SEO
Building a Better Search Engine: Lessons From Neeva’s CEO

After helping to grow Google’s advertising business for over 15 years, Sridhar Ramaswamy began to feel Google’s dependence on ads was limiting the quality of search results.
Determined to prove he could achieve a better search experience without ads, Ramaswamy co-founded and launched Neeva in 2019.
As the CEO of his own search company, Ramaswamy is accountable to the users of his product who pay a monthly subscription to access Neeva.
“No ads” means Neeva doesn’t have an incentive to collect data on its users, making it the only search engine on the market that’s both ad-free with a privacy option.
Ramaswamy is currently on the conference circuit raising awareness about Neeva, and we managed to catch up with him at Collision last week in Toronto.
We profiled Neeva once before and welcomed Ramaswamy as a guest on the Search Engine Journal Show in December.
However, each time we only scratched the surface. Now, we want to dig deeper.
So, what makes Neeva different from the other companies — and what makes Neeva a viable alternative to Google and Bing?
What Are Neeva’s Core Values?
Many companies enter the market making lofty claims of how they’ll do right by users. Even Google once had “don’t be evil” written into its code of conduct: a promise to which some critics argue it hasn’t lived up. Google has de-emphasized “Don’t be evil” in its code of conduct, though it was never removed.
In 2021, Google was sued by three former employees over its “Don’t be evil” motto. They allege that failure to live up to the motto is the equivalent of a breach of contract.
To better understand how Neeva will continue delivering a product that puts users’ needs first, I asked Ramaswamy what Neeva’s core values are.
“It’s not something we have published, but this is something I’ve talked about a lot with Vivek [Raghunathan, co-founder of Neeva], and I feel good about saying it,” Ramaswamy began. “At our core, we think that, as a company, we want to make technology serve people.”
“I think many other technology companies, especially in the last 25, have turned rather exploitative,” he continued. “I think the ad model exemplifies this. Basically, if I can convince you and get you hooked on my product, I can pretty much do anything.”
“It’s Technology Serving People”
Make no mistake: Neeva is a for-profit organization, though Ramaswamy says its subscription-based revenue model is designed to serve people rather than advertisers.
“Yes, companies are for-profit, but I think if you set up your values to be aligned with your user, to be aligned with your customer, you’ll always serve them,” he said. “To me, that part is important. If you had to say, ‘Hey, what exemplifies what you do?’ It’s technology serving people. This is why we do things like offer a flat price for the search utility you get from us.”
“Technology At Scale Is Quite Inexpensive”
Many companies within the sector lead consumers to believe scaling technology is expensive, which is how some justify charging higher fees, for instance, as they grow.
It doesn’t have to be that way, Ramaswamy says, as he believes the cost of technology at scale is overblown.
“It’s our belief that technology at scale is actually quite inexpensive,” he noted. “That’s the magic of technology, but right now, the way all of these companies are structured — as they scale, they squeeze more money from you.”
“It’s not like you’re getting more value, though obviously there are exceptions,” Ramaswamy continued. “But it’s really back to the basics of how you create products that delight people. And to me, that’s an honorable living.”
What Does Neeva Do To ‘Serve People’?
Neeva’s definition of ‘technology serving people’ is exemplified by its feedback system.
Roughly 20% of the Neeva team is tasked solely with listening to customer feedback and using it to shape the product experience.
On the other hand, many criticize Google for not giving users what they want out of a search experience.
I asked Ramaswamy if he could give examples of specific customer feedback that helped shape Neeva into what it is today.
“There’s tons of feedback that comes to us. Sometimes we feel bad about not being about to take care of all of it,” he started. “But to give an example: We did a currency converter because, believe it or not, it was a top request. Initially, I did not understand this feedback. I was like, ‘Really? It’s that hard for you to click on a link and then type in your numbers and get your currency converted?”
“But then,” Ramaswamy said, “I realized a larger truth about how people think about the internet.”
“People Fear Clicking On Links”
Neeva was initially against going the Google route of delivering content directly in the SERPs, but has had to make some concessions.
Through listening to customer feedback, the Neeva team learned there’s a real apprehension toward clicking on links in search results.
“Clicking on a link has now become an adversarial task. People actually fear clicking on links because they don’t know what’s on the other side,” Ramaswamy said. “Is it going to be a pop-up? Is it going to tell you that your computer has a virus? Is it something else? That’s the reason why we put [a currency converter] right into the search engine. So that’s one example.”
