SEO
What It Is & How to Do It Successfully

Digital content creation is the process of creating and publishing content on digital platforms, like websites, social media, and more.
In this post, you’ll learn how to create digital content that people want to see.
The online world is made up of content. Whether you’re searching on Google or scrolling through TikTok, you’re consuming content.
So if you want to build online visibility and drive traffic to your website or business, you need to create digital content. This will allow you to reach your target audience online.
Also, creating digital content allows you to build an audience and develop trust with them. You’ll become the go-to authority for anything related to your niche and topic of choice.
For example, we publish frequently on YouTube. Here’s an example of the type of comments we get:
Finally, you can actually earn a living from it. You could be paid as a content creator for your digital content creation skills, or you could monetize the audience you’ve built—ads, product placements, affiliate marketing, consulting, selling your own products, and more.
Here are some examples of digital content you can create:
- Blog posts – You’re reading one now. They’re one of the most common types of digital content. Learn how to write a great blog post here.
- Videos – They could be longer-form ones (like those we publish on YouTube) or short-form videos (like TikTok, Instagram Reels, YouTube Shorts, and more).
- Podcasts – Audio content that can range from short-form (<5 mins) to long-form ones (I’ve seen seven hours and more). These days, podcasts also come in video formats.
- Photos, images, and GIFs – One of the most common types of digital content on social media. They could be real or AI-generated. This category also includes custom illustrations, charts, diagrams, graphs, infographics, memes, and more.
- Social media posts – These are content published on popular platforms like Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, Reddit, and more. There may be specific formats for each platform (e.g., carousels on LinkedIn, threads on Twitter, and more).
- Newsletters – Emails sent to an audience at a particular frequency. These can be long-form essays, curated links (like our newsletter), or more.
- Courses – A structured series of videos (sometimes together with text and worksheets) intended to teach a subject or topic, like our SEO course for beginners.
The process of creating digital content is similar for every channel.
Here’s how to do it:
1. Decide on your main type of content
Making a video is different from writing a blog post. So each type of digital content requires you to possess different skills.
However, even if your ideal goal is to be able to create any type of digital content, you’ll want to begin by prioritizing. At this stage, getting started and doing the real thing is more important than dreaming about being able to create all types of content.
So choose the one type of digital content you wish to excel at creating and get started.
As writer Scott Young says:
Attempting several pursuits at once is a recipe for accomplishing none of them. Progress requires priorities. We need to tackle projects one at a time—not try to juggle them all at once.
I recommend starting with the content type you have the most affinity with. These can result from your natural strengths or simply the platform you spend the most time on.
For example, if you find yourself wasting spending hours on YouTube, then making videos could be up your alley. For me, I enjoyed reading books and blog posts, so I ended up choosing writing as my main marketing skill.
2. Find proven topics
No matter the type or platform you’re creating content for, you’ll want to ensure you’re creating something that appeals to your target audience.
Nothing beats the good old-fashioned method of asking your target audience what they want to see.
Find friends and family that match your audience profile and ask them what they’d like to see or what type of content is missing/neglected on the internet. For example, I breakdance as a hobby. So if I were to start a YouTube channel about breaking, it would be as easy as hitting up my regular practice spot and asking my fellow breakers some questions.
If you’re a business and have existing customers, reach out and ask them. You can join online groups on Facebook, Reddit, Discord, and Slack and ask them questions.
Beyond that, you can use tools to see what type of topics already performed well. This is an indicator that people are interested—and will continue to be interested—in those topics.
For example, if you’re creating blog posts, you’ll want to know the topics people are searching for on Google. Since they’re searching for those topics, then it’s likely they’ll want to read about them.
To find these topics, you’ll have to do keyword research. This is the process of finding the words and phrases people search for in search engines.
The easiest way to do this is to use a keyword research tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. Here’s how:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter a word that’s relevant to what you want to create content about (e.g., basketball)
- Go to the Matching terms report
- Switch the tab to Questions
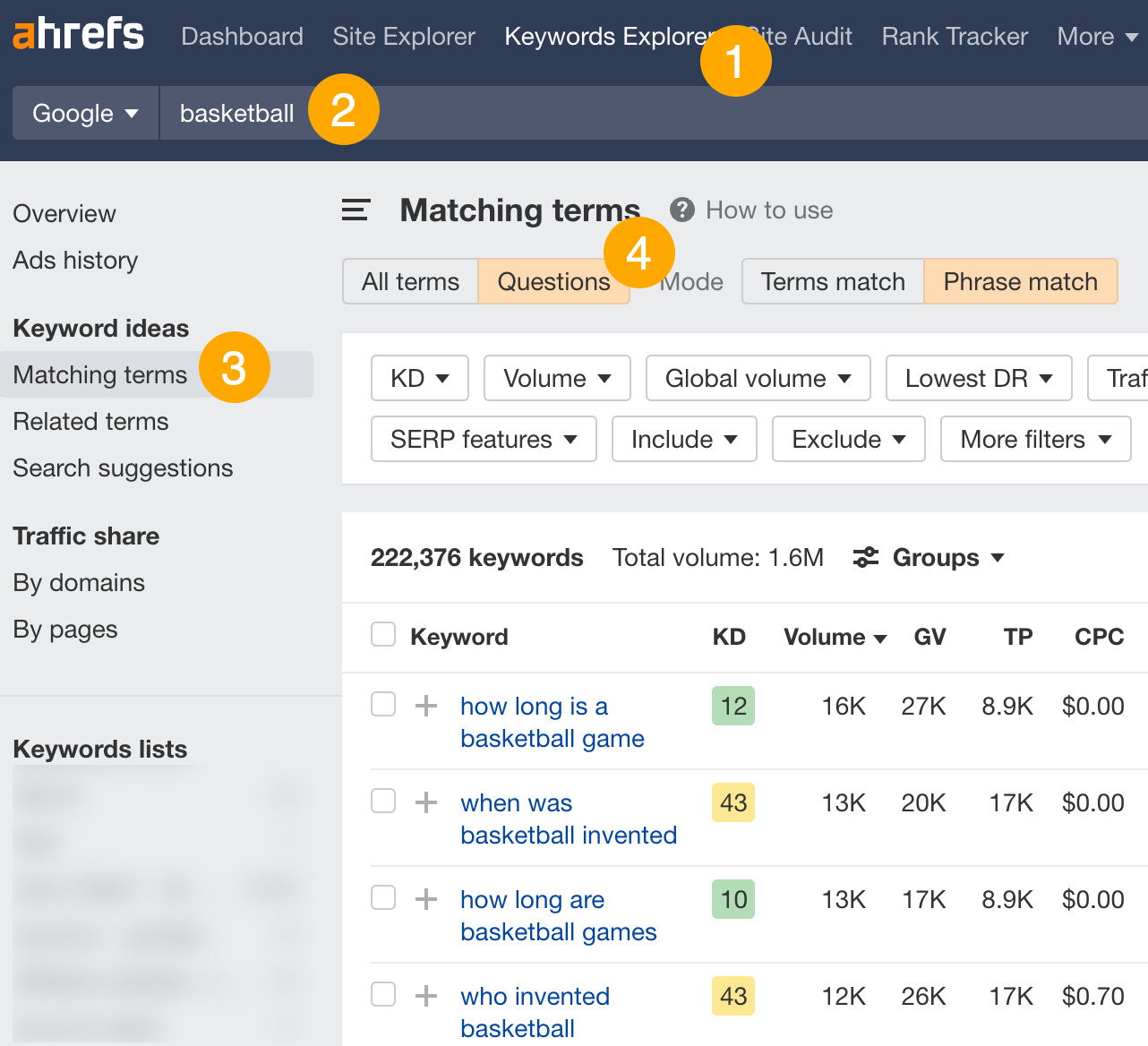
This report will show you all the questions containing “basketball,” sorted by search volume. Look through the report and pick out the questions you want to write about.
Other examples:
- Reddit – Find a relevant subreddit (e.g., r/tennis if you’re making tennis videos) and select “Top” and “All time.” This will show you the most upvoted posts in that subreddit.
- Twitter – Install a Chrome extension like Twemex, which will show you a user’s most popular tweets of all time.
- YouTube – Use tools like TubeBuddy or VidIQ to do keyword research for YouTube.
- Podcasts – Use a search engine like ListenNotes to see which episodes in your niche are trending.
