SEO
7 Successful B2B Content Marketing Examples You Can Learn From

There is no one right way of doing content marketing.
Depending on their goals, resources, target audience, and so on, different companies do content marketing differently.
In this post, we’ll share seven inspiring B2B content marketing examples, why they’ve done well, and how you can replicate their success.
Shopify is an e-commerce platform that helps businesses sell online.

Key stats
Number of referring domains: 9,000
Estimated organic traffic: 1,700,000
Number of keywords the tools rank for: 121,000


What it does well
When it comes to content marketing, Shopify has gone the whole hog. It’s invested in almost every type of content marketing: blogs, podcasts, free courses, free guides, and more.


But I want to drill down into one aspect of its content marketing: free tools. Shopify offers over 20 free tools:


These tools have two things in common. First, they solve problems for budding entrepreneurs. For example, you’ll need a business name for your new company. Shopify solves that by offering a free business name generator:


Second, these queries have thousands of monthly searches on Google. For example, the term “business name generator” gets 81,000 monthly searches in the U.S.:


That’s why its tools page—and each individual tool—is getting hundreds of thousands of search visits:


How to replicate its success
Tools are content too. Consider creating a free tool if you have the ability or resources. This is especially applicable if you’re a software company.
However, don’t just create any free tool. Create those your potential customers are searching for.
Here’s how to find them. You can:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer.
- Enter one or a few broad keywords related to your industry (e.g., if you have a real estate website, these might be mortgage, rent, and down payment).
- Go to the Matching terms report.
- In the Include filter, add words like calculator, tool, tools, and, checker.
- Choose Any word and click Apply.


Look through the list to see if there are any relevant tools you can create.
Make sure you review the top-ranking results to see if you can “beat” them. Ask yourself:
- What’s good about them?
- How could they be improved?
When you’ve created your free tool, know that you’ll likely have to acquire links to rank. There are many ways to do this, but the best starting point for tools is to use the Skyscraper Technique.
Read this post or watch the video below to learn more:
Ahrefs is an all-in-one SEO toolset that allows you to research your competitors, study what your customers are searching for, optimize your website, and more.


Key stats
Number of referring domains: 33,400
Estimated organic traffic: 645,000
Number of keywords the blog ranks for: 107,000


What we do well
Our content strategy is simple. We target topics that have:
- Search traffic potential – Topics that our potential customers are searching for on Google.
- Business potential – Topics where we can pitch our product.
- Ranking potential – Topics where we can rank in the top three with our current resources.


Doing this consistently allows us to rank high for keywords that are relevant to our customers and pitch our product as the best solution to those problems.
This no-frills SEO content strategy has helped grow our annual recurring revenue (ARR) consistently over the years.
How to replicate our success
Use the same process in example #1 to find keywords with search traffic potential:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter one or a few broad keywords related to your industry
- Go to the Matching terms report
- Filter for keywords with Traffic Potential (TP)


Eyeball the list and note down all relevant keywords.
From there, you’ll want to assign a “business potential” score to each keyword. Here’s the cheat sheet we use at Ahrefs:


You’ll also want to give each keyword a “ranking potential” score. We can check each keyword’s ranking difficulty by scrolling to the SERP overview section and analyzing the metrics shown for the current top-ranking pages.


What should you look out for? There are many factors involved in assessing ranking difficulty. But broadly speaking, you’ll want to pay attention to:
- Quantity and quality of backlinks – Links are a Google ranking factor. So the more high-quality backlinks the current top-ranking pages have, the harder it’ll be to compete. Check the Domains column to see how many websites are linking to each top-ranking page. To understand link quality, click on the number in the Backlinks column and review each page’s backlink profile.
- Website authority – You can use a proxy metric like Domain Rating (DR) to gauge a site’s authority. If the DR scores of the top-ranking pages are all higher than yours, you may want to prioritize other keywords.
- Search intent – Search intent is the why behind the query. You’ll want to make sure you’re able to fulfill the search intent for the keywords you want to target.
- Content quality – Can you beat the top-ranking pages on content quality? This is subjective. But if the #1 ranking page reviewed 47 air purifiers for its blog post, can you do the same or more?
To go in-depth about how to assess ranking difficulty, I highly recommend reading our keyword difficulty guide.
After reviewing the keywords for the four attributes, give them a “ranking potential” score:


Learn more: How to Create an SEO Content Strategy (Follow the Ahrefs’ Framework)
Slidebean is a pitch deck design platform for startups and small businesses.


Key stats
Number of YouTube subscribers: 401,000
Total views: 27,325,552
What it does well
I reached out to Slidebean’s CEO, Caya, to find out more. From what he told me, the platform’s approach is twofold.
First, it started with a recurring video series known as Startups 101. For this series, it mainly targeted startup-related keywords on YouTube.


However, it exhausted its list of topics in about a year. This was when it decided to move up the marketing funnel into TOFU-related topics.
Since we had found a “YouTube formula,” we decided to apply it to other kinds of content, and one of them was this idea of exploring failed companies. The first one was WeWork, which was just the right bridge between a startup-focused company and a widely known brand. At this stage, the series was called “Startup Forensics.”
However, there were only so many tech startups to explore, so we quickly opened that up to “Company Forensics” to broaden our horizons.


Slidebean’s goal was to get as many eyeballs as possible. Thanks to the mere exposure effect, people would think of Slidebean in the future if they were ever looking for pitch deck software.
How to replicate its success
Predicting what kind of videos will take off on YouTube is difficult. You could launch a well-produced, expensive, and entertaining video to crickets.
That’s why Caya started his YouTube journey by initially targeting topics his target audience was searching for. Only when he built an audience did he move to other types of content.
Here’s how to find topics people are searching for on YouTube:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter one or a few broad keywords related to your industry
- Select YouTube in the search engine dropdown
- Go to the Matching terms report


Go through the list to find relevant keywords for your YouTube channel.
Then, watch this video to learn how to create videos that will rank on YouTube:
Founded in 2014 by Laura Roeder, MeetEdgar is a social media automation tool.


Key stats
Number of referring domains: 7,300
Number of backlinks: 40,300


What it does well
Appearing on podcasts helped MeetEdgar grow into a thriving business. From 2014 to 2017, founder Laura Roeder appeared on an estimated 100 podcasts.


According to Jen Carvey, a former employee, this strategy helped MeetEdgar reach 1.25 million website visitors, 100,000 email subscribers, and $329,000+ monthly recurring revenue (MRR).
How to replicate its success
There are more than 850,000 active podcasts today. Plenty of them will need guests. So if you can find podcasts with your target audience, you can appear on them. Not only will you generate brand awareness, but you can also get links back to your site.
The easiest way to find podcasts to appear on is to simply search for “best [niche] podcasts”:


Keep in mind that many of them will be popular podcasts that can be challenging to pitch for. So if you’re starting out, try this method:
- Find a prolific podcast guest in your industry (e.g., Laura Roeder)
- Enter their website into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer (set it to Exact URL)
- Go to the Backlinks report
- Filter for results with “episode” in the Referring page title


Once you’ve gathered a list of potential podcasts, find the emails of the hosts and reach out to see if they’re willing to interview you.
Learn more: How to Use Podcasts for Link Building
First Round Capital is a seed-stage venture capital (VC) firm.


Key stats
Number of referring domains: 9,900
Estimated total visits: 368,900
Estimated organic traffic: 43,500
Newsletter subscribers: 127,000


What it does well
At the time, most VC firms were either blogging about market trends or opinion pieces from their partners. First Round decided to position itself differently and focused on writing stories about the operator side (i.e., startups).
With a portfolio of startups it had already invested in, First Round was in a unique position to interview and tell never-seen-before stories.
This was perfect for attracting its target audience too. New or potential founders aren’t interested in market trends; they want content that solves real problems—product development, hiring, marketing, and so on.
How to replicate its success
Camille Ricketts, the ex-editor of First Round Review, started by asking:
“What is the number one thing that all of these early-stage founders want?”
Her answer? To be able to go to coffee with somebody who has done the thing they’re trying to do. That was how The Review was born: a magazine-style blog of “coffee meetups at scale.”
Before you create any content, make sure you know exactly who you’re targeting and what problems they’re facing. If you haven’t created your buyer personas yet, follow this guide on how to do it.
Learn more: Why You Shouldn’t Try to Be the First Round Review: 3 Content Lessons From Camille Ricketts
Kinsta is a managed WordPress hosting provider.