Another perk offered to Neeva subscribers is access to a Slack channel where customers can engage in group discussions with developers.
“A lot of people said, ‘We want to be able to offer feedback to [improve] your search results,’” Ramaswamy said. “So we built a community feedback feature that’s released to some people; it’s not released to everybody.”
The way it works, he explained, is users “can say, ‘Hey, this result is not relevant.’ Or, ‘This result is the top result for this query.’”
“This list sort of goes on and on,” Ramaswamy said. “Customers are really a source of lots of ideas.”
 From left to right: Brittany Kaiser, Own Your Data; Sridhar Ramaswamy, Neeva; Ashley Gold, Axios.
From left to right: Brittany Kaiser, Own Your Data; Sridhar Ramaswamy, Neeva; Ashley Gold, Axios.Neeva Is A Customer-Guided Product
At Collision, Ramaswamy described what he eventually aims to accomplish with Neeva, and how it differs from the goals of larger search engines like Google.
After speaking with him, I asked if he could clarify what he meant by wanting to “let society figure out” what to do with Neeva.
“I spoke about it more in the spirit of: Google spends a billion, makes a hundred billion. My thing was more: We want to make a couple of billion and let society figure out what it wants to do with the service,” Ramaswamy explained. “It’s more of a general argument around not captive capitalism, but competitive capitalism.”
“The beautiful thing about technology is creating a product for 100 million people is not wildly different from creating a product for a billion people,” he continued. “That’s the magic of scale and technology.”
Being paid for by the people who use it gives Neeva unique flexibility regarding future growth.
Users don’t have as much influence over a product like Google Search, considering they typically don’t pay to use it.
Although even for a free product, Ramasamy argues that Google could be doing much more to give users value.
“My point was a customer-paid product makes it much easier for us to release the product to the whole world [and] still run a profitable company, but not at the kind of obscene scale that I see Facebook or Google operating,” he said. “People always say … ‘Well, Google gives me free Gmail. Will they stop giving it?’ And my rough answer is: Well, I’m sure, with 100 billion dollars, a bunch of us are going to make really good decisions about how to use that money.”
Ramaswamy said that users “don’t need a monopolist to make that decision and decide they want to give you free Gmail. We don’t need charity from rich companies in order to do this; we need competition, so more of the money that is being spent on this comes to us.”
 From left to right: Brittany Kaiser, Own Your Data; Sridhar Ramaswamy, Neeva; Ashley Gold, Axios.
From left to right: Brittany Kaiser, Own Your Data; Sridhar Ramaswamy, Neeva; Ashley Gold, Axios.Will Neeva Keep Its Privacy Promises?
DuckDuckGo, another search engine that touts privacy as its key selling point, was recently a source of controversy after it was discovered to be passing along a minor amount of data to Microsoft.
That stemmed from the deal DuckDuckGo has to use Bing’s search index.
I asked Ramasamy what measures Neeva has in place to keep its zero data collection promises.
“Not serving ads is the biggest measure we have in place. And, we are building our own index,” he said, adding that the company is actively “writing down human ratings and getting data back.”
“We truly want to create a differentiated product,” Ramasamy emphasized. “We started with using the Bing API for search [but] in many ways, I think we would have been better off investing in search from day one. We are a product company, and we want to become a much better search engine. That’s the big differentiator.”
“We’re Making Foundational Investments In Search”
In addition to keeping Neeva ad-free, it will be able to maintain its zero-data promise by building its own search index.
DuckDuckGo, for example, ran into trouble because it’s wholly dependent on Microsoft for search results. Ramasamy says Neeva is the only company outside Google and Bing crawling and indexing the web.
That claim is backed up by an October 2020 report on digital competition by the House Judiciary Committee’s Subcommittee on Antitrust. The report states:
“The high cost of maintaining a fresh index, and the decision by many large webpages to block most crawlers, significantly limits new search engine entrants. Today, the only English-language search engines that maintain their own comprehensive webpage index are Google and Bing.”
He acknowledged that, in response, many ask, “What’s the big deal? What difference does it make?”
“It lets us do things like creating a much better shopping experience,” Ramasamy explained, noting that, for instance, Neeva “launched Reddit links in search results … because we work with Reddit to get their index. So we have an index of all the web pages they’re serving.”