3. Create the content
There are three main steps involved in the process of actually creating the content:
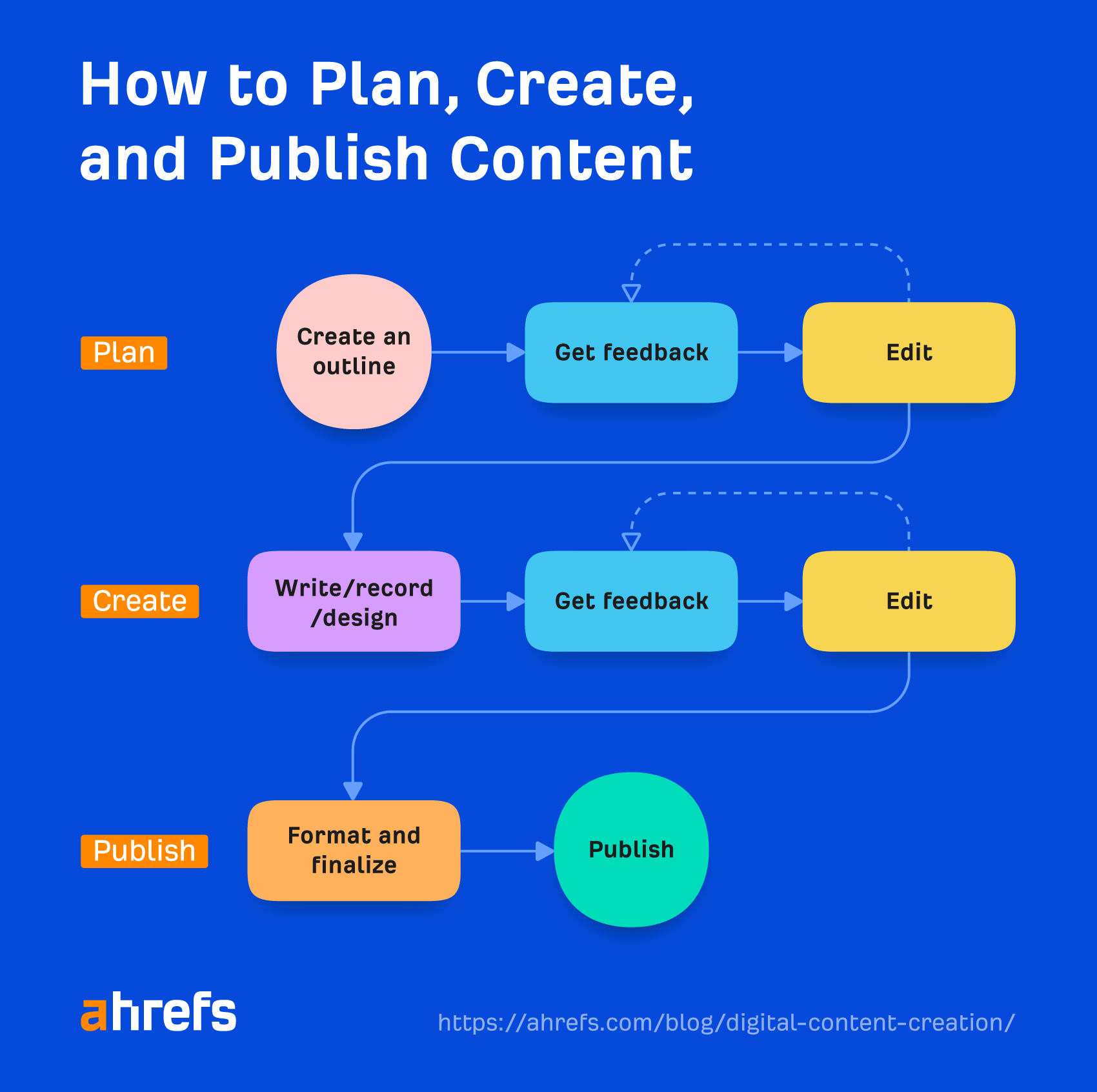
Let’s take a deeper look.
Planning
Before you put pen to paper, you’ll want to have a clear idea of what it is exactly you want to say. Otherwise, there is a real risk of going off-track, missing the main points, and making your audience fall asleep.
You may get away with simply throwing your thoughts out as a tweet or IG story. But even then, those types of posts can benefit from planning and rewriting:
1. Always give value before you ask for value.
2. Spend more time revising your tweets than you think is reasonable. Most of mine take 10-20 minutes to write.
3. Post at least 1 tweet per day.
— James Clear (@JamesClear) August 11, 2020
So this stage means creating an outline (or a storyboard if you’re making a video). For example, this post began as an outline:

To create the outline, I combined a mix of:
- My own personal experience and knowledge.
- Looking at what the top-ranking pages have covered.
- Running a content gap analysis.
Here’s how to do the last one:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter your target topic
- Scroll to the SERP overview
- Select a few of the top-ranking pages
- Click Open in and choose Content gap
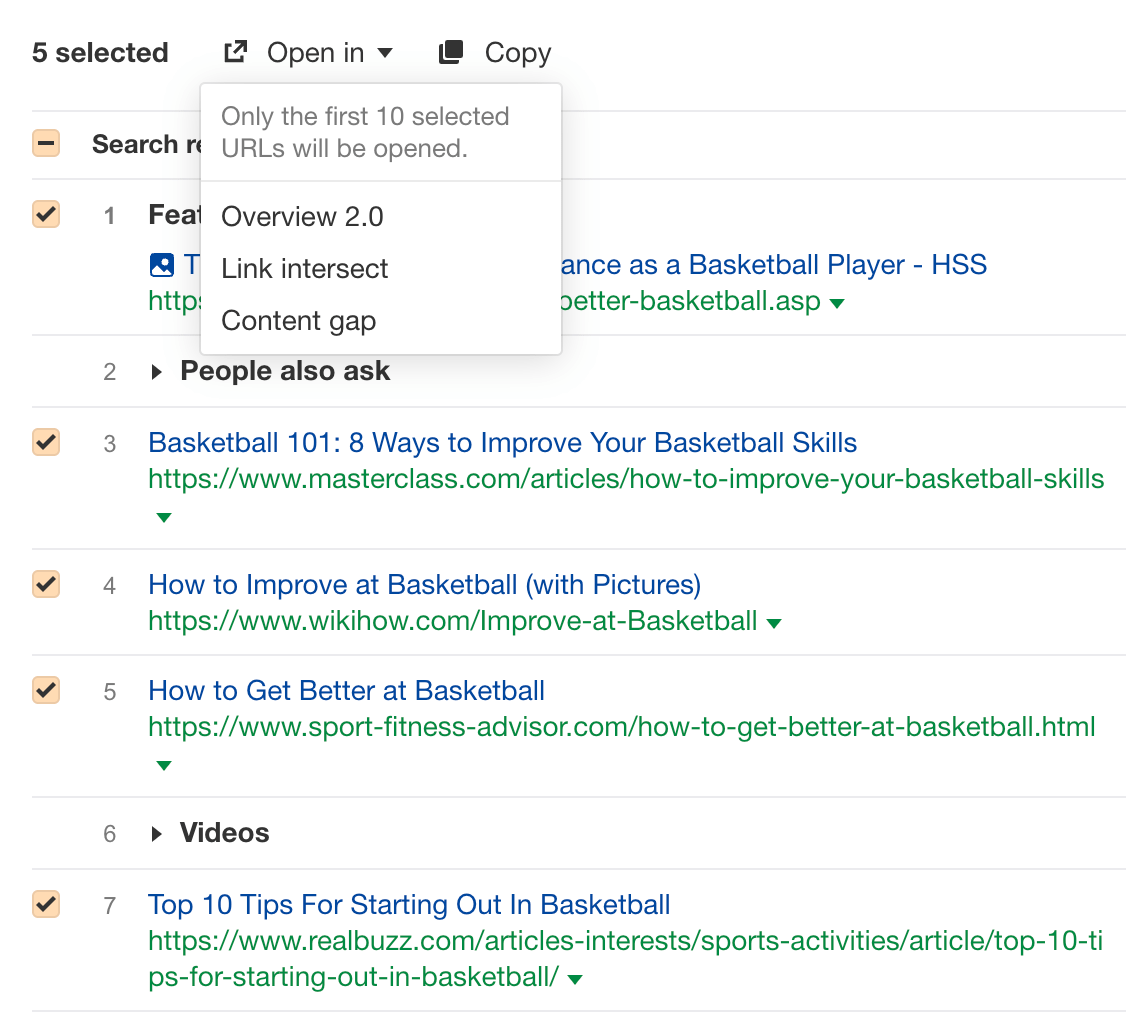
This report shows you all the common keywords the top-ranking pages are ranking for. These could make potential subtopics we could cover. However, we only want to see the most relevant ones, so let’s set the “Intersections” filter to 3, 4, and 5:
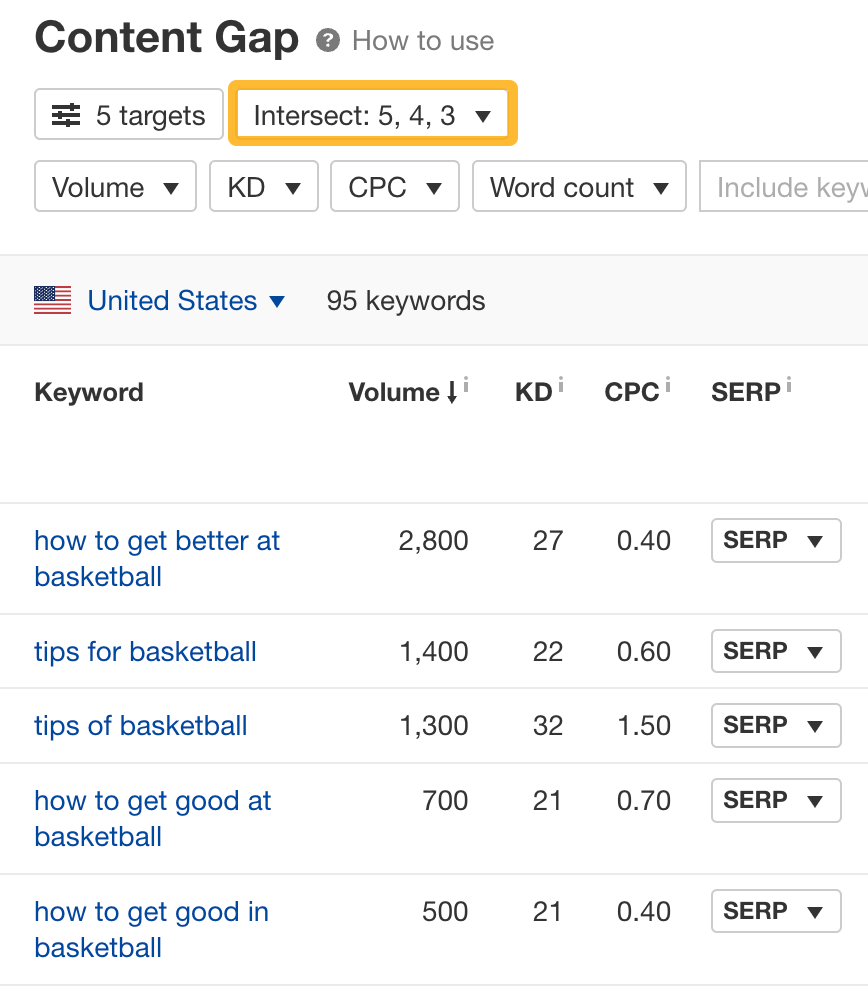
Scrolling through the list, we can see a few subtopics to include:
- how to learn to play basketball
- how to be better at basketball
- tips for basketball
- basketball techniques
- how long does it take to get good at basketball
- how to get the ball more in basketball
If you’re making an educational video on YouTube, this script format has worked well for us:
- Problem – Lead with the problem your video is solving.