Key stats
Number of referring domains: 15,900
Estimated organic traffic: 1,600,000
Number of keywords the blog ranks for: 330,000


What it does well
Like us, Kinsta follows a keyword-driven content strategy. However, what makes its approach unique is what SEO Glen Allsopp calls “error message marketing.”
Here’s the gist of how it works:
- You’ll inadvertently face issues when doing something technical or using a technical tool.
- You’ll probably Google how to solve it.
- Kinsta specifically targets those keywords.
This way, Kinsta builds brand awareness among its target audience—developers, webmasters, site owners, etc.—people who basically fix such technical issues regularly.


How to replicate its success
If there are tools regularly used by people in your niche, determine what problems their users have and target those topics.
For example, let’s say you’re a U.K.-based company that targets boiler engineers. Here’s how to find these topics:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter the names of tools/products your niche uses (e.g., Intergas, Vaillant, Vokera, Worcester Bosch)
- Go to the Matching terms report
- In the Include filter, add words like fault, error, code
- Choose Any word and click Apply


Eyeball the list and find those topics that are relevant to your site.
YouGov is a market research and data analytics firm. It provides a few services, including custom data and research, audience profiling, segmentation, and brand tracking.


Key stats
Number of referring domains: 29,900
Estimated organic traffic: 497,000
Number of keywords the tools rank for: 175,000


What it does well
YouGov makes money by providing custom data and research. Therefore, its marketing strategy aims to achieve two main objectives:
- Build brand awareness among companies who may need its services
- Show that it has high-quality data
YouGov achieves this by publishing content using data on “hot topics.” These articles then get linked to by trusted news organizations like the Guardian, L.A. Times, and The New York Times that are looking for data to support their conclusions:


How to replicate its success
The key idea is to use data to create interesting articles or answer interesting questions in your niche.
If you’re part of the industry, chances are you already know what those questions are. For example, in the SEO industry, many people wonder about how long it’ll take to rank on Google. However, the answers were always based on conjecture and not data.
So we attempted to study this objectively with data. The result? 4,000 backlinks from 2,200 unique websites.


If you’re out of ideas, you can try to recreate popular but outdated studies. Here’s how to find them:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Content Explorer
- Enter a search term like [industry] + “study,” [industry] + “survey,” [industry] + “research,” or [industry] + “data”
- Set the filter to an In title search
- Set the Published filter to an older date range (e.g., 2010–2015)
- Sort the results by referring domains


Once you’re done with the study, you’ll need to reach out and introduce it to people who may be interested. Follow our blogger outreach guide to learn how to do it.
Learn more: Blogger Outreach: How to Do It At Scale (Without Feeling Like a Jerk)
Final thoughts
As you can see, there is no one-size-fits-all approach to content marketing. Depending on your goals, there are a variety of strategies you can use for maximum effectiveness.
If you’re just getting started with content marketing, I recommend reading this comprehensive guide.
Did I miss out on any amazing B2B content marketing examples? Let me know on Twitter.
SEO
Why Google Can’t Tell You About Every Ranking Drop

In a recent Twitter exchange, Google’s Search Liaison, Danny Sullivan, provided insight into how the search engine handles algorithmic spam actions and ranking drops.
The discussion was sparked by a website owner’s complaint about a significant traffic loss and the inability to request a manual review.
Sullivan clarified that a site could be affected by an algorithmic spam action or simply not ranking well due to other factors.
He emphasized that many sites experiencing ranking drops mistakenly attribute it to an algorithmic spam action when that may not be the case.
“I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a algorithmic spam action against them, but they don’t. “
Sullivan’s full statement will help you understand Google’s transparency challenges.
Additionally, he explains why the desire for manual review to override automated rankings may be misguided.
Two different things. A site could have an algorithmic spam action. A site could be not ranking well because other systems that *are not about spam* just don’t see it as helpful.
I’ve looked at many sites where people have complained about losing rankings and decide they have a…
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) May 13, 2024
Challenges In Transparency & Manual Intervention
Sullivan acknowledged the idea of providing more transparency in Search Console, potentially notifying site owners of algorithmic actions similar to manual actions.
However, he highlighted two key challenges:
- Revealing algorithmic spam indicators could allow bad actors to game the system.
- Algorithmic actions are not site-specific and cannot be manually lifted.
Sullivan expressed sympathy for the frustration of not knowing the cause of a traffic drop and the inability to communicate with someone about it.
However, he cautioned against the desire for a manual intervention to override the automated systems’ rankings.
Sullivan states:
“…you don’t really want to think “Oh, I just wish I had a manual action, that would be so much easier.” You really don’t want your individual site coming the attention of our spam analysts. First, it’s not like manual actions are somehow instantly processed. Second, it’s just something we know about a site going forward, especially if it says it has change but hasn’t really.”
Determining Content Helpfulness & Reliability
Moving beyond spam, Sullivan discussed various systems that assess the helpfulness, usefulness, and reliability of individual content and sites.
He acknowledged that these systems are imperfect and some high-quality sites may not be recognized as well as they should be.
“Some of them ranking really well. But they’ve moved down a bit in small positions enough that the traffic drop is notable. They assume they have fundamental issues but don’t, really — which is why we added a whole section about this to our debugging traffic drops page.”
Sullivan revealed ongoing discussions about providing more indicators in Search Console to help creators understand their content’s performance.
“Another thing I’ve been discussing, and I’m not alone in this, is could we do more in Search Console to show some of these indicators. This is all challenging similar to all the stuff I said about spam, about how not wanting to let the systems get gamed, and also how there’s then no button we would push that’s like “actually more useful than our automated systems think — rank it better!” But maybe there’s a way we can find to share more, in a way that helps everyone and coupled with better guidance, would help creators.”
Advocacy For Small Publishers & Positive Progress
In response to a suggestion from Brandon Saltalamacchia, founder of RetroDodo, about manually reviewing “good” sites and providing guidance, Sullivan shared his thoughts on potential solutions.
He mentioned exploring ideas such as self-declaration through structured data for small publishers and learning from that information to make positive changes.
“I have some thoughts I’ve been exploring and proposing on what we might do with small publishers and self-declaring with structured data and how we might learn from that and use that in various ways. Which is getting way ahead of myself and the usual no promises but yes, I think and hope for ways to move ahead more positively.”
Sullivan said he can’t make promises or implement changes overnight, but he expressed hope for finding ways to move forward positively.
Featured Image: Tero Vesalainen/Shutterstock
SEO
56 Google Search Statistics to Bookmark for 2024

