MARKETING
Storytelling: The Secret Sauce to Making More Sales With Email Marketing

Do businesses email their customers too often? According to a recent article on Business Insider, the answer is yes. But not for the reason you may think.
It’s not because customers loathe getting emails from companies. Or because frequent emails are considered spam. It’s actually because most brands nowadays email like this:
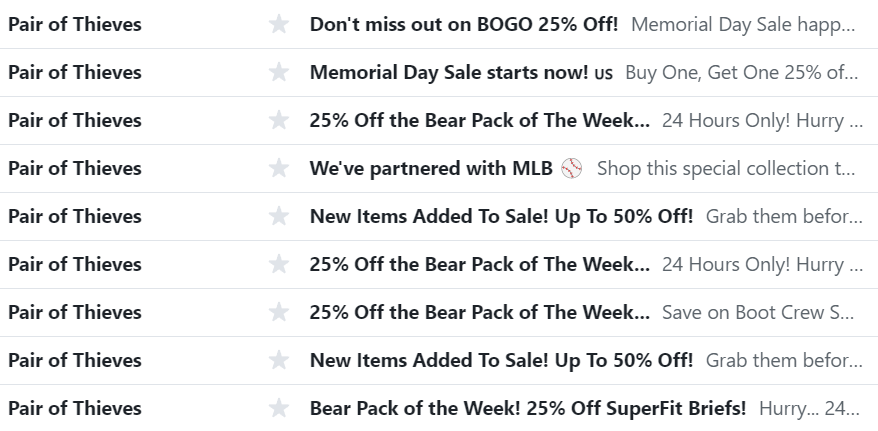
They use discounts as their main strategy to persuade customers to buy. But what happens when your customer’s whole inbox looks like the picture above? The inevitable: they stop paying attention to your emails.
Because here’s the thing.
Why would they open your emails if they can already predict the content inside? Why would they buy now when they can clearly see you’ve got discounts all the time? And, most importantly, why would they pick your brand over your competitors?
If you want to stand out in someone’s crowded inbox, you need to do the one thing that everybody else avoids doing: building strong relationships with your email subscribers. Here’s how:
Storytelling is the most effective way to communicate. That’s not me saying it. It’s the countless studies (such as this one, this one, and this one) that prove it, time and time again. Why?
Because storytelling helps you form positive emotional associations with you and your brand. The emotions you evoke with your stories go a long way in defining how people perceive you, creating a stronger connection in your audience’s mind between you and the problem you solve for them. But that’s only the tip of the iceberg.
The truth is, writing story-based emails makes you more than just a brand that sells a solution to their pain: it makes you an entertainer, too. And as a marketer, being able to entertain while selling is like having a superpower. People hate being sold to. But they love being entertained (ever binge-watched a Netflix show? I know I have).
Plus, with story-based emails, you can easily add more variability to your email calendar. As a result, customers will no longer be able to predict what your next email will be about: a fun story? A new product? Maybe even a discount? Curiosity translates to increased engagement. And increased engagement translates to stronger relationships with your customers.
So by choosing the right stories to tell in your emails (which we’ll discuss in a bit) and by writing them in an engaging way, you’re guaranteed to keep your audience hooked and excited to read your next email. As opposed to adding yet another sales email to their already crowded inbox.
1. Pick the Right Story
The storytelling approach will give you little to no results if the stories you’re telling are flat to begin with. No matter how engaging your writing is.
So the first thing you need to do is to make sure you select story ideas with potential. Okay, but where do you find these ideas? And what does a good story idea look like?
If you’re anything like me, your life isn’t that exciting or eventful. And yet, you may still have a funny conversation with your next-door neighbor. Or your team may geek out about wild adaptogen mushrooms at a team-building event. Or your spouse may accidentally spill coffee on your laptop (true story!).
Any of these can be turned into fun story-based emails that tell your audience a little bit more about who you (or your team) are as a person. Most business owners assume their customers don’t want to know what goes on in their personal and business life. But that couldn’t be farther from the truth.
In fact, customers want to know there are real people behind brand names. According to this report from Sprout Social, 70% of consumers report feeling more connected to a brand when its CEO is active on social media.
And depending on how much you’re willing to share about your life, you can then select the types of personal stories to write about. When in doubt, think about what you’d want to tell your friends/family at the dinner table. More often than not, that’d make a great story for your email list too.