- Teaser – Show that there’s a solution to the problem without giving it away.
- Solution – Teach how to solve the problem.
Once you’re done with your outline or storyboard, I recommend getting a friend or colleague to give feedback. We do this for all our outlines (and drafts too). At this stage, this feedback will be invaluable in helping you identify what’s missing and what could be improved, especially with regard to the structure.
Creating
No matter what you’re creating, this part is really about hunkering down and just making the content.
You’ll have your own quirks and fancies here (for example, I enjoy a cup of strong coffee while writing). But from experience, it’s seriously about blocking out a chunk of time and working on the content with no distractions.
This could mean:
- Creating a non-negotiable block of time on your calendar and committing to it.
- Putting your phone on “airplane” mode or in another room.
- Letting others know you don’t want to be disturbed during that time (especially important if you work from home).
- Using a webpage-blocking Chrome extension.
- Logging out of all social media and team chat software, like Slack or Teams.
- Forcing yourself to create without editing (this pertains especially to writing).
When you’re done creating, you should (again) get feedback from a friend or colleague. Doing this will help reduce inaccuracies, logical loopholes, spelling errors, and grammatical mistakes.
Publishing
This is the easiest part. Once you’re done, it’s really just a matter of formatting, finalizing, and uploading your work onto the target platform.
4. Measure and monitor performance
Content creation is all about the feedback loop. You’ll want to create content and publish it, and you’ll also want to know if it’s hitting the target.
Are people consuming it? Do people like it? What can you improve on or do less of?
Answering these questions will require you to measure your content’s performance. Besides getting qualitative feedback from your audience, you can also use tools to see said performance.
For example, if your main digital content type is blog posts, you’ll want to check Google Search Console and see if you’re generating any search traffic.
You’ll also want to add your main keywords to Ahrefs’ Rank Tracker to see if you’re ranking high on Google:
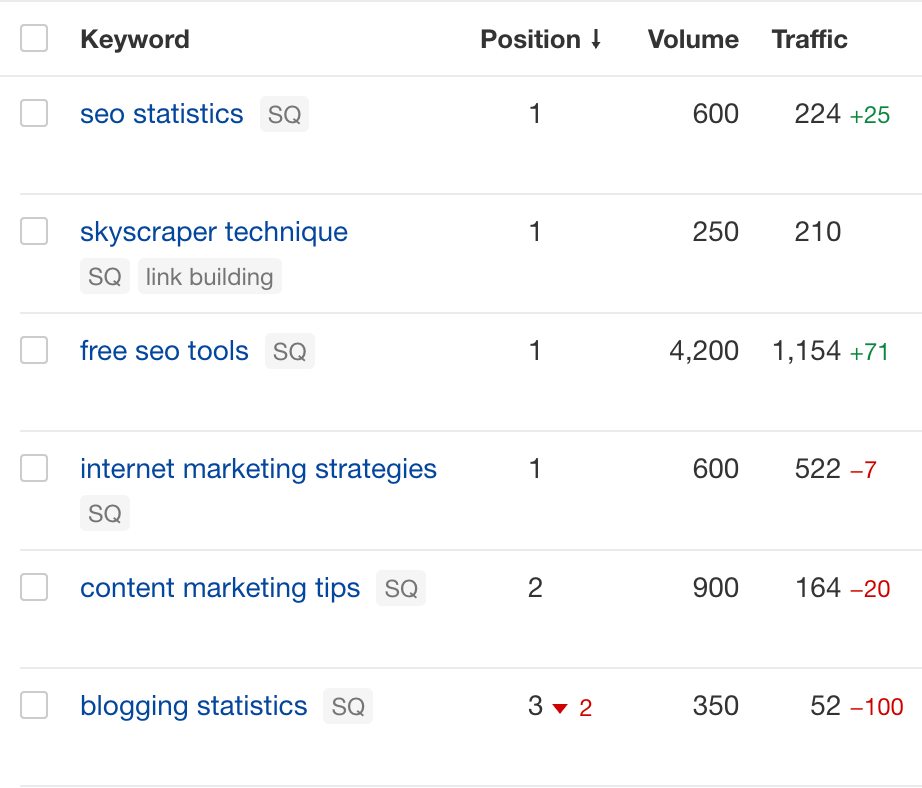
For other platforms, you’ll likely be able to see your analytics via the platform itself. For example, if you’re creating content for YouTube, you’ll want to go to YouTube Studio and check your analytics.
When you see something working, consider doubling down and making more of the same. But don’t be afraid to experiment too. Use the scientific process—if something doesn’t work, can you try a different approach? Perhaps a different hook, structure, or format?
It’s all about playing around, experimenting, and figuring out what works along the way.
Final thoughts
There are two main factors behind successful digital content creation:
- Consistency – Two things here: First, to be good at something, you need to practice consistently. Second, it’s hard for your audience to become a fan of someone who creates once and disappears. So make sure you’re always showing up. Do this by publishing at a frequency you can commit to. But don’t be overly ambitious—you can always ramp up in the future.
- Longevity – According to SEO Jacky Chou, publishing 21 podcast episodes puts you in the world’s top 1% of podcasts. This stat is not telling you how easy it is to produce a podcast but how quickly most people give up. You can win the game simply by outlasting everyone.
Any questions or comments? Let me know on Twitter.
SEO
What Is Social Listening And How To Get Started

Most marketers now understand the value of social media as a marketing tool – and countless companies have now established their own presence across a variety of social platforms.
But while the importance of creating content and building an audience is well understood, many organizations are lacking when it comes to another key strength of social media: social listening.
Social listening is a strategic approach that can help your brand tap into the incredible breadth and depth of social media to hone in on what your target audience is saying and feeling – and why.
By investing in social listening, you can gain a deeper understanding of conversations happening around not just your brand but your broader industry, and extract meaningful insights to inform multiple areas of your business.
In this article, we’ll explore what social listening is, why it’s crucial for businesses today, and the tools that exist to help you do it before diving into tips for getting started with your social listening strategy.
Let’s get started.
What Is Social Listening?
Social listening is the practice of tracking conversations on social media that are related to your brand, analyzing them, and extracting insights to help inform your future marketing efforts.
These conversations can include anything from direct mentions of your brand or product to discussions around your industry, competitors, relevant keywords, or other topics that might be tangential to your business.
The idea of social listening is that you’re really getting to know your audience by sitting back and listening in to what they talk about – what their gripes are, what they’re interested in, what’s getting them excited right now, and much more.
Gathering this data and then examining it can help you in a number of ways, from uncovering useful product development insights to inspiring new content ideas or better ways to serve your customers.
Here are some of the things you can achieve through social listening:
- Tracking mentions of your brand, products, or services across social platforms.
- Evaluating public perception and sentiment towards your brand by assessing whether mentions are positive, negative, or neutral.
- Spotting trends that are emerging among your target market by noting common themes, topics, or keywords in conversations.
- Gaining a better understanding of your audience, including who they are, where they spend time online, what they want, and how your brand can connect with them.
As such, social listening isn’t just a powerful tool for marketing, but can also be leveraged to improve customer engagement and service, product development, and other areas of your business.
What’s The Difference Between Social Listening And Social Monitoring?
If you’re finding yourself a little confused about the difference between social listening and social monitoring, you’re not alone! The terms are often used interchangeably – when, in reality, they have different scopes and objectives.
Generally speaking, social monitoring is narrower and more focused on your brand specifically, while social listening takes more of a big-picture approach to gaining insights.
If social monitoring is about seeking out brand mentions and conversations to hear what people are saying, social listening is diving even deeper to understand why they’re saying those things.
Social monitoring typically involves tracking social activity directly related to your brand so that you can stay abreast of what’s happening at the moment and tackle any pressing issues.
In this regard, it’s often leveraged as a component of a company’s customer support program to help respond to queries, answer questions, and remedy complaints in a timely manner.
It can also help to identify trending topics or industry moments that might apply to your brand. Basically, social monitoring is all about being aware of what’s happening around your brand on social media so you can respond quickly.
Social listening does all of this, but also takes things a few steps further, expanding the scope of what you’re tracking and focusing on obtaining insights to help with brand strategy, content planning, and decision-making.
Where social monitoring might focus on mentions of your brand, social listening goes beyond that to explore broader consumer behavior and emerging industry trends, and make qualitative analyses of the conversations that are happening in those areas.
One analogy I’ve encountered that I find helpful for understanding the difference between the two: If social monitoring is akin to tending your own backyard, social listening is like taking a walk through your neighborhood and eavesdropping on conversations to better understand what your neighbors are interested in and concerned about.
While we are focused on social listening in this particular article, both social monitoring and social listening are important parts of an effective marketing strategy.
Why Is Social Listening Important?
As we’ve touched on, successful social listening can benefit many areas of your business – from your marketing to your product and your customer support. And all of this means it can have a big impact on your bottom line.
Let’s look closer at just some of the reasons why social listening is an important tool in your business’s arsenal.
Reputation Management
Social listening can help you get a sense of how your audience – and the general public – feels about your brand, products, messaging, or services.
By understanding both the positive and negative sentiments around your brand and where they come from, you can work to fill the gaps and improve perceptions of your company.
Understanding Your Audience
On that note, social listening is a great way to learn more about your audience – from your current customers to your prospects and beyond.
It offers a looking glass into what your target consumer is thinking about, their opinions, pain points, desires, etc. With this information, you have the power to customize your content, message, and products to serve their needs better.
Market Analysis
Social listening is a powerful tool for unearthing insights into your industry – trends, consumer behaviors, opportunities, etc. This is the kind of information that you can use to get ahead of your competitors and deliver the ultimate customer experience.
Competitive Insights
Speaking of competitors, social listening enables you to keep a watchful eye on your competitors and learn from their successes and failures.
