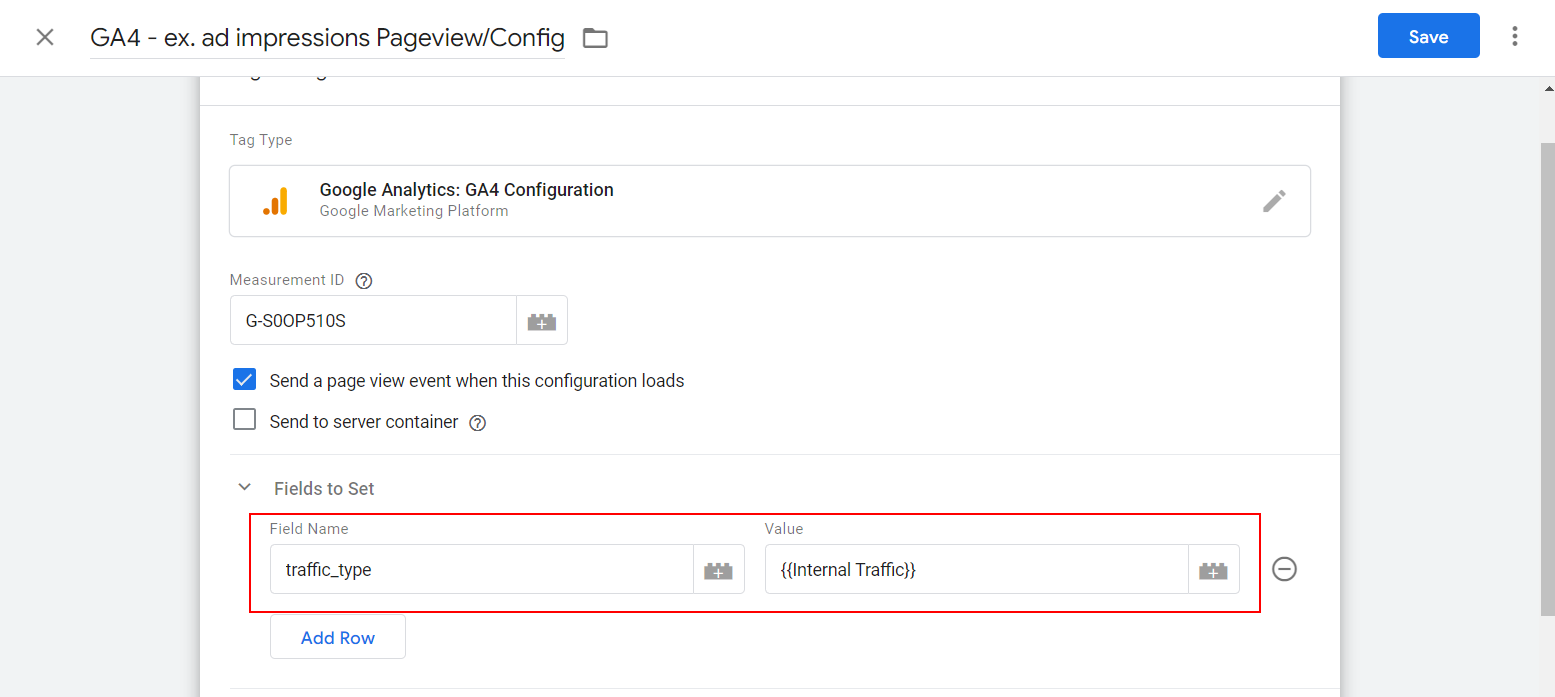 How to setup traffic_type parameter
How to setup traffic_type parameter
Preview it in Google Tag Manager (GTM) by opening any URL of your website with the “?exclude_user=1” query string attached, and check that the “traffic_type” parameter is filled in and that the “tt” hit payload parameter is set to “internal.”
You can switch between “internal” and “developer_view” values just by changing the exclude_user query parameter value from 1 to 2.
Once you are sure that the filters work properly and don’t filter out real users’ traffic by mistake, you can activate them from the data filters page, and you are done.