If you’re curious about the state of Google search in 2024, look no further.
Each year we pick, vet, and categorize a list of up-to-date statistics to give you insights from trusted sources on Google search trends.
- Google has a web index of “about 400 billion documents”. (The Capitol Forum)
- Google’s search index is over 100 million gigabytes in size. (Google)
- There are an estimated 3.5 billion searches on Google each day. (Internet Live Stats)
- 61.5% of desktop searches and 34.4% of mobile searches result in no clicks. (SparkToro)
- 15% of all Google searches have never been searched before. (Google)
- 94.74% of keywords get 10 monthly searches or fewer. (Ahrefs)
- The most searched keyword in the US and globally is “YouTube,” and youtube.com gets the most traffic from Google. (Ahrefs)
- 96.55% of all pages get zero search traffic from Google. (Ahrefs)
- 50-65% of all number-one spots are dominated by featured snippets. (Authority Hacker)
- Reddit is the most popular domain for product review queries. (Detailed)
- Google is the most used search engine in the world, with a mobile market share of 95.32% and a desktop market share of 81.95%. (Statista)
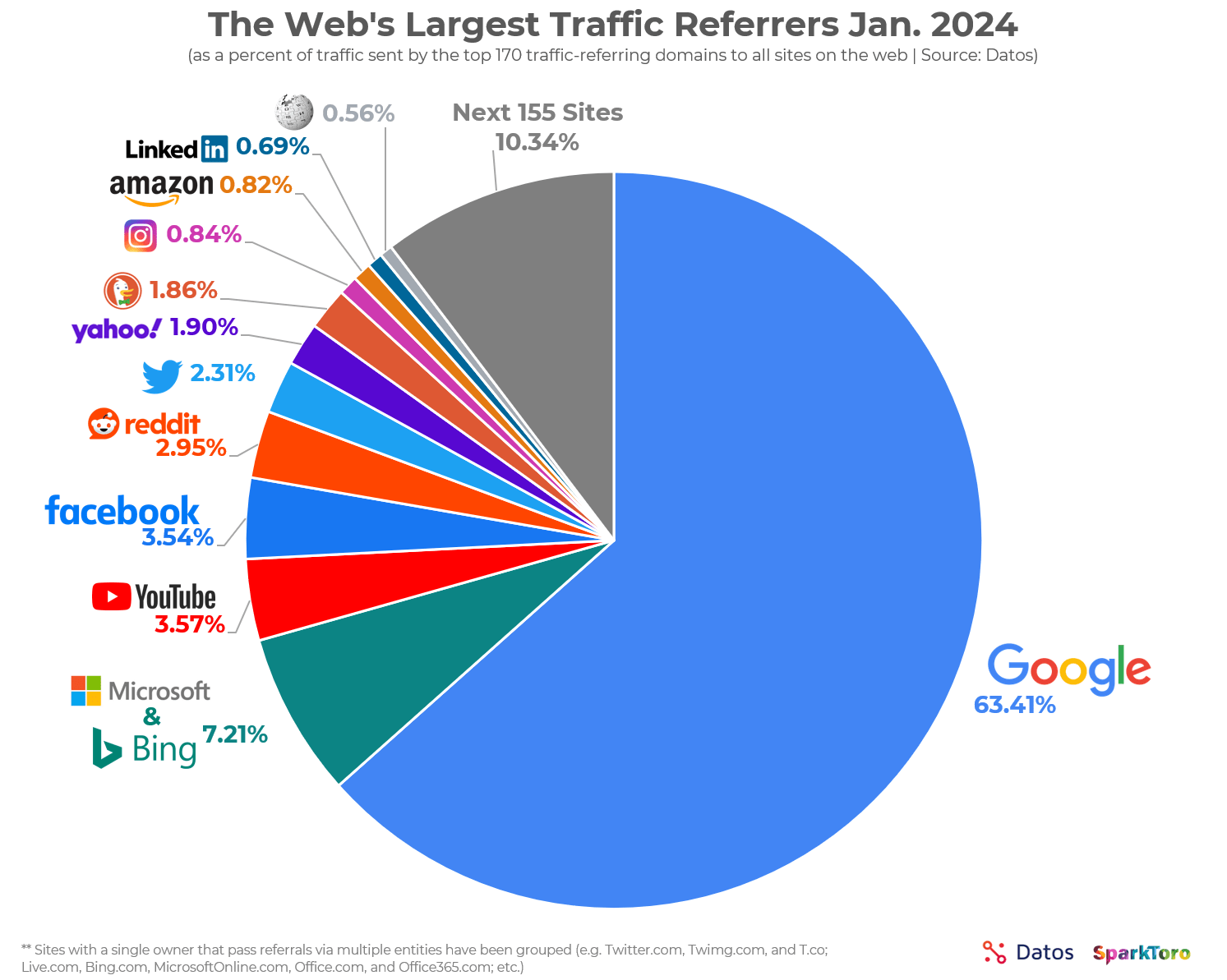

- Google.com generated 84.2 billion visits a month in 2023. (Statista)
- Google generated $307.4 billion in revenue in 2023. (Alphabet Investor Relations)
- 63.41% of all US web traffic referrals come from Google. (SparkToro)
- 92.96% of global traffic comes from Google Search, Google Images, and Google Maps. (SparkToro)
- Only 49% of Gen Z women use Google as their search engine. The rest use TikTok. (Search Engine Land)
- 58.67% of all website traffic worldwide comes from mobile phones. (Statista)
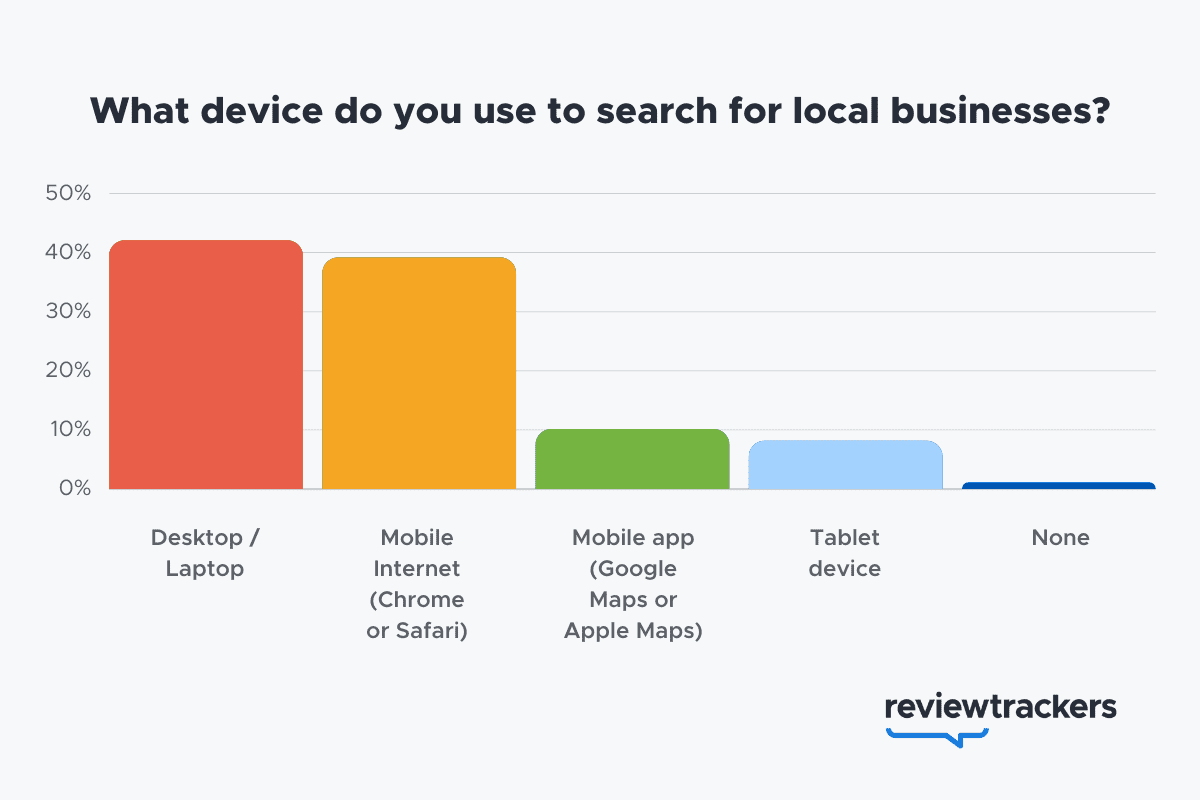
- 57% of local search queries are submitted using a mobile device or tablet. (ReviewTrackers)