You can use active listening to determine how your target market perceives your competitors and apply your findings to differentiate yourself from the pack.
Crisis Management
Let’s face it: Crises happen, no matter what your business or industry. But social listening can help you identify crises before they hit a boiling point, and address them in a timely manner.
Content Strategy
Want to know what content types and formats resonate best with your audience? Try social listening! Once you have the necessary insights, you’ll be able to create more engaging content.
Lead Generation
Social listening can drive lead generation in a number of ways.
You can use it as a tool to discover prospects who are interested in your industry, product niche, or topics related to your business.
Beyond this, by improving your content strategy, reputation, products, customer experience, and more using your social listening insights, you will ultimately boost more leads to your business.
Social Listening Tools
Given that social listening requires pulling data from millions of posts across social media and analyzing it, we would recommend using a tool to help with your efforts.
Here are a few popular social listening tools.
Hootsuite
Known for its social management features, Hootsuite also offers a comprehensive suite of capabilities to help with your social listening efforts.
The platform allows you to create custom streams to track hashtags, keywords, or mentions across a range of social platforms. You can use these to spot conversations in real-time and engage with them.
Using some of Hootsuite’s tools and integrations, you can also do things like track brand sentiment, listen into Reddit conversations, access consumer research, and more.
Pricing:
- 30-day free trial.
- Paid plans start at $99/month for the Professional tier and 249/month for the Team tier (billed annually).
- Hootsuite offers an Enterprise tier with custom pricing.
Sprout Social
Sprout Social is another leader in the social media management space that is super useful for social listening.
With Sprout Social’s Smart Inbox, you can pull all your mentions, comments, and DMs from across your social platforms into one single feed – helping you keep on top of what’s happening.
Other key features include audience analysis, campaign analysis, crisis management, competitor comparison, influencer recognition, sentiment research, and much more.
Pricing:
- 30-day free trial.
- Paid plans start at $249/month for the Standard tier, $399/month for the Professional tier, and $499/month for the Advanced tier (billed annually).
- Sprout Social offers an Enterprise tier with custom pricing.
Brandwatch
Brandwatch is a strong social listening and analytics platform that can help you track and analyze conversations online. It pulls data from 100 million sources, ensuring you’re not missing anything.
The Brandwatch tool will sift through brand mentions in real-time to analyze sentiment and perception, saving you a ton of time and manual effort.
Other key features include AI alerts for unusual mentions activity, conversation translation across multiple languages, tons of historical data, and more.
Pricing:
- Book a meeting with the Brandwatch team to learn more about pricing.
Meltwater
Meltwater’s social listening tool monitors data from a ton of different feeds, from Facebook to Instagram, Twitch, Reddit, YouTube, and many more. It can even recognize when your brand is talked about in a podcast!
Key features include topic and conversation trends analysis, custom dashboard and report building, consumer segmentation and behavior analysis, crisis management, and more.
Pricing:
- Contact the Meltwater team for pricing details.
Talkwalker
Another top name in the social listening space, Talkwalker monitors 150 million websites and 10+ social networks to power your real-time listening experience.
It offers AI-powered sentiment analysis in over 127 languages, notifications for any atypical activity, issue detection, conversation clustering, and much more.
Pricing:
- Contact the Talkwalker team for pricing.
6 Tips For Building A Social Listening Strategy
Now that you understand what social listening is and why it’s important – as well as a few of the tools you can use to power your social listening program – it’s time to start considering your strategy.
Here are six steps we recommend when building out your social listening strategy.
1. Define Your Goals & Objectives
As with any big project, your first step before starting should be to set clear goals for what you want to achieve.
Why are you doing this, and what is the desired result? Sit down with your team and talk through these points in order to align with your objectives.
You might have one key objective or several. Some potential options could be:
- Improve your company’s customer service and support.
- Gain insights to help inform product development and enhance product offerings.
- Track brand sentiment across current and potential customers.
- Develop a deeper understanding of the competitive landscape in your industry, and how your competitors are performing with social audiences.
- Stay on top of industry events and trends so you can spot content gaps and opportunities ahead of time.
Whatever your goals are, make sure you have them set from the beginning so you have clarity as you move forward.
2. Pick Your Tool Of Choice
While social listening can technically be done manually, it will never be as comprehensive as what you can get from leveraging a tool or platform.
Social media listening tools, like the ones we highlighted above, are able to synthesize data from millions of sources at once – not to mention their abilities to analyze sentiment, identify trends, spot activity, and more.
So, while they typically come with a price tag, the good ones are worth their weight in gold.
Do your research and choose a tool that aligns with your objectives and your team’s budget.
Look for something that monitors many different touchpoints, offers comprehensive analytics, is customizable, and integrates with your existing tech stack (if necessary).
3. Identify Target Keywords And Topics
This step is crucial: Take the time to define the keywords, topics, and hashtags that you want to “listen in” to – as these will provide the basis for your listening efforts.
Be sure to include keywords and themes that are relevant to your brand but also your industry, so that you get information that’s most useful to you. You could also discuss any keywords or topics you might want to exclude and why.
These might evolve or change over time, and that’s okay – this is about setting up a well-considered and focused foundation based on what matters most right now, and what will help you achieve your goals.
4. Decide On Your Workflow
Who will be responsible for monitoring your social listening data? Who should be responding to relevant mentions? Whose job is it to analyze the data and report on learnings and progress?
These are all things you should consider early on so that you can develop a clear workflow that outlines responsibilities.
By establishing the process early on, you’ll make sure that your efforts are not in vain and that you’re able to really put your data to use.
One recommendation: Make sure that somebody is regularly monitoring conversations and engaging where necessary. You should be keeping a keen eye on your listening activity – and automated alerts can be very helpful here.
5. Adapt As Needed
As part of the workflow we just discussed, somebody (or several people) should be responsible for routinely analyzing the data you’re collecting – as, unfortunately, it won’t analyze itself.
Set up a consistent process for diving into your data, extracting insights, and then acting on them.
There’s no point in allocating resources to a social listening program if you’re not using the learnings to benefit your business.
So, be sure to adapt your content strategy, marketing efforts, customer service, and so on based on what the insights are telling you.
6. Don’t Forget Measurement
We all know the importance of social media measurement – and this extends to your social listening efforts.
As time goes on, continue to measure the success of your efforts against the goals and objectives you set out for yourself.
This will help you evaluate the impact of your social listening, and whether there are areas you should pivot or refine based on the data you’re seeing.
You can also track social engagement metrics over time to see if your learnings have provided a boost in your social performance as a whole.
In Conclusion
With millions of conversations happening all around us on social media, any brand that isn’t engaging in social listening is missing a major opportunity.
By taking the time to proactively (and attentively) listen to your audience and target consumers, understand them better, and put their feedback to use, you can drive considerable success for your business.
So, take some of the advice we’ve shared here and start building out your social listening strategy today!
More resources:
Featured Image: batjaket/Shutterstock
FAQ
What is the significance of social listening for modern businesses?
Social listening plays a pivotal role for modern businesses by offering critical insights into audience behavior, industry trends, and brand perception. By analyzing conversations on social media related to their brand or market, companies can adequately respond to customer feedback, adapt their marketing strategies, and anticipate consumer needs. It not only aids in shaping product development and content strategy but also enhances customer service, reputation management, and competitive analysis. This strategic approach empowers businesses to make informed decisions based on the direct sentiments and unfiltered conversations of their target audience.
Can you differentiate between social monitoring and social listening?
Social monitoring and social listening are distinct yet complementary components of a comprehensive social media strategy. Social monitoring is more tactical, focusing on tracking and responding to direct brand mentions, queries, and specific conversations related to immediate issues. Its objective is to maintain awareness of what’s currently being said about a brand and to participate in these conversations promptly. Social listening, on the other hand, employs a broader, more strategic approach. It goes beyond mere tracking, analyzing the underlying sentiments, causes, and implications of social discourse to extract actionable insights. This process not only involves engagement but also a deep analysis of consumer behavior patterns and industry trends for a long-term strategy formulation.
Which social listening tools are recommended for businesses to utilize?
For businesses looking to execute an effective social listening strategy, a variety of tools are available that can help streamline the process. These include:
- Hootsuite: Offers custom streams to monitor social conversations and sentiment, alongside integrations for broader consumer research.
- Sprout Social: Features a Smart Inbox to consolidate social interactions for monitoring. It also provides tools for audience and competitor analysis.
- Brandwatch: Analyzes brand mentions from an extensive range of sources, offering AI-powered sentiment analysis and trend spotting.
- Meltwater: Monitors various feeds, from mainstream social media to Reddit and podcasts, enabling comprehensive analysis.
- Talkwalker: Provides monitoring and analytical capabilities over a broad spectrum of online platforms, backed by AI sentiment analysis.
Businesses should select a tool that aligns with their specific needs and objectives, focusing on features like comprehensive analytics, broad monitoring capabilities, and the ability to integrate with existing technological infrastructure.
SEO
Google Performance Max For Marketplaces: Advertise Without A Website

Google has launched a new advertising program called Performance Max for Marketplaces, making it easier for sellers on major e-commerce platforms to promote their products across Google’s advertising channels.
The key draw? Sellers no longer need a website or a Google Merchant Center account to start.
The official Google Ads Help documentation states:
“Performance Max for Marketplaces helps you reach more customers and drive more sales of your products using a marketplace. After you connect your Google Ads account to the marketplace, you can create Performance Max campaigns that send shoppers to your products there.”
The move acknowledges the growing importance of online marketplaces like Amazon in product discovery.
For sellers already listing products on marketplaces, Google is providing a way to tap into its advertising ecosystem, including Search, Shopping, YouTube, Gmail, and more.
As ecommerce marketer Mike Ryan pointed out on LinkedIn:
“Polls vary, but a recent single-choice survey showed that 50% of consumers start product searches on Amazon, while a multiple-choice survey showed that 66% of consumers start on Amazon.”
The source for his data is a 2023 report by PowerReviews.