-
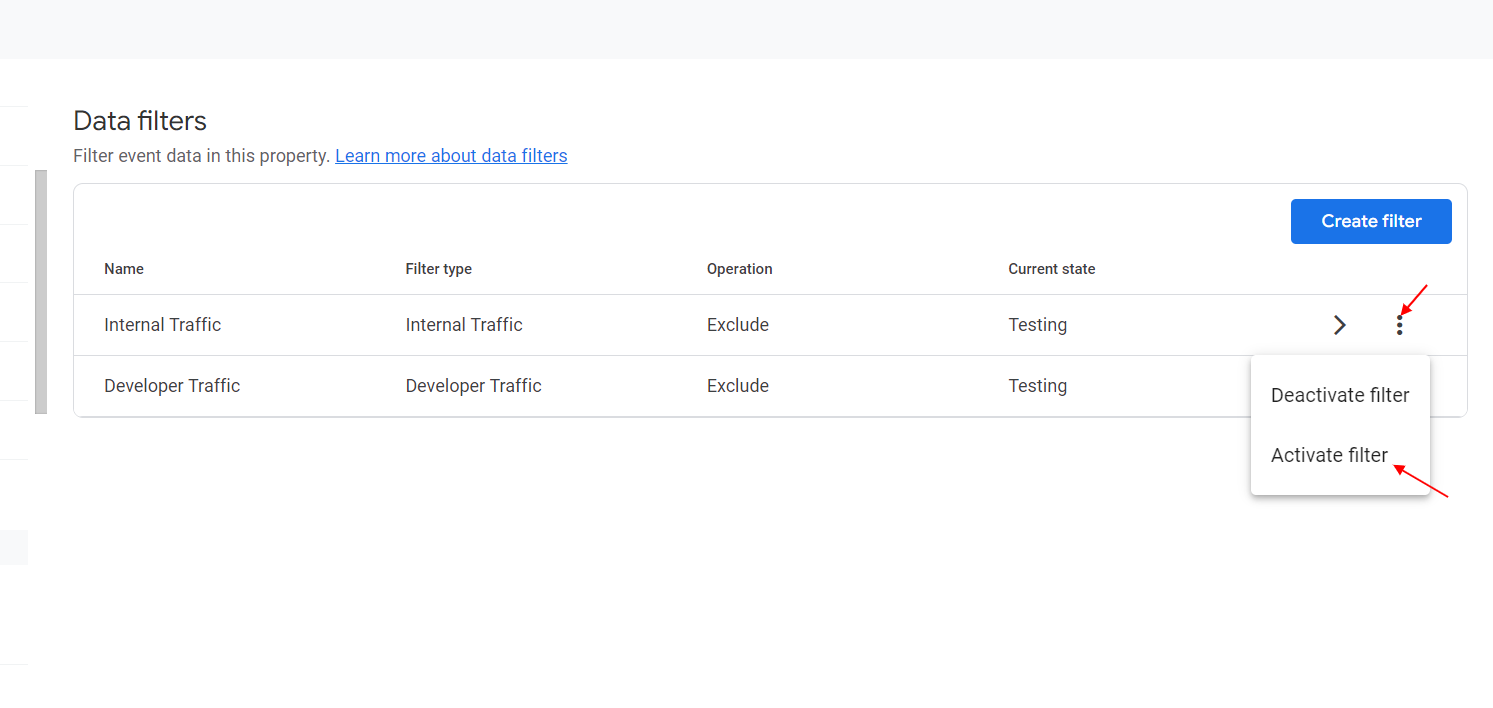 How to activate data filter in GA4
How to activate data filter in GA4In case you have a gtag.js implementation, you need to add a traffic_type parameter equal to “internal” to your tag configuration, as shown below.
gtag('set', { 'traffic_type': 'internal' });
For enabling debug mode, I would suggest using the Chrome extension.
But I highly recommend using a GTM setup because it is easier to scale, and on big projects, maintenance will be more cost-effective.
If you like coding, at least you can go hybrid by using GTM and pushing data parameters into the data layer on your website’s custom JavaScript.
Conclusion
I know what you are thinking after reading this guide.
The path to simplicity is overcomplicated – and where it once took seconds, you now must spend days setting up your filters properly.
You may not even have the technical knowledge required to implement the steps described in this guide.
However, here is where I would suggest using ChatGPT to get extra help.
If you need a different filter that requires additional custom coding, you can ask ChatGPT to code for you.
For example, you can ask it to create a JavaScript variable for GTM that returns “internal” when one visits your website from spammy referrals and excludes spam traffic.
The principle is simple: You should set a traffic_type=”some_value” parameter to whatever value you want and exclude any hits which have traffic_type parameter set to that value by using data filters.
I hope in the future, the Google Analytics team will add more granular and user friendly control over how you can filter your traffic, similar to Universal Analytics.
More resources:
Featured Image: Rajat Chamria/Shutterstock