Ramasamy said that users can receive better-quality results for such queries as, “What are the most interesting Reddit posts that correspond to this query?”
Neeva can “launch features like that, because we’re making foundational investments in search; pretty much the only company outside of Google and Microsoft to be doing this.”
“We increasingly use Bing as a fallback when we cannot answer queries,” Ramasamy acknowledged. However, he said, “Over time, our aspiration is to be able to do more and more of the search results ourselves.”
Neeva’s Sole Focus Is Traditional Web Content (For Now)
With people’s search behavior turning more toward short videos, I asked Ramaswamy if Neeva has any plans to index content like Web Stories or TikTok videos.
For now, Neeva’s sole focus is to solve search for text-based web content.
“Solving for search, especially things like spoken search, is enough of a large problem that we have not quite gone there,” Ramaswamy said. “We have working arrangements. We have partnerships with companies like Twitter and companies like Reddit to better surface their content.
Twitter, he pointed out, “Has a lot of real-time information. So we’re focused on things like that right now and less on video. That would be a fun project to do.”
Neeva’s Greatest Challenge Is Awareness
As we wrapped up our conversation, I asked Ramaswamy: What’s the most significant hurdle for Neeva to overcome on its journey toward mass adoption?
Ramaswamy’s answer: “It really is about competition.”
The product, he said, is not the issue.
“We have a great product. Compared to ad-supported options … the free Neeva search engine is infinitely better,” Ramaswamy explained. “The place where we struggle is getting the word out, getting people to know us as an option, and getting people to set us as the default search in Safari, which is impossible.
“Demand More Choice”
As Ramaswamy explained, there’s no incentive for a company like Google to innovate if it doesn’t have any challengers.
Companies tend to improve their products when faced with more robust competition. But the only way for more competitors to enter the search market is for consumers to demand more options.
“To me, this is the biggest ask that I would have,” Ramaswamy said, “is to demand more choice, because competition produces better products.”
In turn, he said, “That competition creates better products for us. An incumbent that is doing very well has no incentive to innovate [or] to disrupt.”
Conversely, over at Neeva, “We have nothing to lose,” Ramaswamy told me. “We’re going to swing for the fences [and make it] easier for people to switch, for them to try Neeva, for them to decide for themselves if they want it or not.”
What’s Next For Neeva?
Before parting ways, I had to ask what we could expect next from Neeva.
“There’s a lot I’ve learned from Google My Business in terms of local businesses – even in terms of Search Console – that I feel confident we can do better,” Ramaswamy said, adding that “GMB, as you know, is a real problem for lots of people. Especially agencies that want to update information for a bunch of companies that they work with.”
The hope, Ramaswamy said, is that “we’ll have better tools. But not yet.”
SEO
OpenAI Expected to Integrate Real-Time Data In ChatGPT

Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, dispelled rumors that a new search engine would be announced on Monday, May 13. Recent deals have raised the expectation that OpenAI will announce the integration of real-time content from English, Spanish, and French publications into ChatGPT, complete with links to the original sources.
OpenAI Search Is Not Happening
Many competing search engines have tried and failed to challenge Google as the leading search engine. A new wave of hybrid generative AI search engines is currently trying to knock Google from the top spot with arguably very little success.
Sam Altman is on record saying that creating a search engine to compete against Google is not a viable approach. He suggested that technological disruption was the way to replace Google by changing the search paradigm altogether. The speculation that Altman is going to announce a me-too search engine on Monday never made sense given his recent history of dismissing the concept as a non-starter.
So perhaps it’s not a surprise that he recently ended the speculation by explicitly saying that he will not be announcing a search engine on Monday.
He tweeted:
“not gpt-5, not a search engine, but we’ve been hard at work on some new stuff we think people will love! feels like magic to me.”
“New Stuff” May Be Iterative Improvement
It’s quite likely that what’s going to be announced is iterative which means it improves ChatGPT but not replaces it. This fits into how Altman recently expressed his approach with ChatGPT.
He remarked:
“And it does kind of suck to ship a product that you’re embarrassed about, but it’s much better than the alternative. And in this case in particular, where I think we really owe it to society to deploy iteratively.
There could totally be things in the future that would change where we think iterative deployment isn’t such a good strategy, but it does feel like the current best approach that we have and I think we’ve gained a lot from from doing this and… hopefully the larger world has gained something too.”
