SEO
12 Essential On-Page SEO Factors You Need To Know

Did you ever play Tetris? If so, you probably remember how there was no real way to “beat” the game. It basically just got faster and faster with every level.
In some ways, search engine optimization (SEO) is the same.
Not in that it has a catchy 8-bit soundtrack or that it rewrites your dreams, but in that, it never ends.
There’s no point at which you can sit back and relax, content that your site is at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs) once and for all.
Sure, you might have reached the pinnacle today, but an SEO pro’s work is never done.
Every change to Google’s algorithm or competitor content could knock you off that top spot, which means you have to keep up with changes.
And that means your on-page SEO needs to be on point. But before we dive into that, it’s important to have a high-level overview of how Google and other search engines work.
Search Engine Basics
Search engines send out crawlers, or spiders, to explore the internet. They follow links from one site to another, building a map of the content called a search index.
In the process of exploring sites, these crawlers are also evaluating their content, determining what kind of information it contains.
This data is then used by the search engine’s algorithm to determine how well the content of that specific site answers queries from users.
The better it answers the query, the more highly it will be ranked on the SERP.
In Google’s never-ending quest to provide better results to users, its algorithm is updated frequently. This inevitably leads to changes in rankings, which then requires someone to optimize the website to improve or ensure rankings.
What Is On-Page SEO & Why Is It Important?
On-page SEO, which is sometimes called on-site SEO, is the process of tweaking a page’s content, tags, and internal links to improve search visibility and increase traffic.
In other words, it’s a means of optimizing your website to help search engines better understand your website.
And this, of course, comes with a whole host of benefits.
The first is in the amount of traffic.
The first five organic results on a search page get 67.60% of all clicks. The next five account for only 3.73%. And it drops from there. So, if you want to get traffic, you need to be near the top.
Secondly, high-ranking sites have much better click-through rates (CTR). The first Google mobile search result has an average organic CTR of 26.9%.
Now consider that 92.4% of internet users who search on their mobile phones for something nearby visit that business the same day and you can start to see the impact organic SEO can have on your bottom line. And on-page optimization is an important factor in your organic ranking.
Hopefully, by this point, you’ve grasped the importance of on-page SEO. Now it’s time to get started. Let’s dive right in…
12 Essential On-Page SEO Factors
On-page SEO can be broadly divided into three categories: content, HTML, and website architecture. We’ll look at each individually.
Content
You’ve heard it before: Content is king.
SEO without it is like a beautiful new sports car without an engine – it might look nice, but it’s going nowhere. But, not all content is not created equal.
Here are the content factors you need to consider to maximize your on-site SEO:
1. E-A-T
One way Google weights your site is based on E-A-T, or expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
In 175 pages of Google Search Quality Guidelines, it’s mentioned 135 times, which should be an indication of the role it plays in the search engine’s algorithms.
While Google has only confirmed a few elements of E-A-T (PageRank and links), it’s generally accepted in the SEO field that on-page signals play a big part in its evaluations.
For a deeper dive on E-A-T, read this piece.
2. Keywords
The most basic way to tell them your website’s content answers a user’s question is in the language you use.
Pages that feature the keywords used in a query, whether in the body, headings, or both, are more likely to be relevant to the search.
Sometimes this is easy to determine. If you’re optimizing the website of a furniture store, you’re probably going to want to include keywords like [sofa], [dining room set], and [end table].
If it’s a specialized furniture store, you’ll want to make sure you’re including long-tail keywords like [contemporary art-deco sideboards].
In short, you need to know what your target customers are searching for and create content that includes these terms. It’s always a good idea to do research, so you’re not missing any opportunities.
Get started by downloading our ebook on keyword research.
3. SEO Writing
Creating the type of content that both prioritizes search engines and converts human visitors to your site is something of an art.
Unless you’ve done it before, it can be quite challenging to write copy that reads well and still adheres to SEO best practices.
We have an entire piece dedicated to helping you master the art, but some of the key takeaways include:
- Emphasize readability: Your content should be easily scannable, so users can quickly find the information they’re looking for.
- Don’t overuse keywords: Also known as keyword stuffing, this technique was used in the past by unscrupulous SEO professionals to game the system, Google takes a dim view of sites that overuse keywords. If you’re caught doing this, your page could be demoted in SERPs or even removed altogether.
- Keep sentences and paragraphs brief: If you’ve ever clicked on a webpage only to be assaulted by an unbroken wall of text, you know how hard it is to read lengthy pieces of copy. Avoid driving users away by keeping your sentences and paragraphs short.
- Use subheadings: Subheads stand out because of their size, attracting attention from people who are scanning your page. Use an ample amount in your content to guide readers down the page.
- Use bulleted lists: This may feel very meta, but bulleted lists are a good way to break information down into easily digestible chunks. Use them whenever they make sense.
4. Visual Assets
Using images, videos, and infographics do more than making your page visually interesting to visitors. It also gives you opportunities to boost your SEO.
More than 36% of consumers use visual search when they’re doing online shopping, which means if you’re not using images, you’re missing out on traffic.
Make sure you’re optimizing your accompanying text whenever possible.
Be aware of your image file sizes to prevent slow loading. Make your images shareable to identify opportunities for backlinking, which can help boost your E-A-T.
HTML
HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the code used to structure your webpages and their content.
They tell the user’s browser what to show and where to show it. And it tells search engines what your page is all about and where they should rank you.
Here are the on-page SEO HTML factors you need to consider:
5. Title Tags
This is one of those areas where it’s important to focus on the details.
On its own, this snippet of code that allows you to give a webpage a title probably isn’t going to have you shooting up SERP rankings.
But in context with other on-page elements (like the ones discussed here), it can help you build context and demonstrate your site’s relevancy.
For a more thorough look at how to optimize your title tags, read this.
6. Meta Description
Right now, a veteran SEO professional is throwing up her hands at the screen. “Oh, come on,” she’s saying, “Everyone knows meta descriptions aren’t an SEO ranking factor.”
She’s only partly right. While it’s true there is a lot of evidence against meta descriptions as a ranking factor, she’s wrong about everyone knowing that.
And don’t let negative Nancy here dissuade you from adding them to your site.
Despite their relative lack of use in SEO, they do offer two key benefits: They can help Google understand what your web page is all about, and more importantly, they have an outsized influence on your CTRs.
Better meta descriptions give searchers a better understanding of what your page is all about, which in turn leads to more clickthroughs. So, don’t neglect them.
7. Image Optimization
We already briefly touched on the importance of visual assets on your page, but now it’s time to look more closely at their technical aspects.
Here are some tips to help optimize yours:
- Include SEO-friendly alt tags.
- Choose the right format and file size for fast loading.
- Customize file names instead of using something like IMG_08759.
- Ensure your images are mobile-friendly.
Once again, we have an excellent resource for more in-depth information on HTML image optimization. Read it here.
8. Geotagging (For Local Search)
It may be a global economy, but most business is still done at a local level. Connect with the people in your neighborhood by optimizing your on-page local SEO.
While this is less important for mega-corporations like GMC or Pepsi, for small- and medium-sized businesses, this is their bread and butter.
There are three main SEO tactics to consider when focusing on local traffic:
- Optimizing local listings and citations including name, address, and phone number (NAP), website URL, and business descriptions, using third-party apps, and getting reviews.
- Optimizing your local content, including accommodating for “near me” searches, providing location-based content, or buying a local website or blog.