Getting Started
To use Performance Max for Marketplaces, sellers need an active account on a participating marketplace platform and a Google Ads account.
Google has yet to disclose which marketplaces are included. We contacted Google to request a list and will update this article when we receive it.
Once the accounts are linked, sellers can launch Performance Max campaigns, drawing product data directly from the marketplace’s catalog.
Google’s documentation states:
“You don’t need to have your own website or Google Merchant Center account.
And:
“You can use your existing marketplace product data to create ads with product information, prices, and images.”
Conversion tracking for sales is handled by the marketplace, with sales of the advertiser’s products being attributed to their Google campaigns.
While details on Performance Max For Marketplaces are still emerging, Google is providing information when asked directly.
Navah Hopkins states on LinkedIn she received these additional details:
“I finally got a straight answer from Google that we DO need a Merchant Center for this, we just don’t need one to start with.”
Differences From Standard Performance Max
These are the key differences from regular Performance Max campaigns:
- No URL expansion, automatically-created assets, or video assets
- No cross-account conversion tracking or new customer acquisition modeling
- No audience segmentation reporting
Why SEJ Cares
Performance Max for Marketplaces represents a new way to use Google advertising while operating on third-party platforms.
Getting products displayed across Google’s ecosystem without the overhead of a standalone ecommerce presence is a significant opportunity.
How This Can Help You
Through Google’s ecosystem, merchants have new ways to connect with customers.
Performance Max for Marketplaces is a potential difference maker for smaller retailers that have struggled to gain traction through Google’s standard shopping campaigns.
Established merchants invested in Google Ads may find the program opens new merchandising opportunities. By making an entire marketplace catalog available for ad serving, sellers could uncover previously undiscovered pockets of demand.
The success of Performance Max for Marketplaces will depend on its execution and adoption by major players like Amazon and Walmart.
Featured Image: Tada Images/Shutterstock
SEO
The 9 Best Landing Page Builders For 2024

Generating leads is crucial to boosting your sales – but if your landing pages aren’t effective, you’re going to struggle to turn visitors into customers.
Landing pages play a key role in elevating the effectiveness of your marketing efforts and differentiating, refining, and enhancing the user experience.
In this article, we’ll explore how to choose the right landing page builder for your business before highlighting the nine top landing page builders and what makes them stand out.
Let’s get into it.
Choosing The Right Landing Page Builder For Your Business
With so many options to choose from, how can you decide which landing page builder is right for you?
Here are a few things to consider when making your decision.
- Marketing objectives: Start by deciding what you want to achieve with your landing pages. Are you looking to collect email subscribers, drive sales, generate leads, or promote an event? Each platform caters to different use cases, so leading with your goals can help you refine your search.
- Ease of use: Different builders have different learning curves. If you’re a novice, you should probably opt for a tool that caters to beginners. If you have more technical experience, like coding knowledge, you might want to look to more advanced builders to get the most power.
- Integration needs: Do you want your landing pages to integrate with other software or tools you’re already using?
- Mobile optimization: It’s essential that your landing pages cater to mobile users, so make sure your builder considers that with features like responsive design.
- Budget constraints: Unfortunately, budget matters. Landing page builders come with various price tags depending on their capabilities and features. Make sure you’re working within the boundaries of what you can afford.
While this is, by no means, an exhaustive list of considerations, it’s a starting point to help you choose a landing page builder that makes sense for your business needs.
Now, let’s look at nine of the best landing page builders to choose from.
1. Carrd
- Best for: Simple projects, personal use, and small budgets.
Looking for a great landing page builder that won’t break the bank? Look no further than Carrd.
Carrd is a streamlined landing page builder that focuses on creating single-page websites quickly and easily. It’s designed for simplicity, making it ideal for anyone who wants to quickly create a webpage without needing to build a multi-page site.
Think portfolios, personal profiles, project presentations, and small business showcases.
Carrd’s user-friendly interface and selection of themes allow users to create sleek pages in the blink of an eye without even needing an account – you can just visit the website, pick a theme, and get started. However, you will need to sign up to save or publish your site.
It balances simplicity and functionality to help you craft that pages are clean, focused, and responsive across all devices. If you’re just testing the waters or working with slim budgets, this is the right tool for you.
Pros:
- Extremely affordable, with a free tier available.
- Intuitive and user-friendly interface.
- Responsive design.
- Fast and lightweight, making it ideal for quick and simple sites.
Cons:
- Limited to single-page websites.
- Restrictive layouts/themes, which limit creative freedom.
- Lacks advanced features and integrations found in more comprehensive builders.
Pricing:
- Carrd’s free basic plan allows you to launch three sites with Carrd branding to .carrd.co domains.
- Paid plans range from $9 to $49 per year, and offer additional features like no Carrd branding, custom domains, and Google Analytics support (depending on your membership tier).
2. ConvertKit
 Screenshot from ConvertKit.com, April 2024
Screenshot from ConvertKit.com, April 2024- Best for: Content creators, bloggers, and marketers focused on growing their audience through email.
Billing itself as “the creator marketing platform,” ConvertKit’s landing page builder is targeted at creators, bloggers, and marketers who want to expand their email subscriber base.
If your goal is to create a landing page to help you build an email list, ConvertKit might be the right option for you.
ConvertKit’s landing page builder offers a range of high-quality, customizable templates and integrates with third-party tools to help you get the most out of your site.
It also integrates with the stock photo platform Unsplash to offer access to 100,000+ free images for your landing page.
While ConvertKit’s analytics and customization options might not be as extensive as those of some of its competitors, its ease of use and focused approach make it a standout for email-driven campaigns.
Pros:
- No cost for starting (up to 1,000 subscribers).
- Access to thousands of free images.
- Robust third-party integration capabilities.
Cons:
- Limited template customization and flexibility.
- A/B testing and analytics features are less advanced.
- Priced higher than some basic landing page builders.
Pricing:
- Free plan for up to 10,000 subscribers.
- The Creator plan starts at $25/month and includes benefits like automation features and app integrations. Pricing scales are based on subscriber count.
3. Unbounce
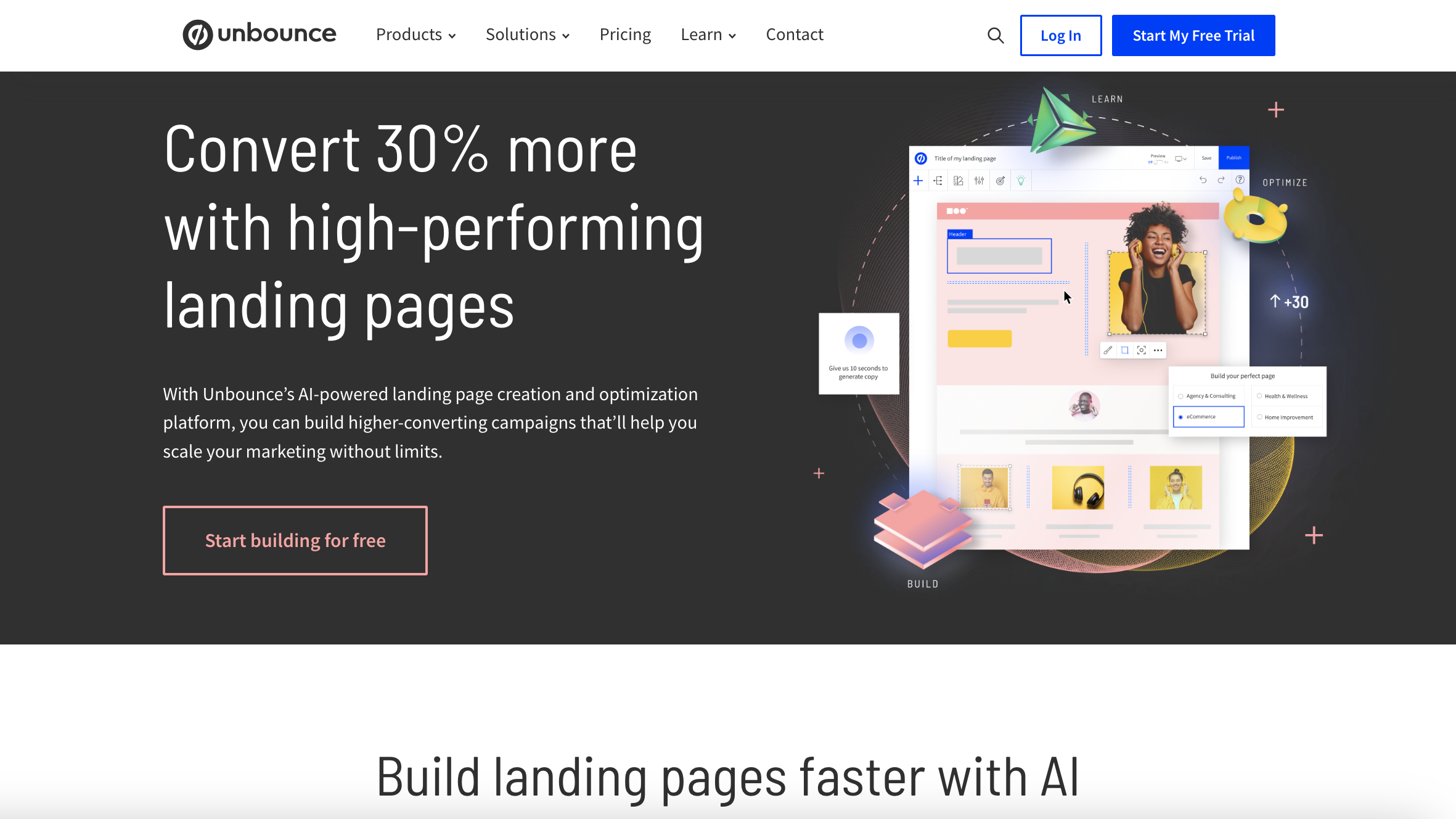 Screenshot from Unbounce.com, April 2024
Screenshot from Unbounce.com, April 2024Unbounce is a leading landing page builder renowned for its focus on conversion rate optimization (CRO). Its website promises to help you “build high-converting landing pages with ease.”
