SEO
A Simple (But Effective) 14-Step SEO Audit & Checklist
An SEO audit is where you find opportunities to improve a site’s search performance. It involves finding technical, on-page, content, and link-related issues to fix or improve.
Everyone’s SEO audit process differs, as there’s no universal approach. But there are a handful of basic issues all site owners should look for.
You’ll learn how to check for 14 of them in this guide.
Manual actions are when a human reviewer at Google decides that your site doesn’t comply with their webmaster guidelines. The result is that some or all of your site won’t be shown in Google’s search results.
You’re unlikely to have a manual action unless you’ve done something drastically wrong. But it’s still arguably the best first thing to check because if you have one, you’re dead in the water before you even start.
To check for manual actions, go to the Manual actions report in Google Search Console.

If it says anything other than “No issues detected,” read our Google penalties guide.
Google updates its search algorithms all the time. Many of these updates target specific things like link spam or content quality.
For that reason, it’s important to check for organic traffic drops coinciding with known Google updates, as these may point to specific issues.
For example, the core update in August 2018 appeared to largely affect health, fitness, and medical sites that failed to demonstrate expertise, authoritativeness, and trust (E-A-T). In fact, Barry Schwartz, a prominent blogger, dubbed it the “Medic” update.
The update all but destroyed some sites, like this one:

You can check your organic traffic trend for free in Google Search Console. Just go to the Search results report and set the period to the past year or two.

You can also see an estimated traffic graph in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, where you can also overlay known Google updates to more easily diagnose issues.
For example, we can see that this site’s traffic drop coincided with a core update:

If you spot a big traffic drop coinciding with a Google update, check our Google Algorithm Updates History page to see the focus of the update.
HTTPS is a secure protocol for transferring data to and from visitors. It helps to keep things like passwords and credit card details secure, and it’s been a small Google ranking factor since 2014.
You can check if your website uses HTTPS by visiting it. If there’s a “lock” icon in the address bar, it’s secure.

However, some websites face issues where certain pages load securely, but other pages and resources don’t. So we recommend digging a bit deeper to make sure there are no HTTPS-related issues. Here’s how:
- Sign up for a free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools account
- Crawl your site with Site Audit
- Go to the Internal pages report
From here, check the “Protocols distribution” graph to see whether any pages are using HTTP. Ideally, you want to see an all-green graph.

Recommendation
- Click on “HTTP”
- Sort the report by status code from low to high
- Add a column for “Final redirect URL”
If the lowest HTTP status code is “301” and the final redirect URLs all begin with HTTPS, everything is fine.

Next, hit the “Issues” tab and look for the “HTTPS/HTTP mixed content” issue. This indicates that while your initial HTML is loading over a secure HTTPS connection, some resource files like images load over an unsecure one.

If you see either of these issues, read our HTTPS guide to learn more about dealing with them.
People should only be able to access one of these four versions of your website:
http://domain.com http://www.domain.com https://domain.com https://www.domain.com
The other three variations should redirect to the canonical (master) version.
This is important because Google sees all four of these as separate site versions. Having more than one accessible can cause crawling and indexing issues. In some cases, it can even dilute link equity and, thus, may negatively impact rankings.
To check that everything works as it should, install Ahrefs’ SEO Toolbar, type each URL version into your browser, then check the HTTP headers to make sure they all redirect to the same “master” version.
For example, if we visit http://ahrefs.com, it redirects to the secure version at https://ahrefs.com.

The same happens if we visit the secure www version (https://www.ahrefs.com).

If this doesn’t happen, you’ll need to implement redirects.
Learn more: Redirects for SEO: A Simple (But Complete) Guide
Google search results come from its index, which is a database of hundreds of billions of webpages. Your pages need to be in this index to stand any chance at ranking.
It’s also important to keep pages that aren’t valuable for searchers out of Google’s index, as this can also cause SEO issues.
Indexing issues can get quite complicated, but you can check for basic issues fairly easily.
First, check the Indexability report in Site Audit for “Noindex page” warnings.

Google can’t index pages with this warning, so it’s worth checking they’re not pages you want indexed. If they are, remove or edit the meta robots tag.
Second, check the number of indexable URLs in the same report.

Investigate further if this looks abnormally high.
For example, given that we only have around 500 published blog posts, 2,164 indexable URLs seem high for the Ahrefs blog. But if we click the number, we see that it’s because it includes versions of our blog in other languages.

If we exclude those pages, along with author, category, and pagination pages, the number of indexable URLs looks pretty much spot on.

Mobile-friendliness has been a ranking factor everywhere since Google moved to mobile-first indexing in 2019.
Checking for mobile-friendliness is easily done. Just go to the Mobile Usability report in Google Search Console. It tells you whether any URLs have errors that affect mobile usability.

If you don’t have access to Google Search Console, plug any page from your website into Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.

In general, assuming that other pages on your website use the same design and layout, the result should apply to most, if not all, of your pages.
Learn more: Mobile-First Indexing: What You Need to Know
Page speed has been a small ranking factor on desktop since 2010 and mobile since 2018. However, there’s no official threshold for how fast a page should load, and there are a confusing number of metrics you can use as a proxy.
For example, Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool shows all kinds of metrics:

The other downside of this tool is that you can only test one page at a time.
For that reason, it’s better to start with a tool that’ll give you speed metrics on all your pages. You can do this in Ahrefs’ Site Audit, which you can use for free with an Ahrefs Webmaster Tools account. Here’s how:
- Crawl your website with Site Audit
- Go to the Performance report
- Check the “Time to first byte” and “Load time distribution” graphs

As a general rule, the more green you see here, the better. If you see lots of red, you may want to work on improving your page speed.
Core Web Vitals are metrics that Google uses to measure user experience. They measure a page’s load time, interactivity, and the stability of the content as it loads.
As they’re currently a weak ranking signal, you shouldn’t obsess over them. But it’s still worth taking a quick look at your site’s performance.
To do this, check the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console.

As this report is based on Chrome User Experience (CrUX) data, there’s a chance you may see a “Not enough data collected” or “Not enough recent usage data” message instead of data.
If that happens, head over to the Performance report in Ahrefs’ Site Audit and check the Lighthouse scores. As this is lab data, it doesn’t rely on user experience data from Google.

Having broken pages on your site is never good. If these pages have backlinks, they are effectively wasted because they point to nothing.
To find broken pages on your website, head to the Internal pages report in Site Audit and click the number under “Broken.”

If you want to see the number of backlinks to each of these pages, add the “No. of referring domains” column to the report.