- Optimizing and building links with other local businesses and organizations.
Be sure to include the name of your target location in your keywords and put them in your content wherever they fit.
For more information on building your own geotagging SEO strategy, read this.
Website Architecture
Having a well-structured website is important for two reasons: First, a website laid out in a logical manner will be crawled more effectively by search engines, and secondly, it will create richer user experiences.
Here are the factors to consider when optimizing your site’s architecture:
9. Site Speed
A clunky, slow-loading site does more than frustrate and drive away visitors – it actually hurts your search ranking too.
Search Engine Journal took a deep dive into the effect a page’s loading time has on SEO and confirmed page speed is a ranking factor in search results.
However, what minimum speed your site needs to meet is constantly changing.
It can currently be met by meeting Google’s Core Web Vitals minimum threshold. If your site isn’t currently meeting these standards, there are several steps you can take, including:
- Enabling compression.
- Reducing redirects.
- Optimizing images.
- Leveraging browser caches.
10. Responsive Design
In 2016, mobile search volume surpassed desktop for the very first time. And in the years following, that number has only grown.
Mobile now accounts for more than 56% of all internet usage, with tablets contributing another 2.4%.
Because more users are on mobile devices, Google followed the logical path and began to prioritize sites with responsive designs in mobile search rankings.
This mobile-friendly update only impacts search results performed on mobile devices, and while it’s still possible to rank in these results without responsive design, Google strongly recommends sites have a mobile version.
You can read more about the affect site responsiveness has on search results here.
11. URL Structure
There was a time when URLs played a large role in SEO. Professionals would make sure their keywords were included in web addresses to help them rank higher.
But Google, doing what Google does, changed the algorithm. And what was once so important to rankings, now plays a much smaller role.
That’s not to say it doesn’t matter. Search engines are still including your URLs in your overall score – they just don’t hold the same prominence they once did.
However, there is evidence they play a role in a site’s initial ranking, and some professionals believe they’re used to group pages. What this means is, that while they shouldn’t be your top SEO priority, you don’t want to ignore them either.
Read more about how URLs factor into Google rankings here.
12. Links
Remember E-A-T from way back at the beginning of this article?
One of the best ways your website can establish expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness is through links from other reputable websites.
Think of it this way: Who would you rather trust your 401(k) to – a financial advisor who manages Warren Buffet’s portfolio or your cousin Jimmy, who lives in your aunt’s basement? Jimmy might do a fine job; he could potentially even outperform Buffet’s guy. But he just doesn’t have the credibility that comes with a strong co-sign.
Links work in the same way.
There are three main types you need to know about for SEO:
- Internal links – or ones that direct to another page on your website like this one.
- Outbound links – also known as external links, these are the links that point to a site on a different domain, like this one pointing to Google’s SEO page.
- Inbound links – sometimes called backlinks, these are links from other websites pointing to your page.
Of the three, inbound links are by far the most important. They provide the biggest SEO benefit, but they’re also the hardest to obtain.
There are a variety of methods SEO professionals use to generate quality incoming links, including using social media, creating sharable infographics, and even just asking for backlinks.
But beware: Not all inbound links are helpful. Some, especially those coming from link farms, forum posts, and guestbooks, can be fake links intended to cheat the rankings system. If you don’t disavow these, it can hurt your ranking.
Here’s information on how and when you should disavow links.
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
We’ve talked a lot about on-page SEO, but there’s also something known as off-page SEO. The difference, as you could probably tell by the names, is where it happens.
On-page SEO is everything you can do internally to boost your rankings, including keyword optimization, meta descriptions, title tags, alt text, and website structure.
Off-page SEO is all the things that happen externally that impact your site’s rankings. This includes backlinks, E-A-T, local SEO, social media mentions, and pay-per-click.
Obviously, you have a lot more control over your on-page SEO, but it’s important to keep off-page SEO in mind as well – you need both to get where you want to go.
But, you should first focus on building a good, relevant webpage that’s fully optimized for search engines before you begin sinking a lot of resources into building links and promoting your site.
On-Page SEO Is An Ongoing Process
At the end of the day, search engine optimization boils down to one thing: Finding the best way to provide valuable information to searchers, and ensuring your website is at the top of SERPs.
Your goal is to provide richer experiences to users, while simultaneously demonstrating your value to search engines. Luckily, these two go hand-in-hand. And they start with on-page optimization.
Start with what you can control, carefully evaluating your current site for weaknesses and opportunities for growth.
Get all your on-site ducks in a row and you’ll start to see results – including an organic improvement in off-site factors.
Just remember, SEO, like Tetris, is never done. But keep reading and keep working, and you’ll get the results you deserve.
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal
SEO
Why Google Can’t Tell You About Every Ranking Drop

In a recent Twitter exchange, Google’s Search Liaison, Danny Sullivan, provided insight into how the search engine handles algorithmic spam actions and ranking drops.
The discussion was sparked by a website owner’s complaint about a significant traffic loss and the inability to request a manual review.
Sullivan clarified that a site could be affected by an algorithmic spam action or simply not ranking well due to other factors.
He emphasized that many sites experiencing ranking drops mistakenly attribute it to an algorithmic spam action when that may not be the case.
“I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a algorithmic spam action against them, but they don’t. “
Sullivan’s full statement will help you understand Google’s transparency challenges.
Additionally, he explains why the desire for manual review to override automated rankings may be misguided.
Two different things. A site could have an algorithmic spam action. A site could be not ranking well because other systems that *are not about spam* just don’t see it as helpful.
I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a…
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) May 13, 2024
Challenges In Transparency & Manual Intervention
Sullivan acknowledged the idea of providing more transparency in Search Console, potentially notifying site owners of algorithmic actions similar to manual actions.
However, he highlighted two key challenges:
- Revealing algorithmic spam indicators could allow bad actors to game the system.
- Algorithmic actions are not site-specific and cannot be manually lifted.
Sullivan expressed sympathy for the frustration of not knowing the cause of a traffic drop and the inability to communicate with someone about it.
However, he cautioned against the desire for a manual intervention to override the automated systems’ rankings.
Sullivan states:
“…you don’t really want to think “Oh, I just wish I had a manual action, that would be so much easier.” You really don’t want your individual site coming the attention of our spam analysts. First, it’s not like manual actions are somehow instantly processed. Second, it’s just something we know about a site going forward, especially if it says it has change but hasn’t really.”
Determining Content Helpfulness & Reliability
Moving beyond spam, Sullivan discussed various systems that assess the helpfulness, usefulness, and reliability of individual content and sites.
He acknowledged that these systems are imperfect and some high-quality sites may not be recognized as well as they should be.
“Some of them ranking really well. But they’ve moved down a bit in small positions enough that the traffic drop is notable. They assume they have fundamental issues but don’t, really — which is why we added a whole section about this to our debugging traffic drops page.”
Sullivan revealed ongoing discussions about providing more indicators in Search Console to help creators understand their content’s performance.
“Another thing I’ve been discussing, and I’m not alone in this, is could we do more in Search Console to show some of these indicators. This is all challenging similar to all the stuff I said about spam, about how not wanting to let the systems get gamed, and also how there’s then no button we would push that’s like “actually more useful than our automated systems think — rank it better!” But maybe there’s a way we can find to share more, in a way that helps everyone and coupled with better guidance, would help creators.”
Advocacy For Small Publishers & Positive Progress
In response to a suggestion from Brandon Saltalamacchia, founder of RetroDodo, about manually reviewing “good” sites and providing guidance, Sullivan shared his thoughts on potential solutions.
