SEO
A Complete Guide to Competitive Intelligence

In the business world, risks and opportunities are everywhere. For example, an industry trend may be sweeping the market for a limited time and favor early adopters, while a competitor that went bust can be a good source for acquiring new customers.
These types of news are not readily available, and by the time you purchase expensive analyst reports, they’re already outdated. So how do you make sure you understand your competition and stay ahead of market trends in a way that’s proactive and doesn’t break the bank?
Competitive intelligence is the answer to ensuring your business doesn’t get caught off guard. Notably, it’s not all data collection. Rather, it’s also about enabling the entire team to win through an actionable and repeatable process.
In this guide, you’ll learn the following:
Competitive intelligence (CI) is the process of gathering, analyzing, and sharing information about competitors, customers, and other market indicators to increase a company’s competitive edge.
It involves a coordinated competitive intelligence program and a centralized collection of data from various sources.
To succeed in business, knowing your competitors’ moves is not enough. Companies also need to be aware of market trends and how those changes will impact stakeholders. For example, unforeseen events in your industry may be cutting your financial gains this quarter.
This is where competitive intelligence steps in as a process to make more informed business decisions, reducing the uncertainty of external events. CI can also help you to:
- Generate more revenue.
- Spot growth opportunities early on.
- Anticipate market shifts with confidence.
- Develop counter-strategies for each of your competitors.
- Benchmark against competitors to discover areas of improvement.
- Measure brand perception in the eyes of your customers.
- Streamline product launches.
All these points can be effectively translated into a competitive intelligence program. But first, let’s look at what you came here for: competitive intelligence sources.
Like any system, the quality of the data you put into your CI program is a good predictor of its success. In the end, your goal is to create a complete profile of your competitor.
To do so, here are eight competitive intelligence sources that you can use today:
Your competitor’s website
It’s no surprise that a good starting point to gather competitive intel is to check out your competitor’s website.
Pay close attention to these:
- Positioning and messaging changes
- Solutions and vertical pages
- Pricing
- Product updates
First, go over the homepage and any marketing-related pages. Have they changed their tagline? What customer logos are they featuring? What buyer personas are they targeting? Signals like these will show you how your competitor wants to be perceived in the customers’ minds and what verticals they are pushing for.

You can learn a lot by analyzing your competitor’s homepage.
Second, move on to the product-related pages, particularly the pricing page. But don’t just settle for the price. Dig deeper. Find out the trial period length, pricing model, onboarding costs, etc.
Your competitor’s FAQ can also be a source of intel—not just for sales reps but also for marketers who can create marketing assets focused on solving difficult-to-solve pain points.
Content
Your competitor’s content is a trove of insights for showing what customers they’re looking for and where they seek to develop thought leadership.
Pay close attention to these:
- Type of content and format
- Frequency of posting
- Keywords and SEO
- Overall CTAs
For example, posting four case studies in a row is a clear indicator of their priorities on chasing a buyer persona. At the same time, the posting frequency can be used as a benchmark to create a sound content strategy.
Here’s how to check your competitor’s posting frequency in Ahrefs, using Asana as an example. I’ve chosen Asana because it’s probably a company you already know and use.
- Go to Ahrefs’ Content Explorer
- Plug in your competitor’s blog URL and switch the search mode to In URL
- Check the published vs. republished ratio in relation to yours

The real challenge is identifying the knowledge gaps between your content. You can then take advantage and develop informative content for keywords that your competitor doesn’t rank for to improve your search ranking.
Here’s how to do it in Ahrefs using the Content Gap tool, using the same Asana example:
- Plug your website into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Go to the Content Gap report and enter your competitor’s website

From this screenshot, we see that Paymo (an Asana competitor) is already ranking for “working remotely” and “fun team building activities”—topics that Asana could target.
Social media
Another valuable competitive source is social media. Although sometimes overwhelming, messages and mentions go a long way in pointing out competing campaign patterns.
Pay close attention to these:
- What channels the competitor is active on
- Frequency of posting
- Who they follow
- Ads
Now, social media ROI is hard to quantify and platform-dependent. The lesson here is to analyze key strategies you can steal from your competition and spot potential pain points. For example, one of your competitors may use Twitter to answer customer inquiries. Let’s look at a conversation from Asana’s Twitter.
@asana I love your product, but it would be really cool if you could list subtasks so that those outstanding were positioned at the top. Even better if it was in due date order.
— Gary Butterfield (@GaryBPT) March 10, 2022
The paint point is clear: There is no possibility to sort subtasks within a task. While this may be an edge case, you may find out that it’s a deal-breaker for large organizations that work with many subtasks.
So if you were a competitor, you could arm your sales reps with this information and formulate a few questions (in a battle card) that would lead prospects to this weakness.
Besides showing your competitor’s employees, LinkedIn is another go-to platform that gives you a feeling about your competitor’s culture, future webinars, and overall content used to promote its brand.
Customer reviews
Customer reviews, either testimonials or case studies, are living proof of a company’s value. They are perhaps the most honest source of external competitive intel.
Pay close attention to these:
- B2B review platforms (Capterra, G2, TrustRadius)
- Analyst reports (Forrester, Gartner)
- Question platforms (Quora, Reddit)
B2B review platforms like Capterra, G2, and TrustRadius are a good starting point to identify what kind of customers your competitor sells to, their buyer journeys, pain points, and satisfaction ratings. You want to pay particular attention to negative reviews that can be brought up in sales conversations.
Next in line, analyst reports like Gartner’s Magic Quadrant and Forrester’s Wave will give you hints on your competitor’s market presence, vision, and how well they execute the said vision. These reports will also hint at the industry and business size your competitor caters to, as they also include anonymous customer reviews.

Source: Cheetah Transformation.
Finally, question platforms such as Quora and Reddit are a great way to see the main concerns and buying process of your competitor’s customers. You can even go undercover and ask an anonymous question about your industry to gauge how well people understand the market.
Resellers
Resellers are equally important for CI as customer reviews and analyst reports, especially since they’re from an intermediary acting on behalf of your competitor.
Pay close attention to these:
- Pricing structures
- Conditions for upsales
- Free add-ons
Resellers sell your competitor’s products and assist with market analysis reports on how to sell them better. If you’ve built a relationship with them, you can get your hands on these reports and gain access to your competitor’s selling strategy.
For example, you may find that your competitors are hitting their enterprise clients hard with storage overcharges. Or that they’re increasing their prices with every yearly renewal. This type of information wins sales deals when you’re head-to-head against a market leader or a competitor with better market exposure.
Don’t forget to also look at what extras they offer with each package. You can match your competitor’s offering and add other services on top to make your product more appealing.
Press
An easily accessible way of conducting competitive research is to go through a company’s news, events, and press releases.
Pay close attention to these:
- Press releases
- Events
- Financial results reports
A company’s news page is a quick teller of its overall direction—whether it has received new funding, wants to tackle new markets, or has acquired a market leader. Some even have public financial reports that can give you the edge to act toward market shifts proactively.
The news page is just one piece of the puzzle. You can research publishers already covering your competition but not your business. Build relationships with them. And who knows? You may get access to a bigger platform to spread the word about your product.
Here’s an easy way to do this using Ahrefs:
- Plug your competitor’s website into Site Explorer
- Go to Backlink profile, then choose Referring Domains
- Check DoFollow links only and Exclude subdomains
It looks like Asana’s competitor, Paymo, has some press coverage for writerraccess.com—a service for covering copywriters. And we’ve got our hands on a reseller too.