- 51% of smartphone users have discovered a new company or product when conducting a search on their smartphones. (Think With Google)
- 54% of smartphone users search for business hours, and 53% search for directions to local stores. (Think With Google)
- 18% of local searches on smartphones lead to a purchase within a day vs. 7% of non-local searches. (Think With Google)
- 56% of in-store shoppers used their smartphones to shop or research items while they were in-store. (Think With Google)
- 60% of smartphone users have contacted a business directly using the search results (e.g., “click to call” option). (Think With Google)
- 63.6% of consumers say they are likely to check reviews on Google before visiting a business location. (ReviewTrackers)
- 88% of consumers would use a business that replies to all of its reviews. (BrightLocal)
- Customers are 2.7 times more likely to consider a business reputable if they find a complete Business Profile on Google Search and Maps. (Google)
- Customers are 70% more likely to visit and 50% more likely to consider purchasing from businesses with a complete Business Profile. (Google)
- 76% of people who search on their smartphones for something nearby visit a business within a day. (Think With Google)
- 28% of searches for something nearby result in a purchase. (Think With Google)
- Mobile searches for “store open near me” (such as, “grocery store open near me” have grown by over 250% in the last two years. (Think With Google)
- People use Google Lens for 12 billion visual searches a month. (Google)
- 50% of online shoppers say images helped them decide what to buy. (Think With Google)
- There are an estimated 136 billion indexed images on Google Image Search. (Photutorial)
- 15.8% of Google SERPs show images. (Moz)
- People click on 3D images almost 50% more than static ones. (Google)
- More than 800 million people use Google Discover monthly to stay updated on their interests. (Google)
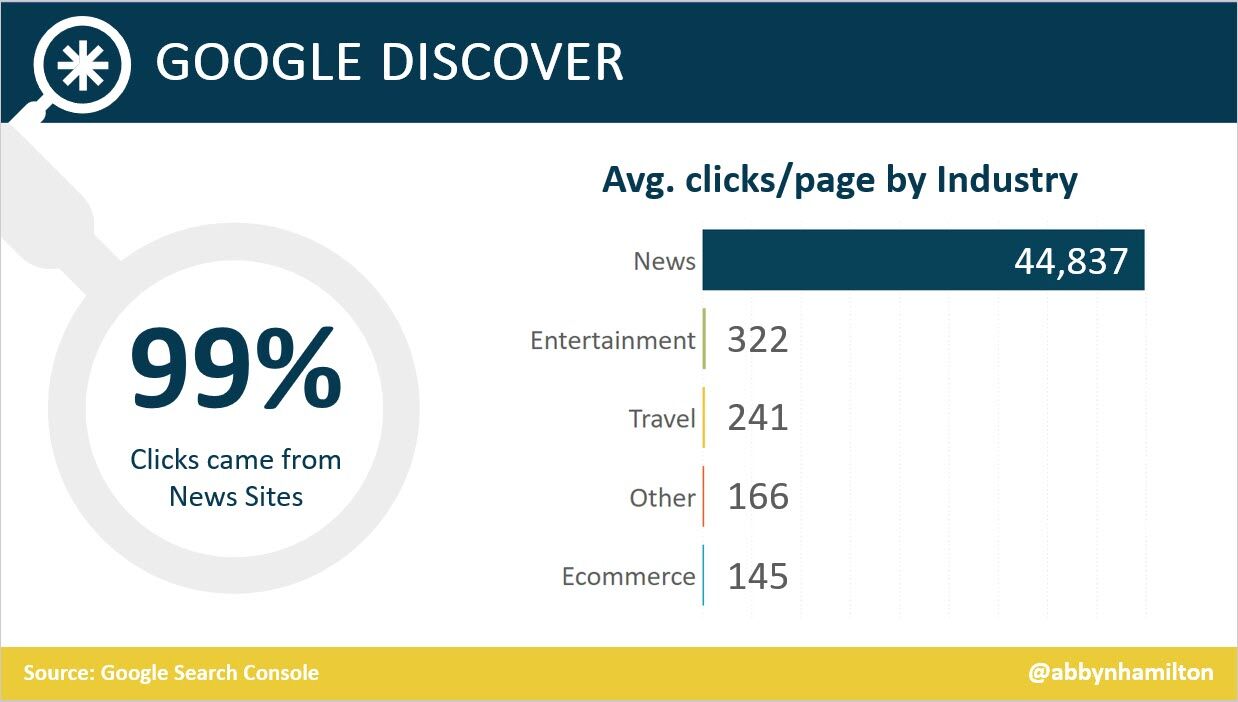
- 46% of Google Discover URLs are news sites, 44% e-commerce, 7% entertainment, and 2% travel. (Search Engine Journal)
- Even though news sites accounted for under 50% of Google Discover URLs, they received 99% of Discover clicks. (Search Engine Journal)

- Most Google Discover URLs only receive traffic for three to four days, with most of that traffic occurring one to two days after publishing. (Search Engine Journal)
- The clickthrough rate (CTR) for Google Discover is 11%. (Search Engine Journal)
- 91.45% of search volumes in Google Ads Keyword Planner are overestimates. (Ahrefs)
- For every $1 a business spends on Google Ads, they receive $8 in profit through Google Search and Ads. (Google)
- Google removed 5.5 billion ads, suspended 12.7 million advertiser accounts, restricted over 6.9 billion ads, and restricted ads from showing up on 2.1 billion publisher pages in 2023. (Google)
- The average shopping click-through rate (CTR) across all industries is 0.86% for Google Ads. (Wordstream)
- The average shopping cost per click (CPC) across all industries is $0.66 for Google Ads. (Wordstream)
- The average shopping conversion rate (CVR) across all industries is 1.91% for Google Ads. (Wordstream)
- 58% of consumers ages 25-34 use voice search daily. (UpCity)
- 16% of people use voice search for local “near me” searches. (UpCity)
- 67% of consumers say they’re very likely to use voice search when seeking information. (UpCity)
- Active users of the Google Assistant grew 4X over the past year, as of 2019. (Think With Google)
- Google Assistant hit 1 billion app installs. (Android Police)
- AI-generated answers from SGE were available for 91% of entertainment queries but only 17% of healthcare queries. (Statista)
- The AI-generated answers in Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) do not match any links from the top 10 Google organic search results 93.8% of the time. (Search Engine Journal)
- Google displays a Search Generative element for 86.8% of all search queries. (Authoritas)
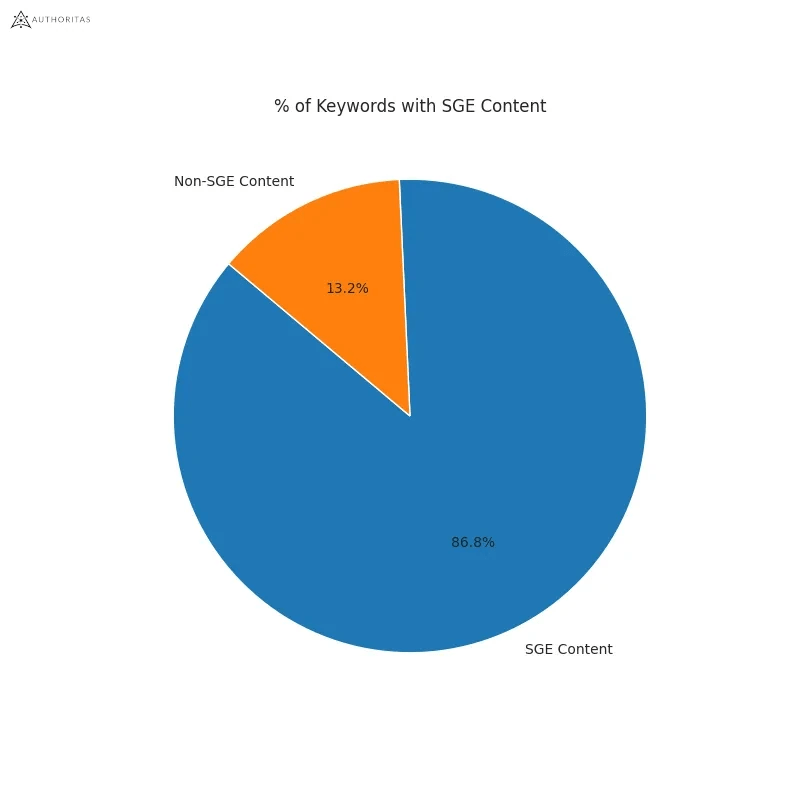