He mentioned exploring ideas such as self-declaration through structured data for small publishers and learning from that information to make positive changes.
“I have some thoughts I’ve been exploring and proposing on what we might do with small publishers and self-declaring with structured data and how we might learn from that and use that in various ways. Which is getting way ahead of myself and the usual no promises but yes, I think and hope for ways to move ahead more positively.”
Sullivan said he can’t make promises or implement changes overnight, but he expressed hope for finding ways to move forward positively.
Featured Image: Tero Vesalainen/Shutterstock
SEO
56 Google Search Statistics to Bookmark for 2024

If you’re curious about the state of Google search in 2024, look no further.
Each year we pick, vet, and categorize a list of up-to-date statistics to give you insights from trusted sources on Google search trends.
Check out more resources on how Google works:
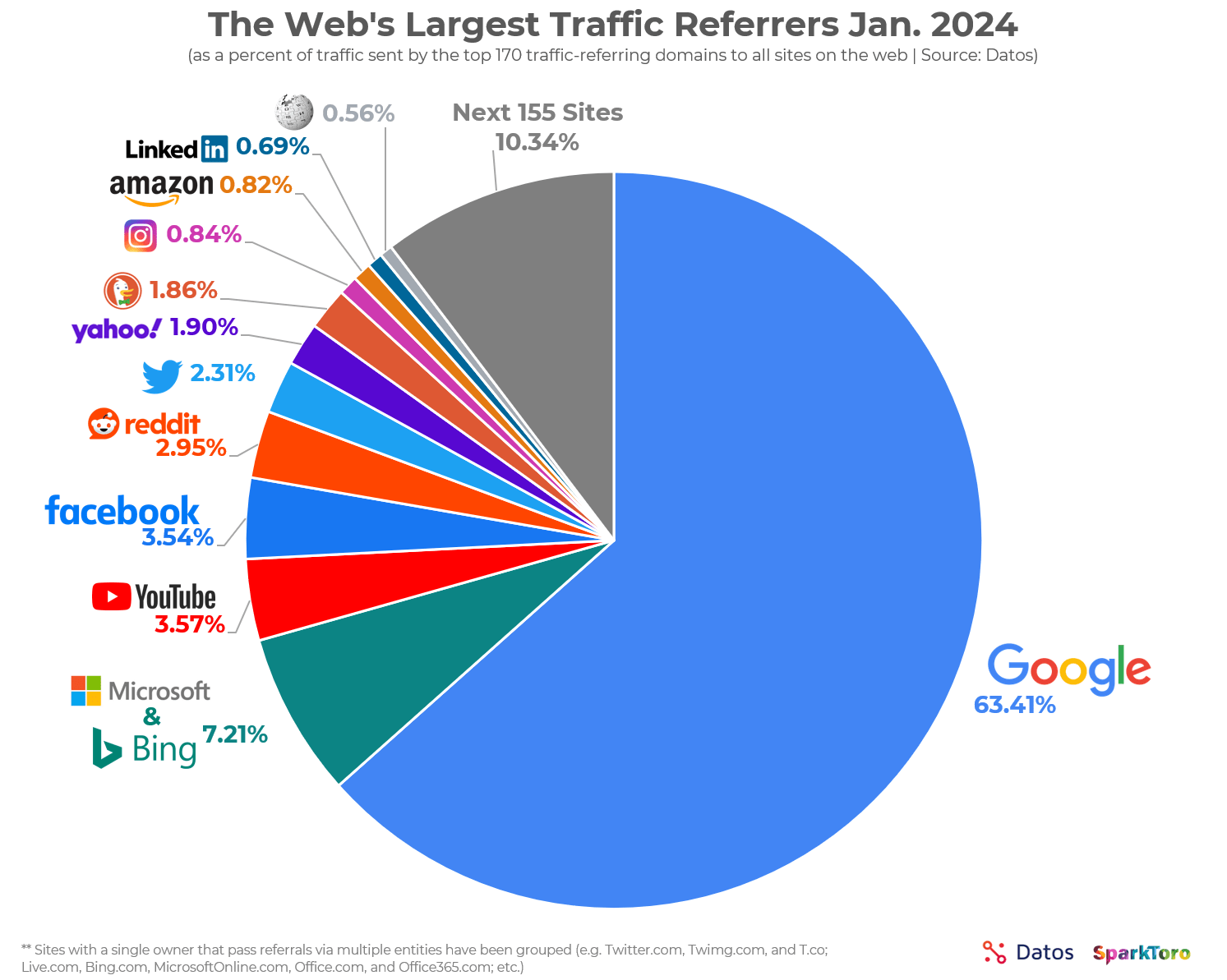

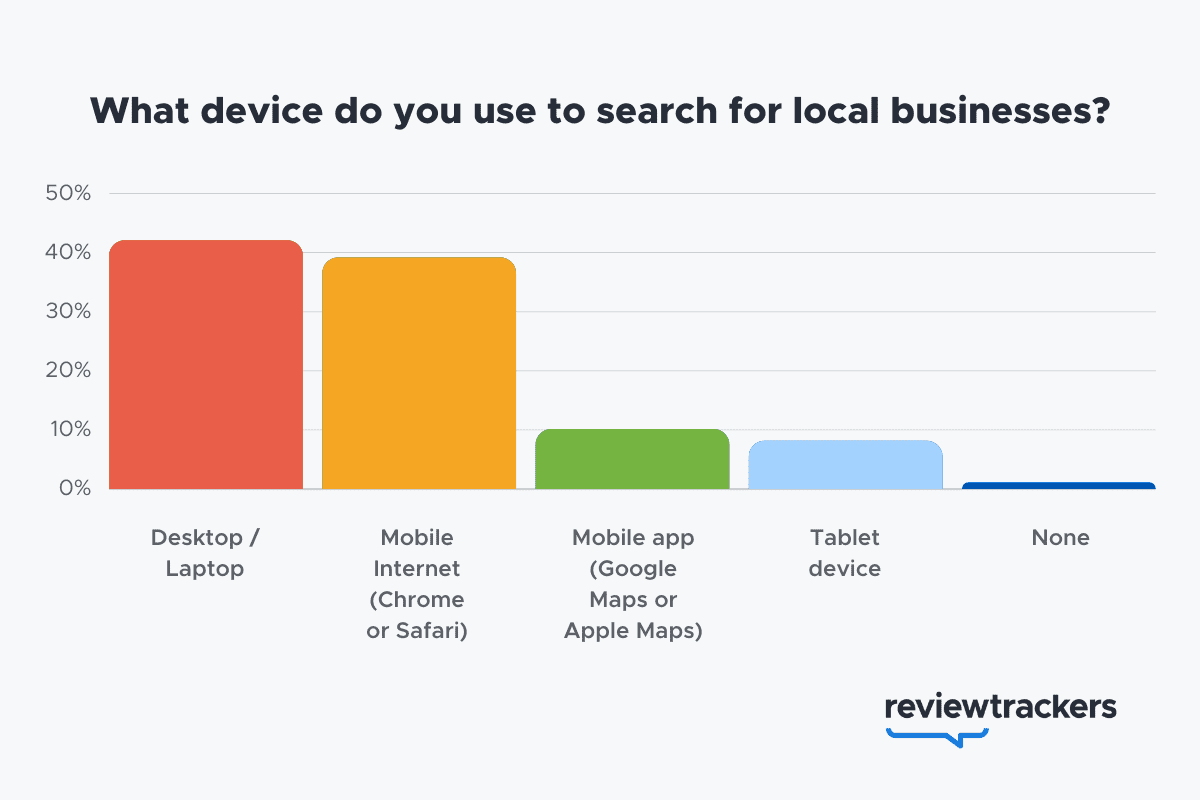

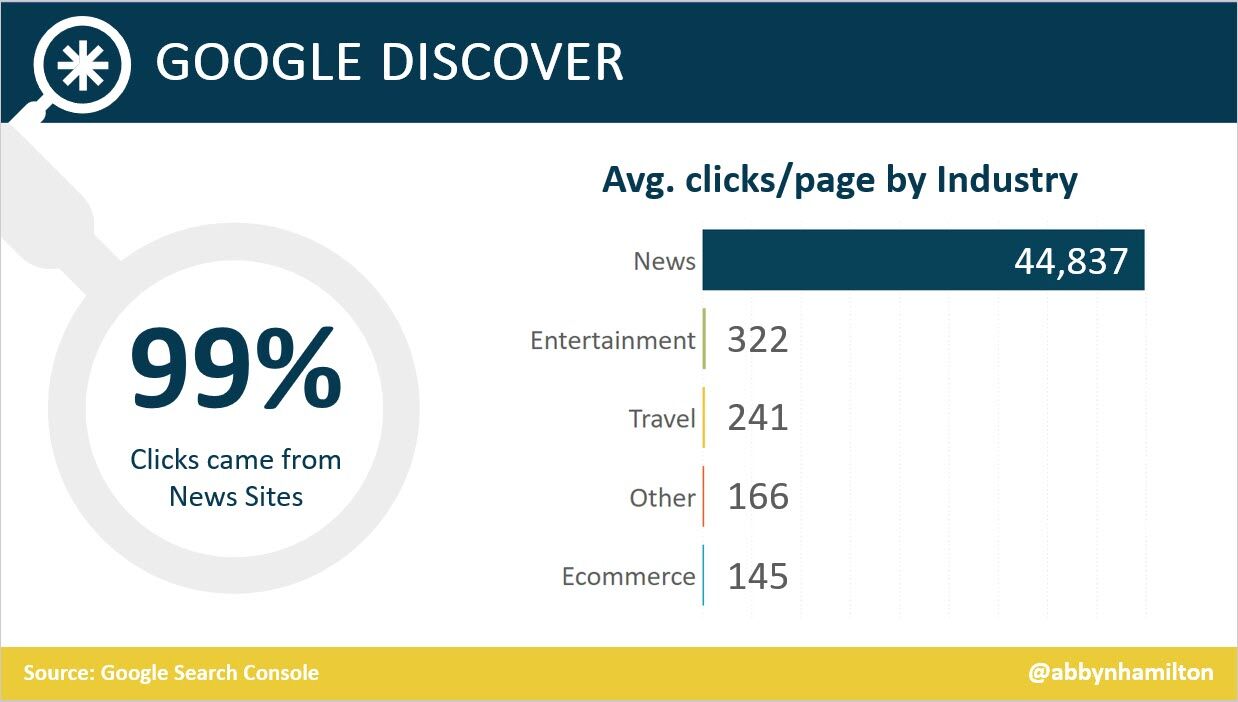

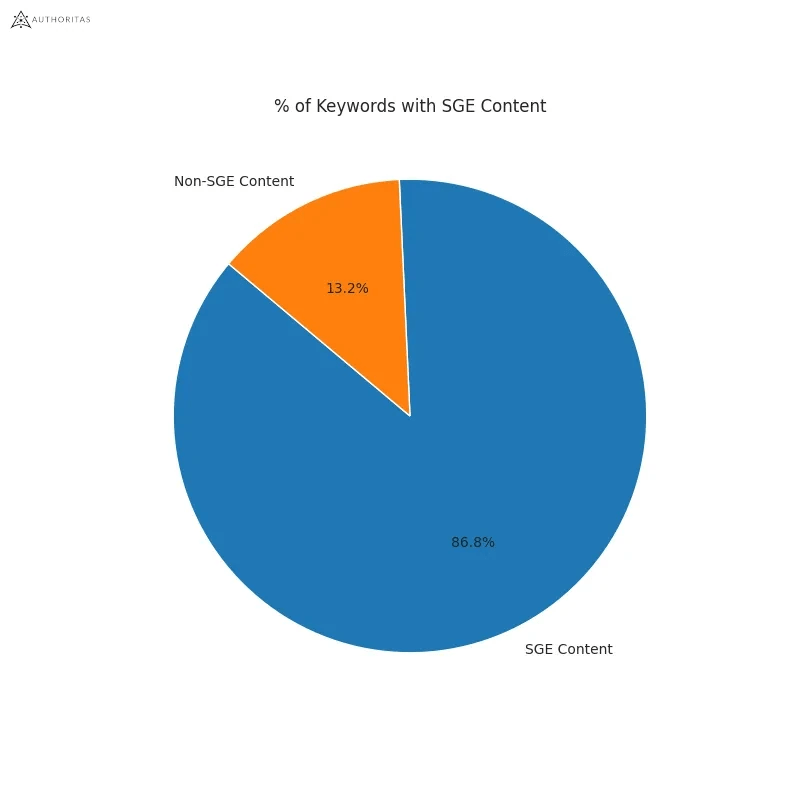

Learn more
SEO
How To Use ChatGPT For Keyword Research

Anyone not using ChatGPT for keyword research is missing a trick.
You can save time and understand an entire topic in seconds instead of hours.
In this article, I outline my most effective ChatGPT prompts for keyword research and teach you how I put them together so that you, too, can take, edit, and enhance them even further.
But before we jump into the prompts, I want to emphasize that you shouldn’t replace keyword research tools or disregard traditional keyword research methods.
ChatGPT can make mistakes. It can even create new keywords if you give it the right prompt. For example, I asked it to provide me with a unique keyword for the topic “SEO” that had never been searched before.