Events are also an opportunity to spy on your competition ethically. Find out what events they attend, how regularly, and the messages used on booths, banners, flyers, t‑shirts, and other swag.
Some may even sponsor events to reinforce their brand to a specific customer segment. This will give you an idea about what events to join and the messages to use for brand awareness.
HR
Your competitor’s employees—perhaps the most overlooked CI resource—and their HR practices are the best barometer for a competitor’s growth.
Pay close attention to these:
- About Us page/Careers page
- Job positions by department
- C‑level hires
- Feedback on culture, salaries, and interviews (Glassdoor)
No one is more well-versed in your competitor’s strengths and weaknesses than their employees. And while the employees may be loyal, they are still having discussions and leaving trails behind that can serve as competitive ammunition.
You can check the overall job satisfaction of current and former employees on Glassdoor. What are the pros and cons of the competitor’s culture? What does the interview process look like? Average salaries? Questions like these can put your HR in a better position to address weaknesses when hiring similar candidates.
Another great place to dig for competitive intel is your competitor’s About Us page or Careers page. The gist is to look beyond job posting details, such as the location, role, and requirements.
If a job goes unfilled for a long time, this probably means the competitor has lots of things going on and needs a high-level specialist to take over the workload.
Similarly, if different positions are advertised within the same department, this can mean they’re putting all their efforts into a specific business area. Are they hiring more engineers? A new product may be just around the corner. Are marketers and customer success reps in high demand? Expansion is close.
Your customers and colleagues
Finally, it’s time to talk about the most accessible source of internal intel: your customers and colleagues.
Before choosing your business, your customers have gone through many hoops trialing other competitors. As a result, they’ll know the problems your competition is trying to solve and what works and doesn’t within the context of their vertical, saving you precious time on research.
One way to extract this information is to get it directly from customers through interviews or surveys. The other is to contact your colleagues.
Check each department for new insights they can share with you. Sales can inform you about common objections, support has intel on the top recurring questions, product knows all feature differentiators, and marketing can advise what collaterals have more priority. Your goal is to pick key takeaways as you carefully comb through the data.
Unfortunately, data will be spread across CRMs, support chat tools, and notes for most cases. A better solution is to use dedicated competitive intelligence tools that centralize this type of data, which brings us to the next point.
A competitive intelligence program needs to be scalable enough to arm every employee with the correct intel and processes for their role.
We’re not talking only about C‑level executives but also sales reps, marketers, and engineers that can benefit from these insights to better fight objections, reach new audiences, and optimize product launches.
The good news is that CI programs are now more affordable than ever—even for SMBs with small budgets—given how easy it is to find information online.
So without further ado, here are the most important steps that go into building an effective CI program:
1. Identify your direct competitors
You may think you don’t have any competitors. But if you’re solving a problem, chances are someone else has already thought about solving it.
In fact, Crayon’s 2022 survey has shown that companies of all sizes experience an 18% increase in competitors every year. The average number of new competitors is 29 in 2020.
Knowing which competitors to keep tabs on is critical for the success of a CI program, but that’s not so obvious. Hence, we need to kick things off with some terminology:
- Direct competitors act in the same market as yours and sell similar products. It’s usually a zero-sum game: If customers don’t buy from you, they buy from them. Think Burger King vs. McDonald’s.
- Indirect competitors act in the same market but sell different products that satisfy the same need. Think Burger King vs. KFC. They are both fast-food restaurants that curb hunger differently.
- Replacement competitors don’t act in the same market, but they can replace your product to satisfy the same need. Think Burger King vs. Beyond Meat (vegan) burgers.
Now that competitor types are clear, gather a list of 5–10 direct competitors and five indirect competitors.
Replacement competitors shouldn’t be your concern unless there are various ways to solve the problem your product is trying to solve.
A reliable way to find your competition is to check if you’re targeting the same keywords. Here’s a quick method using Ahrefs (with Asana as the example):
- Plug your website into Site Explorer.
- Go to Organic search and choose Competing Domains
- Check the Common keywords column
It looks like Asana has the most overlapping keywords with Monday.com.

2. Establish key objectives and metrics for each stakeholder
With your direct competitors mapped out, it’s time to set your key objectives and metrics. This goes hand in hand with identifying the stakeholders you need to get buy-in for the CI program.
A good starting point is to ask the C‑level executives what competitive threats keep them busy at night. This action won’t justify the need for a CI program, but it will point you to the departments that can solve them.
Remember, each function represents a touchpoint between your business and the customer, providing different perspectives of the buying journey.
Let’s look at the most common CI stakeholders and an example goal for each:
- Sales – Increase win rates in competitive deals
- Marketing – Create actionable battle cards
- Engineering – Build true differentiators
- Customer success/support – Retain customers
- C‑level executives – Analyze adjacent EMEA markets to break into
Now, this doesn’t mean goals do not overlap. On the contrary, improved positioning can bring in more leads, while a product that stands out can significantly increase customer retention.
The takeaway at this step is to find out the job roles that will contribute to the CI program and effective ways to measure it.
3. Gather data
Data collection is the foundation and perhaps most time-consuming part of any CI program. The challenge lies in finding qualitative insights to support your team members within their job roles.
We’ve already gone through competitive intelligence resources. On a meta level, though, know that you can categorize them into two data types.
There is external data. It’s the low-hanging fruit type of information available online, sitting on your competitor’s website, social media, review platforms, analyst reports, etc. Albeit harder to dig for, resellers are also a valid source of data on how users interact with your competitor’s product and their main offering’s strengths and weaknesses.
We also have internal data. It’s information that already exists within your business, such as call notes from a sales rep or a competitor’s pricing list sent to one of your customers.
Even though the latter is more qualitative, both are ethical and should be used together to arrive at actionable insights.
4. Analyze data
Great. You’ve identified your direct competitor, established CI goals and metrics, and probably spent a few hours gathering competitive intel.
What follows is transforming that raw data into actual deliverables (aka sales and marketing assets) and feeding them to the right stakeholders.
By far, the most common CI deliverable is the battle card, a sales asset that packs short insights about a specific competitor with the goal of “depositioning” them. Your sales team will love these cards, as long as they’re not too overwhelming and formulated word for word to be consumed right before a sales call.
While there’s no secret recipe on how to craft a battle card, an actionable one should include the following sections:
- Your competitor’s profile
- Quick dismisses to disqualify the competitor early on
- Arguments for why you win and why you lose
- Objection handling answers
- A list of landmine topics that put your competitor in a bad light
For more information on how to create more inclusive battle cards, Klue has already written extensively about a battle card framework.