- 62% of generative links came from sources outside the top 10 ranking organic domains. Only 20.1% of generative URLs directly match an organic URL ranking on page one. (Authoritas)
- 70% of SEOs said that they were worried about the impact of SGE on organic search (Aira)
Learn more
Check out more resources on how Google works:
SEO
How To Use ChatGPT For Keyword Research

Anyone not using ChatGPT for keyword research is missing a trick.
You can save time and understand an entire topic in seconds instead of hours.
In this article, I outline my most effective ChatGPT prompts for keyword research and teach you how I put them together so that you, too, can take, edit, and enhance them even further.
But before we jump into the prompts, I want to emphasize that you shouldn’t replace keyword research tools or disregard traditional keyword research methods.
ChatGPT can make mistakes. It can even create new keywords if you give it the right prompt. For example, I asked it to provide me with a unique keyword for the topic “SEO” that had never been searched before.
“Interstellar Internet SEO: Optimizing content for the theoretical concept of an interstellar internet, considering the challenges of space-time and interplanetary communication delays.”
Although I want to jump into my LinkedIn profile and update my title to “Interstellar Internet SEO Consultant,” unfortunately, no one has searched that (and they probably never will)!
You must not blindly rely on the data you get back from ChatGPT.
What you can rely on ChatGPT for is the topic ideation stage of keyword research and inspiration.
ChatGPT is a large language model trained with massive amounts of data to accurately predict what word will come next in a sentence. However, it does not know how to do keyword research yet.
Instead, think of ChatGPT as having an expert on any topic armed with the information if you ask it the right question.
In this guide, that is exactly what I aim to teach you how to do – the most essential prompts you need to know when performing topical keyword research.
Best ChatGPT Keyword Research Prompts
The following ChatGPT keyword research prompts can be used on any niche, even a topic to which you are brand new.
For this demonstration, let’s use the topic of “SEO” to demonstrate these prompts.
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Topic
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Topic}?
The first prompt is to give you an idea of the niche.
As shown above, ChatGPT did a great job understanding and breaking down SEO into three pillars: on-page, off-page & technical.
The key to the following prompt is to take one of the topics ChatGPT has given and query the sub-topics.
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Sub-topic}?
For this example, let’s query, “What are the most popular sub-topics related to keyword research?”
Having done keyword research for over 10 years, I would expect it to output information related to keyword research metrics, the types of keywords, and intent.
Let’s see.
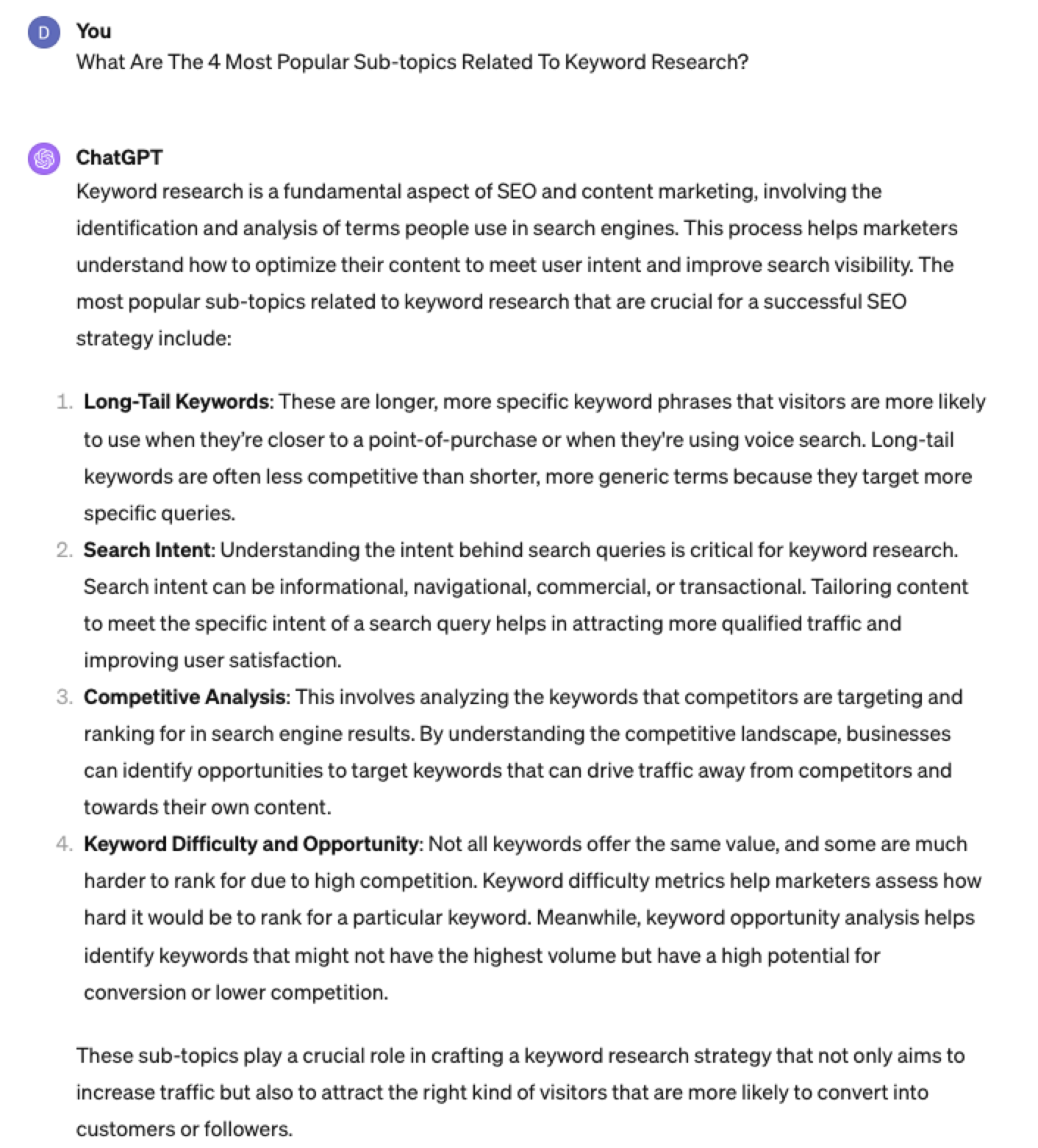 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, right on the money.
To get the keywords you want without having ChatGPT describe each answer, use the prompt “list without description.”
Here is an example of that.
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Keywords For The Topic Of {X}
You can even branch these keywords out further into their long-tail.
Example prompt:
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Long-tail Keywords For The Topic “{X}”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024List Without Description The Top Semantically Related Keywords And Entities For The Topic {X}
You can even ask ChatGPT what any topic’s semantically related keywords and entities are!
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: The Onion Method Of Prompting ChatGPT
When you are happy with a series of prompts, add them all to one prompt. For example, so far in this article, we have asked ChatGPT the following:
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to SEO?
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to keyword research
- List without description the top five most popular keywords for “keyword intent”?