“Interstellar Internet SEO: Optimizing content for the theoretical concept of an interstellar internet, considering the challenges of space-time and interplanetary communication delays.”
Although I want to jump into my LinkedIn profile and update my title to “Interstellar Internet SEO Consultant,” unfortunately, no one has searched that (and they probably never will)!
You must not blindly rely on the data you get back from ChatGPT.
What you can rely on ChatGPT for is the topic ideation stage of keyword research and inspiration.
ChatGPT is a large language model trained with massive amounts of data to accurately predict what word will come next in a sentence. However, it does not know how to do keyword research yet.
Instead, think of ChatGPT as having an expert on any topic armed with the information if you ask it the right question.
In this guide, that is exactly what I aim to teach you how to do – the most essential prompts you need to know when performing topical keyword research.
Best ChatGPT Keyword Research Prompts
The following ChatGPT keyword research prompts can be used on any niche, even a topic to which you are brand new.
For this demonstration, let’s use the topic of “SEO” to demonstrate these prompts.
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Topic
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Topic}?
The first prompt is to give you an idea of the niche.
As shown above, ChatGPT did a great job understanding and breaking down SEO into three pillars: on-page, off-page & technical.
The key to the following prompt is to take one of the topics ChatGPT has given and query the sub-topics.
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Sub-topic}?
For this example, let’s query, “What are the most popular sub-topics related to keyword research?”