2. Write a Strong Hook
Let’s face it.
Nowadays, attention spans are short. And no matter how good your story is, if how you write it isn’t engaging enough, your email subscribers aren’t going to read it.
So the very first thing you want to do is to make sure the first three sentences of your story hook the reader into the action. Once someone reads that much into a story, it’s incredibly difficult for them to stop.
So how do you do it? Any of these hooks have proven to work again and again whenever I write stories for myself or my clients:
- Start in the middle of the action (and explain the context later). For example:
“RUN!”, the police officer yelled at me.
“Okay, thank you!”, I yelled back, running out of Paddington Station and trying to find a cab.
Except, it was 4 in the morning. And I had no idea where to look for one.”
- Start with ‘x time ago’. Recalling a past event hooks people instantly into your story. For example:
“A few months ago, Joanna Wiebe (the original conversion copywriter) slid into my DMs on Slack completely out of nowhere…”
3. Segue to Your Sales Pitch Seamlessly
By the time you get to this part, your readers are entertained and primed to purchase your solution to their problems. Your brand is no longer just another brand in their busy inbox. It’s someone they now know, trust, and like. And so, buying from you feels just right.
But you can’t just end your story abruptly so you can sell your products/services. That’d feel intrusive. In the same way that, when you’re engaged in a YouTube video, an annoying ad interrupts your stream.
So you must find a way to tie your story to your product or service so seamlessly that your readers won’t even notice they’re now reading a sales pitch. Sounds difficult. But you’ll see how easy it actually is. In fact, what most people get wrong about this part is that they try to find the moral of the story and tie that to their sales pitch.
For example, let’s say your story is about how your team went to a team-building event and someone accidentally broke a bunch of glasses. And if you’re selling a service, you might be able to spin that incident into saying something like: when you hire our software developers, your app stops breaking.
But that’s a predictable way to transition from your story to your sales pitch. Plus, not all stories will end with a moral. Most stories will be fragments of conversations you have with someone or something ridiculous that happened throughout the day (like forgetting your keys at the office). There’s no moral in that and there’s no need for one.
What you can do instead is to look back at your entire story and find one or a few phrases/words that could help you build that segway. Here’s an example of a full story-based email. Pay special attention to the part where the story ends and the sale begins.
“SUBJ: Hacker threatens to destroy my reputation in 72 hours straight
This morning, I was at my laptop reading my emails when suddenly, I came across an unread email from…
Me.
What in the world…?
Out of confusion, I open it without reading the subject line.
And once I go past the first sentence, it becomes pretty clear:
I’m being hacked.
“You may have noticed we are using your company’s servers to send you this email: we have hacked into your website, kaleidocopy[dot]com.”
Oh.
Okay… They did send this email from my email address.
Still, I can’t help but wonder… could this be a hoax?
“This is not a hoax.”
Ah! Well, that settles it then.
“We are willing to forget about destroying the reputation of your site and company for a small fee. The current fee is at $2500 in bitcoin.”
I mean… at least they are nice about it, you know? Their willingness to forgive and forget says a lot about a person’s character.
In the following lines, they take me through exactly what they’re going to do to ruin my company and reputation, step by step.
Then they teach me how to buy Bitcoin (I already know how, but I appreciate their thoughtfulness!).
And finally, they assure me that my Bitcoin payment will be anonymous and that no one will know that I complied with their master plan.
Mmmmkay.

GET CERTIFIED. Discover the proven plan for effortless, automated email marketing. Click Here
Now that is a bit suspicious, Mr. Hackerman (or Ms. Hackerwoman — it’s 2022, what the heck.)
I’m willing to bet the $2500 on the fact that I’m not the only person they sent this to.
So if the payment is anonymous, how will they know it was ME who sent it? It just doesn’t make sense, y’know?
Jokes aside, I’ve got to admit: seeing that the email came from my address made me panic a bit.
But then I checked my Sent folder and the email wasn’t there.
I also checked to see if there were any alerts or logins from different devices on my Google account. There were none.
I also checked with my hosting provider, who reassured me no one has broken into anything.
Soooo… hoax? Hopefully, lol.
But if it isn’t, it means you’ve got 72 hours left to get Email Story Alchemy, my mini-course on turning boring day-to-day events from your life into story-based emails that build your fandom and help you stand out.
After that, my business will supposedly disappear from the face of the Earth. And you’ll no longer be able to buy it. Everrr.”
Story is a structure, not a tale. Which means that you can apply it to anything, including email. And when you do it right, amazing things happen.
Like building strong relationships with your customers. And turning a casual customer into a die-hard fan who wants to buy from you because they just can’t get enough of your brand.
Sure, discounts work too. But they work when used strategically and in moderation. So if you’re ever unsure about what to email your customers next, consider story-based emails. They’ll make your brand shine bright in anyone’s crowded inbox.








![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)










You must be logged in to post a comment Login