The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
Pirated Themes and Plugins on Official WordPress

WordPress.org announced that plugins and themes that are pirated versions of paid plugins and themes will be removed from the official WordPress repositories. The WordPress community debated if that approach violated the WordPress Open Source GPL license that allows derivative works to be distributed.
The announcement itself affirmed that premium plugins are developed under the GPL that allows the creation of derivative works. But it also reserved the right to remove the plugins from the official plugin repository.
WordPress Hosts Pirated Themes and Plugins?
Apparently the official WordPress theme and plugin repositories have distributed pirated versions of premium plugins and themes in the past. One developer asserted that WordPress still does.
A developer claimed he had alerted WordPress to plugin privacy and that WordPress had done nothing about it.
“But but… 2 or 3 years ago I alerted you to a plugin which stole code and functions and even ‘word-for-word’ dashboard items from my plugins and you didn’t want to do anything…”
WordPress GPL Open Source
WordPress states that plugins and themes developed for WordPress that contain WordPress code are derivative works. Because of that, those plugins and themes inherit the open source GPL license.
WordPress explains the GPL license like this:
“GPL is an acronym for GNU Public License. It is the standard license WordPress uses for Open Source licensing https://wordpress.org/about/license/.
The GPL is a ‘copyleft’ license https://www.gnu.org/licenses/copyleft.en.html.
This means that derivative work can only be distributed under the same license terms. This is in distinction to permissive free software licenses, of which the BSD license and the MIT License are widely used examples.”
It’s clear that anyone is free to create derivative works based on all plugins and themes that are considered derivative works.
That said, the WordPress.org GNU Public License page acknowledges there may be legal gray areas about what is considered a derivative work.
The WordPress page about the license states:
“There is some legal grey area regarding what is considered a derivative work, but we feel strongly that plugins and themes are derivative work and thus inherit the GPL license.”
Pirated Plugins Prohibited from WordPress Repositories
WordPress.org maintains a directory of free plugins and themes that are available for download. The directory is called a repository. For example, the directory where themes can be downloaded is called “the official WordPress.org theme repository.”
There is an approval process that must be undergone before getting listed in the repositories. But once a theme or plugin is approved they are entered into the WordPress ecosystem and are available to all WordPress publishers for free.
Pirated Software Prohibited on WordPress.org
The announcement said:
“Taking someone’s pay-for code and re-releasing it as free-of-charge is considered to be piracy and is not welcome here.
It doesn’t matter if the code is GPL, it matters than you’re stealing the opportunity of the original developers to make a living, and we feel that is detrimental to the community.
In addition, it’s often in violation of the terms you agreed to when you downloaded the plugin from the developer in the first place.
By you doing that, and rehosting here, you put the entire directory in peril. Arguably we become responsible for your actions. As such, we do not permit plugins that are sold off WordPress.org to be re-hosted here.”
WordPress Community Feedback
The community was largely supportive of the intent behind forbidding pirated premium plugin and theme clones. Yet there was still some unease about whether pirated software might be legal and if perhaps WordPress.org was overstepping by prohibiting the cloned software.
One commenter wrote:
“I think the wording of the post is problematic, whilst I generally agree with the sentiment, its references to the GNU GPL v2 and the use of the term “piracy” (no ship or boat borne attackers were involved) and “stole” (no one lost anything they were entitled to) when people are exercising a right outlined in the WordPress project’s own philosophy.
…WordPress is distributed under the GNU GPLv2, the WordPress project itself asserts that plugins and modules are “derivative works”. The GNU GPLv2 explicitly excludes additional terms being applied to the distribution of source code.
…The WordPress Projects philosophy specifically supports redistribution without needing to ask permission from its creators.”
Another person asserted that piracy of premium plugins and themes still constitute copyright infringement.
“Open source licenses do not supersede copyright. The original author(s) still has that and if someone misrepresents the code as their own, while it is ripped off – or politely put “forked” – from someone else’s code, they *are* violating the author’s copyright.”
The person who published the official announcement asserted that the activity WordPress is banning is indeed a violation of copyright.
“These aren’t people forking and changing code, these are literally people making a copy, where the only changes are to hide who they took the code from. No new features, nothing.”
Beware of Pirated Plugins and Themes
Some plugins cost hundreds of dollars per year because it takes teams of people to develop it. Using such software deprives those people of earnings.
It’s tempting to download a free WordPress theme or plugin that is exactly the same as a premium version that can cost a hundred dollars or more.
Yet it’s important to be aware that pirated software can also contain backdoors and programs designed to take over a website.
Overall it may be a good idea for the entire WordPress community, from software developers to the publishers who rely on WordPress that rogue software thieves are not allowed to distribute their pirated plugins and themes from the official WordPress repositories.
Citation
Read the official WordPress Announcement:
Reminder: Forked Premium Plugins Are Not Permitted
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
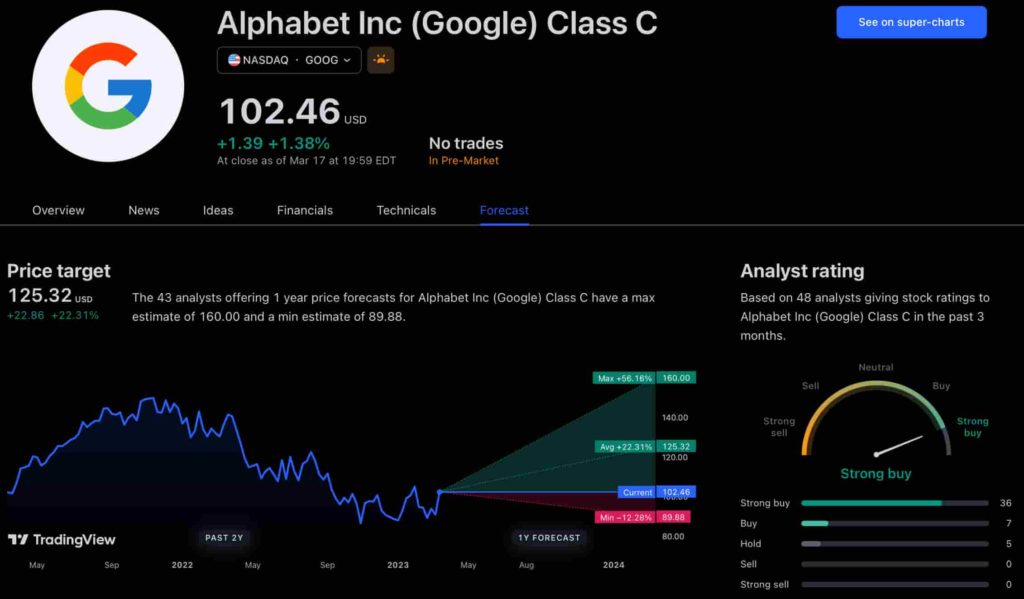
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoThe key to correcting the C-suite trust deficit
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoA Recap of Everything Marketers & Advertisers Need to Know
-

 MARKETING4 days ago
MARKETING4 days agoHow To Protect Your People and Brand
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days agoHow the TikTok Algorithm Works in 2024 (+9 Ways to Go Viral)
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Started Enforcing The Site Reputation Abuse Policy
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days ago128 Top SEO Tools That Are 100% Free
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoHow to Craft Compelling Google Ads for eCommerce
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days agoBlog Post Checklist: Check All Prior to Hitting “Publish”