Having done keyword research for over 10 years, I would expect it to output information related to keyword research metrics, the types of keywords, and intent.
Let’s see.
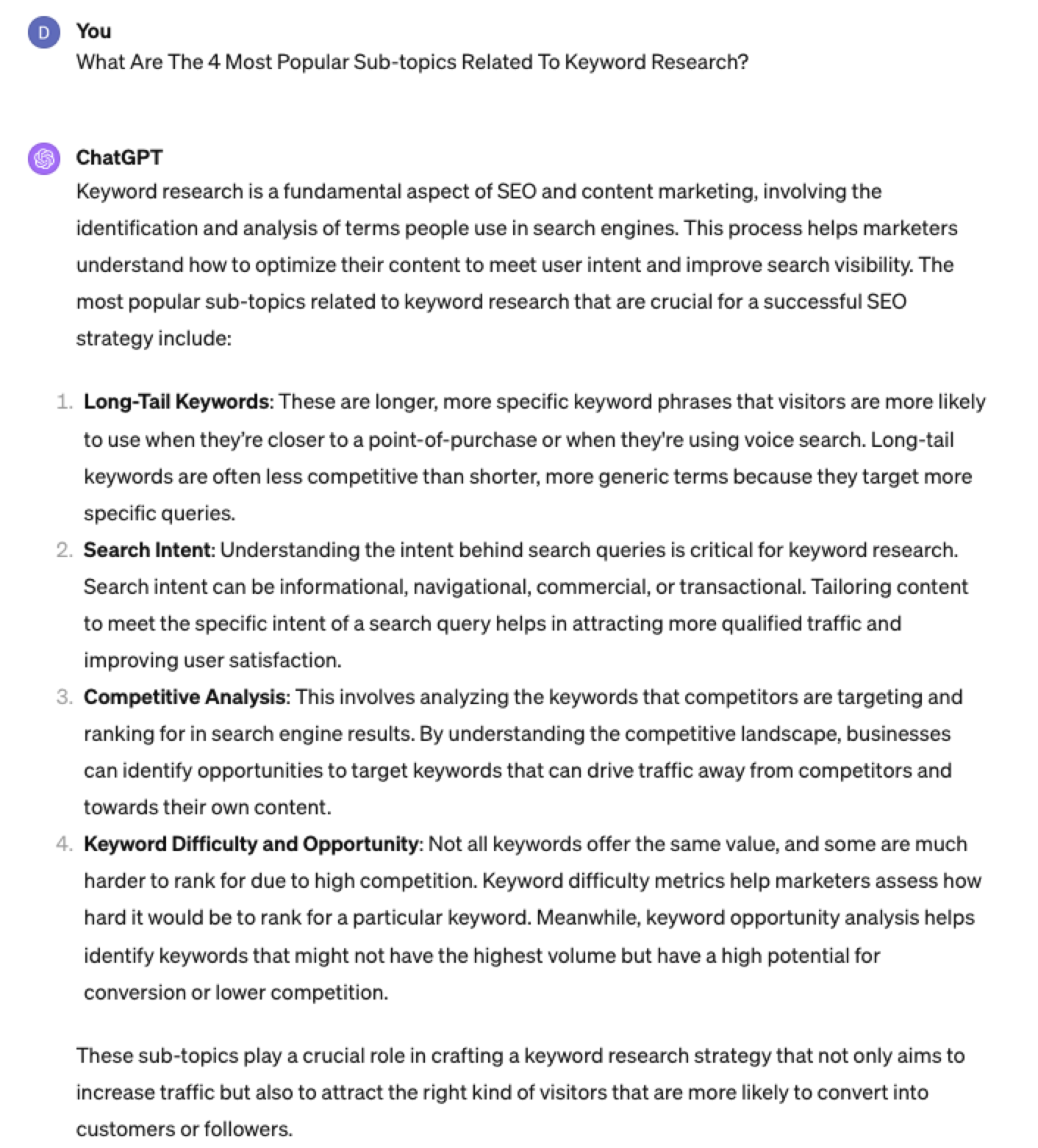 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, right on the money.
To get the keywords you want without having ChatGPT describe each answer, use the prompt “list without description.”
Here is an example of that.
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Keywords For The Topic Of {X}
You can even branch these keywords out further into their long-tail.
Example prompt:
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Long-tail Keywords For The Topic “{X}”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024List Without Description The Top Semantically Related Keywords And Entities For The Topic {X}
You can even ask ChatGPT what any topic’s semantically related keywords and entities are!
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: The Onion Method Of Prompting ChatGPT
When you are happy with a series of prompts, add them all to one prompt. For example, so far in this article, we have asked ChatGPT the following:
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to SEO?
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to keyword research
- List without description the top five most popular keywords for “keyword intent”?
- List without description the top five most popular long-tail keywords for the topic “keyword intent types”?
- List without description the top semantically related keywords and entities for the topic “types of keyword intent in SEO.”
Combine all five into one prompt by telling ChatGPT to perform a series of steps. Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4, and Step 5”
Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4 and Step 5. Step 1 – Generate an answer for the 3 most popular sub-topics related to {Topic}?. Step 2 – Generate 3 of the most popular sub-topics related to each answer. Step 3 – Take those answers and list without description their top 3 most popular keywords. Step 4 – For the answers given of their most popular keywords, provide 3 long-tail keywords. Step 5 – for each long-tail keyword offered in the response, a list without descriptions 3 of their top semantically related keywords and entities.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Question
Taking the steps approach from above, we can get ChatGPT to help streamline getting keyword ideas based on a question. For example, let’s ask, “What is SEO?”
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, and Step 4. Step 1 Generate 10 questions about “{Question}”?. Step 2 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 3 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 4 – Based on the above Steps 1,2,3 suggest a final list of questions avoiding duplicates or semantically similar questions.”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On The Alphabet Soup Method
One of my favorite methods, manually, without even using a keyword research tool, is to generate keyword research ideas from Google autocomplete, going from A to Z.
-
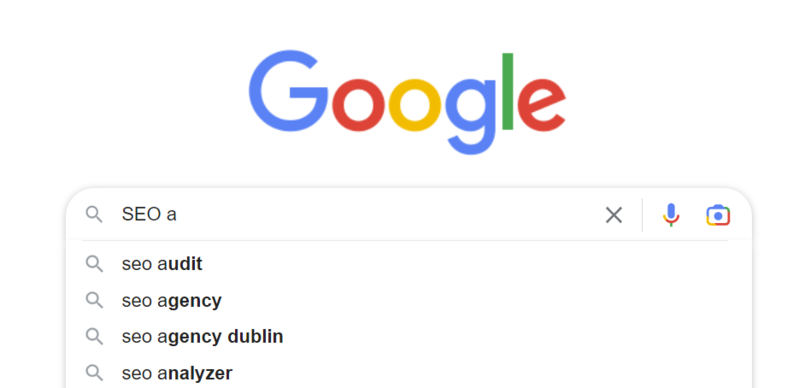 Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
You can also do this using ChatGPT.
Example prompt:
“give me popular keywords that includes the keyword “SEO”, and the next letter of the word starts with a”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: Using the onion prompting method above, we can combine all this in one prompt.
“Give me five popular keywords that include “SEO” in the word, and the following letter starts with a. Once the answer has been done, move on to giving five more popular keywords that include “SEO” for each letter of the alphabet b to z.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On User Personas
When it comes to keyword research, understanding user personas is essential for understanding your target audience and keeping your keyword research focused and targeted. ChatGPT may help you get an initial understanding of customer personas.