- List without description the top five most popular long-tail keywords for the topic “keyword intent types”?
- List without description the top semantically related keywords and entities for the topic “types of keyword intent in SEO.”
Combine all five into one prompt by telling ChatGPT to perform a series of steps. Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4, and Step 5”
Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4 and Step 5. Step 1 – Generate an answer for the 3 most popular sub-topics related to {Topic}?. Step 2 – Generate 3 of the most popular sub-topics related to each answer. Step 3 – Take those answers and list without description their top 3 most popular keywords. Step 4 – For the answers given of their most popular keywords, provide 3 long-tail keywords. Step 5 – for each long-tail keyword offered in the response, a list without descriptions 3 of their top semantically related keywords and entities.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Question
Taking the steps approach from above, we can get ChatGPT to help streamline getting keyword ideas based on a question. For example, let’s ask, “What is SEO?”
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, and Step 4. Step 1 Generate 10 questions about “{Question}”?. Step 2 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 3 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 4 – Based on the above Steps 1,2,3 suggest a final list of questions avoiding duplicates or semantically similar questions.”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On The Alphabet Soup Method
One of my favorite methods, manually, without even using a keyword research tool, is to generate keyword research ideas from Google autocomplete, going from A to Z.
-
 Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
You can also do this using ChatGPT.
Example prompt:
“give me popular keywords that includes the keyword “SEO”, and the next letter of the word starts with a”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: Using the onion prompting method above, we can combine all this in one prompt.
“Give me five popular keywords that include “SEO” in the word, and the following letter starts with a. Once the answer has been done, move on to giving five more popular keywords that include “SEO” for each letter of the alphabet b to z.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On User Personas
When it comes to keyword research, understanding user personas is essential for understanding your target audience and keeping your keyword research focused and targeted. ChatGPT may help you get an initial understanding of customer personas.
Example prompt:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of user personas”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024You could even go a step further and ask for questions based on those topics that those specific user personas may be searching for:
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024As well as get the keywords to target based on those questions:
“For each question listed above for each persona, list the keywords, as well as the long-tail keywords to target, and put them in a table”
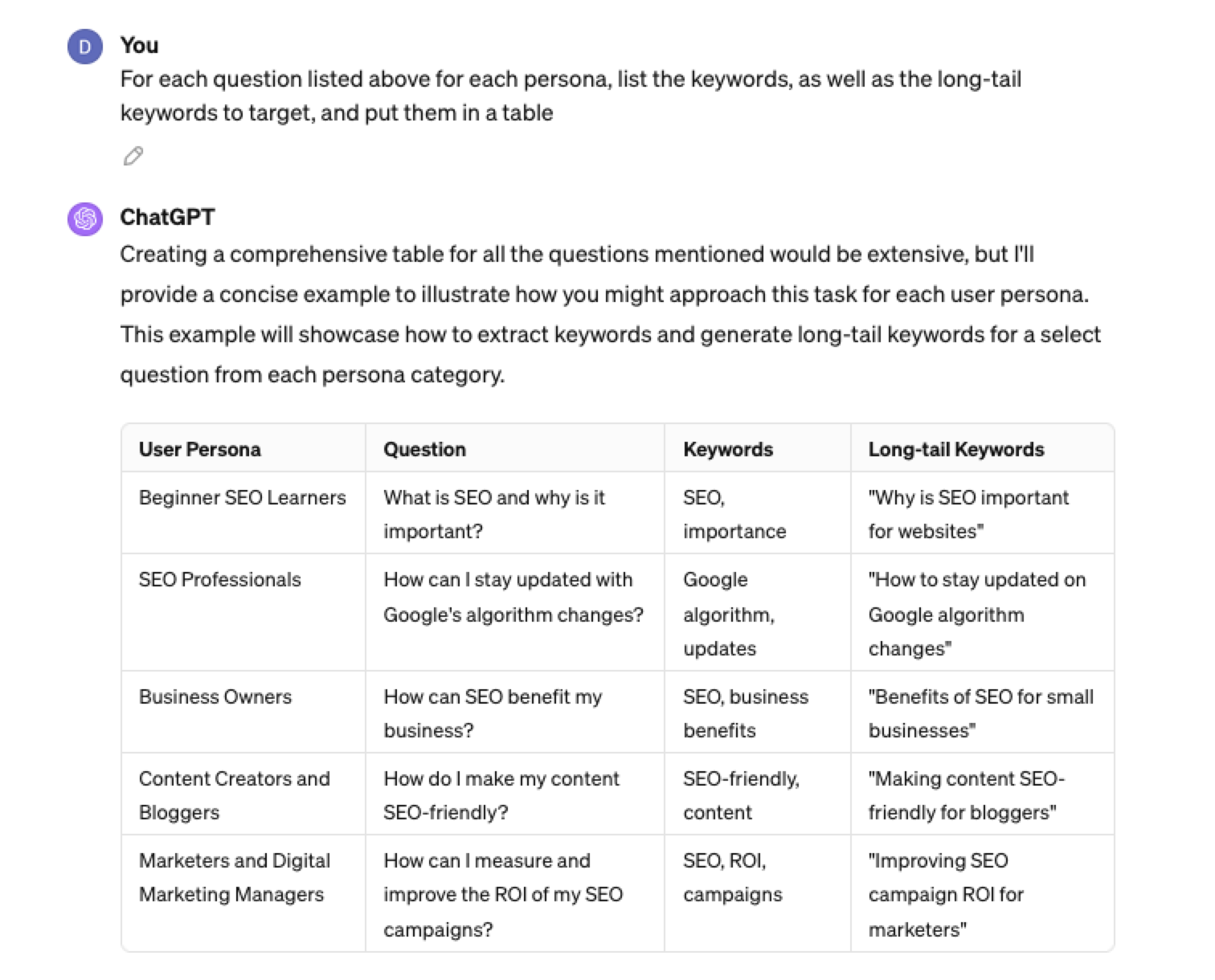 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On Searcher Intent And User Personas
Understanding the keywords your target persona may be searching is the first step to effective keyword research. The next step is to understand the search intent behind those keywords and which content format may work best.
For example, a business owner who is new to SEO or has just heard about it may be searching for “what is SEO.”
However, if they are further down the funnel and in the navigational stage, they may search for “top SEO firms.”
You can query ChatGPT to inspire you here based on any topic and your target user persona.
SEO Example:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of searcher intent that a {Target Persona} would be searching for”
ChatGPT For Keyword Research Admin
Here is how you can best use ChatGPT for keyword research admin tasks.
Using ChatGPT As A Keyword Categorization Tool
One of the use cases for using ChatGPT is for keyword categorization.