It offers a suite of advanced tools, such as A/B testing, dynamic text replacement, and the Smart Traffic system, which uses AI to optimize visitor flow to the highest-converting page variant based on user behavior and characteristics.
It also focuses on features that can help you boost your lead gen efforts, such as opt-in email popups and sticky banners.
With 100+ responsive templates, Unbound makes it easy to create landing pages that are both engaging and effective.
Compared to some other options on this list, Unbounce is a particularly robust platform with tons of customization and integrations – and the price point reflects that.
As a premium offering with a steeper learning curve, it might not be the best for beginners – but its AI-powered features and conversion-focused tools make it a formidable tool for achieving your goals.
Pros:
- Advanced A/B testing and AI-driven optimization.
- Large selection of responsive templates.
- Integrated features for enhancing lead capture.
Cons:
- Higher price point than some other builders, which might not work for those with limited budgets.
- Complex setup and steeper learning curve for new users.
- Some customization limitations.
Pricing
- The Build plan starts at $74/month and covers unlimited conversions, one root domain, and up to 20,000 monthly unique visitors.
- Other paid plans range from $112/month up to $649/month.
4. Leadpages
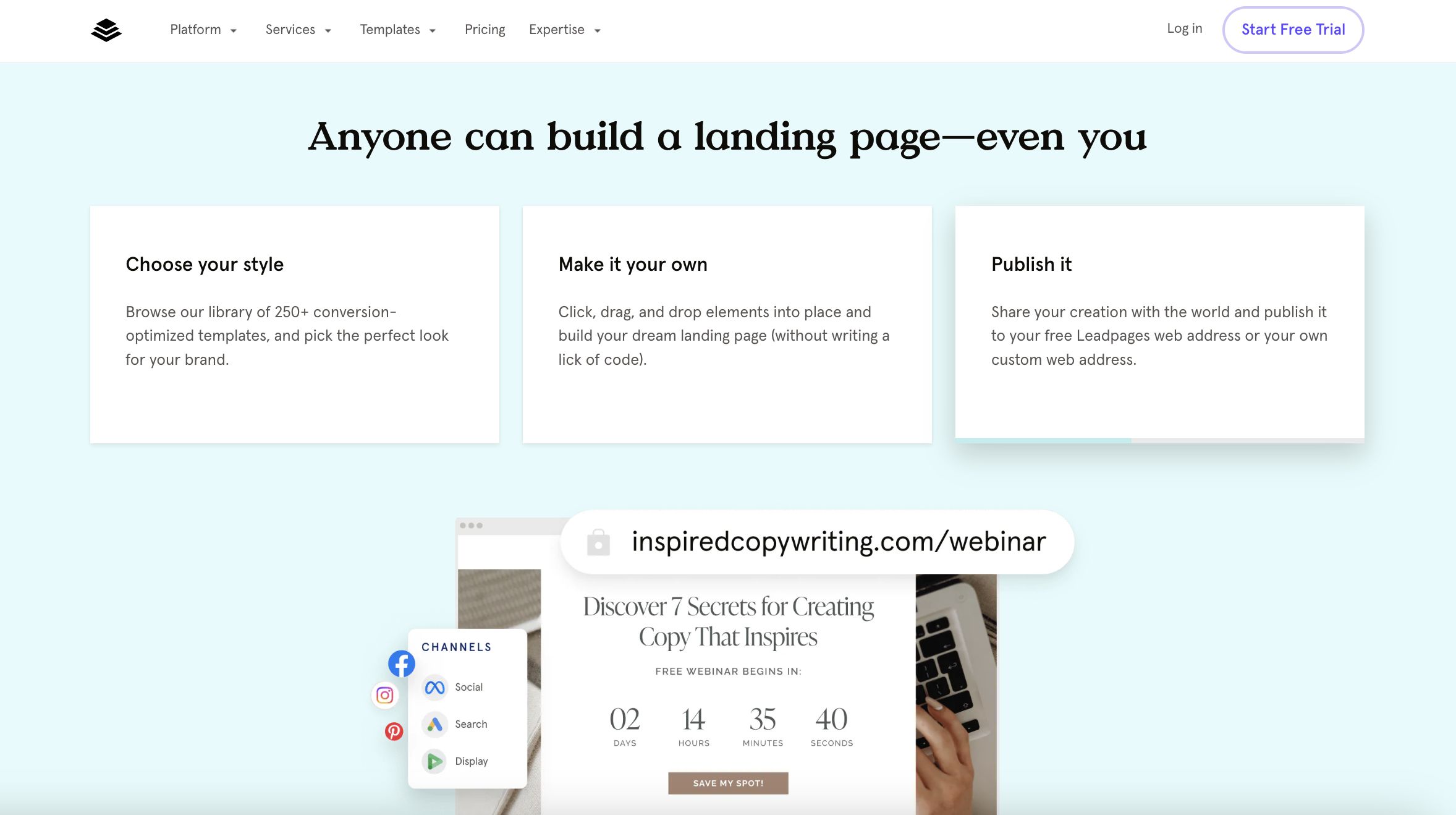 Screenshot from Leadpages.com, April 2024
Screenshot from Leadpages.com, April 2024- Best for: Small businesses and entrepreneurs looking to generate sales.
Need a landing page that will help you generate sales? Consider taking a look at Leadpages.
Its strength lies in its user-friendly, drag-and-drop editor and an extensive collection of templates that streamline the page-building process. Plus, according to the Leadpages website, it’s a platform that converts five times better than the industry average.
Leadages offers CRO tools, real-time analytics, and A/B testing capabilities, enabling users to enhance their page performance effectively.
Its various widgets allow you to add videos, images, forms, and even payment integrations directly onto your landing pages, making it a versatile tool for businesses that want to combine content with sales functionality.
On top of all this, Leadpages now includes an AI Engine for creating headlines and images and an AI writing assistant at some membership tiers, which can help you write better content.
Pros:
- Intuitive no-code editor and easy payment integration.
- Comprehensive A/B testing and real-time analytics.
- Extensive template library with over 250 options.
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to some alternatives.
- Limited ecommerce features and potential mobile responsiveness issues.
- Some users report mobile responsiveness issues.
Pricing:
- The standard plan starts at $37/month for one custom domain, unlimited traffic and leads, and 10,000 monthly AI Engine credits.
- More advanced features are available in higher-tier plans, which start at $74/month.
5. Landingi
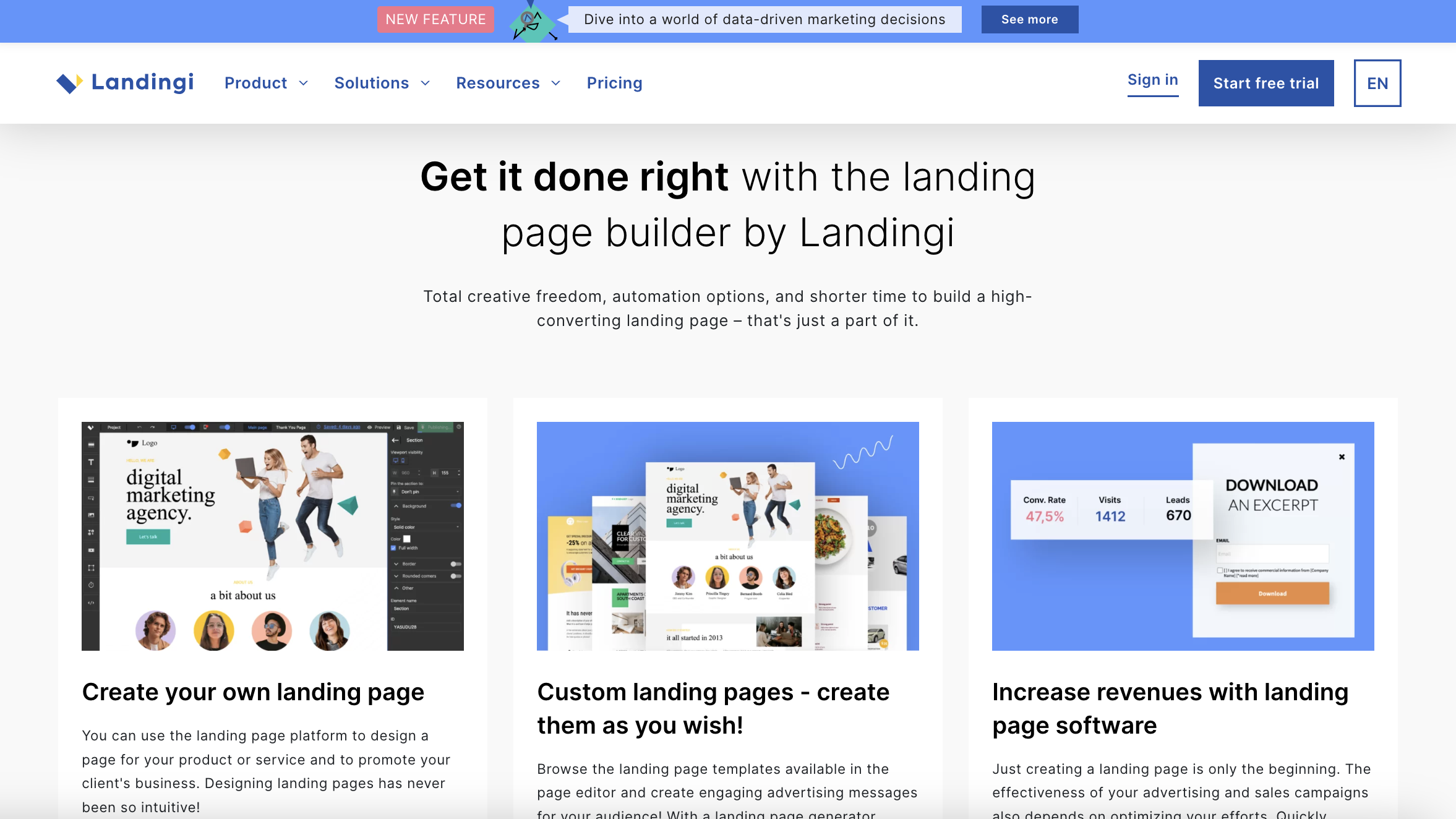 Screenshot from Landingi.com, April 2024
Screenshot from Landingi.com, April 2024- Best for: Businesses seeking a versatile landing page solution with a wide range of features.