Example prompt:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of user personas”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024You could even go a step further and ask for questions based on those topics that those specific user personas may be searching for:
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024As well as get the keywords to target based on those questions:
“For each question listed above for each persona, list the keywords, as well as the long-tail keywords to target, and put them in a table”
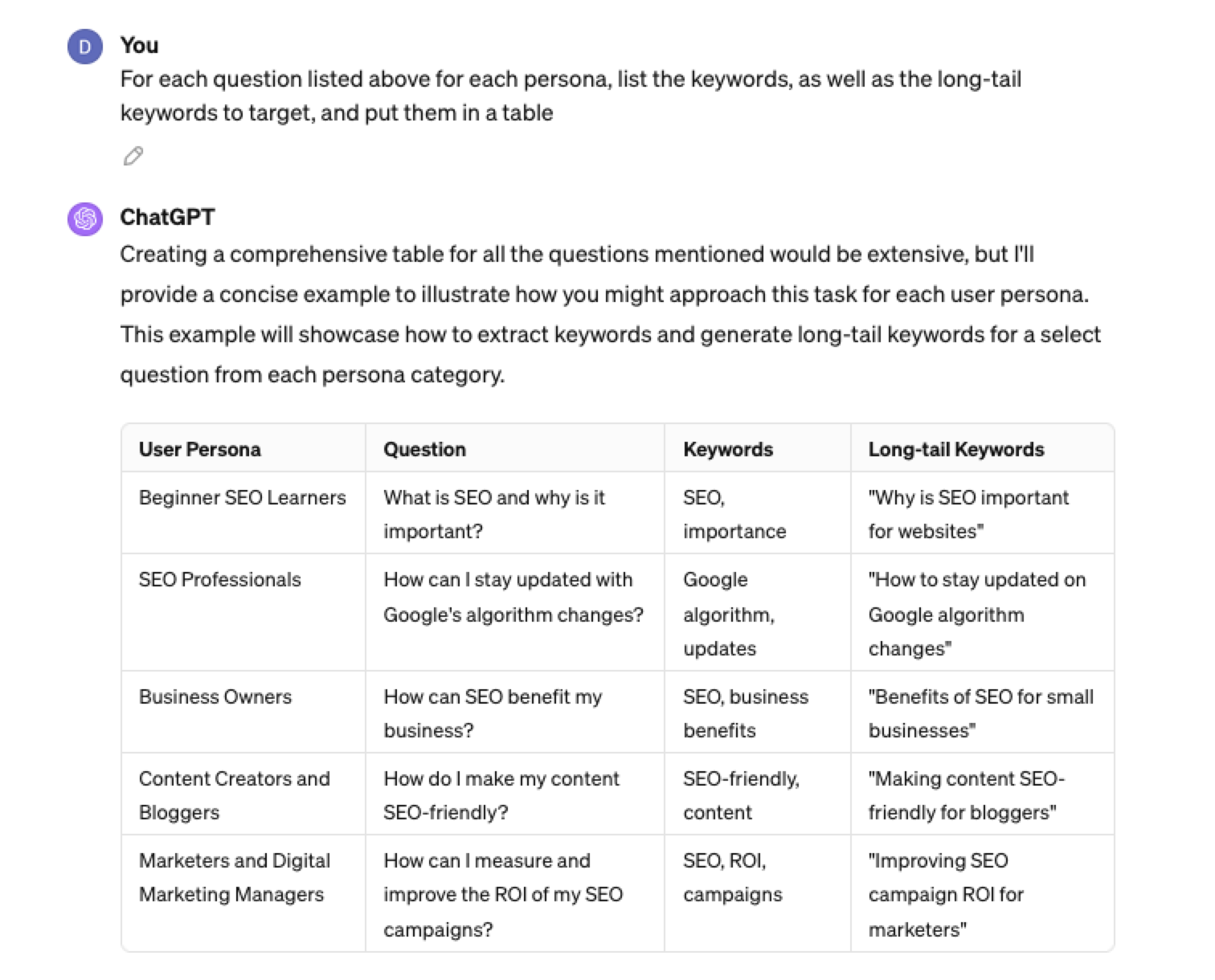 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On Searcher Intent And User Personas
Understanding the keywords your target persona may be searching is the first step to effective keyword research. The next step is to understand the search intent behind those keywords and which content format may work best.
For example, a business owner who is new to SEO or has just heard about it may be searching for “what is SEO.”
However, if they are further down the funnel and in the navigational stage, they may search for “top SEO firms.”
You can query ChatGPT to inspire you here based on any topic and your target user persona.
SEO Example:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of searcher intent that a {Target Persona} would be searching for”
ChatGPT For Keyword Research Admin
Here is how you can best use ChatGPT for keyword research admin tasks.
Using ChatGPT As A Keyword Categorization Tool
One of the use cases for using ChatGPT is for keyword categorization.
In the past, I would have had to devise spreadsheet formulas to categorize keywords or even spend hours filtering and manually categorizing keywords.
ChatGPT can be a great companion for running a short version of this for you.
Let’s say you have done keyword research in a keyword research tool, have a list of keywords, and want to categorize them.
You could use the following prompt:
“Filter the below list of keywords into categories, target persona, searcher intent, search volume and add information to a six-column table: List of keywords – [LIST OF KEYWORDS], Keyword Search Volume [SEARCH VOLUMES] and Keyword Difficulties [KEYWORD DIFFICUTIES].”
-
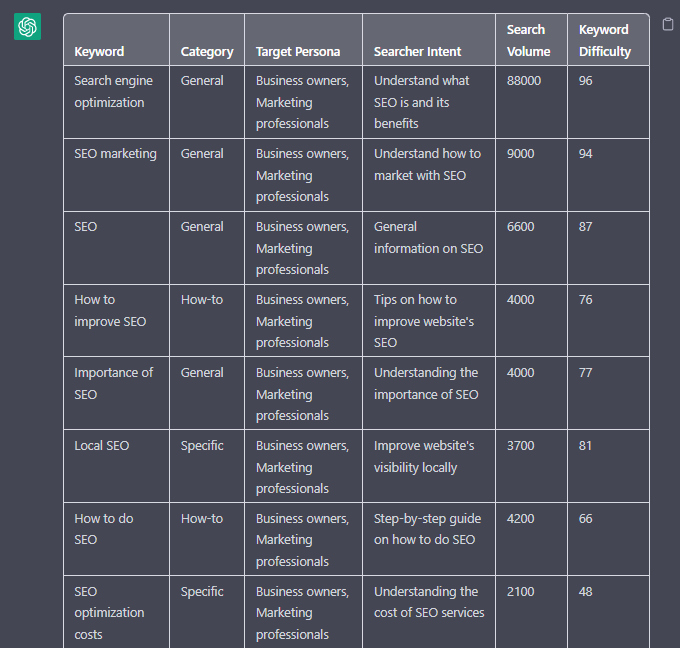 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Tip: Add keyword metrics from the keyword research tools, as using the search volumes that a ChatGPT prompt may give you will be wildly inaccurate at best.
Using ChatGPT For Keyword Clustering
Another of ChatGPT’s use cases for keyword research is to help you cluster. Many keywords have the same intent, and by grouping related keywords, you may find that one piece of content can often target multiple keywords at once.