Battle cards aside, other popular CI deliverables are product sheets—1:1 feature comparisons between your product and your competitor’s product—and executive slide decks to inform executives about the long-term strategy.
How many you can deliver will largely depend on your marketing team’s size and budget. This is only half of the story, though. Equally important is how and when you deliver them.
5. Share insights with key stakeholders
Competitive intelligence has no value if it sits in a corner and doesn’t impact stakeholders.
At the final step of the CI program, your job is twofold: (1) identify your stakeholder’s preferred communication channels and (2) increase the frequency of delivering competitive insights.
For the first endeavor, ask your stakeholders how they communicate. Sales reps may be more inclined to hang out in Slack channels, while executives probably rely heavily on email. Always meet them on their turf to ensure that information is consumed on time.
As for the second one, consider sharing competitive insights during daily and weekly stand-ups. According to a study by Crayon, businesses that do so frequently have seen a direct revenue impact; in the study, 69% of the respondents share competitive intent daily and 72% do so weekly.
Ultimately, sharing competitive insights is an ongoing process that will reinforce the adoption of a CI program and guarantee its success.
By now, you’ve probably realized how time-consuming competitive research is.
It doesn’t have to be. Even though you may not have a CI function, let alone a budget, you can collect, analyze, and share data about competitors with affordable, competitive software.
Owler

Best for: Digging into a company’s history
Pricing: Free trial available; paid plans start from $35/month
Alternative: Crunchbase
With a community of 3.5 million crowd-sourced users, Owler has the largest and most up-to-date data set of company insights.
This means you can surface all sorts of strategic information like funding, acquisitions, and the latest news to understand how a competitor has grown over time. The tool even goes the extra mile and compiles a brief analysis of your competitors.
You can also follow companies to receive daily or real-time notifications about their most relevant content, including press releases, blog articles, social media posts, or product videos.
Visualping

Best for: Monitoring website changes
Pricing: Free trial available; paid plans start from $10/month (personal account) and $50/month (business account)
Alternatives: Change Tower, Competitors App
Visualping is a competitive intelligence tool for monitoring website changes.
All you have to do is enter a competitor’s URL, select the website area you wish to monitor, the threshold of changes (1%, 10%, 25%, 50%), frequency checks (every day, week, month), and your email address to receive the alerts. Quite simple? You bet. But effective in identifying more subtle messaging and visual changes.
This is not all. Visualping also trains bots to perform actions on your behalf, such as entering passwords or clicking on elements, saving you time during the competitive research process.
Ahrefs

Best for: Analyzing website traffic and SEO
Pricing: Paid plans start from $83/month, but you can use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools for free
Alternatives: None
Ahrefs is an industry-leading SEO and marketing tool that can help you uncover a competitor’s website traffic and reverse-engineer their efforts.
Here are some of its most popular competitive intelligence tools:
- Site Explorer – Research competitor backlinks and get publishers to cover you too
- Content Gap tool – Find keywords that a competitor ranks for that you don’t
- Ads – Deconstruct your competitor’s ads from ad copy to CTAs
- Email alerts – Stay in the loop about new backlinks and mentions of your competitor
Social Searcher

Best for: Comparing social media strategies
Pricing: Free trial available; paid plans start from €3.49/month for 200 searches/day
Alternatives: Talkwalker, Rival IQ
Social Searcher works like a search engine for social media, gathering mentions about your competitor’s brand.
The tool crawls data across 11 social media networks, displaying keywords, post types, and users. In addition, its “audience insights” feature gives you hints about the preferred post types, publishing times, and go-to social media channels of your competitor’s customers.
But perhaps the most vital feature in its arsenal is the sentiment analysis report, making it easy to spot negative feedback about your competitor’s products and services. You can translate these weaknesses into sales enablement material later on.
SendView

Best for: Tracking competitor email marketing
Pricing: Plans start from $49/month for 10 company newsletters
Alternative: Owletter
SendView is an excellent tool for tracking your competitor’s email marketing efforts.
The process goes something like this: You create a separate email address and then subscribe to your competitor’s newsletter. After that, all emails go straight into SendView without bloating your inbox.
On top of this, you can access each email to analyze its subject line length, word count, email provider, spam score, source code, and whether or not it’s mobile-friendly. These are all valuable sources of inspiration for optimizing email marketing campaigns that resonate with your audience.
Final thoughts
Despite the abundant information about markets and competitors, teams today are hungrier than ever for knowledge and guidance—whether that’s ways to do an SEO competitor analysis or conduct a market analysis from A to Z (including mystery shopping).
Competitive intelligence is the long-awaited answer to navigate the business world with more clarity. Don’t think of it as a one-off action. Rather, see it as an ongoing process that equips every team member with information relevant to their job role and tools to make better business decisions.
Feel free to use this guide to start your own CI program or to convince your executive board about the importance of competitive intelligence.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.
SEO
How To Use ChatGPT For Keyword Research