Improving ChatGPT iteratively is Sam Altman’s preference and recent clues point to what those changes may be.
Recent Deals Contain Clues
OpenAI has been making deals with news media and User Generated Content publishers since December 2023. Mainstream media has reported these deals as being about licensing content for training large language models. But they overlooked a a key detail that we reported on last month which is that these deals give OpenAI access to real-time information that they stated will be used to give attribution to that real-time data in the form of links.
That means that ChatGPT users will gain the ability to access real-time news and to use that information creatively within ChatGPT.
Dotdash Meredith Deal
Dotdash Meredith (DDM) is the publisher of big brand publications such as Better Homes & Gardens, FOOD & WINE, InStyle, Investopedia, and People magazine. The deal that was announced goes way beyond using the content as training data. The deal is explicitly about surfacing the Dotdash Meredith content itself in ChatGPT.
The announcement stated:
“As part of the agreement, OpenAI will display content and links attributed to DDM in relevant ChatGPT responses. …This deal is a testament to the great work OpenAI is doing on both fronts to partner with creators and publishers and ensure a healthy Internet for the future.
Over 200 million Americans each month trust our content to help them make decisions, solve problems, find inspiration, and live fuller lives. This partnership delivers the best, most relevant content right to the heart of ChatGPT.”
A statement from OpenAI gives credibility to the speculation that OpenAI intends to directly show licensed third-party content as part of ChatGPT answers.
OpenAI explained:
“We’re thrilled to partner with Dotdash Meredith to bring its trusted brands to ChatGPT and to explore new approaches in advancing the publishing and marketing industries.”
Something that DDM also gets out of this deal is that OpenAI will enhance DDM’s in-house ad targeting in order show more tightly focused contextual advertising.
Le Monde And Prisa Media Deals
In March 2024 OpenAI announced a deal with two global media companies, Le Monde and Prisa Media. Le Monde is a French news publication and Prisa Media is a Spanish language multimedia company. The interesting aspects of these two deals is that it gives OpenAI access to real-time data in French and Spanish.
Prisa Media is a global Spanish language media company based in Madrid, Spain that is comprised of magazines, newspapers, podcasts, radio stations, and television networks. It’s reach extends from Spain to America. American media companies include publications in the United States, Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Mexico, and Panama. That is a massive amount of real-time information in addition to a massive audience of millions.
OpenAI explicitly announced that the purpose of this deal was to bring this content directly to ChatGPT users.
The announcement explained:
“We are continually making improvements to ChatGPT and are supporting the essential role of the news industry in delivering real-time, authoritative information to users. …Our partnerships will enable ChatGPT users to engage with Le Monde and Prisa Media’s high-quality content on recent events in ChatGPT, and their content will also contribute to the training of our models.”
That deal is not just about training data. It’s about bringing current events data to ChatGPT users.
The announcement elaborated in more detail:
“…our goal is to enable ChatGPT users around the world to connect with the news in new ways that are interactive and insightful.”
As noted in our April 30th article that revealed that OpenAI will show links in ChatGPT, OpenAI intends to show third party content with links to that content.
OpenAI commented on the purpose of the Le Monde and Prisa Media partnership:
“Over the coming months, ChatGPT users will be able to interact with relevant news content from these publishers through select summaries with attribution and enhanced links to the original articles, giving users the ability to access additional information or related articles from their news sites.”
There are additional deals with other groups like The Financial Times which also stress that this deal will result in a new ChatGPT feature that will allow users to interact with real-time news and current events .
OpenAI’s Monday May 13 Announcement
There are many clues that the announcement on Monday will be that ChatGPT users will gain the ability to interact with content about current events. This fits into the terms of recent deals with news media organizations. There may be other features announced as well but this part is something that there are many clues pointing to.
Watch Altman’s interview at Stanford University
Featured Image by Shutterstock/photosince
SEO
Google’s Strategies For Dealing With Content Decay

In the latest episode of the Search Off The Record podcast, Google Search Relations team members John Mueller and Lizzi Sassman did a deep dive into dealing with “content decay” on websites.
Outdated content is a natural issue all sites face over time, and Google has outlined strategies beyond just deleting old pages.
While removing stale content is sometimes necessary, Google recommends taking an intentional, format-specific approach to tackling content decay.