However, be careful not to rely only on LLM data for clustering. What ChatGPT may cluster as a similar keyword, the SERP or the user may not agree with. But it is a good starting point.
The big downside of using ChatGPT for keyword clustering is actually the amount of keyword data you can cluster based on the memory limits.
So, you may find a keyword clustering tool or script that is better for large keyword clustering tasks. But for small amounts of keywords, ChatGPT is actually quite good.
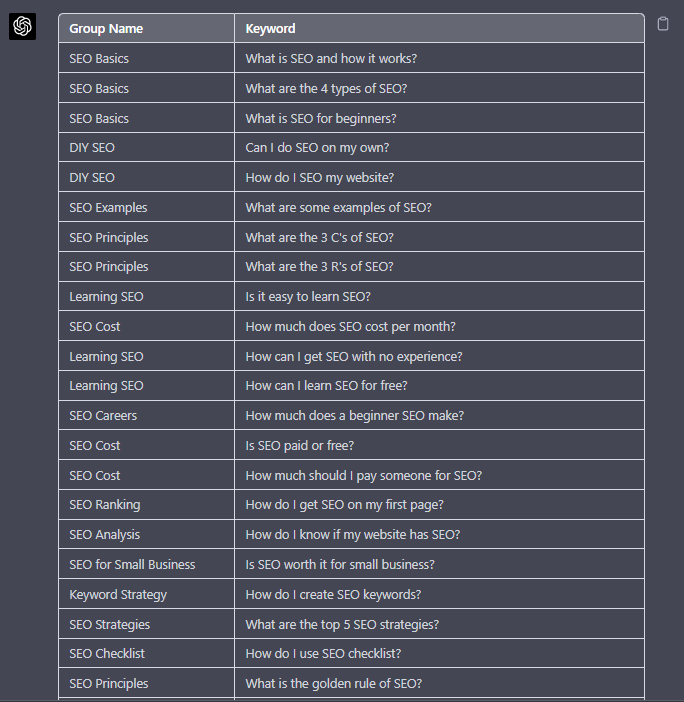
A great use small keyword clustering use case using ChatGPT is for grouping People Also Ask (PAA) questions.
Use the following prompt to group keywords based on their semantic relationships. For example:
“Organize the following keywords into groups based on their semantic relationships, and give a short name to each group: [LIST OF PAA], create a two-column table where each keyword sits on its own row.
-
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Using Chat GPT For Keyword Expansion By Patterns
One of my favorite methods of doing keyword research is pattern spotting.
Most seed keywords have a variable that can expand your target keywords.
Here are a few examples of patterns:
1. Question Patterns
(who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will)
“Generate [X] keywords for the topic “[Topic]” that contain any or all of the following “who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20242. Comparison Patterns
Example:
“Generate 50 keywords for the topic “{Topic}” that contain any or all of the following “for, vs, alternative, best, top, review”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20243. Brand Patterns
Another one of my favorite modifiers is a keyword by brand.
We are probably all familiar with the most popular SEO brands; however, if you aren’t, you could ask your AI friend to do the heavy lifting.
Example prompt:
“For the top {Topic} brands what are the top “vs” keywords”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20244. Search Intent Patterns
One of the most common search intent patterns is “best.”
When someone is searching for a “best {topic}” keyword, they are generally searching for a comprehensive list or guide that highlights the top options, products, or services within that specific topic, along with their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks, to make an informed decision.
Example:
“For the topic of “[Topic]” what are the 20 top keywords that include “best”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, this guide to keyword research using ChatGPT has emphasized the ease of generating keyword research ideas by utilizing ChatGPT throughout the process.
Keyword Research Using ChatGPT Vs. Keyword Research Tools
Free Vs. Paid Keyword Research Tools
Like keyword research tools, ChatGPT has free and paid options.
However, one of the most significant drawbacks of using ChatGPT for keyword research alone is the absence of SEO metrics to help you make smarter decisions.
To improve accuracy, you could take the results it gives you and verify them with your classic keyword research tool – or vice versa, as shown above, uploading accurate data into the tool and then prompting.
However, you must consider how long it takes to type and fine-tune your prompt to get your desired data versus using the filters within popular keyword research tools.
For example, if we use a popular keyword research tool using filters, you could have all of the “best” queries with all of their SEO metrics:
-
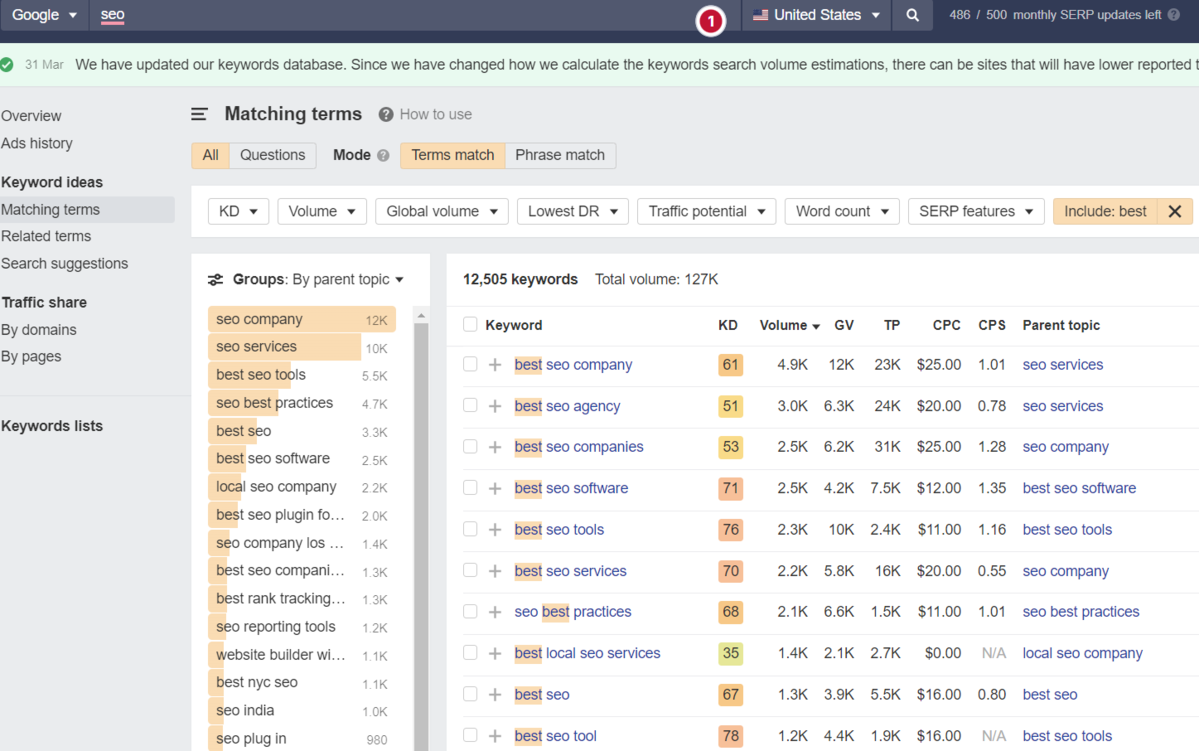 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
And unlike ChatGPT, generally, there is no token limit; you can extract several hundred, if not thousands, of keywords at a time.
As I have mentioned multiple times throughout this piece, you cannot blindly trust the data or SEO metrics it may attempt to provide you with.
The key is to validate the keyword research with a keyword research tool.