In the past, I would have had to devise spreadsheet formulas to categorize keywords or even spend hours filtering and manually categorizing keywords.
ChatGPT can be a great companion for running a short version of this for you.
Let’s say you have done keyword research in a keyword research tool, have a list of keywords, and want to categorize them.
You could use the following prompt:
“Filter the below list of keywords into categories, target persona, searcher intent, search volume and add information to a six-column table: List of keywords – [LIST OF KEYWORDS], Keyword Search Volume [SEARCH VOLUMES] and Keyword Difficulties [KEYWORD DIFFICUTIES].”
-
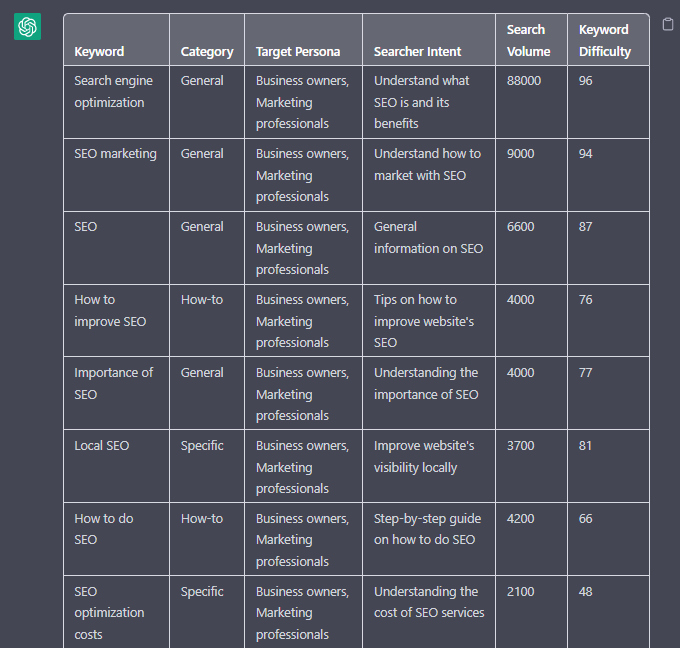 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Tip: Add keyword metrics from the keyword research tools, as using the search volumes that a ChatGPT prompt may give you will be wildly inaccurate at best.
Using ChatGPT For Keyword Clustering
Another of ChatGPT’s use cases for keyword research is to help you cluster. Many keywords have the same intent, and by grouping related keywords, you may find that one piece of content can often target multiple keywords at once.
However, be careful not to rely only on LLM data for clustering. What ChatGPT may cluster as a similar keyword, the SERP or the user may not agree with. But it is a good starting point.
The big downside of using ChatGPT for keyword clustering is actually the amount of keyword data you can cluster based on the memory limits.
So, you may find a keyword clustering tool or script that is better for large keyword clustering tasks. But for small amounts of keywords, ChatGPT is actually quite good.
A great use small keyword clustering use case using ChatGPT is for grouping People Also Ask (PAA) questions.
Use the following prompt to group keywords based on their semantic relationships. For example:
“Organize the following keywords into groups based on their semantic relationships, and give a short name to each group: [LIST OF PAA], create a two-column table where each keyword sits on its own row.
-
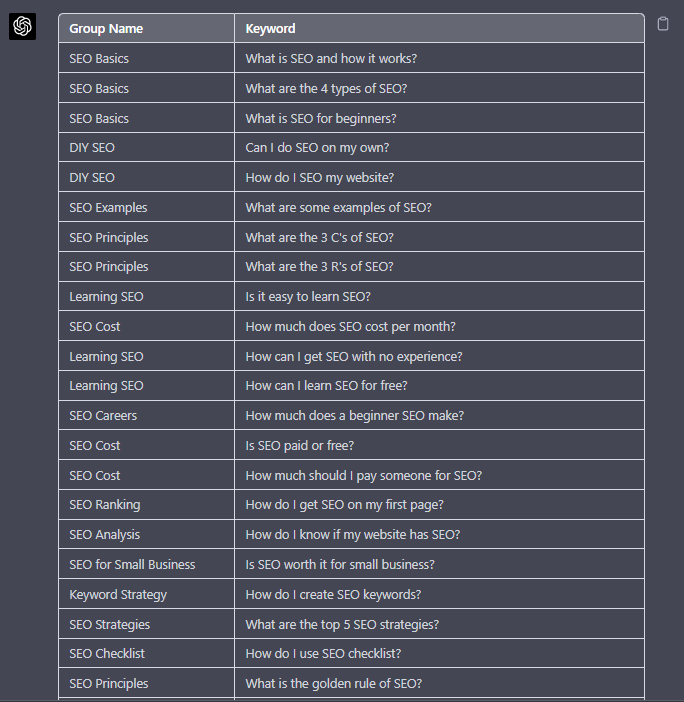 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Using Chat GPT For Keyword Expansion By Patterns
One of my favorite methods of doing keyword research is pattern spotting.
Most seed keywords have a variable that can expand your target keywords.
Here are a few examples of patterns:
1. Question Patterns
(who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will)
“Generate [X] keywords for the topic “[Topic]” that contain any or all of the following “who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20242. Comparison Patterns
Example:
“Generate 50 keywords for the topic “{Topic}” that contain any or all of the following “for, vs, alternative, best, top, review”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20243. Brand Patterns
Another one of my favorite modifiers is a keyword by brand.
We are probably all familiar with the most popular SEO brands; however, if you aren’t, you could ask your AI friend to do the heavy lifting.
Example prompt:
“For the top {Topic} brands what are the top “vs” keywords”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20244. Search Intent Patterns
One of the most common search intent patterns is “best.”
When someone is searching for a “best {topic}” keyword, they are generally searching for a comprehensive list or guide that highlights the top options, products, or services within that specific topic, along with their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks, to make an informed decision.
Example:
“For the topic of “[Topic]” what are the 20 top keywords that include “best”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, this guide to keyword research using ChatGPT has emphasized the ease of generating keyword research ideas by utilizing ChatGPT throughout the process.
Keyword Research Using ChatGPT Vs. Keyword Research Tools
Free Vs. Paid Keyword Research Tools
Like keyword research tools, ChatGPT has free and paid options.
However, one of the most significant drawbacks of using ChatGPT for keyword research alone is the absence of SEO metrics to help you make smarter decisions.