Anyone not using ChatGPT for keyword research is missing a trick.
You can save time and understand an entire topic in seconds instead of hours.
In this article, I outline my most effective ChatGPT prompts for keyword research and teach you how I put them together so that you, too, can take, edit, and enhance them even further.
But before we jump into the prompts, I want to emphasize that you shouldn’t replace keyword research tools or disregard traditional keyword research methods.
ChatGPT can make mistakes. It can even create new keywords if you give it the right prompt. For example, I asked it to provide me with a unique keyword for the topic “SEO” that had never been searched before.
“Interstellar Internet SEO: Optimizing content for the theoretical concept of an interstellar internet, considering the challenges of space-time and interplanetary communication delays.”
Although I want to jump into my LinkedIn profile and update my title to “Interstellar Internet SEO Consultant,” unfortunately, no one has searched that (and they probably never will)!
You must not blindly rely on the data you get back from ChatGPT.
What you can rely on ChatGPT for is the topic ideation stage of keyword research and inspiration.
ChatGPT is a large language model trained with massive amounts of data to accurately predict what word will come next in a sentence. However, it does not know how to do keyword research yet.
Instead, think of ChatGPT as having an expert on any topic armed with the information if you ask it the right question.
In this guide, that is exactly what I aim to teach you how to do – the most essential prompts you need to know when performing topical keyword research.
Best ChatGPT Keyword Research Prompts
The following ChatGPT keyword research prompts can be used on any niche, even a topic to which you are brand new.
For this demonstration, let’s use the topic of “SEO” to demonstrate these prompts.
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Topic
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Topic}?
The first prompt is to give you an idea of the niche.
As shown above, ChatGPT did a great job understanding and breaking down SEO into three pillars: on-page, off-page & technical.
The key to the following prompt is to take one of the topics ChatGPT has given and query the sub-topics.
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Sub-topic}?
For this example, let’s query, “What are the most popular sub-topics related to keyword research?”
Having done keyword research for over 10 years, I would expect it to output information related to keyword research metrics, the types of keywords, and intent.
Let’s see.
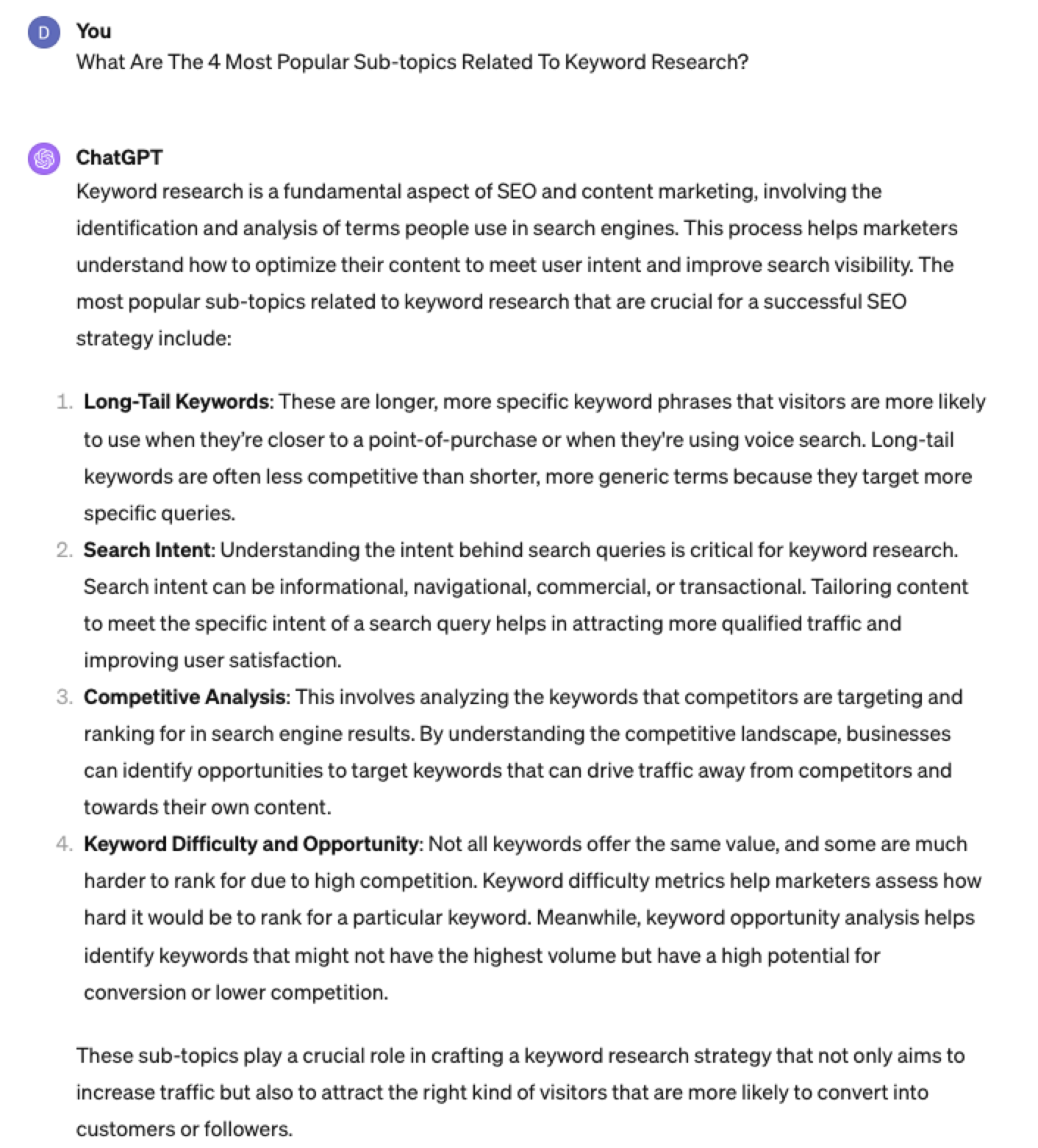 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, right on the money.
To get the keywords you want without having ChatGPT describe each answer, use the prompt “list without description.”
Here is an example of that.
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Keywords For The Topic Of {X}
You can even branch these keywords out further into their long-tail.
Example prompt:
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Long-tail Keywords For The Topic “{X}”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024List Without Description The Top Semantically Related Keywords And Entities For The Topic {X}
You can even ask ChatGPT what any topic’s semantically related keywords and entities are!
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: The Onion Method Of Prompting ChatGPT
When you are happy with a series of prompts, add them all to one prompt. For example, so far in this article, we have asked ChatGPT the following:
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to SEO?
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to keyword research
- List without description the top five most popular keywords for “keyword intent”?
- List without description the top five most popular long-tail keywords for the topic “keyword intent types”?
- List without description the top semantically related keywords and entities for the topic “types of keyword intent in SEO.”
Combine all five into one prompt by telling ChatGPT to perform a series of steps. Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4, and Step 5”
Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4 and Step 5. Step 1 – Generate an answer for the 3 most popular sub-topics related to {Topic}?. Step 2 – Generate 3 of the most popular sub-topics related to each answer. Step 3 – Take those answers and list without description their top 3 most popular keywords. Step 4 – For the answers given of their most popular keywords, provide 3 long-tail keywords. Step 5 – for each long-tail keyword offered in the response, a list without descriptions 3 of their top semantically related keywords and entities.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Question
Taking the steps approach from above, we can get ChatGPT to help streamline getting keyword ideas based on a question. For example, let’s ask, “What is SEO?”