ChatGPT For International SEO Keyword Research
ChatGPT can be a terrific multilingual keyword research assistant.
For example, if you wanted to research keywords in a foreign language such as French. You could ask ChatGPT to translate your English keywords;
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024- The key is to take the data above and paste it into a popular keyword research tool to verify.
- As you can see below, many of the keyword translations for the English keywords do not have any search volume for direct translations in French.
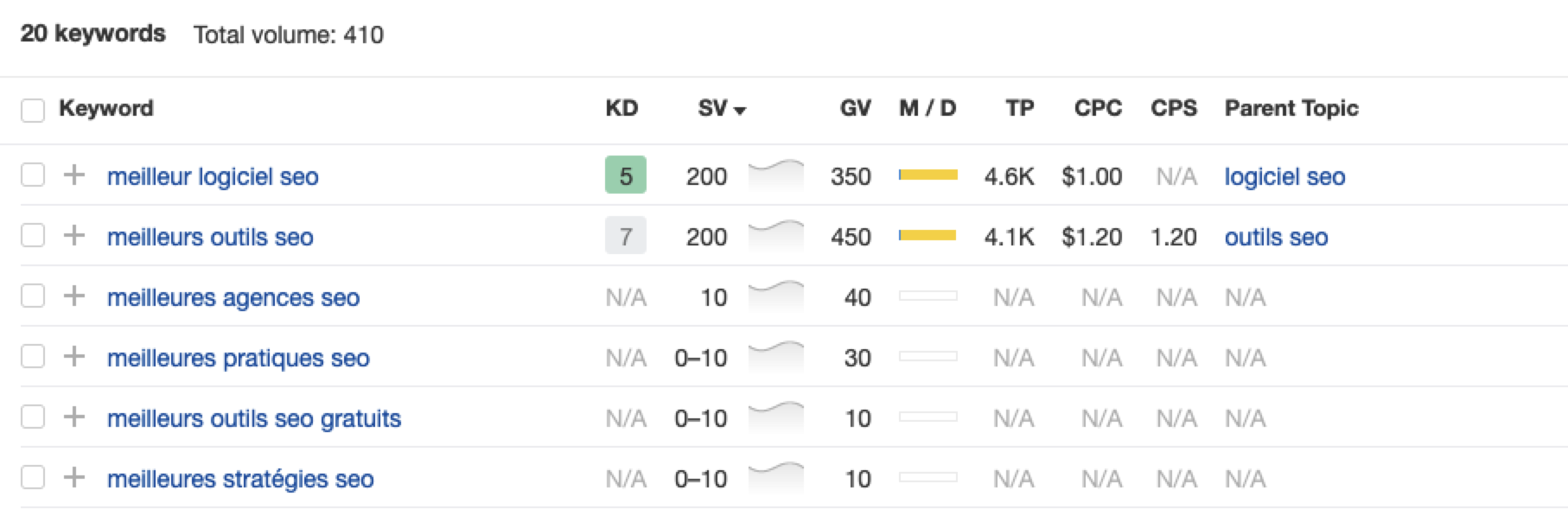 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024But don’t worry, there is a workaround: If you have access to a competitor keyword research tool, you can see what webpage is ranking for that query – and then identify the top keyword for that page based on the ChatGPT translated keywords that do have search volume.
-
-
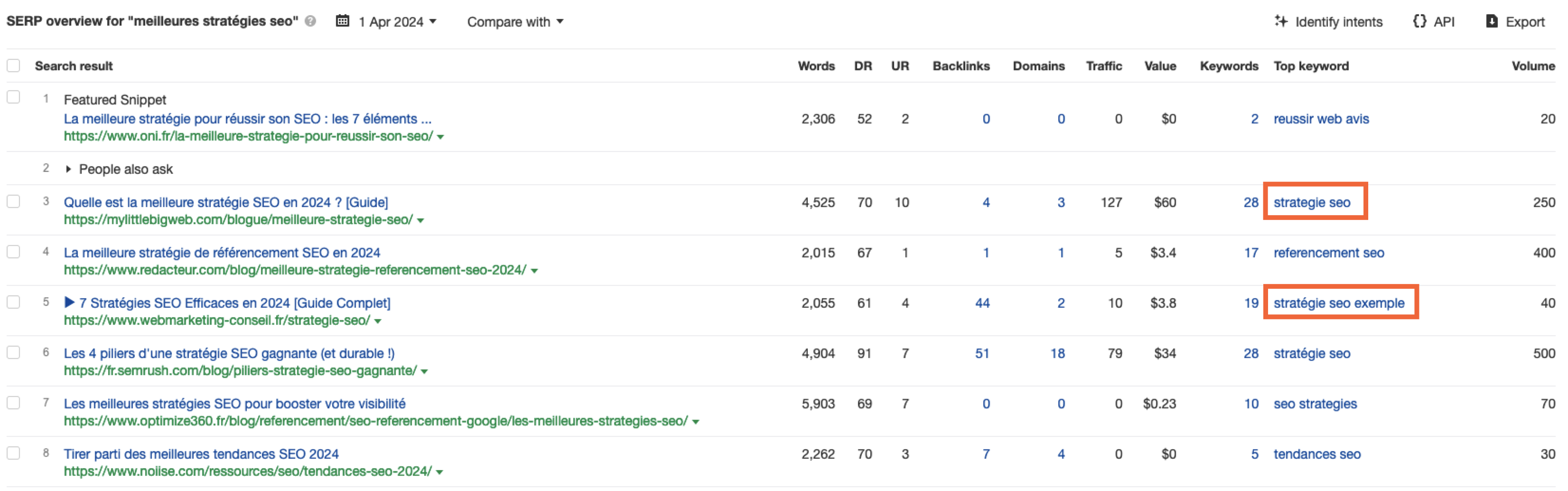 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Or, if you don’t have access to a paid keyword research tool, you could always take the top-performing result, extract the page copy, and then ask ChatGPT what the primary keyword for the page is.
Key Takeaway
-
ChatGPT can be an expert on any topic and an invaluable keyword research tool. However, it is another tool to add to your toolbox when doing keyword research; it does not replace traditional keyword research tools.
As shown throughout this tutorial, from making up keywords at the beginning to inaccuracies around data and translations, ChatGPT can make mistakes when used for keyword research.
You cannot blindly trust the data you get back from ChatGPT.
However, it can offer a shortcut to understanding any topic for which you need to do keyword research and, as a result, save you countless hours.
But the key is how you prompt.
The prompts I shared with you above will help you understand a topic in minutes instead of hours and allow you to better seed keywords using keyword research tools.
It can even replace mundane keyword clustering tasks that you used to do with formulas in spreadsheets or generate ideas based on keywords you give it.
Paired with traditional keyword research tools, ChatGPT for keyword research can be a powerful tool in your arsenal.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tatiana Shepeleva/Shutterstock
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoHow the TikTok Algorithm Works in 2024 (+9 Ways to Go Viral)
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoBlog Post Checklist: Check All Prior to Hitting “Publish”
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days agoHow to Use Keywords for SEO: The Complete Beginner’s Guide
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoHow To Protect Your People and Brand
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days agoHow to Craft Compelling Google Ads for eCommerce
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Started Enforcing The Site Reputation Abuse Policy
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoElevating Women in SEO for a More Inclusive Industry
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoHow to Brainstorm Business Ideas: 9 Fool-Proof Approaches















You must be logged in to post a comment Login