To improve accuracy, you could take the results it gives you and verify them with your classic keyword research tool – or vice versa, as shown above, uploading accurate data into the tool and then prompting.
However, you must consider how long it takes to type and fine-tune your prompt to get your desired data versus using the filters within popular keyword research tools.
For example, if we use a popular keyword research tool using filters, you could have all of the “best” queries with all of their SEO metrics:
-
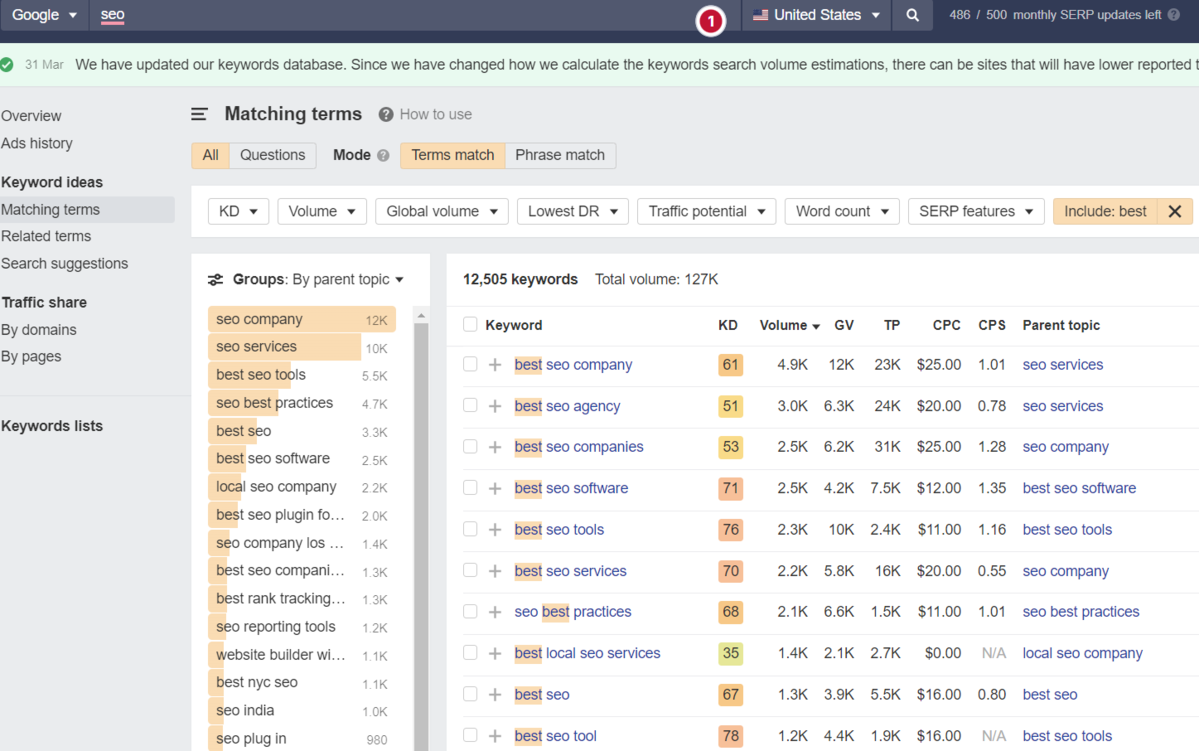 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
And unlike ChatGPT, generally, there is no token limit; you can extract several hundred, if not thousands, of keywords at a time.
As I have mentioned multiple times throughout this piece, you cannot blindly trust the data or SEO metrics it may attempt to provide you with.
The key is to validate the keyword research with a keyword research tool.
ChatGPT For International SEO Keyword Research
ChatGPT can be a terrific multilingual keyword research assistant.
For example, if you wanted to research keywords in a foreign language such as French. You could ask ChatGPT to translate your English keywords;
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024- The key is to take the data above and paste it into a popular keyword research tool to verify.
- As you can see below, many of the keyword translations for the English keywords do not have any search volume for direct translations in French.
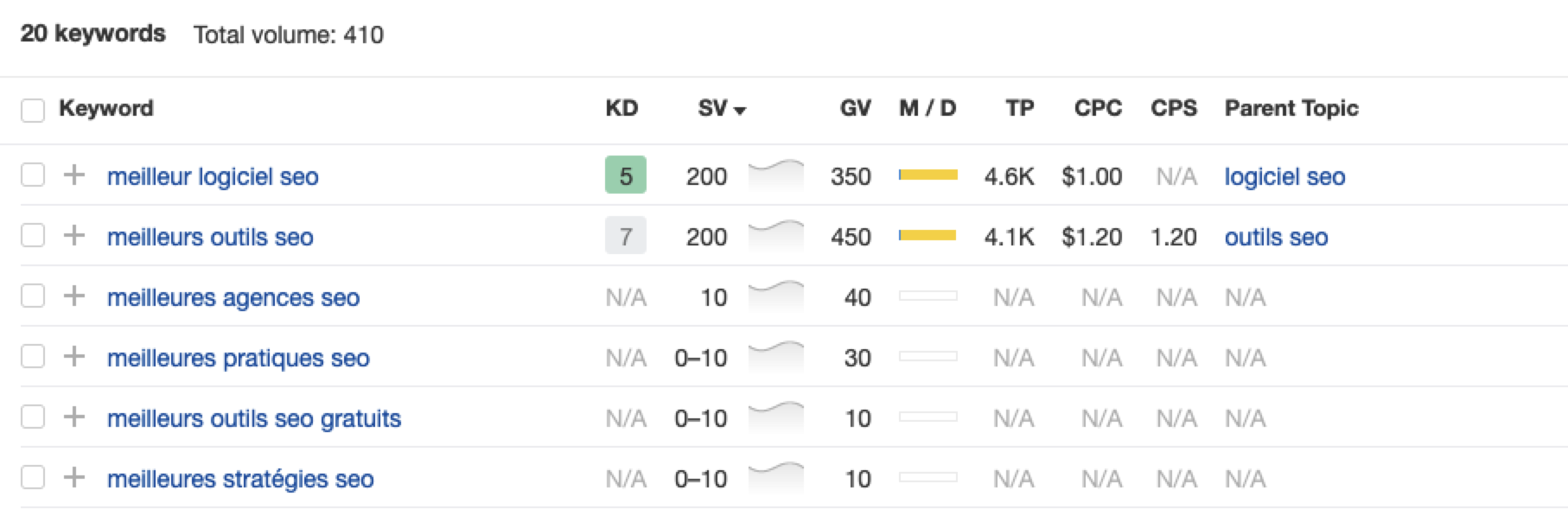 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024But don’t worry, there is a workaround: If you have access to a competitor keyword research tool, you can see what webpage is ranking for that query – and then identify the top keyword for that page based on the ChatGPT translated keywords that do have search volume.
-
-
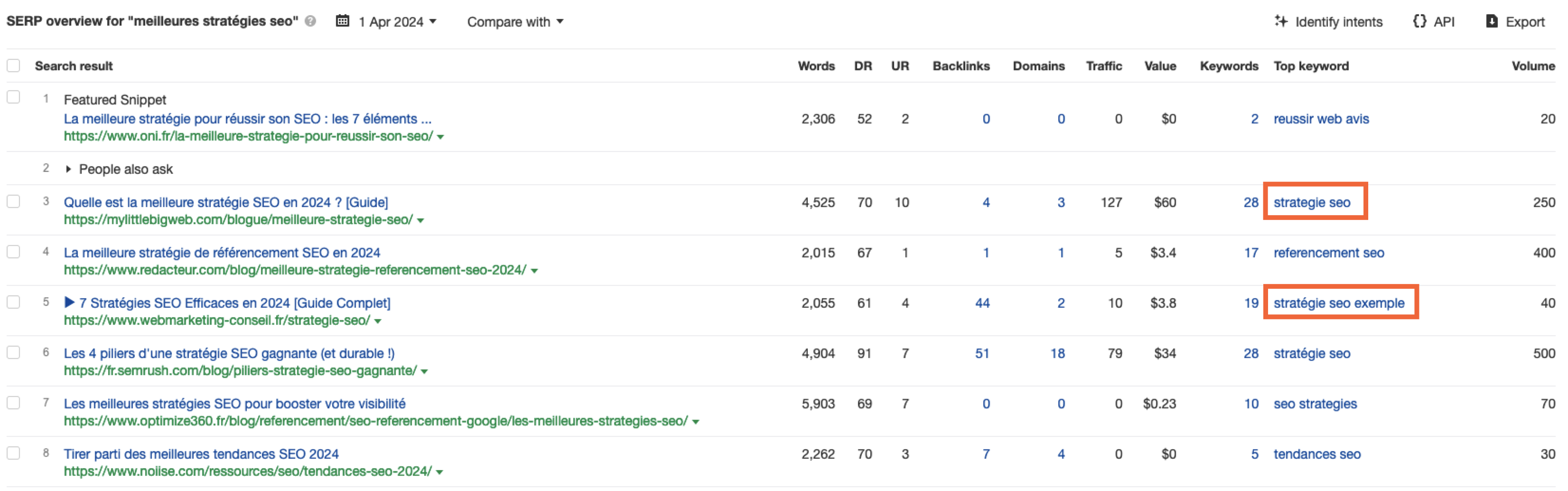 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Or, if you don’t have access to a paid keyword research tool, you could always take the top-performing result, extract the page copy, and then ask ChatGPT what the primary keyword for the page is.
Key Takeaway
-
ChatGPT can be an expert on any topic and an invaluable keyword research tool. However, it is another tool to add to your toolbox when doing keyword research; it does not replace traditional keyword research tools.
As shown throughout this tutorial, from making up keywords at the beginning to inaccuracies around data and translations, ChatGPT can make mistakes when used for keyword research.
You cannot blindly trust the data you get back from ChatGPT.
However, it can offer a shortcut to understanding any topic for which you need to do keyword research and, as a result, save you countless hours.
But the key is how you prompt.
The prompts I shared with you above will help you understand a topic in minutes instead of hours and allow you to better seed keywords using keyword research tools.
It can even replace mundane keyword clustering tasks that you used to do with formulas in spreadsheets or generate ideas based on keywords you give it.
Paired with traditional keyword research tools, ChatGPT for keyword research can be a powerful tool in your arsenal.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tatiana Shepeleva/Shutterstock
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoHow the TikTok Algorithm Works in 2024 (+9 Ways to Go Viral)
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days agoHow to Use Keywords for SEO: The Complete Beginner’s Guide
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoBlog Post Checklist: Check All Prior to Hitting “Publish”
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoHow To Protect Your People and Brand
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days agoHow to Brainstorm Business Ideas: 9 Fool-Proof Approaches
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoElevating Women in SEO for a More Inclusive Industry
-

 MARKETING3 days ago
MARKETING3 days agoAdvertising on Hulu: Ad Formats, Examples & Tips
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoThe Ultimate Guide to Email Marketing
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login