You can also find broken URLs with backlinks in Site Explorer. Just plug in your domain, go to the Best by links report, add a “404 not found” filter, then sort the report by referring domains from high to low.

The benefit of using Site Explorer is that it shows URLs that people linked to accidentally.
For example, we have links from three referring domains to this URL:

This page never existed. The linkers just linked to the wrong URL. It should have an “s” at the end.
Here’s our recommended process for dealing with broken links:

A sitemap lists the pages that you want search engines to index. It shouldn’t list things like redirects, non-canonicals, or dead pages because those send mixed signals to Google.
To check for sitemap issues, head to the All issues report in Site Audit and scroll to the “Other” section.

You’ll see any issues here relating to:
- Dead or inaccessible pages in the sitemap.
- Noindexed pages in the sitemap.
- Non-canonical pages in the sitemap.
If you have any of these issues, hit the caret and follow the advice on fixing them.
Every indexable page on your site should have a title tag, meta description, and H1 tag. These basic on-page elements help Google understand your content and help you to win more clicks from your rankings.
To check for issues, head to the “Issues” tab in the Content report in Site Audit.

For example, the website above has 724 pages with a missing or empty title tag. This isn’t ideal because Google shows them in the search results, so the site could be missing out on clicks as a result.
It also has the same number of pages with an empty or missing meta description, and thousands with a missing or empty H1 tag.
Google often shows meta descriptions in the search results, so you should try to write an enticing one for every important page. Missing H1 tags, on the other hand, usually point to bigger issues like an improperly coded theme.
You can see which URLs are affected by clicking an issue and hitting “View affected URLs.”

If you want to prioritize fixes, sort the report by estimated organic traffic from high to low.

Rankings rarely last forever. As content becomes outdated, its search traffic will often start to drop off. But you can often solve this by refreshing and republishing the content.
For example, our list of top Google searches declined massively in 2021.

This is because we didn’t update the post for over a year, so the content became outdated. The recent spike in traffic is a result of us updating and republishing the piece.
Here’s an easy way to find declining content in Google Search Console:
- Go to the Search results report
- Set the date filter to compare mode
- Choose “Compare last 6 months to previous period”
- Click the “Pages” tab
- Sort the table by “Clicks Difference” from low to high
For example, this shows us that our list of the most visited websites has declined massively over the last six months. So this is probably ripe for an update.

If you’re a WordPress user, you can automate this process with our free SEO plugin. It monitors for pages that no longer perform well and gives recommendations on how to fix them.
For example, it’s suggesting that we rewrite our list of the best keyword tools because it used to rank in the top three for its target keyword but now doesn’t even rank in the top 100.

Content gaps occur when you miss important subtopics in your content. The result is that you don’t rank for as many long-tail keywords and potentially not as high as you could for your main target keyword.
Here’s an easy way to find content gaps:
- Paste one of your page’s URLs into Site Explorer
- Go to the Content Gap report
- Paste in the URLs of a few similar pages outranking you

Hit “Show keywords.” You’ll see all of the keywords that these pages rank for where yours don’t.
Many of these will just be different ways of searching for the same thing, but some may represent subtopics you’ve missed.
For example, when we do this for our page about “what is seo,” we see that competing pages are ranking for quite a few keywords relating to what SEO stands for.

This is an interesting case because we kind of covered this in our definition on the page:

However, we didn’t explicitly state that this is what SEO stands for. Many of our competitors did.


For that reason, it may be worth us stating this in a more explicit way.
Many other technical issues can hinder your rankings. That’s why it’s always worth crawling your site with a tool like Ahrefs’ Site Audit to check for other SEO issues.
For example, if we do this for Ahrefs’ blog, we find a redirect loop:

Redirect loops are something you’re unlikely to spot by chance. So this issue would have likely gone unnoticed without a crawl-based audit.
It looks like we also have missing alt text on over 2,400 images:

This is arguably not a huge problem, but the sheer number of affected images in this instance points to a likely hole in our processes.
Final thoughts
Running this SEO audit gives you three things to take action on to improve SEO.
- Technical SEO issues – Fixing these may boost your site’s overall search performance.
- On-page SEO issues – Fixing these may increase your organic clicks.
- Content opportunities – Pursuing these may rank pages higher and for more keywords.
If you want to run a deeper audit, read our guide to running a technical SEO audit.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.
SEO
How To Use ChatGPT For Keyword Research