Archiving vs. Transitional Guides
Google advises against immediately removing content that becomes obsolete, like materials referencing discontinued products or services.
Removing content too soon could confuse readers and lead to a poor experience, Sassman explains:
“So, if I’m trying to find out like what happened, I almost need that first thing to know. Like, “What happened to you?” And, otherwise, it feels almost like an error. Like, “Did I click a wrong link or they redirect to the wrong thing?””
Sassman says you can avoid confusion by providing transitional “explainer” pages during deprecation periods.
A temporary transition guide informs readers of the outdated content while steering them toward updated resources.
Sassman continues:
“That could be like an intermediary step where maybe you don’t do that forever, but you do it during the transition period where, for like six months, you have them go funnel them to the explanation, and then after that, all right, call it a day. Like enough people know about it. Enough time has passed. We can just redirect right to the thing and people aren’t as confused anymore.”
When To Update Vs. When To Write New Content
For reference guides and content that provide authoritative overviews, Google suggests updating information to maintain accuracy and relevance.
However, for archival purposes, major updates may warrant creating a new piece instead of editing the original.
Sassman explains:
“I still want to retain the original piece of content as it was, in case we need to look back or refer to it, and to change it or rehabilitate it into a new thing would almost be worth republishing as a new blog post if we had that much additional things to say about it.”
Remove Potentially Harmful Content
Google recommends removing pages in cases where the outdated information is potentially harmful.
Sassman says she arrived at this conclusion when deciding what to do with a guide involving obsolete structured data:
“I think something that we deleted recently was the “How to Structure Data” documentation page, which I thought we should just get rid of it… it almost felt like that’s going to be more confusing to leave it up for a period of time.
And actually it would be negative if people are still adding markup, thinking they’re going to get something. So what we ended up doing was just delete the page and redirect to the changelog entry so that, if people clicked “How To Structure Data” still, if there was a link somewhere, they could still find out what happened to that feature.”
Internal Auditing Processes
To keep your content current, Google advises implementing a system for auditing aging content and flagging it for review.
Sassman says she sets automated alerts for pages that haven’t been checked in set periods:
“Oh, so we have a little robot to come and remind us, “Hey, you should come investigate this documentation page. It’s been x amount of time. Please come and look at it again to make sure that all of your links are still up to date, that it’s still fresh.””
Context Is Key
Google’s tips for dealing with content decay center around understanding the context of outdated materials.
You want to prevent visitors from stumbling across obsolete pages without clarity.
Additional Google-recommended tactics include:
- Prominent banners or notices clarifying a page’s dated nature
- Listing original publish dates
- Providing inline annotations explaining how older references or screenshots may be obsolete
How This Can Help You
Following Google’s recommendations for tackling content decay can benefit you in several ways:
- Improved user experience: By providing clear explanations, transition guides, and redirects, you can ensure that visitors don’t encounter confusing or broken pages.
- Maintained trust and credibility: Removing potentially harmful or inaccurate content and keeping your information up-to-date demonstrates your commitment to providing reliable and trustworthy resources.
- Better SEO: Regularly auditing and updating your pages can benefit your website’s search rankings and visibility.
- Archival purposes: By creating new content instead of editing older pieces, you can maintain a historical record of your website’s evolution.
- Streamlined content management: Implementing internal auditing processes makes it easier to identify and address outdated or problematic pages.
By proactively tackling content decay, you can keep your website a valuable resource, improve SEO, and maintain an organized content library.
Listen to the full episode of Google’s podcast below:
Featured Image: Stokkete/Shutterstock
SEO
25 Snapchat Statistics & Facts For 2024

Snapchat, known for its ephemeral content, innovative augmented reality (AR) features, and fiercely loyal user base, is a vital player in the social media landscape.
While it sometimes flies under the radar – as other platforms like TikTok, YouTube, and Instagram tend to dominate the cultural conversation – Snapchat is an incredibly powerful marketing tool that holds a unique place in the hearts and minds of its users.
In this article, we’ll explore what you need to know about Snapchat, with insights that shed light on what audiences think of the app and where its strengths lie.
From user growth trends to advertising effectiveness, let’s look at the state of Snapchat right now.
What Is Snapchat?
Snapchat is a social media app that allows users to share photos and videos with friends and followers online.