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, and Step 4. Step 1 Generate 10 questions about “{Question}”?. Step 2 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 3 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 4 – Based on the above Steps 1,2,3 suggest a final list of questions avoiding duplicates or semantically similar questions.”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On The Alphabet Soup Method
One of my favorite methods, manually, without even using a keyword research tool, is to generate keyword research ideas from Google autocomplete, going from A to Z.
-
 Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
You can also do this using ChatGPT.
Example prompt:
“give me popular keywords that includes the keyword “SEO”, and the next letter of the word starts with a”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: Using the onion prompting method above, we can combine all this in one prompt.
“Give me five popular keywords that include “SEO” in the word, and the following letter starts with a. Once the answer has been done, move on to giving five more popular keywords that include “SEO” for each letter of the alphabet b to z.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On User Personas
When it comes to keyword research, understanding user personas is essential for understanding your target audience and keeping your keyword research focused and targeted. ChatGPT may help you get an initial understanding of customer personas.
Example prompt:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of user personas”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024You could even go a step further and ask for questions based on those topics that those specific user personas may be searching for:
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024As well as get the keywords to target based on those questions:
“For each question listed above for each persona, list the keywords, as well as the long-tail keywords to target, and put them in a table”
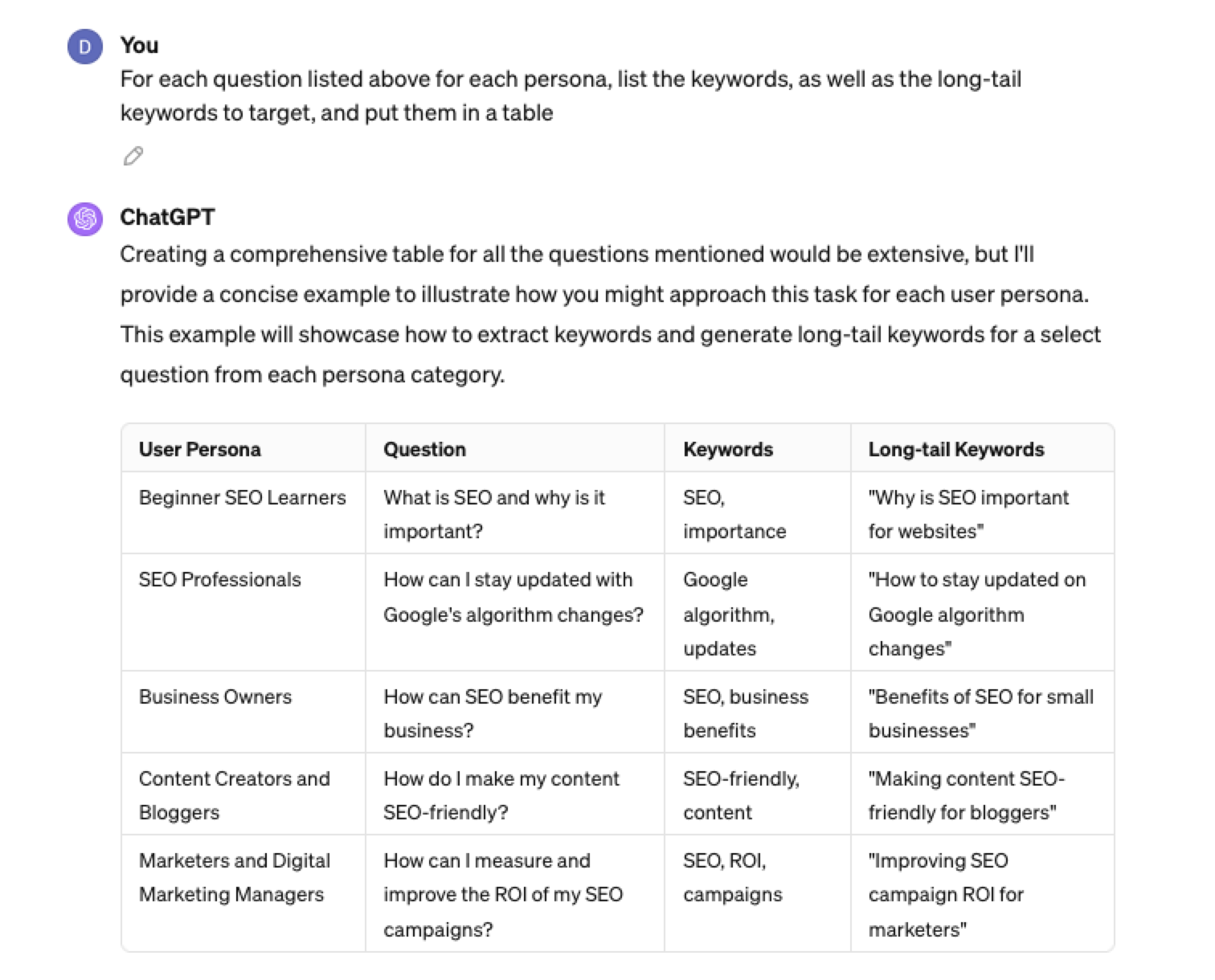 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On Searcher Intent And User Personas
Understanding the keywords your target persona may be searching is the first step to effective keyword research. The next step is to understand the search intent behind those keywords and which content format may work best.
For example, a business owner who is new to SEO or has just heard about it may be searching for “what is SEO.”
However, if they are further down the funnel and in the navigational stage, they may search for “top SEO firms.”
You can query ChatGPT to inspire you here based on any topic and your target user persona.
SEO Example:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of searcher intent that a {Target Persona} would be searching for”
ChatGPT For Keyword Research Admin
Here is how you can best use ChatGPT for keyword research admin tasks.
Using ChatGPT As A Keyword Categorization Tool
One of the use cases for using ChatGPT is for keyword categorization.
In the past, I would have had to devise spreadsheet formulas to categorize keywords or even spend hours filtering and manually categorizing keywords.
ChatGPT can be a great companion for running a short version of this for you.
Let’s say you have done keyword research in a keyword research tool, have a list of keywords, and want to categorize them.
You could use the following prompt:
“Filter the below list of keywords into categories, target persona, searcher intent, search volume and add information to a six-column table: List of keywords – [LIST OF KEYWORDS], Keyword Search Volume [SEARCH VOLUMES] and Keyword Difficulties [KEYWORD DIFFICUTIES].”
-
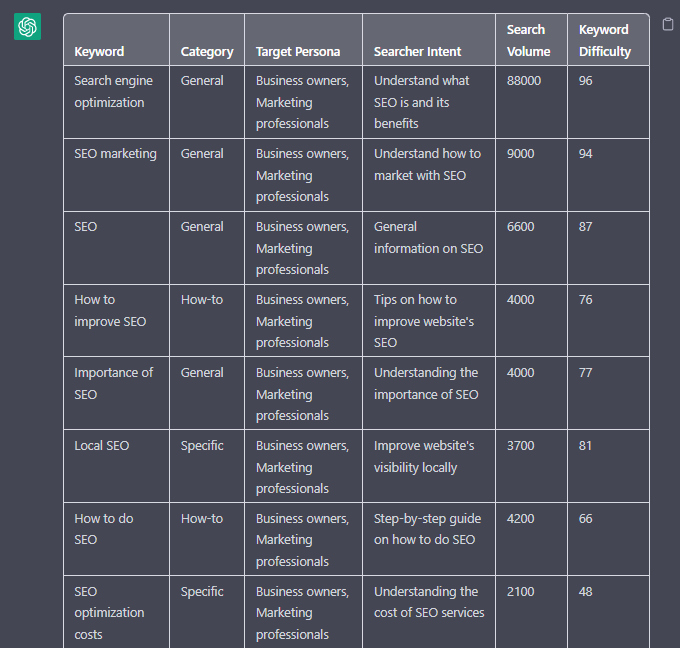 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Tip: Add keyword metrics from the keyword research tools, as using the search volumes that a ChatGPT prompt may give you will be wildly inaccurate at best.
Using ChatGPT For Keyword Clustering
Another of ChatGPT’s use cases for keyword research is to help you cluster. Many keywords have the same intent, and by grouping related keywords, you may find that one piece of content can often target multiple keywords at once.
However, be careful not to rely only on LLM data for clustering. What ChatGPT may cluster as a similar keyword, the SERP or the user may not agree with. But it is a good starting point.
The big downside of using ChatGPT for keyword clustering is actually the amount of keyword data you can cluster based on the memory limits.
So, you may find a keyword clustering tool or script that is better for large keyword clustering tasks. But for small amounts of keywords, ChatGPT is actually quite good.
A great use small keyword clustering use case using ChatGPT is for grouping People Also Ask (PAA) questions.
Use the following prompt to group keywords based on their semantic relationships. For example:
“Organize the following keywords into groups based on their semantic relationships, and give a short name to each group: [LIST OF PAA], create a two-column table where each keyword sits on its own row.
-
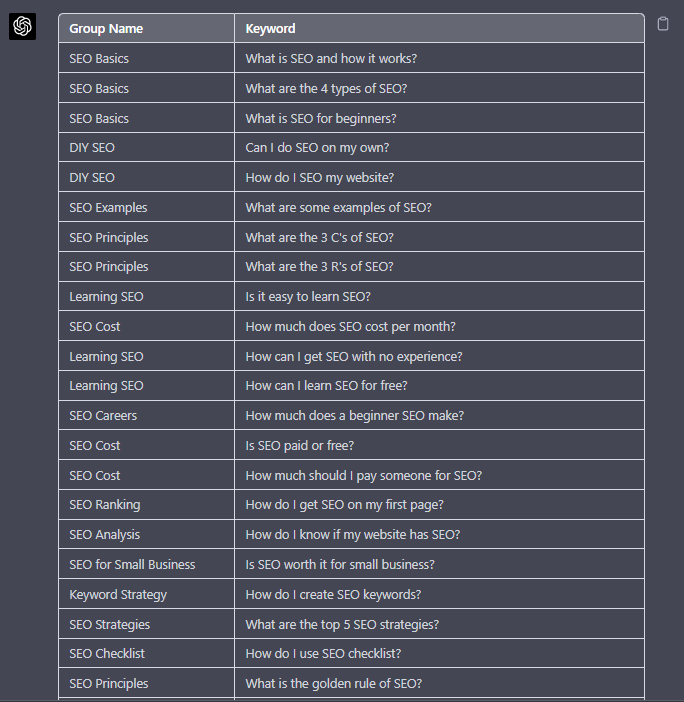 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Using Chat GPT For Keyword Expansion By Patterns
One of my favorite methods of doing keyword research is pattern spotting.
Most seed keywords have a variable that can expand your target keywords.