Anyone not using ChatGPT for keyword research is missing a trick.
You can save time and understand an entire topic in seconds instead of hours.
In this article, I outline my most effective ChatGPT prompts for keyword research and teach you how I put them together so that you, too, can take, edit, and enhance them even further.
But before we jump into the prompts, I want to emphasize that you shouldn’t replace keyword research tools or disregard traditional keyword research methods.
ChatGPT can make mistakes. It can even create new keywords if you give it the right prompt. For example, I asked it to provide me with a unique keyword for the topic “SEO” that had never been searched before.
“Interstellar Internet SEO: Optimizing content for the theoretical concept of an interstellar internet, considering the challenges of space-time and interplanetary communication delays.”
Although I want to jump into my LinkedIn profile and update my title to “Interstellar Internet SEO Consultant,” unfortunately, no one has searched that (and they probably never will)!
You must not blindly rely on the data you get back from ChatGPT.
What you can rely on ChatGPT for is the topic ideation stage of keyword research and inspiration.
ChatGPT is a large language model trained with massive amounts of data to accurately predict what word will come next in a sentence. However, it does not know how to do keyword research yet.
Instead, think of ChatGPT as having an expert on any topic armed with the information if you ask it the right question.
In this guide, that is exactly what I aim to teach you how to do – the most essential prompts you need to know when performing topical keyword research.
Best ChatGPT Keyword Research Prompts
The following ChatGPT keyword research prompts can be used on any niche, even a topic to which you are brand new.
For this demonstration, let’s use the topic of “SEO” to demonstrate these prompts.
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Topic
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Topic}?
The first prompt is to give you an idea of the niche.
As shown above, ChatGPT did a great job understanding and breaking down SEO into three pillars: on-page, off-page & technical.
The key to the following prompt is to take one of the topics ChatGPT has given and query the sub-topics.
What Are The {X} Most Popular Sub-topics Related To {Sub-topic}?
For this example, let’s query, “What are the most popular sub-topics related to keyword research?”
Having done keyword research for over 10 years, I would expect it to output information related to keyword research metrics, the types of keywords, and intent.
Let’s see.
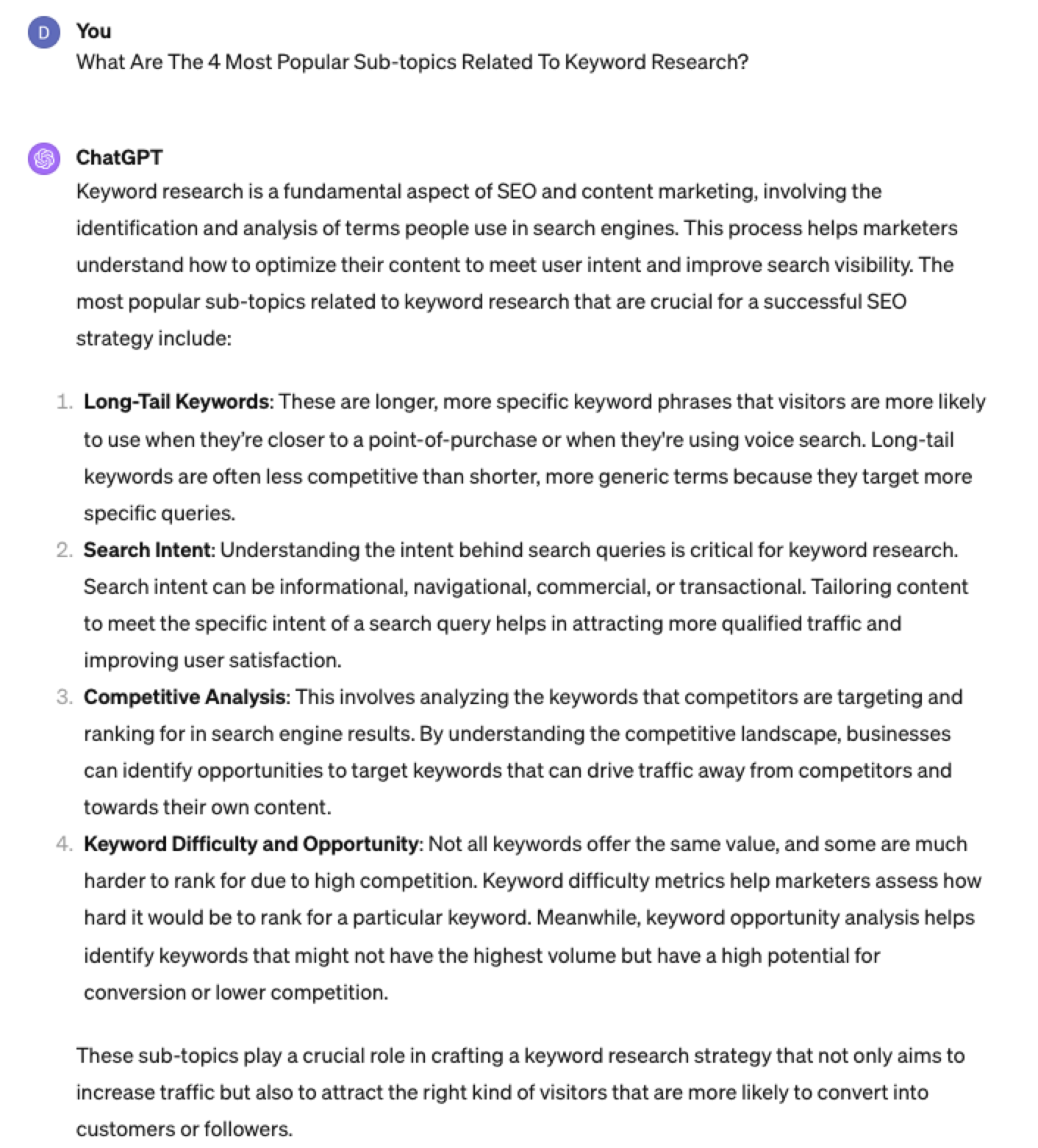 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, right on the money.
To get the keywords you want without having ChatGPT describe each answer, use the prompt “list without description.”
Here is an example of that.
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Keywords For The Topic Of {X}
You can even branch these keywords out further into their long-tail.
Example prompt:
List Without Description The Top {X} Most Popular Long-tail Keywords For The Topic “{X}”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4,April 2024List Without Description The Top Semantically Related Keywords And Entities For The Topic {X}
You can even ask ChatGPT what any topic’s semantically related keywords and entities are!
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: The Onion Method Of Prompting ChatGPT
When you are happy with a series of prompts, add them all to one prompt. For example, so far in this article, we have asked ChatGPT the following:
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to SEO?
- What are the four most popular sub-topics related to keyword research
- List without description the top five most popular keywords for “keyword intent”?
- List without description the top five most popular long-tail keywords for the topic “keyword intent types”?