If you’re in the market for versatility, Landingi is worth investigating.
Landingi offers a flexible, comprehensive landing page builder with a robust set of features, including an advanced editor, popups, A/B testing, and a substantial library of 300+ templates.
Its unique Smart Sections feature allows you to reuse and easily update specific page elements across multiple designs, saving time and headaches.
Designed to serve businesses of all sizes, Landingi’s simple, drag-and-drop builder can help you create and optimize various types of landing pages – and if you have any HTML and CSS knowledge, it can be a pretty impressive editor.
Landingi is a particularly strong choice for small businesses looking to target different customer segments with unique landing pages. The integration capabilities with numerous apps, including payment gateways like Stripe, make it a great choice for companies looking to sell products.
While its rich feature set can be overwhelming for newcomers, and creating pages might take a bit longer compared to other platforms, the level of customization and control it offers makes Landingi one of the best landing page builders out there.
Pros:
- Extensive template library with 300+ customizable options.
- Powerful editing capabilities with Smart Sections for efficient design.
- Broad integration with various apps, including payment systems.
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve for beginners.
- Potentially longer time to create landing pages compared to simpler platforms.
Pricing:
- The Lite plan starts at $35/month and gives you 10 digital assets, unlimited conversions, 5,000 visits per month, and one custom domain.
- Landingi also offers Professional and Unlimited tiers with more advanced features and capabilities.
6. Instapage
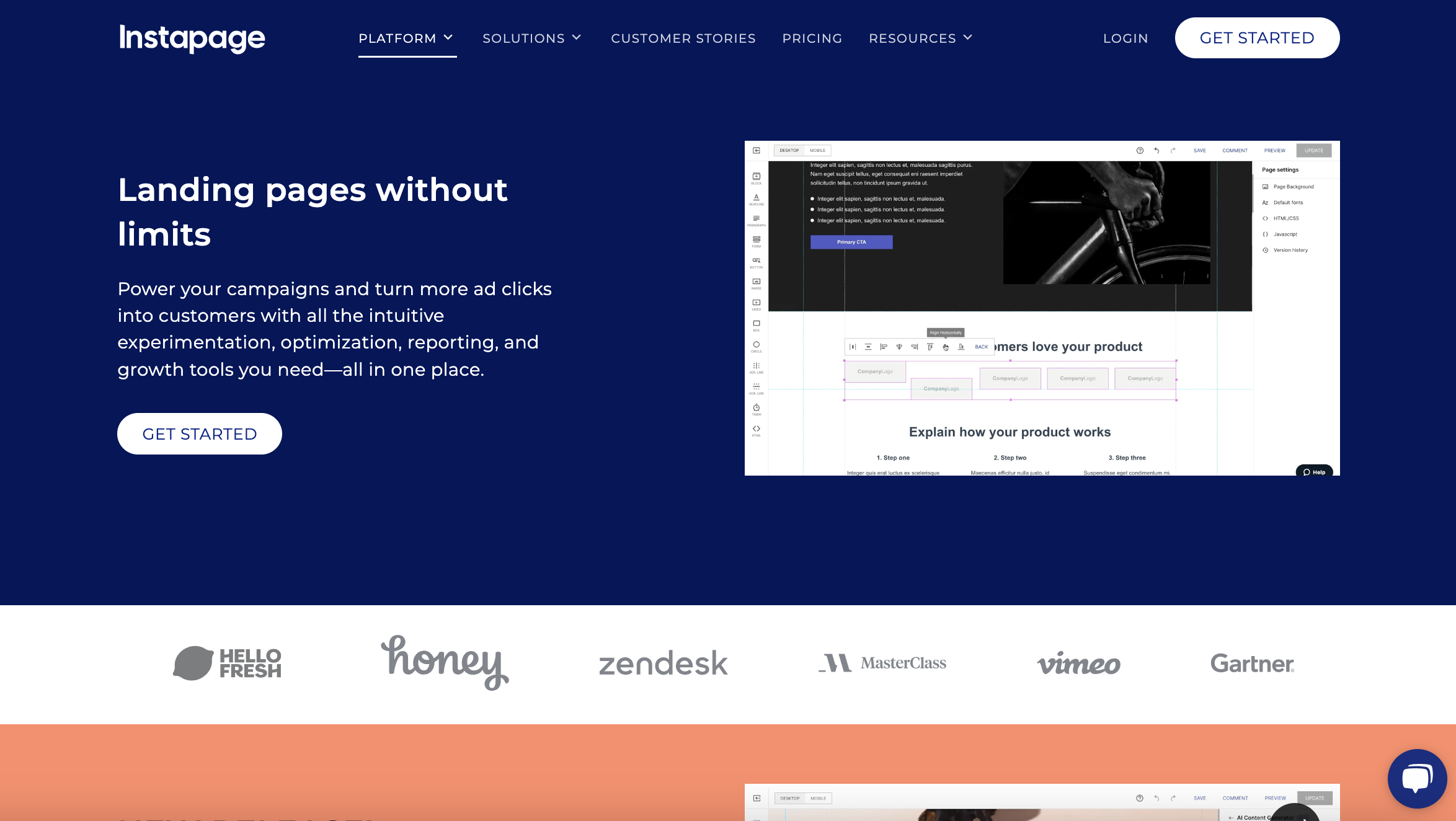 Screenshot from Instapage.com, April 2024
Screenshot from Instapage.com, April 2024- Best for: Large businesses, marketing teams, or agencies that require collaboration and advanced optimization features.
If you’re seeking a more high-end landing page platform, Instapage might be the one for you. It offers advanced features tailored for professional marketing teams and agencies with a need to create optimized landing pages at scale.
In addition to a drag-and-drop builder and plenty of high-quality templates, Instapage offers a bevy of features, including advanced cloud-based team collaboration tools, heatmaps for user engagement analysis, robust A/B testing capabilities, AI-generated content creation, and more.
One of its standout features is Instablocks, which allows users to create custom page components that can be easily reused across different projects.
Instapage supports advanced marketing goals with features like AdMap to align ads with page content. Plus, its mobile-friendly design ensures a fast, seamless user experience.
While Instapage offers a premium experience with its comprehensive set of tools and features, its higher price point and complex functionalities may be a barrier for smaller businesses or those new to landing page optimization.
Pros:
- Extensive customization with a library of professional templates.
- Instablocks for efficient design and asset reuse.
- Effective team collaboration features.
Cons:
- Premium pricing will be a barrier for many businesses.
- Steep learning curve for utilizing advanced features.
- Limitations in reporting and visitor tracking for lower-tier plans.
Pricing:
- The Build plan starts at $199/month, with a 14-day free trial.
- Customers will need to upgrade to a customized Convert plan to access some of the more complex features, such as AdMap, heatmaps, and more.
7. Wix
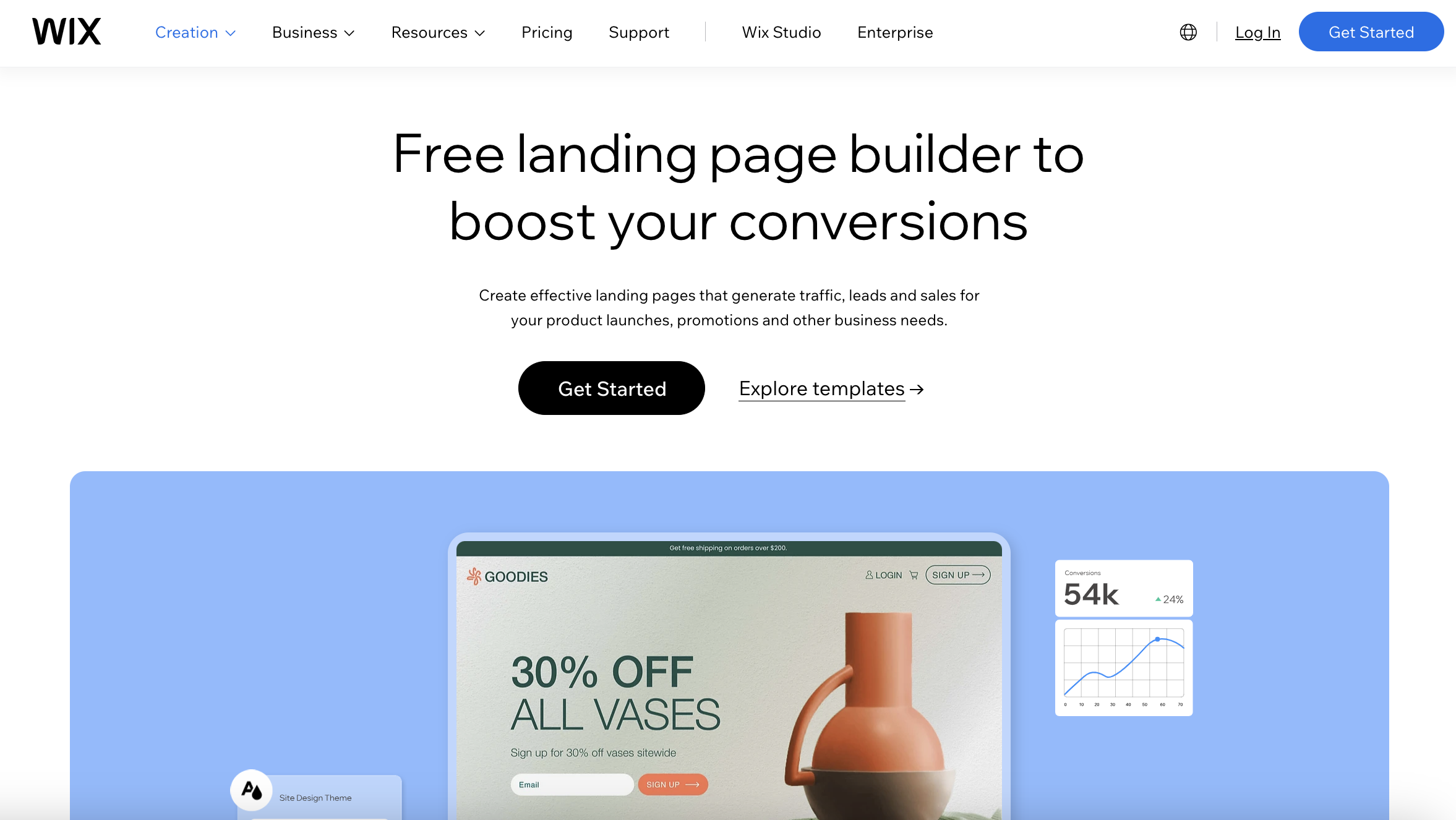 Screenshot from Wix.com, April 2024
Screenshot from Wix.com, April 2024- Best for: Individuals and small businesses seeking creative control without advanced coding.