Here are a few examples of patterns:
1. Question Patterns
(who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will)
“Generate [X] keywords for the topic “[Topic]” that contain any or all of the following “who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20242. Comparison Patterns
Example:
“Generate 50 keywords for the topic “{Topic}” that contain any or all of the following “for, vs, alternative, best, top, review”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20243. Brand Patterns
Another one of my favorite modifiers is a keyword by brand.
We are probably all familiar with the most popular SEO brands; however, if you aren’t, you could ask your AI friend to do the heavy lifting.
Example prompt:
“For the top {Topic} brands what are the top “vs” keywords”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20244. Search Intent Patterns
One of the most common search intent patterns is “best.”
When someone is searching for a “best {topic}” keyword, they are generally searching for a comprehensive list or guide that highlights the top options, products, or services within that specific topic, along with their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks, to make an informed decision.
Example:
“For the topic of “[Topic]” what are the 20 top keywords that include “best”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, this guide to keyword research using ChatGPT has emphasized the ease of generating keyword research ideas by utilizing ChatGPT throughout the process.
Keyword Research Using ChatGPT Vs. Keyword Research Tools
Free Vs. Paid Keyword Research Tools
Like keyword research tools, ChatGPT has free and paid options.
However, one of the most significant drawbacks of using ChatGPT for keyword research alone is the absence of SEO metrics to help you make smarter decisions.
To improve accuracy, you could take the results it gives you and verify them with your classic keyword research tool – or vice versa, as shown above, uploading accurate data into the tool and then prompting.
However, you must consider how long it takes to type and fine-tune your prompt to get your desired data versus using the filters within popular keyword research tools.
For example, if we use a popular keyword research tool using filters, you could have all of the “best” queries with all of their SEO metrics:
-
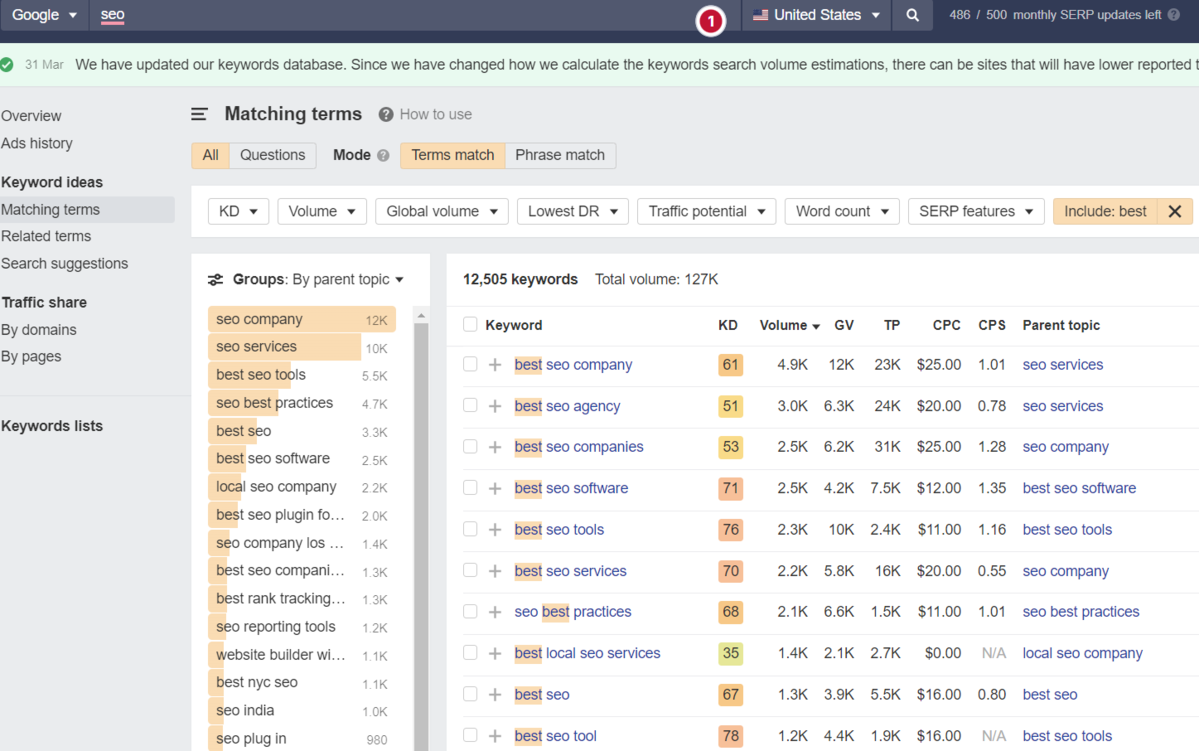 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
And unlike ChatGPT, generally, there is no token limit; you can extract several hundred, if not thousands, of keywords at a time.
As I have mentioned multiple times throughout this piece, you cannot blindly trust the data or SEO metrics it may attempt to provide you with.
The key is to validate the keyword research with a keyword research tool.
ChatGPT For International SEO Keyword Research
ChatGPT can be a terrific multilingual keyword research assistant.
For example, if you wanted to research keywords in a foreign language such as French. You could ask ChatGPT to translate your English keywords;
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024- The key is to take the data above and paste it into a popular keyword research tool to verify.
- As you can see below, many of the keyword translations for the English keywords do not have any search volume for direct translations in French.
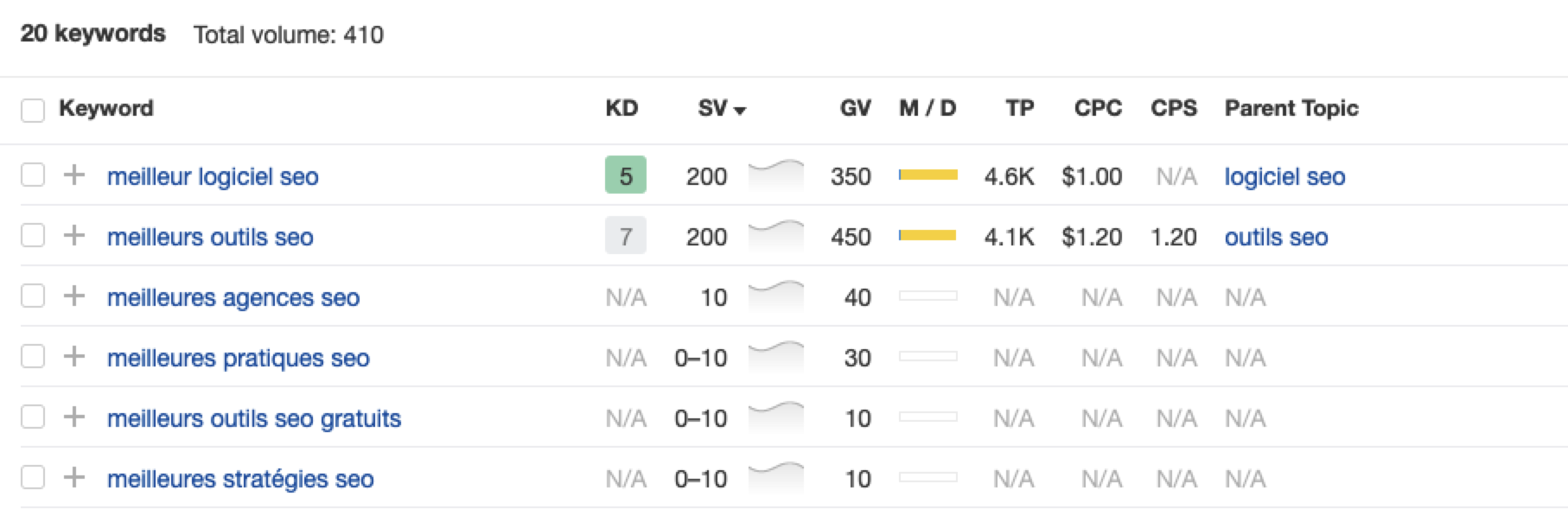 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024But don’t worry, there is a workaround: If you have access to a competitor keyword research tool, you can see what webpage is ranking for that query – and then identify the top keyword for that page based on the ChatGPT translated keywords that do have search volume.
-
-
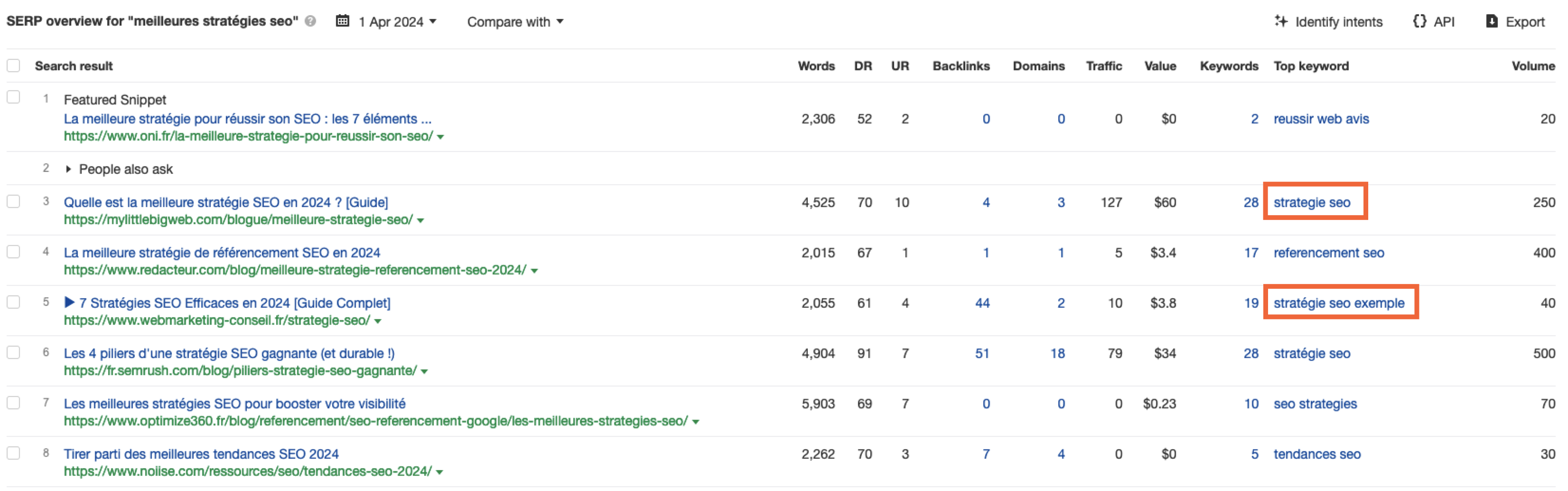 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Or, if you don’t have access to a paid keyword research tool, you could always take the top-performing result, extract the page copy, and then ask ChatGPT what the primary keyword for the page is.
Key Takeaway
-
ChatGPT can be an expert on any topic and an invaluable keyword research tool. However, it is another tool to add to your toolbox when doing keyword research; it does not replace traditional keyword research tools.
As shown throughout this tutorial, from making up keywords at the beginning to inaccuracies around data and translations, ChatGPT can make mistakes when used for keyword research.
You cannot blindly trust the data you get back from ChatGPT.
However, it can offer a shortcut to understanding any topic for which you need to do keyword research and, as a result, save you countless hours.
But the key is how you prompt.
The prompts I shared with you above will help you understand a topic in minutes instead of hours and allow you to better seed keywords using keyword research tools.
It can even replace mundane keyword clustering tasks that you used to do with formulas in spreadsheets or generate ideas based on keywords you give it.
Paired with traditional keyword research tools, ChatGPT for keyword research can be a powerful tool in your arsenal.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tatiana Shepeleva/Shutterstock
SEO
OpenAI Expected to Integrate Real-Time Data In ChatGPT

Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, dispelled rumors that a new search engine would be announced on Monday, May 13. Recent deals have raised the expectation that OpenAI will announce the integration of real-time content from English, Spanish, and French publications into ChatGPT, complete with links to the original sources.
OpenAI Search Is Not Happening
Many competing search engines have tried and failed to challenge Google as the leading search engine. A new wave of hybrid generative AI search engines is currently trying to knock Google from the top spot with arguably very little success.
Sam Altman is on record saying that creating a search engine to compete against Google is not a viable approach. He suggested that technological disruption was the way to replace Google by changing the search paradigm altogether. The speculation that Altman is going to announce a me-too search engine on Monday never made sense given his recent history of dismissing the concept as a non-starter.
So perhaps it’s not a surprise that he recently ended the speculation by explicitly saying that he will not be announcing a search engine on Monday.
He tweeted:
“not gpt-5, not a search engine, but we’ve been hard at work on some new stuff we think people will love! feels like magic to me.”
“New Stuff” May Be Iterative Improvement
It’s quite likely that what’s going to be announced is iterative which means it improves ChatGPT but not replaces it. This fits into how Altman recently expressed his approach with ChatGPT.
He remarked:
“And it does kind of suck to ship a product that you’re embarrassed about, but it’s much better than the alternative. And in this case in particular, where I think we really owe it to society to deploy iteratively.
There could totally be things in the future that would change where we think iterative deployment isn’t such a good strategy, but it does feel like the current best approach that we have and I think we’ve gained a lot from from doing this and… hopefully the larger world has gained something too.”
Improving ChatGPT iteratively is Sam Altman’s preference and recent clues point to what those changes may be.
Recent Deals Contain Clues
OpenAI has been making deals with news media and User Generated Content publishers since December 2023. Mainstream media has reported these deals as being about licensing content for training large language models. But they overlooked a a key detail that we reported on last month which is that these deals give OpenAI access to real-time information that they stated will be used to give attribution to that real-time data in the form of links.
That means that ChatGPT users will gain the ability to access real-time news and to use that information creatively within ChatGPT.
Dotdash Meredith Deal
Dotdash Meredith (DDM) is the publisher of big brand publications such as Better Homes & Gardens, FOOD & WINE, InStyle, Investopedia, and People magazine. The deal that was announced goes way beyond using the content as training data. The deal is explicitly about surfacing the Dotdash Meredith content itself in ChatGPT.
The announcement stated:
“As part of the agreement, OpenAI will display content and links attributed to DDM in relevant ChatGPT responses. …This deal is a testament to the great work OpenAI is doing on both fronts to partner with creators and publishers and ensure a healthy Internet for the future.
Over 200 million Americans each month trust our content to help them make decisions, solve problems, find inspiration, and live fuller lives. This partnership delivers the best, most relevant content right to the heart of ChatGPT.”
A statement from OpenAI gives credibility to the speculation that OpenAI intends to directly show licensed third-party content as part of ChatGPT answers.
OpenAI explained:
“We’re thrilled to partner with Dotdash Meredith to bring its trusted brands to ChatGPT and to explore new approaches in advancing the publishing and marketing industries.”
Something that DDM also gets out of this deal is that OpenAI will enhance DDM’s in-house ad targeting in order show more tightly focused contextual advertising.
Le Monde And Prisa Media Deals
In March 2024 OpenAI announced a deal with two global media companies, Le Monde and Prisa Media. Le Monde is a French news publication and Prisa Media is a Spanish language multimedia company. The interesting aspects of these two deals is that it gives OpenAI access to real-time data in French and Spanish.
Prisa Media is a global Spanish language media company based in Madrid, Spain that is comprised of magazines, newspapers, podcasts, radio stations, and television networks. It’s reach extends from Spain to America. American media companies include publications in the United States, Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Mexico, and Panama. That is a massive amount of real-time information in addition to a massive audience of millions.
OpenAI explicitly announced that the purpose of this deal was to bring this content directly to ChatGPT users.
The announcement explained:
“We are continually making improvements to ChatGPT and are supporting the essential role of the news industry in delivering real-time, authoritative information to users. …Our partnerships will enable ChatGPT users to engage with Le Monde and Prisa Media’s high-quality content on recent events in ChatGPT, and their content will also contribute to the training of our models.”
That deal is not just about training data. It’s about bringing current events data to ChatGPT users.
The announcement elaborated in more detail:
“…our goal is to enable ChatGPT users around the world to connect with the news in new ways that are interactive and insightful.”
As noted in our April 30th article that revealed that OpenAI will show links in ChatGPT, OpenAI intends to show third party content with links to that content.
OpenAI commented on the purpose of the Le Monde and Prisa Media partnership:
“Over the coming months, ChatGPT users will be able to interact with relevant news content from these publishers through select summaries with attribution and enhanced links to the original articles, giving users the ability to access additional information or related articles from their news sites.”
There are additional deals with other groups like The Financial Times which also stress that this deal will result in a new ChatGPT feature that will allow users to interact with real-time news and current events .
OpenAI’s Monday May 13 Announcement
There are many clues that the announcement on Monday will be that ChatGPT users will gain the ability to interact with content about current events. This fits into the terms of recent deals with news media organizations. There may be other features announced as well but this part is something that there are many clues pointing to.
Watch Altman’s interview at Stanford University
Featured Image by Shutterstock/photosince
SEO
Google’s Strategies For Dealing With Content Decay