- List without description the top semantically related keywords and entities for the topic “types of keyword intent in SEO.”
Combine all five into one prompt by telling ChatGPT to perform a series of steps. Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4, and Step 5”
Example:
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4 and Step 5. Step 1 – Generate an answer for the 3 most popular sub-topics related to {Topic}?. Step 2 – Generate 3 of the most popular sub-topics related to each answer. Step 3 – Take those answers and list without description their top 3 most popular keywords. Step 4 – For the answers given of their most popular keywords, provide 3 long-tail keywords. Step 5 – for each long-tail keyword offered in the response, a list without descriptions 3 of their top semantically related keywords and entities.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On A Question
Taking the steps approach from above, we can get ChatGPT to help streamline getting keyword ideas based on a question. For example, let’s ask, “What is SEO?”
“Perform the following steps in a consecutive order Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, and Step 4. Step 1 Generate 10 questions about “{Question}”?. Step 2 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 3 – Generate 5 more questions about “{Question}” that do not repeat the above. Step 4 – Based on the above Steps 1,2,3 suggest a final list of questions avoiding duplicates or semantically similar questions.”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On The Alphabet Soup Method
One of my favorite methods, manually, without even using a keyword research tool, is to generate keyword research ideas from Google autocomplete, going from A to Z.
-
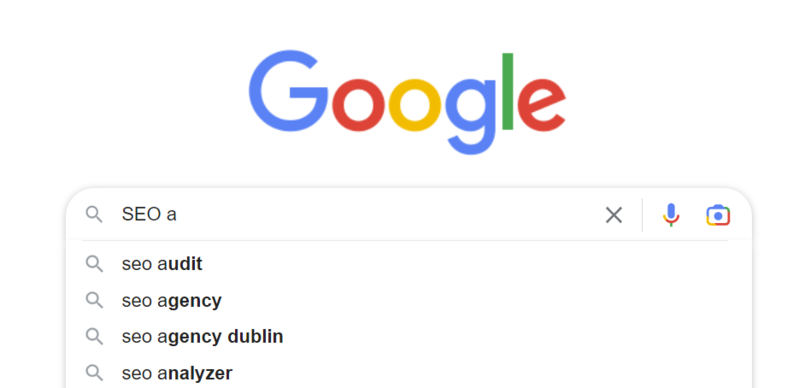 Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
Screenshot from Google autocomplete, April 2024
You can also do this using ChatGPT.
Example prompt:
“give me popular keywords that includes the keyword “SEO”, and the next letter of the word starts with a”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Tip: Using the onion prompting method above, we can combine all this in one prompt.
“Give me five popular keywords that include “SEO” in the word, and the following letter starts with a. Once the answer has been done, move on to giving five more popular keywords that include “SEO” for each letter of the alphabet b to z.”
Generating Keyword Ideas Based On User Personas
When it comes to keyword research, understanding user personas is essential for understanding your target audience and keeping your keyword research focused and targeted. ChatGPT may help you get an initial understanding of customer personas.
Example prompt:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of user personas”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024You could even go a step further and ask for questions based on those topics that those specific user personas may be searching for:
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024As well as get the keywords to target based on those questions:
“For each question listed above for each persona, list the keywords, as well as the long-tail keywords to target, and put them in a table”
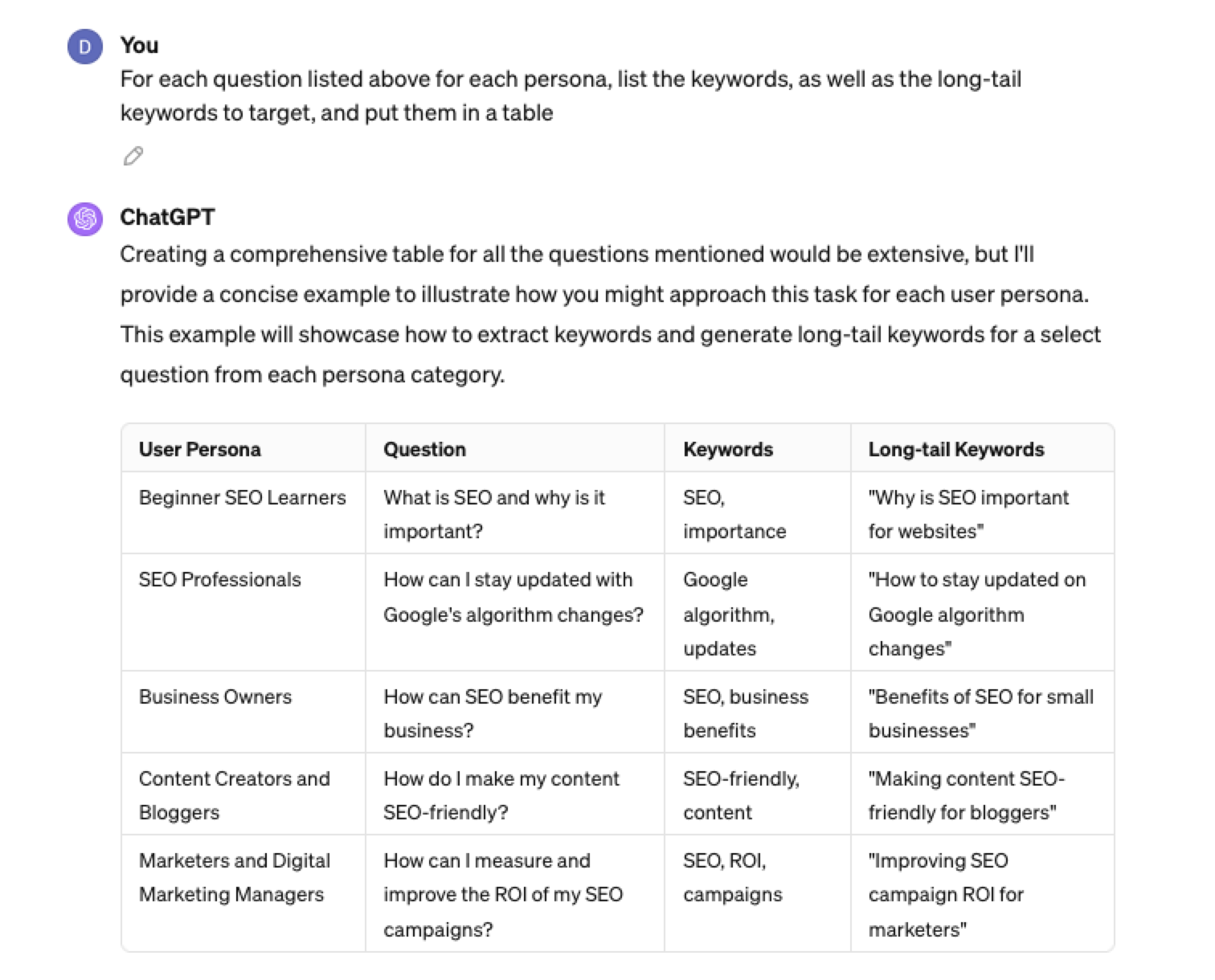 Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT 4, April 2024Generating Keyword Ideas Using ChatGPT Based On Searcher Intent And User Personas
Understanding the keywords your target persona may be searching is the first step to effective keyword research. The next step is to understand the search intent behind those keywords and which content format may work best.
For example, a business owner who is new to SEO or has just heard about it may be searching for “what is SEO.”
However, if they are further down the funnel and in the navigational stage, they may search for “top SEO firms.”
You can query ChatGPT to inspire you here based on any topic and your target user persona.
SEO Example:
“For the topic of “{Topic}” list 10 keywords each for the different types of searcher intent that a {Target Persona} would be searching for”
ChatGPT For Keyword Research Admin
Here is how you can best use ChatGPT for keyword research admin tasks.
Using ChatGPT As A Keyword Categorization Tool
One of the use cases for using ChatGPT is for keyword categorization.
In the past, I would have had to devise spreadsheet formulas to categorize keywords or even spend hours filtering and manually categorizing keywords.
ChatGPT can be a great companion for running a short version of this for you.
Let’s say you have done keyword research in a keyword research tool, have a list of keywords, and want to categorize them.
You could use the following prompt:
“Filter the below list of keywords into categories, target persona, searcher intent, search volume and add information to a six-column table: List of keywords – [LIST OF KEYWORDS], Keyword Search Volume [SEARCH VOLUMES] and Keyword Difficulties [KEYWORD DIFFICUTIES].”
-
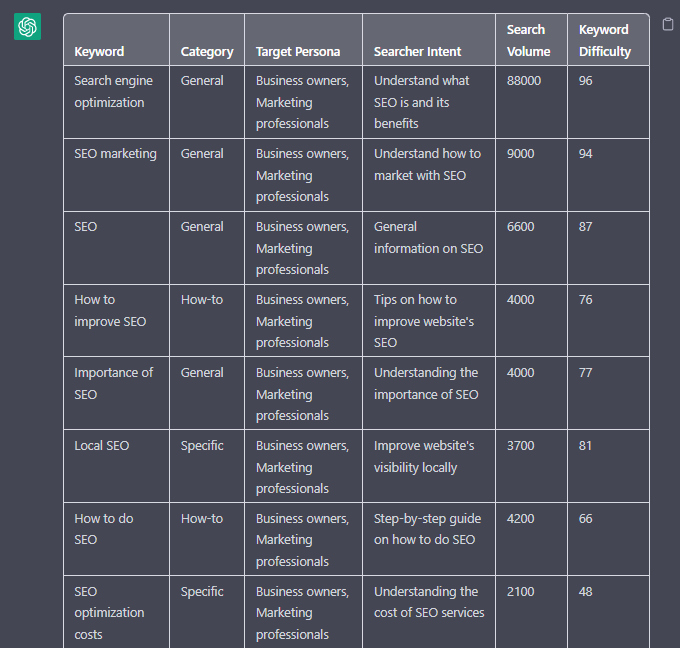 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Tip: Add keyword metrics from the keyword research tools, as using the search volumes that a ChatGPT prompt may give you will be wildly inaccurate at best.
Using ChatGPT For Keyword Clustering
Another of ChatGPT’s use cases for keyword research is to help you cluster. Many keywords have the same intent, and by grouping related keywords, you may find that one piece of content can often target multiple keywords at once.
However, be careful not to rely only on LLM data for clustering. What ChatGPT may cluster as a similar keyword, the SERP or the user may not agree with. But it is a good starting point.
The big downside of using ChatGPT for keyword clustering is actually the amount of keyword data you can cluster based on the memory limits.
So, you may find a keyword clustering tool or script that is better for large keyword clustering tasks. But for small amounts of keywords, ChatGPT is actually quite good.
A great use small keyword clustering use case using ChatGPT is for grouping People Also Ask (PAA) questions.
Use the following prompt to group keywords based on their semantic relationships. For example:
“Organize the following keywords into groups based on their semantic relationships, and give a short name to each group: [LIST OF PAA], create a two-column table where each keyword sits on its own row.
-
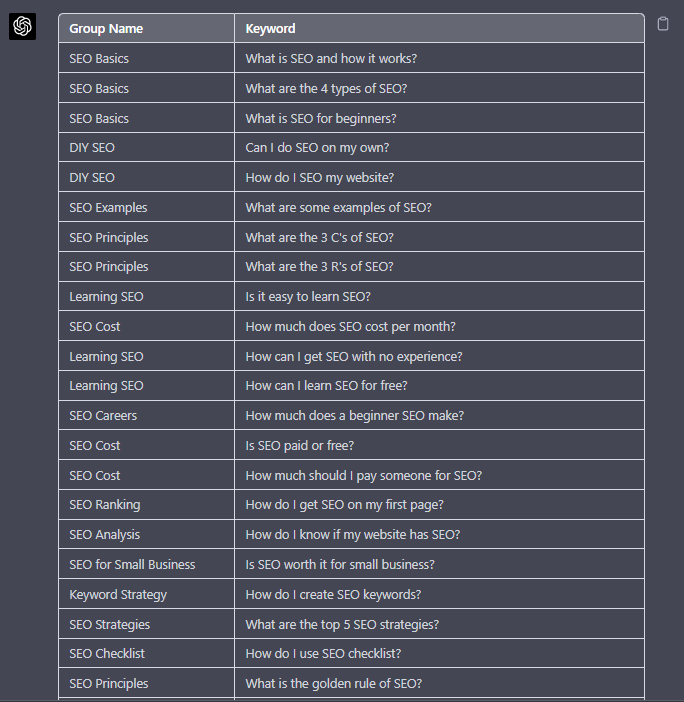 Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Screenshot from ChatGPT, April 2024
Using Chat GPT For Keyword Expansion By Patterns
One of my favorite methods of doing keyword research is pattern spotting.
Most seed keywords have a variable that can expand your target keywords.
Here are a few examples of patterns:
1. Question Patterns
(who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will)
“Generate [X] keywords for the topic “[Topic]” that contain any or all of the following “who, what, where, why, how, are, can, do, does, will”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20242. Comparison Patterns
Example:
“Generate 50 keywords for the topic “{Topic}” that contain any or all of the following “for, vs, alternative, best, top, review”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20243. Brand Patterns
Another one of my favorite modifiers is a keyword by brand.
We are probably all familiar with the most popular SEO brands; however, if you aren’t, you could ask your AI friend to do the heavy lifting.
Example prompt:
“For the top {Topic} brands what are the top “vs” keywords”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 20244. Search Intent Patterns
One of the most common search intent patterns is “best.”
When someone is searching for a “best {topic}” keyword, they are generally searching for a comprehensive list or guide that highlights the top options, products, or services within that specific topic, along with their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks, to make an informed decision.
Example:
“For the topic of “[Topic]” what are the 20 top keywords that include “best”