Unlike other social platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok – where much of the content is stored permanently – Snapchat prioritizes ephemeral content only.
Once viewed, Snapchat content disappears, which adds a layer of spontaneity and privacy to digital interactions.
Snapchat leverages the power of augmented reality to entertain its audience by creating interactive and immersive experiences through features like AR lenses.
Users can also explore a variety of stickers, drawing tools, and emojis to add a personal touch to everything they post.
What started as a small collection of tools in 2011 has now expanded to a massive library of innovative features, such as a personalized 3D Snap Map, gesture recognition, audio recommendations for lenses, generative AI capabilities, and much more.
Creating an account on Snapchat is easy. Simply download the app on Google Play or the App Store. Install it on your device, and you’re ready!
-
Screenshot from Google Play, December 2023
25 Surprising Facts You Didn’t Know About Snapchat
Let’s dive in!
1. Snapchat Has 406 Million Daily Active Users
That number, released by the company in October 2023, represents an increase of 43 million year-over-year – a 12% increase.
Here’s a chart from Statista showing Snapchat’s user growth from 2014 to 2023:
-
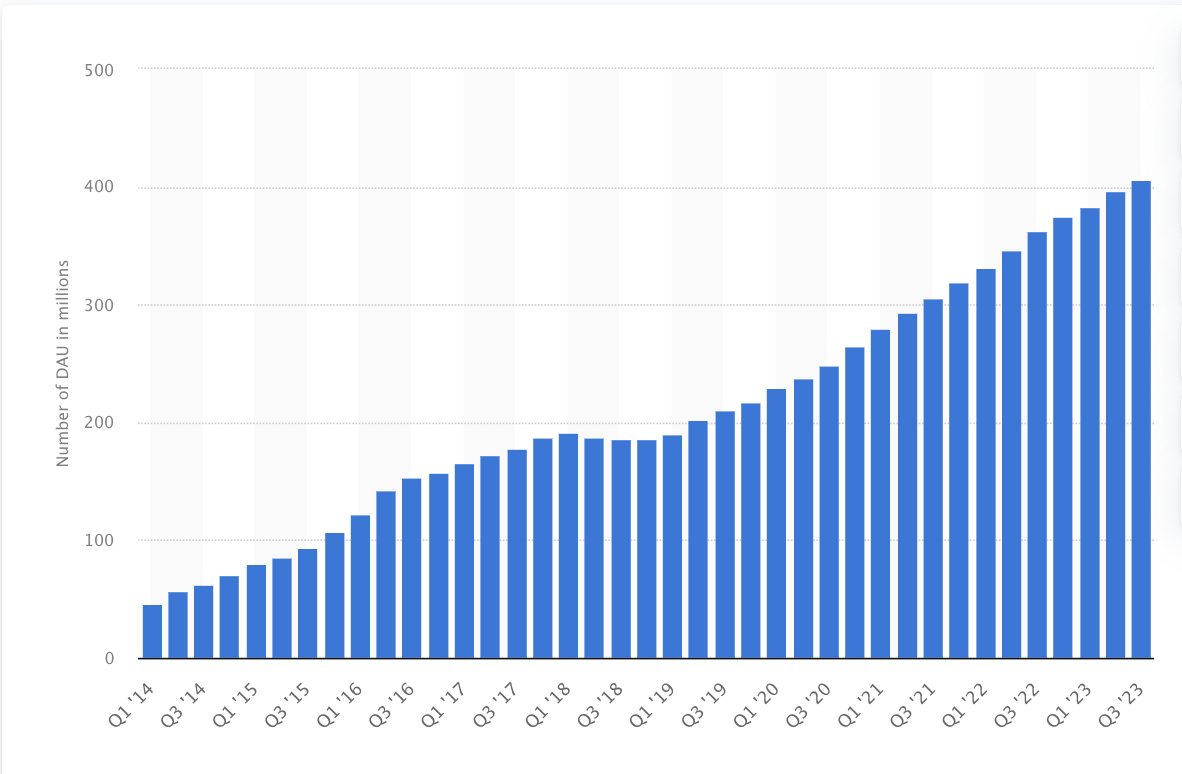 Screenshot from Statista.com, December 2023
Screenshot from Statista.com, December 2023
And with 750 million monthly active users (MAUs), Snapchat is the fifth-biggest social media network in the world.