Now for something much more accessible: Wix is renowned for its user-friendly platform, which is ideal for creating attractive landing pages with minimal effort.
Like other options on this list, Wix offers an accessible drag-and-drop editor and a range of existing templates to help users craft aesthetically pleasing and functional landing pages.
Wix’s platform has a reputation for being particularly beginner-friendly, with a low learning curve and a free plan to help new users get started without any upfront investment.
For those focused on ecommerce, Wix provides specific features to build landing pages that showcase products and promotions, supported by over 50 payment solutions and tools like heatmaps to enhance user engagement and conversion rates.
While it offers a free starter plan, accessing more advanced functionalities and removing Wix ads requires upgrading to a paid subscription.
Wix’s balance of user-friendly design tools, ecommerce support, and cost-effective pricing makes it a favorable option for those new to web design or businesses needing straightforward, visually appealing landing pages.
Pros:
- User-friendly with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
- Free plan available, making it accessible for beginners.
- Ecommerce capabilities with extensive payment integration.
Cons:
- Advanced features and ad-free experience require a paid plan.
- Potential limitations in customization for complex requirements.
- Site speed may decrease with more intricate designs.
Pricing:
- A free plan is available, but it includes Wix branding and lacks more advanced features like payments.
- Paid plans start at $17/month, offering additional features.
8. Elementor
 Screenshot from Elementor.com, April 2024
Screenshot from Elementor.com, April 2024- Best for: WordPress users looking for a powerful and intuitive landing page builder.
If you’re a WordPress user, you’ll want to know about Elementor.
It’s a WordPress page builder that has gained popularity for its flexibility, comprehensive customization capabilities, and user-friendly interface.
Elementor allows users to design dynamic and detailed landing pages within WordPress. This feature makes it the perfect choice for WordPress users who want to extend the functionality of their website with sleek landing pages that maintain a consistent look and feel with their existing content.
Its real-time editing features allow for immediate feedback on design changes without any coding.
It also offers dozens of designer-made templates to choose from. You can add custom forms and popups to your landing page, save page components for reuse, and seamlessly integrate with your customer relationship management (CRM) tools to create a powerful customer experience.
While Elementor offers a ton in terms of design flexibility and integration, it’s important to note that it’s exclusively for WordPress users and can be resource-intensive – so it might impact site performance, especially on more complex websites.
Pros:
- Advanced customization and design flexibility.
- Real-time editing and instant feedback.
- Seamless WordPress integration.
Cons:
- Exclusively for WordPress users.
- Potentially impacts site performance due to resource intensity.
Pricing:
- Free version with limited functionality.
- Paid versions start at $59/year, providing advanced features and support.
9. Taplink
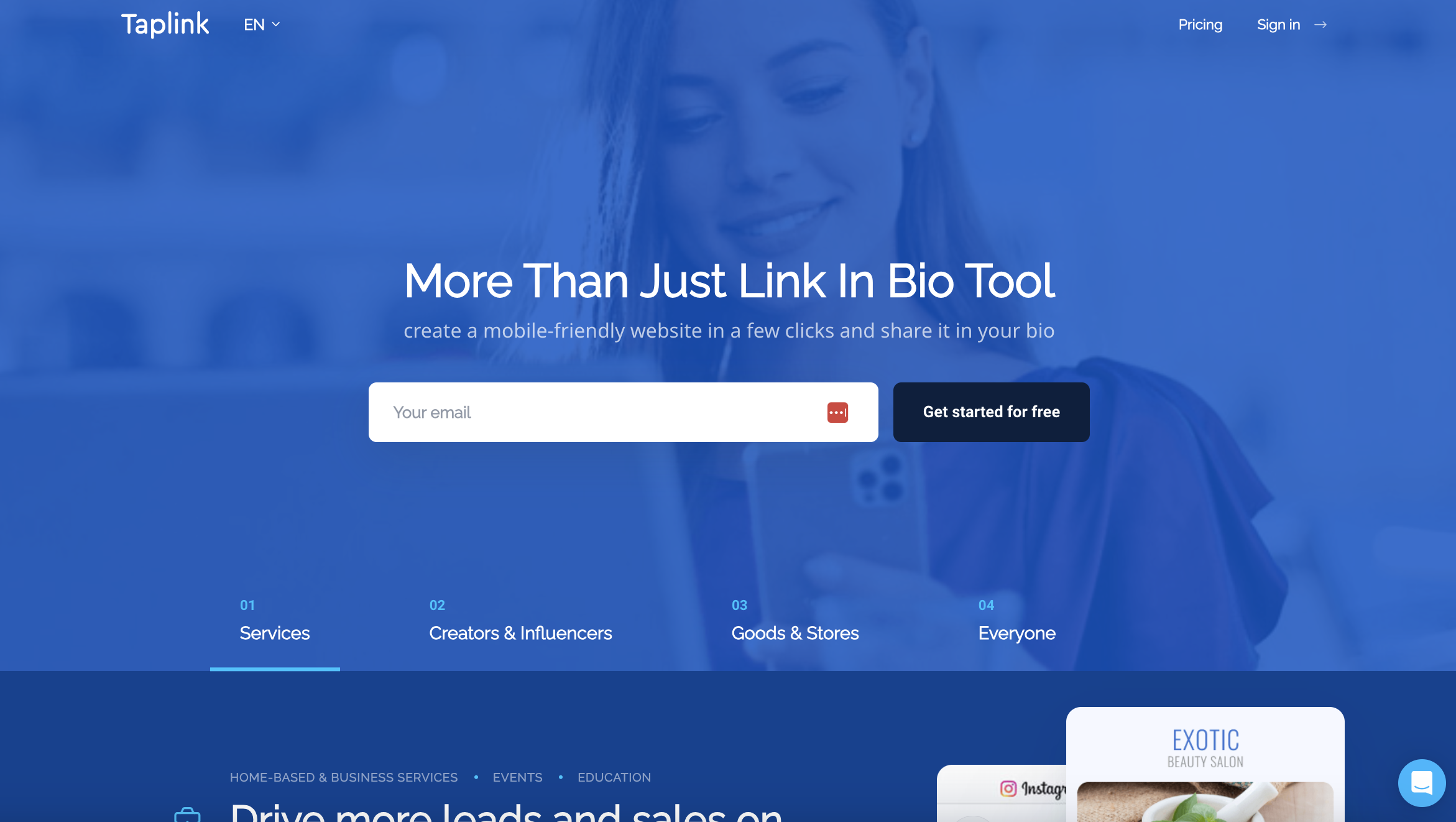 Screenshot from Taplink.at, April 2024
Screenshot from Taplink.at, April 2024- Best for: Social media influencers and businesses looking to direct traffic from social platforms to other content or actions.
This one’s a little different than some of the other examples here, but it deserves highlighting.
Taplink is a specialized micro-landing page builder optimized for social media profiles. It’s perfect for businesses and influencers that want to drive traffic from social media to other content or actions. You just use Taplink to create landing pages and share them on your social profiles.
Taplink stands out for its simplicity and mobile optimization, which is crucial when targeting social media audiences.
The focus on quick, effective page creation allows users to engage with their audience without the complexities of traditional website development.
For those aiming to convert social media interest into tangible outcomes – such as lead generation, sales, or content promotion – Taplink is a winner.
While its feature set is more limited than some of the more comprehensive builders featured here, its affordability and user-friendly design make it a great tool for those looking to maximize their social engagement with minimal effort and investment.
Pros:
- Simple and quick setup.
- Mobile-optimized for social media engagement.
- Cost-effective for targeted campaigns.
Cons:
- Designed primarily for micro-landing pages, limiting the scope.
- Fewer features and customization options than extensive landing page builders.
Pricing:
- Taplink offers a free basic plan, with premium features available on paid plans starting from $3/month. The most expensive tier, the Business tier, is $6/month.
There’s A Landing Page Platform To Help You Convert Visitors
Choosing the right landing page builder for your business can significantly impact your marketing success – but the decision will depend on your specific goals and needs.
As we’ve explored, each tool has unique strengths and caters to different aspects of the landing page creation and optimization process.
Whether you’re looking for advanced design capabilities, a user-friendly interface, or specific functionalities like CRO, there’s a platform that can help you not just streamline your landing page design process, but start converting visitors into loyal customers.
More resources:
Featured Image: Griboedov/Shutterstock
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 29, 2024
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoOffline For Last Days Of Passover 5784
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoQuiet Quitting vs. Setting Healthy Boundaries: Where’s The Line?
-

 MARKETING4 days ago
MARKETING4 days agoHow To Develop a Great Creative Brief and Get On-Target Content
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 30, 2024
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoHow to Promote Your Digital Marketing Agency: 4 Growth Strategies
-

 SEO4 days ago
SEO4 days agoWhy Big Companies Make Bad Content
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle’s John Mueller On Website Recovery After Core Updates