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, April 2024Again, this guide to keyword research using ChatGPT has emphasized the ease of generating keyword research ideas by utilizing ChatGPT throughout the process.
Keyword Research Using ChatGPT Vs. Keyword Research Tools
Free Vs. Paid Keyword Research Tools
Like keyword research tools, ChatGPT has free and paid options.
However, one of the most significant drawbacks of using ChatGPT for keyword research alone is the absence of SEO metrics to help you make smarter decisions.
To improve accuracy, you could take the results it gives you and verify them with your classic keyword research tool – or vice versa, as shown above, uploading accurate data into the tool and then prompting.
However, you must consider how long it takes to type and fine-tune your prompt to get your desired data versus using the filters within popular keyword research tools.
For example, if we use a popular keyword research tool using filters, you could have all of the “best” queries with all of their SEO metrics:
-
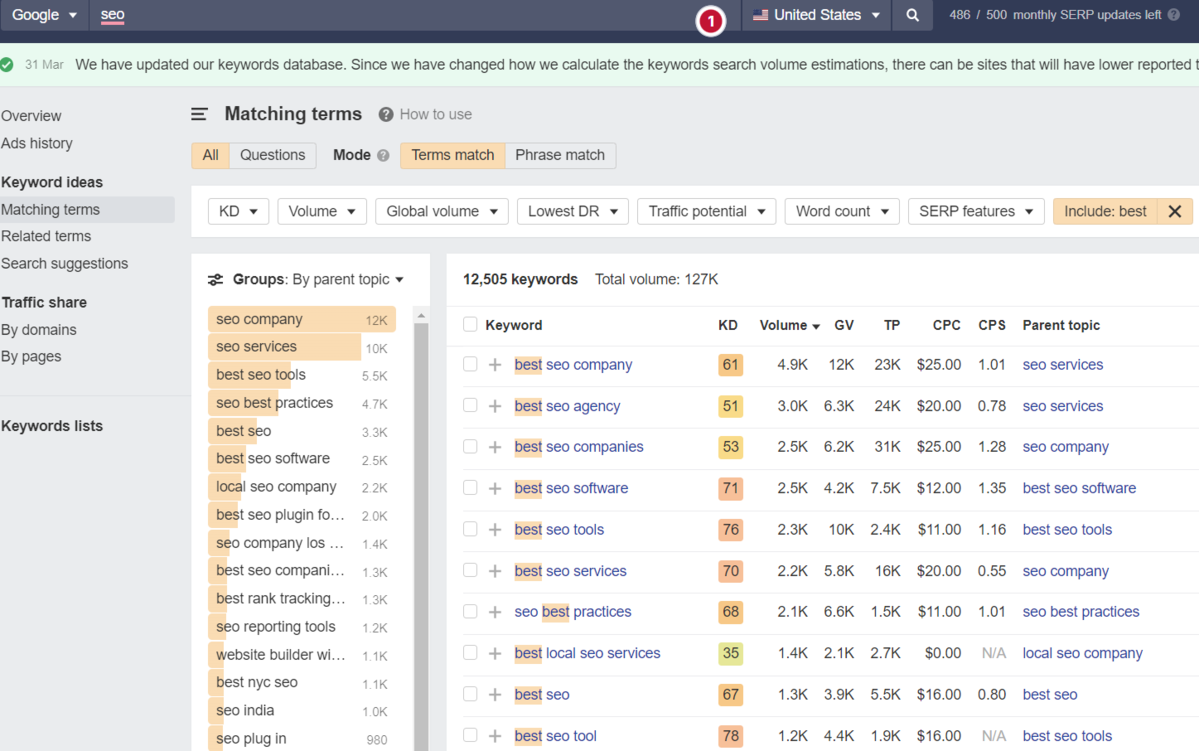 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, March 2024
And unlike ChatGPT, generally, there is no token limit; you can extract several hundred, if not thousands, of keywords at a time.
As I have mentioned multiple times throughout this piece, you cannot blindly trust the data or SEO metrics it may attempt to provide you with.
The key is to validate the keyword research with a keyword research tool.
ChatGPT For International SEO Keyword Research
ChatGPT can be a terrific multilingual keyword research assistant.
For example, if you wanted to research keywords in a foreign language such as French. You could ask ChatGPT to translate your English keywords;
 Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024
Screenshot ChatGPT 4, Apil 2024- The key is to take the data above and paste it into a popular keyword research tool to verify.
- As you can see below, many of the keyword translations for the English keywords do not have any search volume for direct translations in French.
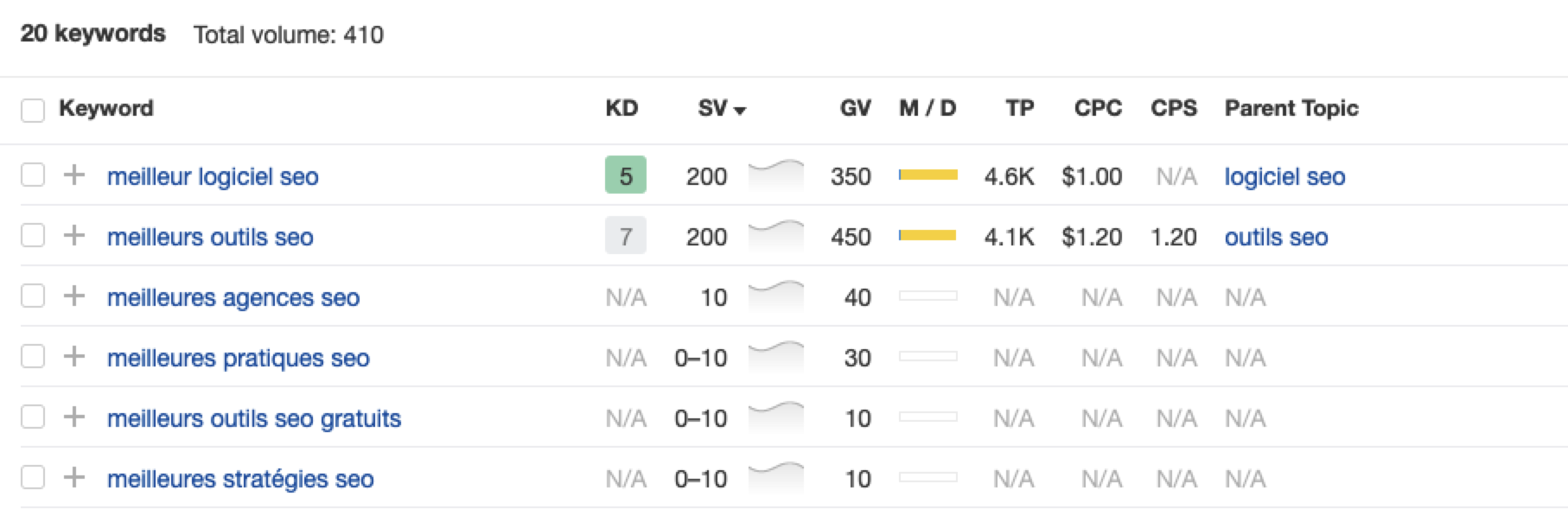 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024But don’t worry, there is a workaround: If you have access to a competitor keyword research tool, you can see what webpage is ranking for that query – and then identify the top keyword for that page based on the ChatGPT translated keywords that do have search volume.
-
-
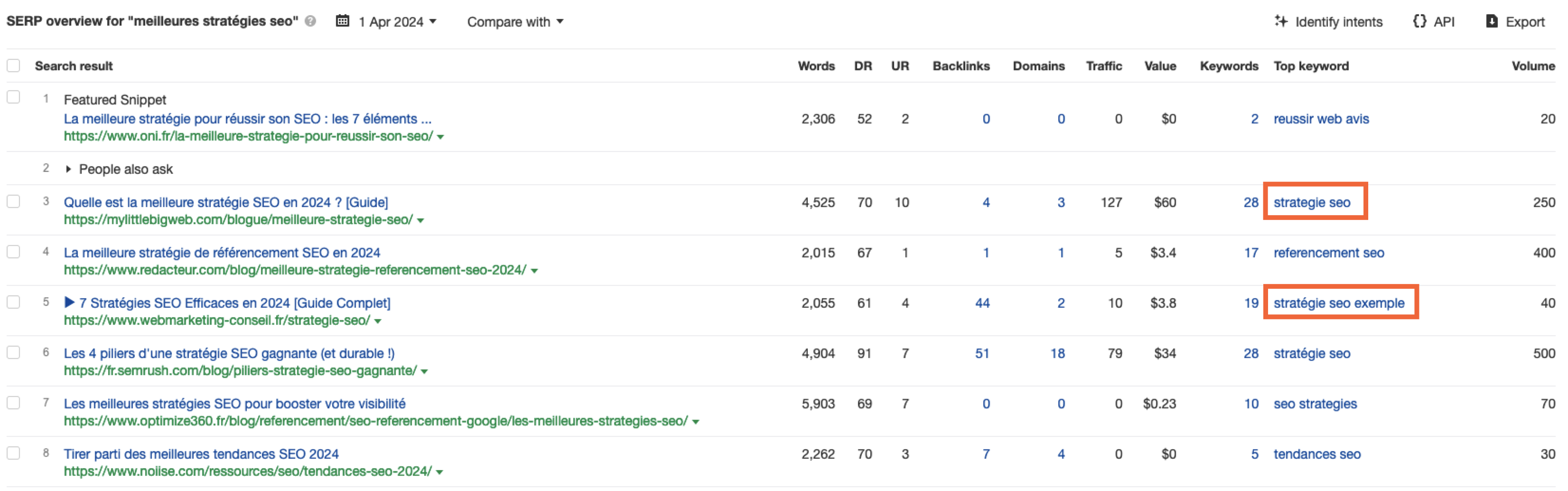 Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, April 2024
Or, if you don’t have access to a paid keyword research tool, you could always take the top-performing result, extract the page copy, and then ask ChatGPT what the primary keyword for the page is.
Key Takeaway
-
ChatGPT can be an expert on any topic and an invaluable keyword research tool. However, it is another tool to add to your toolbox when doing keyword research; it does not replace traditional keyword research tools.
As shown throughout this tutorial, from making up keywords at the beginning to inaccuracies around data and translations, ChatGPT can make mistakes when used for keyword research.
You cannot blindly trust the data you get back from ChatGPT.
However, it can offer a shortcut to understanding any topic for which you need to do keyword research and, as a result, save you countless hours.
But the key is how you prompt.
The prompts I shared with you above will help you understand a topic in minutes instead of hours and allow you to better seed keywords using keyword research tools.
It can even replace mundane keyword clustering tasks that you used to do with formulas in spreadsheets or generate ideas based on keywords you give it.
Paired with traditional keyword research tools, ChatGPT for keyword research can be a powerful tool in your arsenal.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tatiana Shepeleva/Shutterstock
SEO
OpenAI Expected to Integrate Real-Time Data In ChatGPT

Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, dispelled rumors that a new search engine would be announced on Monday, May 13. Recent deals have raised the expectation that OpenAI will announce the integration of real-time content from English, Spanish, and French publications into ChatGPT, complete with links to the original sources.
OpenAI Search Is Not Happening
Many competing search engines have tried and failed to challenge Google as the leading search engine. A new wave of hybrid generative AI search engines is currently trying to knock Google from the top spot with arguably very little success.
Sam Altman is on record saying that creating a search engine to compete against Google is not a viable approach. He suggested that technological disruption was the way to replace Google by changing the search paradigm altogether. The speculation that Altman is going to announce a me-too search engine on Monday never made sense given his recent history of dismissing the concept as a non-starter.
So perhaps it’s not a surprise that he recently ended the speculation by explicitly saying that he will not be announcing a search engine on Monday.
He tweeted:
“not gpt-5, not a search engine, but we’ve been hard at work on some new stuff we think people will love! feels like magic to me.”
“New Stuff” May Be Iterative Improvement
It’s quite likely that what’s going to be announced is iterative which means it improves ChatGPT but not replaces it. This fits into how Altman recently expressed his approach with ChatGPT.
He remarked:
“And it does kind of suck to ship a product that you’re embarrassed about, but it’s much better than the alternative. And in this case in particular, where I think we really owe it to society to deploy iteratively.
There could totally be things in the future that would change where we think iterative deployment isn’t such a good strategy, but it does feel like the current best approach that we have and I think we’ve gained a lot from from doing this and… hopefully the larger world has gained something too.”
Improving ChatGPT iteratively is Sam Altman’s preference and recent clues point to what those changes may be.
Recent Deals Contain Clues
OpenAI has been making deals with news media and User Generated Content publishers since December 2023. Mainstream media has reported these deals as being about licensing content for training large language models. But they overlooked a a key detail that we reported on last month which is that these deals give OpenAI access to real-time information that they stated will be used to give attribution to that real-time data in the form of links.
That means that ChatGPT users will gain the ability to access real-time news and to use that information creatively within ChatGPT.
Dotdash Meredith Deal
Dotdash Meredith (DDM) is the publisher of big brand publications such as Better Homes & Gardens, FOOD & WINE, InStyle, Investopedia, and People magazine. The deal that was announced goes way beyond using the content as training data. The deal is explicitly about surfacing the Dotdash Meredith content itself in ChatGPT.
The announcement stated:
“As part of the agreement, OpenAI will display content and links attributed to DDM in relevant ChatGPT responses. …This deal is a testament to the great work OpenAI is doing on both fronts to partner with creators and publishers and ensure a healthy Internet for the future.
Over 200 million Americans each month trust our content to help them make decisions, solve problems, find inspiration, and live fuller lives. This partnership delivers the best, most relevant content right to the heart of ChatGPT.”
A statement from OpenAI gives credibility to the speculation that OpenAI intends to directly show licensed third-party content as part of ChatGPT answers.
OpenAI explained:
“We’re thrilled to partner with Dotdash Meredith to bring its trusted brands to ChatGPT and to explore new approaches in advancing the publishing and marketing industries.”
Something that DDM also gets out of this deal is that OpenAI will enhance DDM’s in-house ad targeting in order show more tightly focused contextual advertising.
Le Monde And Prisa Media Deals
In March 2024 OpenAI announced a deal with two global media companies, Le Monde and Prisa Media. Le Monde is a French news publication and Prisa Media is a Spanish language multimedia company. The interesting aspects of these two deals is that it gives OpenAI access to real-time data in French and Spanish.
Prisa Media is a global Spanish language media company based in Madrid, Spain that is comprised of magazines, newspapers, podcasts, radio stations, and television networks. It’s reach extends from Spain to America. American media companies include publications in the United States, Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Mexico, and Panama. That is a massive amount of real-time information in addition to a massive audience of millions.
OpenAI explicitly announced that the purpose of this deal was to bring this content directly to ChatGPT users.
The announcement explained:
“We are continually making improvements to ChatGPT and are supporting the essential role of the news industry in delivering real-time, authoritative information to users. …Our partnerships will enable ChatGPT users to engage with Le Monde and Prisa Media’s high-quality content on recent events in ChatGPT, and their content will also contribute to the training of our models.”
That deal is not just about training data. It’s about bringing current events data to ChatGPT users.
The announcement elaborated in more detail:
“…our goal is to enable ChatGPT users around the world to connect with the news in new ways that are interactive and insightful.”
As noted in our April 30th article that revealed that OpenAI will show links in ChatGPT, OpenAI intends to show third party content with links to that content.
OpenAI commented on the purpose of the Le Monde and Prisa Media partnership:
“Over the coming months, ChatGPT users will be able to interact with relevant news content from these publishers through select summaries with attribution and enhanced links to the original articles, giving users the ability to access additional information or related articles from their news sites.”
There are additional deals with other groups like The Financial Times which also stress that this deal will result in a new ChatGPT feature that will allow users to interact with real-time news and current events .
OpenAI’s Monday May 13 Announcement
There are many clues that the announcement on Monday will be that ChatGPT users will gain the ability to interact with content about current events. This fits into the terms of recent deals with news media organizations. There may be other features announced as well but this part is something that there are many clues pointing to.
Watch Altman’s interview at Stanford University
Featured Image by Shutterstock/photosince
SEO
Google’s Strategies For Dealing With Content Decay