2. Users 18-24 Years Old Account For The Biggest Chunk Of Snapchat’s Audience
According to Snapchat’s own advertising data, the platform has 243.5 million users aged 18 to 24 – representing 38.6% of its total ad audience.
The second largest group of users are between the ages of 25 and 34, followed by 13-17-year-olds – proving that Snapchat is reaching young people around the world.
On the flip side, the platform isn’t huge with older users; people aged 50 and over account for only 3.8% of Snapchat’s total ad audience.
As a marketer, you can take a hint on what your campaign should focus on if you use Snapchat. As Snapchat’s own report puts it:
“From its inception, Snapchat has inherently created a frictionless space where Gen Z creatives can experiment with their identities, yet not have to feel like they’re ‘on brand’ in communicating to their close friend groups.”
3. Snapchat Reaches 90% Of The 13 To 24-Year-Old Population
It also reaches 75% of people between the ages of 13 and 34 in over 25 countries, according to Snapchat’s estimates.
In the US, 59% of American teenagers (between the ages of 13 and 17) report using Snapchat. This number amounts to roughly six in 10 US teens.
4. Snapchat Users Open The App Nearly 40 Times A Day
According to the company, this means people interact with their social circles on Snapchat more than any other social network.
In the US, about half of teenagers (51%) report using Snapchat at least once a day – making it slightly more popular than Instagram, but not quite as popular as YouTube or TikTok.
5. Taco Bell Paid $75,000 For 24 Hours Of The Taco Filter/Ad
To boost sales, Taco Bell launched the taco filter on Snapchat. Here’s what it looked like.
Today only: turn yourself into a taco using our @Snapchat lens. Because Cinco de Mayo. pic.twitter.com/P4KwLdFNFZ
— Taco Bell (@tacobell) May 5, 2016
The filter is humorous, relevant, and unique. Users adored it, and it got 224 million views.
That’s great, considering Taco Bell paid $75,000 for the ad – which actually proved to be a great investment for the exposure the brand received.
6. More Than Half (50.6%) Of Snapchat Users Are Female
In contrast, 48.7% of the platform’s global users are male.
While there is not a huge discrepancy between the demographics here, it’s helpful information for any marketers looking to put together Snapchat campaigns.
7. Snapchat Is The No. 1 App People Use To Share What They Bought
Is your brand looking to reach young social media users around the world? Snapchat could be the perfect platform for you.
People are 45% more likely to recommend brands to friends on Snapchat compared to other platforms.
They’re also 2X more likely to post about a gift after receiving it – making Snapchat a powerful tool for influencer marketing and brand partnerships.
8. Snapchat Pioneered Vertical Video Ads
Once a novelty in the social media industry, vertical video ads have become one of the most popular ways to advertise on social media and reach global audiences.
What are vertical video ads? It’s self-explanatory: They’re ads that can be viewed with your phone held vertically. The ad format is optimized for how we use our mobile devices and designed to create a non-disruptive experience for users.
You’ve definitely seen countless video ads by now, but did you know Snapchat pioneered them?
9. You Can Follow Rock Star Business Experts On Snapchat
Who knew Snapchat could be a powerful business tool? Here are the top three experts you should follow right now:
10. More Than 250 Million Snapchatters Engage With AR Every Day, On Average
Snapchat was the first social media app to really prioritize the development of AR features, and it’s paid off.
Over 70% of users engage with AR on the first day that they download the app – and, to date, there have been more than 3 million lenses launched on Snapchat.
11. People Are 34% More Likely To Purchase Products They See Advertised On Snapchat
When compared to watching the same ad on other social media platform, Snapchat proves to be an effective way to reach and convert.
12. Snapchat Is The King Of Ephemeral Content Marketing
Ephemeral content marketing uses video, photos, and media that are only accessible for a limited time.
Here are three reasons it works:
- It creates a sense of urgency.
- It appeals to buyers who don’t want to feel “sold.”
- It’s more personalized than traditional sales funnel marketing.
Guess who’s one of the kings of ephemeral content marketing? That’s right: Snapchat.
Consider that if it weren’t for Snapchat, Instagram Stories would likely not exist right now.
13. More Than 5 Million People Subscribe To Snapchat+
Snapchat+ is the platform’s paid subscription service that gives users access to exclusive and pre-release features on the platform.