In the latest episode of the Search Off The Record podcast, Google Search Relations team members John Mueller and Lizzi Sassman did a deep dive into dealing with “content decay” on websites.
Outdated content is a natural issue all sites face over time, and Google has outlined strategies beyond just deleting old pages.
While removing stale content is sometimes necessary, Google recommends taking an intentional, format-specific approach to tackling content decay.
Archiving vs. Transitional Guides
Google advises against immediately removing content that becomes obsolete, like materials referencing discontinued products or services.
Removing content too soon could confuse readers and lead to a poor experience, Sassman explains:
“So, if I’m trying to find out like what happened, I almost need that first thing to know. Like, “What happened to you?” And, otherwise, it feels almost like an error. Like, “Did I click a wrong link or they redirect to the wrong thing?””
Sassman says you can avoid confusion by providing transitional “explainer” pages during deprecation periods.
A temporary transition guide informs readers of the outdated content while steering them toward updated resources.
Sassman continues:
“That could be like an intermediary step where maybe you don’t do that forever, but you do it during the transition period where, for like six months, you have them go funnel them to the explanation, and then after that, all right, call it a day. Like enough people know about it. Enough time has passed. We can just redirect right to the thing and people aren’t as confused anymore.”
When To Update Vs. When To Write New Content
For reference guides and content that provide authoritative overviews, Google suggests updating information to maintain accuracy and relevance.
However, for archival purposes, major updates may warrant creating a new piece instead of editing the original.
Sassman explains:
“I still want to retain the original piece of content as it was, in case we need to look back or refer to it, and to change it or rehabilitate it into a new thing would almost be worth republishing as a new blog post if we had that much additional things to say about it.”
Remove Potentially Harmful Content
Google recommends removing pages in cases where the outdated information is potentially harmful.
Sassman says she arrived at this conclusion when deciding what to do with a guide involving obsolete structured data:
“I think something that we deleted recently was the “How to Structure Data” documentation page, which I thought we should just get rid of it… it almost felt like that’s going to be more confusing to leave it up for a period of time.
And actually it would be negative if people are still adding markup, thinking they’re going to get something. So what we ended up doing was just delete the page and redirect to the changelog entry so that, if people clicked “How To Structure Data” still, if there was a link somewhere, they could still find out what happened to that feature.”
Internal Auditing Processes
To keep your content current, Google advises implementing a system for auditing aging content and flagging it for review.
Sassman says she sets automated alerts for pages that haven’t been checked in set periods:
“Oh, so we have a little robot to come and remind us, “Hey, you should come investigate this documentation page. It’s been x amount of time. Please come and look at it again to make sure that all of your links are still up to date, that it’s still fresh.””
Context Is Key
Google’s tips for dealing with content decay center around understanding the context of outdated materials.
You want to prevent visitors from stumbling across obsolete pages without clarity.
Additional Google-recommended tactics include:
- Prominent banners or notices clarifying a page’s dated nature
- Listing original publish dates
- Providing inline annotations explaining how older references or screenshots may be obsolete
How This Can Help You
Following Google’s recommendations for tackling content decay can benefit you in several ways:
- Improved user experience: By providing clear explanations, transition guides, and redirects, you can ensure that visitors don’t encounter confusing or broken pages.
- Maintained trust and credibility: Removing potentially harmful or inaccurate content and keeping your information up-to-date demonstrates your commitment to providing reliable and trustworthy resources.
- Better SEO: Regularly auditing and updating your pages can benefit your website’s search rankings and visibility.
- Archival purposes: By creating new content instead of editing older pieces, you can maintain a historical record of your website’s evolution.
- Streamlined content management: Implementing internal auditing processes makes it easier to identify and address outdated or problematic pages.
By proactively tackling content decay, you can keep your website a valuable resource, improve SEO, and maintain an organized content library.
Listen to the full episode of Google’s podcast below:
Featured Image: Stokkete/Shutterstock
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoHow the TikTok Algorithm Works in 2024 (+9 Ways to Go Viral)
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoA Recap of Everything Marketers & Advertisers Need to Know
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoBlog Post Checklist: Check All Prior to Hitting “Publish”
-

 SEO4 days ago
SEO4 days agoHow to Use Keywords for SEO: The Complete Beginner’s Guide
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoHow To Protect Your People and Brand
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Started Enforcing The Site Reputation Abuse Policy
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoHow to Craft Compelling Google Ads for eCommerce
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoElevating Women in SEO for a More Inclusive Industry













You must be logged in to post a comment Login