In the latest episode of the Search Off The Record podcast, Google Search Relations team members John Mueller and Lizzi Sassman did a deep dive into dealing with “content decay” on websites.
Outdated content is a natural issue all sites face over time, and Google has outlined strategies beyond just deleting old pages.
While removing stale content is sometimes necessary, Google recommends taking an intentional, format-specific approach to tackling content decay.
Archiving vs. Transitional Guides
Google advises against immediately removing content that becomes obsolete, like materials referencing discontinued products or services.
Removing content too soon could confuse readers and lead to a poor experience, Sassman explains:
“So, if I’m trying to find out like what happened, I almost need that first thing to know. Like, “What happened to you?” And, otherwise, it feels almost like an error. Like, “Did I click a wrong link or they redirect to the wrong thing?””
Sassman says you can avoid confusion by providing transitional “explainer” pages during deprecation periods.
A temporary transition guide informs readers of the outdated content while steering them toward updated resources.
Sassman continues:
“That could be like an intermediary step where maybe you don’t do that forever, but you do it during the transition period where, for like six months, you have them go funnel them to the explanation, and then after that, all right, call it a day. Like enough people know about it. Enough time has passed. We can just redirect right to the thing and people aren’t as confused anymore.”
When To Update Vs. When To Write New Content
For reference guides and content that provide authoritative overviews, Google suggests updating information to maintain accuracy and relevance.
However, for archival purposes, major updates may warrant creating a new piece instead of editing the original.
Sassman explains:
“I still want to retain the original piece of content as it was, in case we need to look back or refer to it, and to change it or rehabilitate it into a new thing would almost be worth republishing as a new blog post if we had that much additional things to say about it.”
Remove Potentially Harmful Content
Google recommends removing pages in cases where the outdated information is potentially harmful.
Sassman says she arrived at this conclusion when deciding what to do with a guide involving obsolete structured data:
“I think something that we deleted recently was the “How to Structure Data” documentation page, which I thought we should just get rid of it… it almost felt like that’s going to be more confusing to leave it up for a period of time.
And actually it would be negative if people are still adding markup, thinking they’re going to get something. So what we ended up doing was just delete the page and redirect to the changelog entry so that, if people clicked “How To Structure Data” still, if there was a link somewhere, they could still find out what happened to that feature.”
Internal Auditing Processes
To keep your content current, Google advises implementing a system for auditing aging content and flagging it for review.
Sassman says she sets automated alerts for pages that haven’t been checked in set periods:
“Oh, so we have a little robot to come and remind us, “Hey, you should come investigate this documentation page. It’s been x amount of time. Please come and look at it again to make sure that all of your links are still up to date, that it’s still fresh.””
Context Is Key
Google’s tips for dealing with content decay center around understanding the context of outdated materials.
You want to prevent visitors from stumbling across obsolete pages without clarity.
Additional Google-recommended tactics include:
- Prominent banners or notices clarifying a page’s dated nature
- Listing original publish dates
- Providing inline annotations explaining how older references or screenshots may be obsolete
How This Can Help You
Following Google’s recommendations for tackling content decay can benefit you in several ways:
- Improved user experience: By providing clear explanations, transition guides, and redirects, you can ensure that visitors don’t encounter confusing or broken pages.
- Maintained trust and credibility: Removing potentially harmful or inaccurate content and keeping your information up-to-date demonstrates your commitment to providing reliable and trustworthy resources.
- Better SEO: Regularly auditing and updating your pages can benefit your website’s search rankings and visibility.
- Archival purposes: By creating new content instead of editing older pieces, you can maintain a historical record of your website’s evolution.
- Streamlined content management: Implementing internal auditing processes makes it easier to identify and address outdated or problematic pages.
By proactively tackling content decay, you can keep your website a valuable resource, improve SEO, and maintain an organized content library.
Listen to the full episode of Google’s podcast below:
Featured Image: Stokkete/Shutterstock
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoHow the TikTok Algorithm Works in 2024 (+9 Ways to Go Viral)
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoA Recap of Everything Marketers & Advertisers Need to Know
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoBlog Post Checklist: Check All Prior to Hitting “Publish”
-

 SEO4 days ago
SEO4 days agoHow to Use Keywords for SEO: The Complete Beginner’s Guide
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoHow To Protect Your People and Brand
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Started Enforcing The Site Reputation Abuse Policy
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoHow to Craft Compelling Google Ads for eCommerce
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoElevating Women in SEO for a More Inclusive Industry














You must be logged in to post a comment Login