Subscribers also receive a range of other perks, including options to customize their app experience and the ability to see how many times their content has been rewatched.
The fact that so many millions of users are willing to pay for special access and features to Snapchat should be a sign to brands and marketers everywhere that the platform has a strong pull with its audience.
Beyond that, the fact that Snapchat+ drew 5 million subscribers within just a year or so of launching is impressive on its own.
14. Snapchat Reaches Nearly Half Of US Smartphone Users
According to Statista, approximately 309 million American adults use smartphones today.
Snapchat’s ability to reach such a considerable portion of US smartphone users is notable.
15. Snapchat Users Spend An Average Of 19 Minutes Per Day On The App
That’s 19 minutes brands can use to connect with people, grow brand awareness, and convey their message.
16. Snapchat’s Original Name Was Picaboo
In fact, Snapchat did run as Picaboo for about a year.
17. Snapchat Was Created After 34 Failures
Snapchat creators Evan Spiegel, Bobby Murphy, and Frank Reginald Brown worked on the Snapchat project while they were studying at Stanford University.
After 34 failures, they finally developed the app as we know it today.
18. Snapchat’s Creators Had A Major Falling-Out Before The App Was Released
Frank Reginald Brown was ousted from the Snapchat project by his friends.
Although no one knows the real story, Brown claims Spiegel and Murphy changed the server passwords and ceased communication with him a month before Snapchat was launched.
19. Snapchat Downloads Doubled After The Launch Of The Toddler & Gender Swap Filters
Users downloaded Snapchat 41.5 million times in a month after the release of these filters!
20. Mark Zuckerberg Tried To Buy Snapchat
Snapchat’s owners refused to sell Snapchat to Zuckerberg (even though the offer went as high as $3 billion!).
21. Snapchat’s Mascot Is Called Ghostface Chillah
The mascot was inspired by Ghostface Killah of the Wu-Tang Clan – and when you consider that the app was once called “Picaboo,” the ghost logo makes more sense.
Apparently, Snapchat co-founder and CEO Evan Spiegel has said that he developed the mascot himself and chose a ghost based on the ephemeral nature of Snapchat content.
22. Facebook And Instagram Borrowed Ephemeral Content From Snapchat
As we mentioned above, we have Snapchat to thank for Facebook and Instagram Stories, which have since become integral to the social media experience.
Snapchat also pioneered the use of AR filters, which were adopted by Instagram and paved the way for the filters that dominate the world of TikTok today.
23. 75% Of Gen Z And Millennials Say Snapchat Is The No. 1 Platform For Sharing Real-Life Experiences
Social media is all about authentic moments and human connection – and social media marketing is no different.
With such a large number of young people preferring Snapchat over other platforms for sharing their life experiences, marketers should follow suit.
Find ways to share behind-the-scenes moments with your team and company, and emphasize the humans behind the brand.
24. Snapchat Users Have Over $4.4 Trillion In Global Spending Power
That’s nothing to sneeze at.
25. In 2022, Snapchat Generated $4.6 Billion In Revenue
It is currently valued at over $20 billion.
Looking Ahead With Snapchat
Snapchat’s ephemeral content, intimacy, and spontaneity are strong points for everyday users, content creators, and businesses alike.
Marketers should keep a keen eye on emerging trends within the platform, such as new AR advancements and evolving user demographics.
Those looking to reach younger audiences or show an authentic, human side of their brand should consider wading into the waters of Snapchat.
By harnessing the power of ephemeral content and engaging features, brands can effectively use Snapchat to grow their brand awareness, engage with audiences on a more personal level, and stay relevant in the fast-paced world of digital marketing.
More resources:
Featured Image: Trismegist san/Shutterstock
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoThe key to correcting the C-suite trust deficit
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoA Recap of Everything Marketers & Advertisers Need to Know
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days agoHow the TikTok Algorithm Works in 2024 (+9 Ways to Go Viral)
-

 MARKETING4 days ago
MARKETING4 days agoHow To Protect Your People and Brand
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Started Enforcing The Site Reputation Abuse Policy
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days ago128 Top SEO Tools That Are 100% Free
-

 SEO3 days ago
SEO3 days agoHow to Use Keywords for SEO: The Complete Beginner’s Guide
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days agoBlog Post Checklist: Check All Prior to Hitting “Publish”














You must be logged in to post a comment Login